编程代码基础技巧,File 、PCL、theta、Sophus、Velodyne、TensorRT、matlab、Lidar-FOV、平面法向量旋转
rostopic echo /turtle1/pose
一、文件操作
0: zip解压
unzip -O cp936 test.zip
// 避免出现乱码
unzip -O gbk file.zip
或者python
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import os
import sys
import zipfile
#print "Processing File " + sys.argv[1]
file=zipfile.ZipFile(sys.argv[1],"r");
for name in file.namelist():
utf8name=name.decode('gbk')
# print "Extracting " + utf8name
pathname = os.path.dirname(utf8name)
if not os.path.exists(pathname) and pathname!= "":
os.makedirs(pathname)
data = file.read(name)
if not os.path.exists(utf8name):
fo = open(utf8name, "w")
fo.write(data)
fo.close
file.close()
1: 查找特定后缀的某个文件
替换 onnx trt
保存txt pcd
std::string rosbag_file_path;
int path_end_pos = cmdline_file_path.find_last_of('.');
rosbag_file_path = cmdline_file_path.substr(0, path_end_pos);
rosbag_file_path += ".bag";
2:查找特定后缀的文件下 “ .jpg” " .pcd" “.onnx”
getFiles(filePath, "JPG", imageFilePathNames2);
void getFiles(string path, string exd, vector<string> &files)
{
//文件句柄
long hFile = 0;
//文件信息
struct _finddata_t fileinfo;
string pathName, exdName;
if (0 != strcmp(exd.c_str(), ""))
{
exdName = "\\*." + exd;
}
else
{
exdName = "\\*";
}
if ((hFile = _findfirst(pathName.assign(path).append(exdName).c_str(), &fileinfo)) != -1)
{
do
{
{
if (strcmp(fileinfo.name, ".") != 0 && strcmp(fileinfo.name, "..") != 0)
files.push_back(pathName.assign(path).append("\\").append(fileinfo.name));
}
} while (_findnext(hFile, &fileinfo) == 0);
_findclose(hFile);
}
}
3: bag变pcd数据,pcl读取txt pcd
bag 2pcd
rosbag info *.bag
rosrun pcl_ros bag_to_pcd data.bag /velodyne_points ./pcd
read pcd
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud_result(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
if (pcl::io::loadPCDFile<pcl::PointXYZ>("box-1.pcd", *cloud_result) == -1)
{
PCL_ERROR("Couldn't read file calibration_cloud_result.pcd\n");
//return (-1);
}
#include可视化点云坐标轴方向:
#include 4: C++读取文件夹下图片
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
std::string folder_name = argv[1];
std::vector<std::string> sample_images = read_Folder(folder_name);
}
std::vector<std::string> read_Folder(const std::string &image_path)
{
std::vector<std::string> image_names;
auto dir = opendir(image_path.c_str());
if ((dir) != nullptr)
{
struct dirent *entry;
entry = readdir(dir);
while (entry)
{
auto temp = image_path + "/" + entry->d_name;
if (strcmp(entry->d_name, "") == 0 || strcmp(entry->d_name, ".") == 0 || strcmp(entry->d_name, "..") == 0)
{
entry = readdir(dir);
continue;
}
image_names.push_back(temp);
entry = readdir(dir);
}
}
return image_names;
}
5: video2img
import sys
sys.path.remove('/opt/ros/kinetic/lib/python2.7/dist-packages')
import cv2
cap = cv2.VideoCapture("/home/REC_1615422002917.mp4")
i=0
while(1):
ret,frame = cap.read() #ret:True/False,
cv2.imshow("capture",frame)
#if (cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF) == ord('s'):
#gray = cv2.cvtColor(frame,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
#gray = cv2.resize(gray,(320,240))
if(i%20==0):
#cv2.imwrite('/home/test_car/'+'13_'+'%03d.jpg'%i,frame)
cv2.imwrite('/home/test_car/'+'%03d.jpg'%i,frame)
#cv2.imwrite('/home/test_car/'+'%d.jpg'%i,frame)
i += 1
if (cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF) == ord('q'):
break
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
6: save %o4d.png
char fileName[100];
sprintf(fileName, "%04d.png", save_num); //保存图片的路径
cv::Rect a;
a.x = 30;
a.y = 0;
a.width = org_img.cols - 100;
a.height = org_img.rows - 50;
cv::imwrite(root_path + fileName, org_img(a));
7: 文件路径操作
// 获取当前路径两种方法:
char *path;
path = get_current_dir_name();
std::string current_path = path;
// method 1:
// char *path;
// path = get_current_dir_name();
// current_path = path;
// method 2:
char tmp[PATH_MAX];
current_path = getcwd(tmp, sizeof(tmp)) ? std::string(tmp) : std::string("");
// creat floder
std::string save_path = root_path + "/data/";
if (access(save_path.c_str(), 0) == -1) {
int flag = mkdir(save_path.c_str(), 0777);
if (flag != 0) {
std::string error_str = "creat path error: " + save_path;
camera_driver_error(error_str);
return;
}
}
8: rosbag
rosbag 常用命令列表如下:
命令 作用
check 确定一个包是否可以在当前系统中进行,或者是否可以迁移。
decompress 压缩一个或多个包文件。
filter 解压一个或多个包文件。
fix 在包文件中修复消息,以便在当前系统中播放。
help 获取相关命令指示帮助信息
info 总结一个或多个包文件的内容。
play 以一种时间同步的方式回放一个或多个包文件的内容。
record 用指定主题的内容记录一个包文件。
reindex 重新索引一个或多个包文件。
rosbag record -help
rosbag record -a
rosbag record -O filename.bag /topic_name1
rostopic 常用命令列表如下:
命令 详细说明
rostopic list 显示活动的话题目录
rostopic echo [话题名称] 实时显示指定话题的消息内容
rostopic find [类型名称] 显示使用指定类型的消息的话题
rostopic type [话题名称] 显示指定话题的消息类型
rostopic bw [话题名称] 显示指定话题的消息带宽(bandwidth)
rostopic hz [话题名称] 显示指定话题的消息数据发布周期
rostopic info [话题名称] 显示指定话题的信息
rostopic pub [话题名称] [消息类型] [参数] 用指定的话题名称发布消息
rostopic echo /turtle1/pose
rostopic hz /turtle1/pose
rostopic list -v
9: vec2 mat
// save mat
Eigen::Matrix4f rot_rotation_translation =
VecPoseToMatrix(0, 0, yaw, x_offset, y_offset, z_offset);
cv::eigen2cv(rot_rotation_translation, parallel_mat);
// define
Eigen::Matrix4f Calibrator::VecPoseToMatrix(float roll, float pitch, float yaw,
float x, float y, float z)
{
/// generate transform matrix according to current pose
Eigen::AngleAxisf current_rotation_x(roll, Eigen::Vector3f::UnitX());
Eigen::AngleAxisf current_rotation_y(pitch, Eigen::Vector3f::UnitY());
Eigen::AngleAxisf current_rotation_z(yaw, Eigen::Vector3f::UnitZ());
Eigen::Translation3f current_translation(x, y, z);
Eigen::Matrix4f transform_matrix = (current_translation * current_rotation_z *
current_rotation_y * current_rotation_x)
.matrix();
return transform_matrix;
}
二、ROS订阅发布
订阅
ros::NodeHandle node_handle_;
ros::Subscriber livox_points_sub_;
ros::Publisher calibrated_cloud_publisher_;
livox_points_sub_ = node_handle_.subscribe("/livox/lidar", 10,
&laserCloudHandler, this);
if (mode == 1)
{
std::cout << "Into ndt lm." << std::endl;
ros::Rate loop_rate(10);
while (ros::ok())
{
ros::spinOnce();
// start NDT process
// PerformNdtOptimize();
// start LM process
// PerformLMOptimize();
if (!if_calibration)
{
break;
}
loop_rate.sleep();
}
ros::spin();
}
else
{
ros::spin();
}
发布
sensor_msgs::PointCloud2 tmp_msg;
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZRGB>::Ptr calibration_publish_result(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZRGB>);
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZRGB> roi_points;
float container_length = 16;
float container_width = 2.83;
float container_height = 3.45;
float box_min_x = 0.1;
float box_max_x = container_length - 0.05;
float box_min_y = 0.1;
float box_max_y = container_width - 0.1;
float box_min_z = 0.1;
float box_max_z = container_height - 0.15;
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < calibration_cloud_result->points.size(); i++)
{
pcl::PointXYZ lidar_point = calibration_cloud_result->points[i];
pcl::PointXYZRGB pt;
pt.x = lidar_point.x;
pt.y = lidar_point.y;
pt.z = lidar_point.z;
if (lidar_point.x > box_min_x && lidar_point.x < box_max_x &&
lidar_point.y > box_min_y && lidar_point.y < box_max_y &&
lidar_point.z > box_min_z && lidar_point.z < box_max_z)
{
pt.r = 255;
pt.g = 0;
pt.b = 0;
roi_points.points.push_back(pt);
}
else
{
pt.r = 255;
pt.g = 255;
pt.b = 255;
roi_points.points.push_back(pt);
}
}
calibration_publish_result = roi_points.makeShared();
pcl::toROSMsg(*calibration_publish_result, tmp_msg);
tmp_msg.header.frame_id = "livox_frame";
ros::Rate loop_rate(10);
while (ros::ok())
{
show_cloud_pub.publish(tmp_msg);
loop_rate.sleep();
}
三、PCL函数库
ros编译:
source /opt/ros/kinetic/setup.bash
// 编译某个包
catkin_make -DCATKIN_WHITELIST_PACKAGES="object_tracking"
pcl::SACSegmentation< PointT >
关键成员函数 :
SACSegmentation ()
空的构造函数
~SACSegmentation ()
空的析构函数
void setModelType (int model)
设置随机采样一致性所构造的几何模型的类型〈用户给定的参数) , model 为指定的模型类型参数,本章节中涉及的模型类型如下:
SACMODEL_PLANE:定义平面模型,共设置四个参数[normal_x normal_y normal_z d],其中(normal_x normal_y normal_x)为 Hessian范式中法向量的坐标及常量值d,ax+by+cz+d=0,熊点云中粉葛提取的内点都处在估计参数对应的平面上或者与平面距离在一定范围内。
SACMODEL_LINE:定义为直线模型 ,共设置 6 个参数 [ point_ on_line. x point_on_line. y point_on_line. z line_direction. x line_direction. y line_direction. z], 其中( point_on_line. x, point_on_line. y, poin t_on_line . 。为直线上一点的三维坐标,
Oine_direction. x, line_direction. y, line_direction. z)为直线方向向量的三维坐标,从点云中分割提取的内点都处在估计参数对应直线 上 或与直线的距离在一定范围内 。
SACMODEL_CIRCLE2D:定义为二维圆的圆周模型,共设置 3 个参数[ center. x center. y radius] ,其中( center. x, center. y)为圆周中心点的二维坐标, radius 为圆周半径,从点云中分割提取的内点都处在估计参数对应的圆周上或距离圆
周边线的距离在一定范围内 。
SACMODEL_CIRCLE3D:
SACMODEL_SPHERE:定义为三维球体模型,共设置 4 个参数[center. x center. y c·enter. z radius] ,其中( center. x, center. y, center. z)为球体中心的三维坐标, radius 为球体半径,从点云中分割提取的内点都处在估计参数对应的球体上或距离球体边线的距离在一定范围内 。
SACMODEL_CYLINDER:定义为圆柱体模型 , 共设置 7 个参数[ point_on_axis. x point_on_axis. y point_on_axis. z axis_direction. x axis_direction. y axis_direction. z radius] ,其中,( point_on_axis. x, point_on_axis. y, point_on_axis. 。为轴线上点的三维坐标,( direction. x ,axis_d让ection. y, axis_direction. 。为轴线方向向量的三维坐标, radius 为圆柱体半径,从点云中分割提取的内点都处在估计参数对应的圆柱体上或距离圆柱体表面的距离在一定范围内 。
SACMODEL_CONE:定义为圆锥模型,尚未实现。
SACMODEL_TORUS:定义为圆环面模型,尚未实现。
SACMODEL_PARALLEL_LINE:定义为有条件限制的直线模型,在规定的最大角度偏差限制下,直线模型与给定轴线平行,其参数设置参见 SACMODEL_LINE 模型。
SACMODEL_PERPENDICULAR_PLANE:定义为有条件限制的平面模型,在规定的最大角度偏差限制下,平面模型与给定轴线垂直,参数设置参见 SACMODEL_PLANE 模型 。
SACMODEL_PARALLEL_LINES:
SACMODEL_NORMAL_PLANE:定义为有条件限制的平面模型,在规定的最大角度偏差限制下,每一个局内点的法线必须与估计的平面模型的法线平行,参数设置参见 SACMODEL_PLANE 模型 。
SACMODEL_NORMAL_SPHERE:
SACMODEL_REGISTRATION:
SACMODEL_REGISTRATION_2D:
SACMODEL_PARALLEL_PLANE:定义为有条件限制的平面模型,在规定的最大角度偏差限制下,平面模型与给定的轴线平行,参数设置参见 SACMODEL_PLANE 模型。
SACMODEL_NORMAL_PARALLEL_PLANE:定义为有条件限制的平面模型,在法线约束下, 三维平面模型必须与用户设定的轴线平行,参数设置参见SACMODEL_PLANE 模型。
SACMODEL_STICK:
void setMethodType (int method)
设置使用采样一致性方法的类型(用户给定参数〉,采样一致性方法的类型有SAC_RANSAC 、 SAC_ LMEDS 、 SAC_MSAC 、 SAC_RRANSAC 、 SAC_RRANSAC 、SAC_MLESAC 、 SAC_PROSAC,具体算法描述详见随机采样一致性这章 。
void setDistanceThreshold (double threshold)
该函数配合用户指定的模型,设置点到模型的距离阔值 threshold (用户给定参数) ,如果点到模型的距离不超过这个距离阑值,认为该点为局内点,否则认为是局外点,被剔除。
void setMaxIterations (int max_iterations)
设置迭代次数的上限 max_iterations.
void setProbability (double probability)
设置每次从数据集中选取至少一个局内点的概率 probability 。
void setOptimizeCoefficients (bool optimize)
设置是否对估计的模型参数进行优化, optimize 为 true 时进行优化,否则不进行优化。
void setRadiusLimits (const double &min_radius, const double &max_radius)
该函数配合,当用户设定带有半径参数的模型类型时,设置模型半径参数的最大最小半径阑值 max_radius 、min_radius.
void setSamplesMaxDist (const double &radius, SearchPtr search)
设置随机采样时搜索所用的最大半径 Radius.
void setAxis (const Eigen::Vector3f &ax)
该函数配合,当用户设定与轴线平行或垂直有关的模型类型时,设置垂直或平行于所要建立模型的轴线 。
void setEpsAngle (double ea)
该函数配合,当用户设定有平行或垂直限定有关的模型类型时,设置判断是否平行或垂直时的角度阑值, ea 是最大角度差,采用弧度制。
virtual void segment (PointIndices &inliers, ModelCoefficients &model_coefficients)
对通过 setlnputCloud ( ) 和 setlndices ( )共同指定的输人点云进行聚类分割,参数 inliers 是基于模型分割所得到的点集合索引, model_coefficients 是估计得到的模型系数。
pcl save pcd
pcl::PointCloudpcl::PointXYZ cloud_plane;
// get plane points
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ> cloud_plane;
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud_ptr(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
for (int j = 0; j < pointNumCur; ++j)
{
pcl::PointXYZ tmp_pt;
tmp_pt.x = pointData.pts[regions[i][j]].x;
tmp_pt.y = pointData.pts[regions[i][j]].y;
tmp_pt.z = pointData.pts[regions[i][j]].z;
cloud_plane.push_back(tmp_pt);
}
cloud_ptr = cloud_plane.makeShared();
pcl::PointCloudpcl::PointXYZRGB plane_ptr;
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZRGB> plane_ptr;
test_pcs(this->cloud, pre_planes, plane_ptr, all_plane_points);
plane_ptr.height = 1;
plane_ptr.width = static_cast<uint>(plane_ptr.points.size());
std::string save_path = "../result/plane.pcd";
pcl::io::savePCDFileASCII(save_path, plane_ptr);
pcl::PointCloudpcl::PointXYZ::Ptr test_cloud;
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr test_cloud;
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr boundPoints(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
if (recognition_waist(pre_planes, test_cloud) == 1)
{
std::cout << "****************************** show data **********************" << std::endl;
//vector2pcd(pre_planes[1], test_cloud);
pcl::io::savePCDFileASCII("../result/show.pcd", *test_cloud);
}
savePCDFileASCII
pcl::PointCloud raw_ptr;
// save plane pcd
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZRGB> raw_ptr;
int numPatches = regions.size();
for (int i = 0; i < numPatches; ++i)
{
int R = rand() % 255;
int G = rand() % 255;
int B = rand() % 255;
int pointNumCur = regions[i].size();
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZRGB> plane_raw_ptr;
for (int j = 0; j < pointNumCur; ++j)
{
pcl::PointXYZRGB tmp_pt;
tmp_pt.x = this->cloud.pts[regions[i][j]].x;
tmp_pt.y = this->cloud.pts[regions[i][j]].y;
tmp_pt.z = this->cloud.pts[regions[i][j]].z;
tmp_pt.r = R;
tmp_pt.g = G;
tmp_pt.b = B;
raw_ptr.push_back(tmp_pt);
plane_raw_ptr.push_back(tmp_pt);
}
if (0)
{
if (plane_raw_ptr.points.size() > 0)
{
std::string save_pcd_name_livox = std::to_string(i) + ".pcd";
pcl::io::savePCDFileBinary(save_pcd_name_livox, plane_raw_ptr);
}
}
}
if (raw_ptr.points.size() > 0)
{
raw_ptr.height = 1;
raw_ptr.width = static_cast<uint>(raw_ptr.points.size());
pcl::io::savePCDFileASCII(save_path, raw_ptr);
}
pcl::PointCloudpcl::PointXYZRGB::Ptr pcd_cloud(new pcl::PointCloudpcl::PointXYZRGB);
std::cout << "saveXYZRGB" << std::endl;
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZRGB>::Ptr pcd_cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZRGB>);
fstream txtRead;
pcl::PCDWriter writer;
txtRead.open(txt_path, std::ios_base::in);
pcl::PointXYZRGB pclPnt;
int k = 0;
std::string str;
std::string substr;
string x = "";
string y = "";
string z = "";
string r = "";
string g = "";
string b = "";
while (!txtRead.eof())
{
getline(txtRead, str);
stringstream word(str);
word >> x;
word >> y;
word >> z;
word >> r;
word >> g;
word >> b;
pclPnt.x = atof(z.c_str()) * 0.01;
pclPnt.y = -1 * atof(x.c_str()) * 0.01;
pclPnt.z = -1 * atof(y.c_str()) * 0.01;
pclPnt.r = atoi(r.c_str());
pclPnt.g = atoi(g.c_str());
pclPnt.b = atoi(b.c_str());
k++;
// tmp_cloud.push_back(pclPnt);
pcd_cloud->points.push_back(pclPnt);
}
//cloud = tmp_cloud.makeShared();
pcd_cloud->width = 1;
pcd_cloud->height = pcd_cloud->points.size();
txtRead.close();
// save pcd
int n = txt_path.find_last_of(".");
txt_path = txt_path.substr(0, n);
writer.write(txt_path + "_rgb.pcd", *pcd_cloud);
std::cout << "save xyzrgb Total num of points: " << pcd_cloud->points.size() << "\n";
int j = 0;
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud_extract(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
for (int i = 0; i < cloud->points.size(); i++)
{
pcl::PointXYZ p;
//设定提取范围内的点的范围
if (cloud->points[i].x > 0.018|| cloud->points[i].z<-0.018)
{
p.x = cloud->points[i].x;
p.y = cloud->points[i].y;
p.z = cloud->points[i].z;
cloud_extract->push_back(p);
j++;
}
}
//对于无序点云hight默认是1
cloud_extract->height = 1;
//cloud_extract点云文件中push_back了j个点,故width=j
cloud_extract->width = j;
查看点云方向,过滤点云数据:
例如:
std::string name_pcd = “/home/Downloads/cloud5.pcd”;
pcl::PointCloudpcl::PointXYZ::Ptr tof_cloud(new pcl::PointCloudpcl::PointXYZ);
if (pcl::io::loadPCDFilepcl::PointXYZ(name_pcd, *tof_cloud) == -1) //*打开点云文件
{
PCL_ERROR(“Couldn’t read file middle_pcd.pcd\n”);
//return (-1);
}
pcl::PointCloudpcl::PointXYZ::Ptr result(new pcl::PointCloudpcl::PointXYZ);
filter_points(tof_cloud, result);
#include 简单过滤算法
RadiusOutlinerRemoval 、 ConditionalRemoval、setFilterLimits
如何在滤波模块使用几种不同的方法移除离群点,对于ConditionalRemoval滤波器,可以一次删除满足对输入的点云设定的一个或多个条件指标的所有的数据点,RadiusOutlinerRemoval滤波器,它可以删除在输入点云一定范围内没有至少达到足够多近邻的所有数据点。
关于RadiusOutlinerRemoval的理解,在点云数据中,设定每个点一定范围内周围至少有足够多的近邻,不满足就会被删除
关于ConditionalRemoval 这个滤波器删除点云中不符合用户指定的一个或者多个条件的数据点
#include pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud_filtered_x(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
pcl::PassThrough<pcl::PointXYZ> pass; //设置滤波器对象
pass.setInputCloud(range_cond); //设置输入点云
pass.setFilterFieldName("x"); //设置过滤时所需要点云类型的Z字段
pass.setFilterLimits(-15.0, 5.0); //设置在过滤字段上的范围
//pass.setFilterLimitsNegative (false);//设置保留范围内的还是过滤掉范围内的:算法内部默认false,即保留范围内的,滤掉范围外的;若设为true,则保留范围外的,滤掉范围内的;
//pass.setNegative (true);//作用同setFilterLimitsNegative
pass.filter(*cloud_filtered_x); //执行过滤,过滤结果在cloud_filtered
四、向量绕一个固定轴的旋转
如下代码
两种方式进行求解:
#include 五、Sophus
Eigen库提供了几何模块,但是没有提供李代数的支持。一个较好的 李代数库是由Strasdat维护的Sophus库。Sophus库支持三维运动的 SO(3)、 SE(3),此外还支持二维运动的 SO(2)、 SE(2)和相似变换 Sim(3)等内容。它是直接在Eigen库基础上开发的,因此我们不需要安装额外的依赖库。读者可以直接从github上获取Sophus库 [2],Sophus库有模板类库和非模板类库两个版本, 本书选择的是非模板类库。可以通过输入以下命令获得非模板类的Sophus库:
git clone http://github.com/strasdat/Sophus.git
Sophus库本身是一个cmake工程,使用以下命令对它进行编译(Sophus库只需编译,无需安装)。
git checkout a621ff 版本
* 在cmake编译
mv Sophus /usr/local/include
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ..
make
make install
cmake 设置路径
set(Sophus_INCLUDE_DIRS "放置你的Sophus头文件文件夹路径")
set(Sophus_LIBRARIES "放置你的Sophus库文件的文件夹路径,指明相应的库文件")
比如,我的是这样的:
set(Sophus_INCLUDE_DIRS "/usr/local/include/sophus")
set(Sophus_LIBRARIES "/usr/local/lib/libSophus.so")
include_directories(
${Sophus_INCLUDE_DIRS}
)
TARGET_LINK_LIBRARIES(${PROJECT_NAME}
${Sophus_LIBRARIES})
然后再将你的执行文件链接上Sophus库文件
再次编译Sophus时出现如下错误:
../lib/libmyslam.so: undefined reference to `Sophus::SO3::SO3(double, double, double)'
../lib/libmyslam.so: undefined reference to `Sophus::SE3::operator*(Eigen::Matrix<double, 3, 1, 0, 3, 1> const&) const'
../lib/libmyslam.so: undefined reference to `Sophus::SE3::SE3(Sophus::SO3 const&, Eigen::Matrix<double, 3, 1, 0, 3, 1> const&)'
../lib/libmyslam.so: undefined reference to `Sophus::SE3::operator*(Sophus::SE3 const&) const'
../lib/libmyslam.so: undefined reference to `Sophus::SE3::log() const'
../lib/libmyslam.so: undefined reference to `Sophus::SE3::operator=(Sophus::SE3 const&)'
../lib/libmyslam.so: undefined reference to `Sophus::SE3::inverse() const'
../lib/libmyslam.so: undefined reference to `Sophus::SE3::SE3()'
../lib/libmyslam.so: undefined reference to `Sophus::SE3::SE3(Sophus::SE3 const&)'
collect2: error: ld returned 1 exit status
原因分析:
安装Sophus时,有个lib文件“libSophus.so”会出现在/usr/local/lib/libSophus.so (本人编译时最后执行了 sudo make install, 因此在系统文件夹里面有该lib文件)。 当执行FIND_PACKAGE(sophus REQUIRED)时,libSophus.so 应该被链接到 Sophus_LIBRARIES, 但cmake却没链接上(原因未知),因此出现这个错误。
解决办法:
显式将Sophus_LIBRARIES 链接到libSophus.so,CMakeLists.txt的代码如下:
FIND_PACKAGE(sophus REQUIRED)
set(Sophus_LIBRARIES libSophus.so)
TARGET_LINK_LIBRARIES(${PROJECT_NAME}
${Sophus_LIBRARIES})
六、Velodyne的ring通道
Failed to find match for field 'ring'.
Failed to find match for field 'range'.
在你launch后可能会出现这样的错误 Failed to find match for field ‘ring’
因为Velodyne的雷达单独有一个ring通道,而robosense的雷达好像并没有。
因此可以添加,响应驱动或者代码;
void addRange(pcl::PointCloud<Velodyne::Point> &pc) {
for (pcl::PointCloud<Point>::iterator pt = pc.points.begin();
pt < pc.points.end(); pt++) {
pt->range = sqrt(pt->x * pt->x + pt->y * pt->y + pt->z * pt->z);
}
}
Velodyne 数据类型
然而对有序点云进行操作(降采样、刚体变换)后,有序点云就会变成无序点云。velodyne选择给每个点多加了一个属性ring,详细定义如下:
namespace velodyne_pointcloud
{
struct PointXYZIR
{
PCL_ADD_POINT4D; // quad-word XYZ
float intensity;
uint16_t ring;
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW // ensure proper alignment
} EIGEN_ALIGN16;
}; // namespace velodyne_pointcloud
这个ring表示每个点之前属于哪个线的,16线的话,这个值为0~15。并且高度自低向高排列。
ring作用:
在点云上画出四条边,拟合四条边为四条直线等等。我们运行程序时,显示的直接就是硬纸板的轮廓让你去框

七、角度弧度
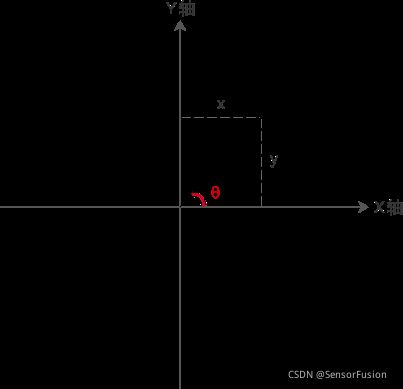 角度转弧度: π/180 × 角度
角度转弧度: π/180 × 角度
弧度变角度 : 180/π × 弧度
double rad2deg(double radians)
{
return radians * 180.0 / M_PI;
}
double deg2rad(double degrees)
{
return degrees * M_PI / 180.0;
}
函数名: asin
函数原型: double asin(double x); (x > -1 && x < 1)
功 能: 返回 x 的弧度制反正弦值
函数名: acos
函数原型: double acos(double x); (x > -1 && x < 1)
功 能: 返回的是一个数值的反余弦弧度值,其范围是 0~ pi 。 例如: acos(1) 返回值是 0 。
acos(- 0.5) 返回的是 2.0944 弧度。
函数名: atan
函数原型: double atan(double x); x ∈ (-∞,+∞)
(注:受限于形式参数的范围,实际输入范围为double型的范围,即负值取值范围为 -1.7976E+308 到 -4.94065645841246544E-324,正值取值范围为 4.94065645841246544E-324 到 1.797693E+308)
功 能: 可返回数字的反正切值,范围为 -pi/2~pi/2
函数名: atan2
函数原型: double atan2(double y, double x);
x-- 代表 x 轴坐标的浮点值。
y-- 代表 y 轴坐标的浮点值。
功 能: atan2函数返回的是原点至点(x,y)的方位角,即与 x 轴的夹角。返回值的单位为弧度,取值范围为 (-pai, pai] 。
八、TensorRT
template <typename T>
using UniquePtr = std::unique_ptr<T, common::InferDeleter>;
转换
只需要初始化一次 engine和context
推理的时候初始化context会不断增加显卡
导致out of memory
使用engine、context 的定义
nvinfer1::ICudaEngine *engine = nullptr; //!< The TensorRT engine used to run the network
std::shared_ptr<nvinfer1::ICudaEngine> mEngine; //!< The TensorRT engine used to run the network
UniquePtr<nvinfer1::IExecutionContext> context;
互相转换:
mEngine = std::shared_pt r < nvinfer1::ICudaEngine > (engine, common::InferDeleter());
context = UniquePtr < nvinfer1::IExecutionContext> (mEngine->createExecutionContext());
九、Python Sort
针对 camera_top_0_1594202073405.jpg
camera_top_1_1594202073405.jpg
camera_top_10_1594202073405.jpg
排序文件 0 1 2 … 9 10 11 12 … 19 20 21
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import os
#top_name.sort()
# sort 0 1 2 3 .. 9 10 11 ...19 20 21 ...
#camera_top_0_1594202073405.jpg
#camera_top_1_1594202073472.jpg
def sort_num(top_name):
for i in top_name:
print(i)
print (top_name)
for i in range(len(top_name)):
#camera_bottom_0_1594202073394.jpg
top_name[i] = top_name[i].split('_')
#print(top_name[i])
top_name[i][2] = int(top_name[i][2])
top_name.sort()
print ('after',top_name)
print (top_name)
for i in range(len(top_name)):
top_name[i][2] = str(top_name[i][2])
top_name[i] = top_name[i][0] + '_' + top_name[i][1]+'_' + top_name[i][2]+'_' + top_name[i][3]
print (top_name)
if __name__ == "__main__":
filePath = '/home/top/'
top_name = os.listdir(filePath)
sort_num(top_name)
生成一一对应的图片序列
1_t.img 2_t.img 3_t.img 4_t.img
1_d.img 2_d.img 3_d.img 4_d.img
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import os
import numpy as np
#top_name.sort()
# sort 0 1 2 3 .. 9 10 11 ...19 20 21 ...
#camera_top_0_1594202073405.jpg
#camera_top_1_1594202073472.jpg
root_path = "/home/sequence/"
def sort_num(top_name):
#for i in top_name:
# print(i)
#print (top_name)
for i in range(len(top_name)):
#camera_bottom_0_1594202073394.jpg
top_name[i] = top_name[i].split('_')
#print(top_name[i])
top_name[i][2] = int(top_name[i][2])
top_name.sort()
#print ('after',top_name)
print (top_name)
for i in range(len(top_name)):
top_name[i][2] = str(top_name[i][2])
top_name[i] = top_name[i][0] + '_' + top_name[i][1]+'_' + top_name[i][2]+'_' + top_name[i][3]
print (top_name)
if __name__ == "__main__":
filePath = '/home/sequence/top/'
top_name = os.listdir(filePath)
sort_num(top_name)
print('top_name',top_name)
filePath = '/home/sequence/bottom/'
bottom_name = os.listdir(filePath)
sort_num(bottom_name)
print('bottom_name',bottom_name)
print('right_name',right_name)
txtName = "file_list_2021.txt"
f=open(txtName, "a+")
for i in range(0,1000):
result=root_path+top_name[i]+' '+ root_path+bottom_name[i]+'\n'
f.write(result)
十、Python-OpenCV
https://github.com/strawlab/python-pcl
pip install cython
pip install numpy
python setup.py build_ext -i
python setup.py install
2d - 3d
https://elody-07.github.io/
由内参和深度图生成点云数据:
import cv2
depth = cv2.imread("depth.png",-1)
import pcl
cloud = pcl.PointCloud() # 存储图像的点云
rows = len(depth)
cols = len(depth[0])
pointcloud = []
#camera_factor = 1
#camera_cx = 0
#camera_cy = 0
camera_fx = 588.03
camera_fy = 587.07
for m in range(0, rows):
for n in range(0, cols):
d = depth[m][n][0] + depth[m][n][1]*256
if d == 0:
pass
else:
z = float(d)
x = n * z / camera_fx
y = m * z / camera_fy
points = [x, y, z]
pointcloud.append(points)
#由于pcl库不会直接识别列表格式的点云数据,所以我们需要使用numpy库进行数据格式转换,并将点云保存pcd文件中。
import numpy as np
pointcloud = np.array(pointcloud, dtype = np.float32)
cloud.from_array(pointcloud)
pcl.save(cloud, "cloud.pcd", format = 'pcd')
sudo apt-get install python-pip
sudo apt-get install python-dev
sudo pip install Cython==0.25.2
sudo pip install numpy
sudo apt-get install git
git clone https://github.com/strawlab/python-pcl.git
cd python-pcl/
python setup.py build_ext -i
python setup.py install
十一、matlab
matlab, 发现matlab偏爱列,发现matlab和Fortran一样,都是列优先的.
与之相反的是C++, 是行优先的.
例如:
clearclca = ones(3, 5)sum(a) % 每一列的元素相加
结果为:
a =
1 1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1 1
ans =
3 3 3 3 3
十二、lidar bin2map 3d-box-index
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:UTF-8 -*-
import numpy as np
import os
import sys
import glob
import math
import struct
#import pcl
def bin2sperate(raw_lidar,new_lidar):
f_lidar = glob.glob(os.path.join(raw_lidar,'bin_data_truck','*.bin'))
f_label = glob.glob(os.path.join(raw_lidar,'txt_label_truck','*.txt'))
f_lidar.sort()
f_label.sort()
assert len(f_lidar) == len(f_label),"dataset ok"
labels,raw_lidar,xyzi_lidar,lables,boxes3d= [],[],[],[],[]
bin_num = len(f_lidar)
for i in range(len(f_label)):
print 'deal with bin:',i
raw_lidar.append(np.fromfile(f_lidar[i], dtype=np.float32).reshape((-1, 4)))
point_cloud = raw_lidar[-1] # delete dtype=float32
xyzi_lidar = point_cloud[:,:4]
filename = new_lidar +str(i)+'_db'+'.bin'
print 'save bin filename:',filename
f_bin = open(filename,'a+')
obj_Point_num = 0
print 'point bin num:',len(xyzi_lidar)
point_label_num = 0
Dontcare_label = 0
for j in range(len(xyzi_lidar)):
x,y,z,ii= xyzi_lidar[j,0],xyzi_lidar[j,1],xyzi_lidar[j,2],xyzi_lidar[j,3]
fopen = open(f_label[i],'r')
point_category = True
for line in fopen.readlines():
#print (line)
ret = line.strip("\n").split(" ")
r_x,r_y,l_x,l_y,point_label = [float(k) for k in ret[0:5]]
#print 'point_label',point_label
if (x <= r_x)and( x >= l_x)and(y <= r_y)and(y >= l_y)and (z< 1.0):
point_category = False
x_bin = struct.pack('f',x)
f_bin.write(x_bin)
y_bin = struct.pack('f',y)
f_bin.write(y_bin)
z_bin = struct.pack('f',z)
f_bin.write(z_bin)
i_bin = struct.pack('f',ii)
f_bin.write(i_bin)
l_bin = struct.pack('f',point_label)
f_bin.write(l_bin)
point_label_num = point_label_num + 1
#print 'label =',point_label
if point_category:
x_bin = struct.pack('f',x)
f_bin.write(x_bin)
y_bin = struct.pack('f',y)
f_bin.write(y_bin)
z_bin = struct.pack('f',z)
f_bin.write(z_bin)
i_bin = struct.pack('f',ii)
f_bin.write(i_bin)
l_bin = struct.pack('f',Dontcare_label)
f_bin.write(l_bin)
obj_Point_num = obj_Point_num + 1
print 'deal with Point num :',obj_Point_num
print 'deal with label num :',point_label_num
print 'deal with bin:',i
f_bin.close()
if __name__=='__main__':
raw_lidar = '/home/lidar_data/'
new_lidar = '/home/lidar_data/seg_data_truck/'
bin2sperate(raw_lidar,new_lidar)
十三、lidar FOV 3d-box-index
右手坐标系 x前y左上,安装yzx排列 求解index
//
class BoxAtt
{
public:
int x_index;
int y_index;
int z_index;
bool flag;
};
std::vector<BoxAtt> box_att;
int init_num = 0;
// #pragma omp parallel for
for (int num = 0; num < box_size; ++num)
{
// get box index
int integer = num / (box_size_y * box_size_z);
int remainder = num % (box_size_y * box_size_z);
int remainder_int = remainder / box_size_z;
int remainder_rem = remainder % box_size_z;
int i = integer;
int j = remainder_int;
int k = remainder_rem;
box_att[num].x_index = i;
box_att[num].y_index = j;
box_att[num].z_index = k;
}
任意一个盒子内激光覆盖范围
如果点云没有旋转变化,则
float lidar_angle = 50;
double threshold_lidar = lidar_angle * CV_PI / 180;
double threshold_cos = cos(threshold_lidar);
//点云进行了旋转平移,矩阵为trans_rot;
//如果点云做过旋转变化,则光心由
//Eigen::Vector3f(1, 0, 0) 变为 trans_rot.block(0, 0, 3, 3) * Eigen::Vector3f(1, 0, 0);
lidar_light_vector = trans_rot.block(0, 0, 3, 3) * Eigen::Vector3f(1, 0, 0); // 取旋转量
// 加速点云即旋转又平移了
lidar_ori = rans_rot.block(0, 3, 3, 1); //取平移量
//则任意一点旋转平移后的坐标 Eigen::Vector3f curr_box_point 的最终向量为:
Eigen::Vector3f box_vector = curr_box_point- lidar_ori; // 基于只旋转,不平移,和光心向量求解
float dot = lidar_light_vector.dot(box_vector);
float cos_theta = dot / (lidar_light_vector.norm() * box_vector.norm());
if (cos_theta >= threshold_cos)
{
std::cout<<"覆盖区域"
}
else
{
std::cout<<"盲区"
}
方法一:利用定义直接求角,在欧拉角转RT
方法二:求绕轴旋转角度,轴角转RT


void preprocess(pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>::Ptr laserCloud,
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>::Ptr laserCloud_out)
{
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>::Ptr laser_cloud_in(
new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>);
for (int i = 0; i < laserCloud->points.size(); ++i)
{
Eigen::Vector2f xy_pos(laserCloud->points[i].x, laserCloud->points[i].y);
float distance = xy_pos.norm();
if (distance < 15 && laserCloud->points[i].z < -height)
{
laser_cloud_in->points.push_back(laserCloud->points[i]);
}
}
///方法一:
// get SolveCovariance
Eigen::Vector3f normals;
// SolveCovariance(laser_cloud_in, normals);
ransac_plane(laser_cloud_in, normals);
std::cout << "preprocess_ground normals " << normals[0] << "" << normals[1] << "" << normals[2] << std::endl;
float roll = atan2f(normals[1], normals[2]);
std::cout << "wen roll :" << roll << std::endl;
float pitch =
atan2f(-normals[0], sqrtf(powf(normals[1], 2) + powf(normals[2], 2)));
// roll pith yaw x y z , get transform
std::cout << "pitch pitch pitch:" << pitch << std::endl;
Eigen::Matrix4f lidar_rot = vec_pose_to_matrix(roll, pitch, 0, 0, 0, 0);
std::cout << "ground trans is " << std::endl;
std::cout << lidar_rot << std::endl;
///方法二:
///
Eigen::Vector3f xoy_normals;
xoy_normals << 0, 0, 1;
// get angle
float normals_dot = normals.dot(xoy_normals);
float xoy_abs = xoy_normals.norm();
float normals_abs = normals.norm();
//float xoy_abs = 1;
//float normals_abs = sqrt(normals[0] * normals[0] + normals[1] * normals[1] +
// normals[2] * normals[2]);
float xoy_x_normals = xoy_abs * normals_abs;
float acos_angle = acos(normals_dot / xoy_x_normals);
std::cout << "two vector angle :" << acos_angle* 180 / CV_PI << std::endl;
// get chou
Eigen::Vector3f cross_xoy;
cross_xoy = normals.cross(xoy_normals);
std::cout<<"two vector axis:"<<cross_xoy<<std::endl;
//get RotationMatrix
Eigen::AngleAxisf a_axisd(acos_angle,cross_xoy.normalize());
Eigen::AngleAxisf a_axisd(acos_angle,cross_xoy.normalized());
//Eigen::AngleAxisd a_axisd(M_PI/4, Eigen::Vector3d(0,0,1));
std::cout << "a_axisd: Angle is: " << a_axisd.angle()<<std::endl;//旋转角
std::cout << "a_axisd: Axis is: " << a_axisd.axis().transpose() << std::endl;//旋转轴
std::cout << "my eigen rotation: " << std::endl;
std::cout << a_axisd.toRotationMatrix() << std::endl;
//opencv Rodrigues
Eigen::Vector3f vector_rot = acos_angle* cross_xoy.normalized();
cv::Mat vector_mat;
cv::Mat rotation;
cv::eigen2cv(vector_rot,vector_mat);
cv::Rodrigues(vector_mat,rotation);
std::cout<<"my opencv Rodrigues rotation"<<rotation<<std::endl;
pcl::transformPointCloud(*laserCloud, *laserCloud_out, lidar_rot);
// test save
std::string save_pcd_name = map_file + "/ground.pcd";
pcl::io::savePCDFileBinary(save_pcd_name, *laser_cloud_in);
std::string save_pcd_name1 = map_file + "/transform_ground_roll_pitch.pcd";
pcl::io::savePCDFileBinary(save_pcd_name1, *laserCloud_out);
// save mat
std::cout << "saving ..." << std::endl;
cv::Mat transform;
// roll pith yaw x y z , get transform
Eigen::Matrix4f lidar_rot2 = vec_pose_to_matrix(roll, pitch, 0, 0, 0, 0);
lidar_rot = lidar_rot * lidar_rot2;
cv::eigen2cv(lidar_rot, transform);
}
十三、flann冲突
PCL OpenCV
不要使用unsing namespace cv;
替换掉其中一个即可
十四、opencv图片旋转
一张图片围绕中心旋转90°、180°等
// 用到2个函数:
transpose(Mat src,Mat &dst); //转置
flip(Mat src,Mat &dst,int nFlag) ; //镜像
Mat src = imread("1.jpg");
Mat temp, dst0, dst1, dst_1;
//先转置一下图片,此时图片是转置并和原图像呈现镜像,因此使用镜像一次
transpose(src, temp);
//使用镜像操作转换过来,第三个参数为1,镜像后相当于原图像的顺时针旋转了90°
flip(temp, dst1, 1);
//第三个参数,0时,镜像后相当于原图逆时针90°
flip(temp, dst0, 0);
//第三个参数为-1时,镜像后相当于旋转180度
flip(temp, dst_1, -1);
imshow("src", src);
imshow("transpose", temp);
imshow("flip:1", dst1);
imshow("flip:0", dst0);
imshow("flip:-1", dst_1);
waitKey();
补充
// 需顺时针90°旋转时,transpose(src,tmp) + flip(tmp,dst,1)
// 需逆时针90°旋转时,transpose(src,tmp) + flip(tmp,dst,0)
// 需180°旋转时,直接flip(src,dst,-1)
// app show
cv::Mat tmp;
transpose(show_result_, tmp);
flip(tmp,show_result_,1);
// app show img
// save
cv::imwrite(test_data_path + "/Calibration_ROI_APP.png",
show_result_);

