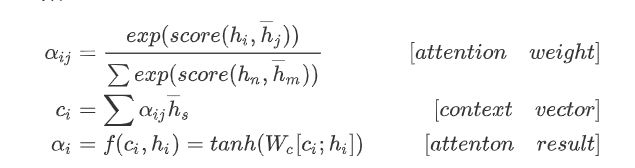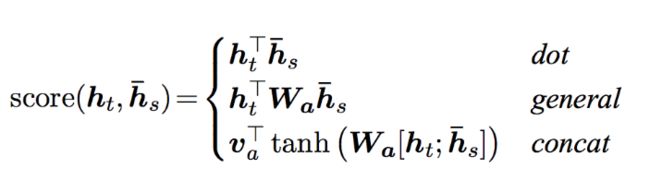Attention的原理和实现
Attention的原理和实现
目标
- 知道Attention的作用
- 知道Attention的实现机制
- 能够使用代码完成Attention代码的编写
1. Attention的介绍
在普通的RNN结构中,Encoder需要把一个句子转化为一个向量,然后在Decoder中使用,这就要求Encoder把源句子中所有的信息都包含进去,但是当句子长度过长的时候,这个要求就很难达到,或者说会产生瓶颈(比如,输入一篇文章等场长内容),当然我们可以使用更深的RNN和大多的单元来解决这个问题,但是这样的代价也很大。那么有没有什么方法能够优化现有的RNN结构呢?
为此,Bahdanau等人在2015年提出了Attenion机制,Attention翻译成为中文叫做注意力,把这种模型称为Attention based model。就像我们自己看到一副画,我们能够很快的说出画的主要内容,而忽略画中的背景,因为我们注意的,更关注的往往是其中的主要内容。
通过这种方式,在我们的RNN中,我们有通过LSTM或者是GRU得到的所有信息,那么这些信息中只去关注重点,而不需要在Decoder的每个time step使用全部的encoder的信息,这样就可以解决第一段所说的问题了
那么现在要讲的Attention机制就能够帮助我们解决这个问题
2. Attenion的实现机制
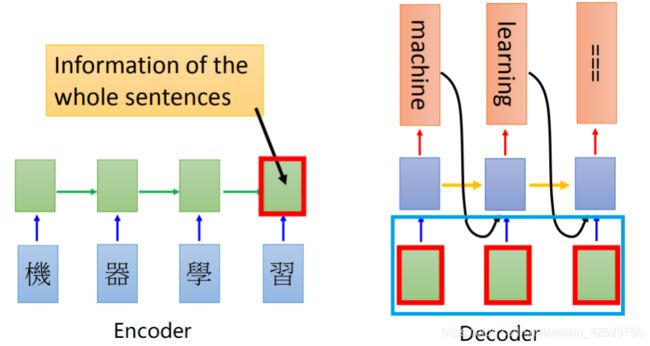
假设我们现在有一个文本翻译的需求,即机器学习翻译为machine learning。那么这个过程通过前面所学习的Seq2Seq就可以实现
上图的左边是Encoder,能够得到hidden_state在右边使用
Deocder中蓝色方框中的内容,是为了提高模型的训练速度而使用teacher forcing手段,否则的话会把前一次的输出作为下一次的输入(但是在Attention模型中不再是这样了)
那么整个过程中如果使用Attention应该怎么做呢?
在之前我们把encoder的最后一个输出,作为decoder的初始的隐藏状态,现在我们不再这样做
2.1 Attention的实现过程
-
初始化一个Decoder的隐藏状态 z 0 z_0 z0
-
这个 z o z_o zo会和encoder第一个time step的output进行match操作(或者是socre操作),得到 α 0 1 \alpha_0^1 α01 ,这里的match可以使很多中操作,比如:
-
encoder中的每个output都和 z 0 z_0 z0进行计算之后,得到的结果进行softmax,让他们的和为1(可以理解为权重)
-
之后把所有的softmax之后的结果和原来encoder的输出 h i h_i hi进行相加求和得到 c 0 c^0 c0
即 : c 0 = ∑ α ^ 0 i h i 即: c^0 = \sum\hat{\alpha}_0^ih^i 即:c0=∑α^0ihi -
得到 c 0 c^0 c0之后,把它作为decoder的input,同和传入初始化的 z 0 z^0 z0,得到第一个time step的输出和hidden_state( Z 1 Z^1 Z1)
-
把 Z 1 Z_1 Z1再和所有的encoder的output进行match操作,得到的结果进行softmax之后作为权重和encoder的每个timestep的结果相乘求和得到 c 1 c^1 c1
-
再把 c 1 c^1 c1作为decoder的input,和 Z 1 Z^1 Z1作为输入得到下一个输出,如此循环,只到最终decoder的output为终止符
-
上述参考:http://speech.ee.ntu.edu.tw/~tlkagk/courses_MLSD15_2.html
-
- 先计算attention权重
- 在计算上下文向量,图中的 c i c^i ci
- 最后计算结果,往往会把当前的output([batch_size,1,hidden_size])和上下文向量进行拼接然后使用
2.2 不同Attention的介绍
在上述过程中,使用decoder的状态和encoder的状态的计算后的结果作为权重,乘上encoder每个时间步的输出,这需要我们去训练一个合适的match函数,得到的结果就能够在不同的时间步上使用不同的encoder的相关信息,从而达到只关注某一个局部的效果,也就是注意力的效果
2.2.1 Soft-Attention 和 Hard-Attention
最开始Bahdanau等人提出的Attention机制通常被称为soft-attention,所谓的soft-attention指的是encoder中输入的每个词语都会计算得到一个注意力的概率。
在进行图像捕捉的时候,提出了一种hard-attenion的方法,希望直接从input中找到一个和输出的某个词对应的那一个词。但是由于NLP中词语和词语之间往往存在联系,不会只关注某一个词语,所以都会使用soft-attention,所以这里的就不多介绍hard-attention
2.2.3 Global-Attention 和Local Attention
Bahdanau等人提出的Bahdanau Attention 被称为local attention,后来Luong等人提出的Luong Attention是一种全局的attenion。
所谓全局的attenion指的是:使用的全部的encoder端的输入的attenion的权重
local-attenion就是使用了部分的encoder端的输入的权重(当前时间步上的encoder的hidden state),这样可以减少计算量,特别是当句子的长度比较长的时候。
2.2.4 Bahdanau Attention和 Luong Attenion的区别
区别在于两个地方:
-
attention的计算数据和位置
-
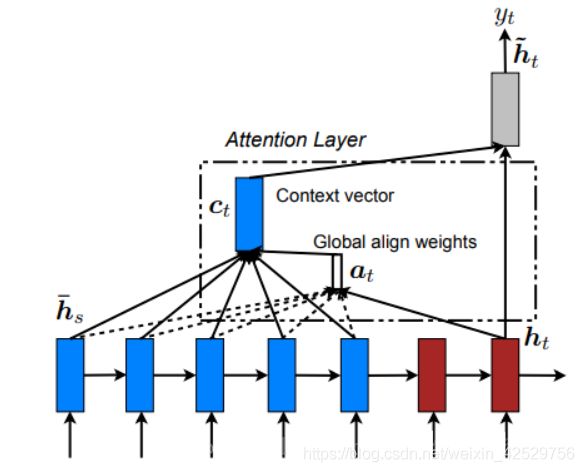
Bahdanau Attention会使用前一次的隐藏状态来计算attention weight,所以我们会在代码中的GRU之前使用attention的操作,同时会把attention的结果和word embedding的结果进行concat,作为GRU的输出(参考的是pytorch Toritul)。Bahdanau使用的是双向的GRU,会使用正反的encoder的output的concat的结果作为encoder output,如下图所示

-
Luong Attenion使用的是当前一次的decoder的output来计算得到attention weight,所以在代码中会在GRU的后面进行attention的操作,同时会把context vector和gru的结果进行concat的操作,最终的output。Luong使用的是多层GRU,只会使用最后一层的输出(encoder output)
-
-
计算attention weights的方法不同
-
Bahdanau Attention的match函数, a i j = v a T t a n h ( W a Z i − 1 , + U a h j ) a_i^j = v^T_a tanh (W_aZ_{i-1},+U_ah_j) aij=vaTtanh(WaZi−1,+Uahj),计算出所有的 a i j a_i^j aij之后,在计算softmax,得到 a ^ i j \hat{a}_i^j a^ij,即 a ^ i j = e x p ( a i j ) ∑ e x p ( a i j ) \hat{a}_i^j = \frac{exp(a_i^j)}{\sum exp(a_i^j)} a^ij=∑exp(aij)exp(aij)其中
- v a T 是 一 个 参 数 矩 阵 , 需 要 被 训 练 , W a 是 实 现 对 Z i − 1 的 形 状 变 化 v_a^T是一个参数矩阵,需要被训练,W_a是实现对Z_{i-1}的形状变化 vaT是一个参数矩阵,需要被训练,Wa是实现对Zi−1的形状变化,
- U a 实 现 对 h j 的 形 状 变 化 ( 矩 阵 乘 法 , 理 解 为 线 性 回 归 , 实 现 数 据 形 状 的 对 齐 ) U_a实现对h_j的形状变化(矩阵乘法,理解为线性回归,实现数据形状的对齐) Ua实现对hj的形状变化(矩阵乘法,理解为线性回归,实现数据形状的对齐),
- Z i − 1 是 d e c o d e r 端 前 一 次 的 隐 藏 状 态 , h j 是 e n c o d e r 的 o u t p u t Z_{i-1}是decoder端前一次的隐藏状态,h_j是encoder的output Zi−1是decoder端前一次的隐藏状态,hj是encoder的output
-
Luong Attenion整体比Bahdanau Attention更加简单,他使用了三种方法来计算得到权重-
矩阵乘法:general
- 直接对decoder的隐藏状态进行一个矩阵变换(线性回归),然后和encoder outputs进行矩阵乘法
-
dot
- 直接对decoder的隐藏状态和encoder outputs进行矩阵乘法
-
concat
- 把decoder的隐藏状态和encoder的output进行concat,把这个结果使用tanh进行处理后的结果进行对齐计算之后,和encoder outputs进行矩阵乘法
-
h t 是当前的decoder hidden state, h s 是所有的encoder 的hidden state(encoder outputs) h_t\text{是当前的decoder hidden state,}h_s\text{是所有的encoder 的hidden state(encoder outputs)} ht是当前的decoder hidden state,hs是所有的encoder 的hidden state(encoder outputs)
-
-
最终两个attention的结果区别并不太大,所以以后我们可以考虑使用Luong attention完成代码
3. Attention的代码实现
完成代码之前,我们需要确定我们的思路,通过attention的代码,需要实现计算的是attention weight
通过前面的学习,我们知道attention_weight = f(hidden,encoder_outputs),主要就是实现Luong attention中的三种操作

class Attention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,method,batch_size,hidden_size):
super(Attention,self).__init__()
self.method = method
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
assert self.method in ["dot","general","concat"],"method 只能是 dot,general,concat,当前是{}".format(self.method)
if self.method == "dot":
pass
elif self.method == "general":
self.Wa = nn.Linear(hidden_size,hidden_size,bias=False)
elif self.method == "concat":
self.Wa = nn.Linear(hidden_size*2,hidden_size,bias=False)
self.Va = nn.Parameter(torch.FloatTensor(batch_size,hidden_size))
def forward(self, hidden,encoder_outputs):
"""
:param hidden:[1,batch_size,hidden_size]
:param encoder_outputs: [batch_size,seq_len,hidden_size]
:return:
"""
batch_size,seq_len,hidden_size = encoder_outputs.size()
hidden = hidden.squeeze(0) #[batch_size,hidden_size]
if self.method == "dot":
return self.dot_score(hidden,encoder_outputs)
elif self.method == "general":
return self.general_score(hidden,encoder_outputs)
elif self.method == "concat":
return self.concat_score(hidden,encoder_outputs)
def _score(self,batch_size,seq_len,hidden,encoder_outputs):
# 速度太慢
# [batch_size,seql_len]
attn_energies = torch.zeros(batch_size,seq_len).to(config.device)
for b in range(batch_size):
for i in range(seq_len):
#encoder_output : [batch_size,seq_len,hidden_size]
#deocder_hidden :[batch_size,hidden_size]
#torch.Size([256, 128]) torch.Size([128]) torch.Size([256, 24, 128]) torch.Size([128])
# print("attn size:",hidden.size(),hidden[b,:].size(),encoder_output.size(),encoder_output[b,i].size())
attn_energies[b,i] = hidden[b,:].dot(encoder_outputs[b,i]) #dot score
return F.softmax(attn_energies).unsqueeze(1) # [batch_size,1,seq_len]
def dot_score(self,hidden,encoder_outputs):
"""
dot attention
:param hidden:[batch_size,hidden_size] --->[batch_size,hidden_size,1]
:param encoder_outputs: [batch_size,seq_len,hidden_size]
:return:
"""
#hiiden :[hidden_size] -->[hidden_size,1] ,encoder_output:[seq_len,hidden_size]
hidden = hidden.unsqueeze(-1)
attn_energies = torch.bmm(encoder_outputs, hidden)
attn_energies = attn_energies.squeeze(-1) #[batch_size,seq_len,1] ==>[batch_size,seq_len]
return F.softmax(attn_energies).unsqueeze(1) # [batch_size,1,seq_len]
def general_score(self,hidden,encoder_outputs):
"""
general attenion
:param batch_size:int
:param hidden: [batch_size,hidden_size]
:param encoder_outputs: [batch_size,seq_len,hidden_size]
:return:
"""
x = self.Wa(hidden) #[batch_size,hidden_size]
x = x.unsqueeze(-1) #[batch_size,hidden_size,1]
attn_energies = torch.bmm(encoder_outputs,x).squeeze(-1) #[batch_size,seq_len,1]
return F.softmax(attn_energies,dim=-1).unsqueeze(1) # [batch_size,1,seq_len]
def concat_score(self,hidden,encoder_outputs):
"""
concat attention
:param batch_size:int
:param hidden: [batch_size,hidden_size]
:param encoder_outputs: [batch_size,seq_len,hidden_size]
:return:
"""
#需要先进行repeat操作,变成和encoder_outputs相同的形状,让每个batch有seq_len个hidden_size
x = hidden.repeat(1,encoder_outputs.size(1),1) ##[batch_size,seq_len,hidden_size]
x = torch.tanh(self.Wa(torch.cat([x,encoder_outputs],dim=-1))) #[batch_size,seq_len,hidden_size*2] --> [batch_size,seq_len,hidden_size]
#va [batch_size,hidden_size] ---> [batch_size,hidden_size,1]
attn_energis = torch.bmm(x,self.Va.unsqueeze(2)) #[batch_size,seq_len,1]
attn_energis = attn_energis.squeeze(-1)
# print("concat attention:",attn_energis.size(),encoder_outputs.size())
return F.softmax(attn_energis,dim=-1).unsqueeze(1) #[batch_size,1,seq_len]
完成了attention weight的计算之后,需要再对代码中forward_step的内容进行修改
def forward_step(self,decoder_input,decoder_hidden,encoder_outputs):
"""
:param decoder_input:[batch_size,1]
:param decoder_hidden: [1,batch_size,hidden_size]
:param encoder_outputs: encoder中所有的输出,[batch_size,seq_len,hidden_size]
:return: out:[batch_size,vocab_size],decoder_hidden:[1,batch_size,didden_size]
"""
embeded = self.embedding(decoder_input) #embeded: [batch_size,1 , embedding_dim]
#TODO 可以把embeded的结果和前一次的context(初始值为全0tensor) concate之后作为结果
#rnn_input = torch.cat((embeded, last_context.unsqueeze(0)), 2)
# gru_out:[256,1, 128] decoder_hidden: [1, batch_size, hidden_size]
gru_out,decoder_hidden = self.gru(embeded,decoder_hidden)
gru_out = gru_out.squeeze(1)
#TODO 注意:如果是单层,这里使用decoder_hidden没问题(output和hidden相同)
# 如果是多层,可以使用GRU的output作为attention的输入
#开始使用attention
attn_weights = self.attn(decoder_hidden,encoder_outputs)
# attn_weights [batch_size,1,seq_len] * [batch_size,seq_len,hidden_size]
context = attn_weights.bmm(encoder_outputs) #[batch_size,1,hidden_size]
gru_out = gru_out.squeeze(0) # [batch_size,hidden_size]
context = context.squeeze(1) # [batch_size,hidden_size]
#把output和attention的结果合并到一起
concat_input = torch.cat((gru_out, context), 1) #[batch_size,hidden_size*2]
concat_output = torch.tanh(self.concat(concat_input)) #[batch_size,hidden_size]
output = F.log_softmax(self.fc(concat_output),dim=-1) #[batch_Size, vocab_size]
# out = out.squeeze(1)
return output,decoder_hidden,attn_weights
attetnion的Bahdanau实现可以参考:https://github.com/spro/practical-pytorch/blob/master/seq2seq-translation/seq2seq-translation.ipynb