JAVA常用工具-文件操作相关IO
IO技术在JDK中算是极其复杂的模块,文件管理都依赖IO技术,而且都是编程的难点,想要整体理解IO流,先从Linux操作系统开始,
Linux空间隔离
Linux使用是区分用户的,这个是基础常识,其底层也区分用户和内核两个模块:
- User space:用户空间
- Kernel space:内核空间
用户空间本身无法直接向系统发布调度指令,必须通过内核,对于内核中数据的操作,也是需要先拷贝到用户空间,这种隔离机制可以有效的保护系统的安全性和稳定性
IO模型分析
当应用端发起IO操作的请求时,请求沿着链路上的各个节点流转,有两个核心概念:
- 节点交互模式:同步与异步;
- IO数据操作:阻塞与非阻塞;
三、File文件类
1、基础描述
File类作为文件和目录路径名的抽象表示,用来获取磁盘文件的相关元数据信息,例如:文件名称、大小、修改时间、权限判断等
public class File01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 1、读取指定文件
File speFile = new File(IoParam.BASE_PATH+"fileio-03.text") ;
if (!speFile.exists()){
boolean creFlag = speFile.createNewFile() ;
System.out.println("创建:"+speFile.getName()+"; 结果:"+creFlag);
}
// 2、读取指定位置
File dirFile = new File(IoParam.BASE_PATH) ;
// 判断是否目录
boolean dirFlag = dirFile.isDirectory() ;
if (dirFlag){
File[] dirFiles = dirFile.listFiles() ;
printFileArr(dirFiles);
}
// 3、删除指定文件
if (speFile.exists()){
boolean delFlag = speFile.delete() ;
System.out.println("删除:"+speFile.getName()+"; 结果:"+delFlag);
}
}
private static void printFileArr (File[] fileArr){
if (fileArr != null && fileArr.length>0){
for (File file : fileArr) {
printFileInfo(file) ;
}
}
}
private static void printFileInfo (File file) {
System.out.println("名称:"+file.getName());
System.out.println("长度:"+file.length());
System.out.println("路径:"+file.getPath());
System.out.println("文件判断:"+file.isFile());
System.out.println("目录判断:"+file.isDirectory());
System.out.println("最后修改:"+new Date(file.lastModified()));
System.out.println();
}
}2、文件业务场景
在常规的文件流任务中,会涉及【文件、流、数据】三种基本形式的转换:
任何节点都无法适配所有文件处理策略,比如类型与编码,面对复杂场景下的问题,规则约束是常用的解决策略,即在约定规则之内的事情才处理。
四、基础流模式
1、整体概述
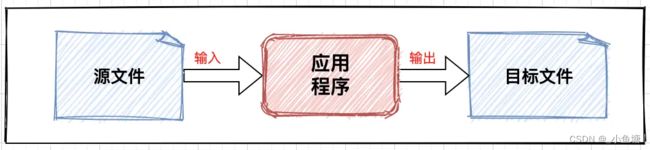
基本编码逻辑:源文件->输入流->逻辑处理->输出流->目标文件;
- 流动方向:输入流、输出流;
- 流数据类型:字节流、字符流
基础API
-
字节流:InputStream输入、OutputStream输出;数据传输的基本单位是字节;
- read():输入流中读取数据的下一个字节;
- read(byte b[]):读数据缓存到字节数组;
- write(int b):指定字节写入输出流;
- write(byte b[]):数组字节写入输出流;
-
字符流:Reader读取、Writer写出;数据传输的基本单位是字符;
- read():读取一个单字符;
- read(char cbuf[]):读取到字符数组;
- write(int c):写一个指定字符;
- write(char cbuf[]):写一个字符数组;
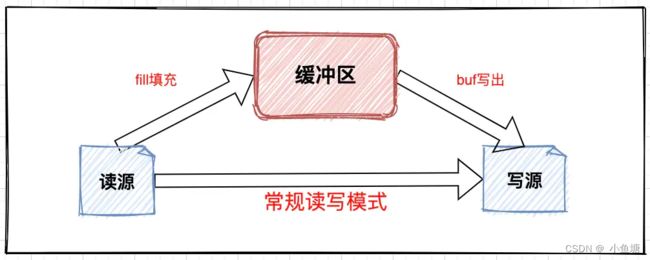
缓冲模式
在BufferedInputStream、BufferedReader类中是对缓冲逻辑的具体实现
2、字节流
字节流应用场景:数据是文件本身,例如图片,视频,音频等。
基础api操作实例:
public class IoByte01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 源文件 目标文件
File source = new File(IoParam.BASE_PATH+"fileio-01.png") ;
File target = new File(IoParam.BASE_PATH+"copy-"+source.getName()) ;
// 输入流 输出流
InputStream inStream = new FileInputStream(source) ;
OutputStream outStream = new FileOutputStream(target) ;
// 读入 写出
byte[] byteArr = new byte[1024];
int readSign ;
while ((readSign=inStream.read(byteArr)) != -1){
outStream.write(byteArr);
}
// 关闭输入、输出流
outStream.close();
inStream.close();
}
}public class IoByte02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 源文件 目标文件
File source = new File(IoParam.BASE_PATH+"fileio-02.png") ;
File target = new File(IoParam.BASE_PATH+"backup-"+source.getName()) ;
// 缓冲:输入流 输出流
InputStream bufInStream = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(source));
OutputStream bufOutStream = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(target));
// 读入 写出
int readSign ;
while ((readSign=bufInStream.read()) != -1){
bufOutStream.write(readSign);
}
// 关闭输入、输出流
bufOutStream.close();
bufInStream.close();
}
}3、字符流
字符流应用场景:文件作为数据的载体,例如Excel、CSV、TXT等。
基本api操作实例
public class IoChar01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 读文本 写文本
File readerFile = new File(IoParam.BASE_PATH+"io-text.txt") ;
File writerFile = new File(IoParam.BASE_PATH+"copy-"+readerFile.getName()) ;
// 字符输入输出流
Reader reader = new FileReader(readerFile) ;
Writer writer = new FileWriter(writerFile) ;
// 字符读入和写出
int readSign ;
while ((readSign = reader.read()) != -1){
writer.write(readSign);
}
writer.flush();
// 关闭流
writer.close();
reader.close();
}
}public class IoChar02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 读文本 写文本
File readerFile = new File(IoParam.BASE_PATH+"io-text.txt") ;
File writerFile = new File(IoParam.BASE_PATH+"line-"+readerFile.getName()) ;
// 缓冲字符输入输出流
BufferedReader bufReader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(readerFile)) ;
BufferedWriter bufWriter = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(writerFile)) ;
// 字符读入和写出
String line;
while ((line = bufReader.readLine()) != null){
bufWriter.write(line);
bufWriter.newLine();
}
bufWriter.flush();
// 关闭流
bufWriter.close();
bufReader.close();
}
}4、编码解码
- 编码:字符转换为字节;
- 解码:字节转换为字符;
public class EnDeCode {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String var = "IO流" ;
// 编码
byte[] enVar = var.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8) ;
for (byte encode:enVar){
System.out.println(encode);
}
// 解码
String deVar = new String(enVar,StandardCharsets.UTF_8) ;
System.out.println(deVar);
// 乱码
String messyVar = new String(enVar,StandardCharsets.ISO_8859_1) ;
System.out.println(messyVar);
}
}5、序列化
- 序列化:对象转换为流的过程;
- 反序列化:流转换为对象的过程;
public class SerEntity implements Serializable {
private Integer id ;
private String name ;
}
public class Seriali01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 序列化对象
OutputStream outStream = new FileOutputStream("SerEntity.txt") ;
ObjectOutputStream objOutStream = new ObjectOutputStream(outStream);
objOutStream.writeObject(new SerEntity(1,"Cicada"));
objOutStream.close();
// 反序列化对象
InputStream inStream = new FileInputStream("SerEntity.txt");
ObjectInputStream objInStream = new ObjectInputStream(inStream) ;
SerEntity serEntity = (SerEntity) objInStream.readObject();
System.out.println(serEntity);
inStream.close();
}
}五、NIO模式
1、基础概念
NIO即(NonBlockingIO),面向数据块的处理机制,同步非阻塞模型,服务端的单个线程可以处理多个客户端请求,对IO流的处理速度有极高的提升,三大核心组件:
- Buffer(缓冲区):底层维护数组存储数据;
- Channel(通道):支持读写双向操作;
- Selector(选择器):提供Channel多注册和轮询能力;
public class IoNew01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 源文件 目标文件
File source = new File(IoParam.BASE_PATH+"fileio-02.png") ;
File target = new File(IoParam.BASE_PATH+"channel-"+source.getName()) ;
// 输入字节流通道
FileInputStream inStream = new FileInputStream(source);
FileChannel inChannel = inStream.getChannel();
// 输出字节流通道
FileOutputStream outStream = new FileOutputStream(target);
FileChannel outChannel = outStream.getChannel();
// 直接通道复制
// outChannel.transferFrom(inChannel, 0, inChannel.size());
// 缓冲区读写机制
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(1024);
while (true) {
// 读取通道中数据到缓冲区
int in = inChannel.read(buffer);
if (in == -1) {
break;
}
// 读写切换
buffer.flip();
// 写出缓冲区数据
outChannel.write(buffer);
// 清空缓冲区
buffer.clear();
}
outChannel.close();
inChannel.close();
}
}2、网络通信
服务端的单线程可以处理多个客户端请求,通过轮询多路复用器查看是否有IO请求,这样一来,服务端的并发能力得到极大的提升,并且显著降低了资源的消耗
服务端模拟
public class SecServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
//启动服务开启监听
ServerSocketChannel socketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
socketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 8089));
// 设置非阻塞,接受客户端
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
// 打开多路复用器
Selector selector = Selector.open();
// 服务端Socket注册到多路复用器,指定兴趣事件
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
// 多路复用器轮询
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(1024);
while (selector.select() > 0){
Set selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator selectionKeyIter = selectionKeys.iterator();
while (selectionKeyIter.hasNext()){
SelectionKey selectionKey = selectionKeyIter.next() ;
selectionKeyIter.remove();
if(selectionKey.isAcceptable()) {
// 接受新的连接
SocketChannel client = socketChannel.accept();
// 设置读非阻塞
client.configureBlocking(false);
// 注册到多路复用器
client.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
} else if (selectionKey.isReadable()) {
// 通道可读
SocketChannel client = (SocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();
int len = client.read(buffer);
if (len > 0){
buffer.flip();
byte[] readArr = new byte[buffer.limit()];
buffer.get(readArr);
System.out.println(client.socket().getPort() + "端口数据:" + new String(readArr));
buffer.clear();
}
}
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
} 客户端模拟
public class SecClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// 连接服务端
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 8089));
ByteBuffer writeBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
String conVar = "[hello-8089]";
writeBuffer.put(conVar.getBytes());
writeBuffer.flip();
// 每隔5S发送一次数据
while (true) {
Thread.sleep(5000);
writeBuffer.rewind();
socketChannel.write(writeBuffer);
writeBuffer.clear();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}