Ansible playbook和Ansible Roles(三)
文章目录
-
- 1. playbook判断语句
- 2. playbook循环语句
- 3. playbook handlers
- 4. Playbook任务标签
- 5. Playbook文件复用
- 6. Playbook忽略错误
- 7. Playbook异常处理
- 8. Ansible Valut概述
-
- 8.1 Ansible Valut实践
- 9. Ansible Jinja2模板
- 10. Ansible Roles
- 11. AnsibleGalaxy
- 12. 自我总结
1. playbook判断语句
判断在Ansible任务中得使用频率非常高。比如yum模块可以检测软件包是否已被安装,而在这个过程中我们不用做太多得人工干预
但是也有不放呢任务需要进行判断,比如:web服务器角色都需要安装nginx仓库,但其他服务器角色并不需要,此时就会用到when判断。
比如:Centos与Ubuntu系统都需要安装httpd服务,那么就需要使用when判断主机系统,然后调用不同得模块执行。
实践案例1: 根据不同操作系统,安装相同的软件包
[root@m01 when]# cat when.yml
- hosts: webservers
tasks:
- name: Install httpd Server
yum: name=httpd state=present
when: ansible_distribution == "CentOS"
- name: Install httpd Server
apt: name=httpd2 state=present
when: ansible_distribution == "Ubuntu"
实践案例2:所有为web主机名的添加nginx仓库,其余的都跳过添加
1.如何添加yum仓库
2.如何判断,判断什么内容
---
[root@m01 when]# cat when.yml
- hosts: web
tasks:
- name: Add Nginx Repos
yum_repository: #模块
name: nginx_tet #它代表/etc/yum.repos.d/nginx_tet.repo
description: Nginx YUM repo #描述 (不加会报错)
baseurl: http://nginx.org/packages/centos/7/$basearch/
gpgcheck: no #把效验本地给关掉
when: (ansible_hostname is match ("web*")) or (ansible_hostname is match ("lb*")) #根据官方的写法
1.通过register将命令执行结果保存至变量,然后通过when语句进行判断
- hosts: webservers
tasks:
- name: Check Httpd Server
command: systemctl is-active httpd
ignore_errors: yes
register: check_httpd
#- name: debug outprint #仅仅只是输出结果
# debug: var=check_httpd
- name: Httpd Restart
service: name=httpd state=restarted
when: check_httpd.rc == 0
==========================================
(1)按照不同的主机名称进行判断
[root@m01 when]# cat when.yml
- hosts: web
vars:
remote_ip: "{{ ansible_default_ipv4.address }}"
host_name: "{{ ansible_fqdn }}"
tasks:
- name: Print ip # 进行测试的
debug:
msg:
- "{{ remote_ip }}"
- "{{ host_name }}"
- name: Reboot Server
command: reboot
when: ansible_fqdn == "web02"
(2)按照不同的IP地址进行判断
[root@m01 when]# cat when.yml
- hosts: web
vars:
remote_ip: "{{ ansible_default_ipv4.address }}"
host_name: "{{ ansible_fqdn }}"
tasks:
- name: Print ip
debug:
msg:
- "{{ remote_ip }}"
- "{{ host_name }}"
- name: Reboot Server
command: reboot
when: ansible_default_ipv4.address == "10.0.0.7"
(3)按照获取客户端的某参数值得大小判断
- hosts: web
vars:
remote_ip: "{{ ansible_default_ipv4.address }}"
host_name: "{{ ansible_fqdn }}"
host_mem: "{{ ansible_memtotal_mb }}"
tasks:
- name: Print ip
debug:
msg:
- "{{ remote_ip }}"
- "{{ host_name }}"
- "{{ host_mem }}"
- name: Reboot Server
command: reboot
when: ansible_memtotal_mb|int < "2000"
(4)列表方式判断 and关系 并且关系
[root@m01 when]# cat when.yml
- hosts: web
vars:
remote_ip: "{{ ansible_default_ipv4.address }}"
host_name: "{{ ansible_fqdn }}"
host_mem: "{{ ansible_memtotal_mb }}"
host_ver: "{{ ansible_distribution }}"
tasks:
- name: Print ip
debug:
msg:
- "{{ remote_ip }}"
- "{{ host_name }}"
- "{{ host_mem }}"
- "{{ host_ver }}"
- name: Reboot Server
file:
path: /root/web01.txt
state: touch
when:
- ansible_distribution == "CentOS"
- ansible_fqdn == "web01"
(6)或者关系判断
[root@m01 when]# cat when.yml
- hosts: web
vars:
remote_ip: "{{ ansible_default_ipv4.address }}"
host_name: "{{ ansible_fqdn }}"
host_mem: "{{ ansible_memtotal_mb }}"
host_ver: "{{ ansible_distribution }}"
tasks:
- name: Print ip
debug:
msg:
- "{{ remote_ip }}"
- "{{ host_name }}"
- "{{ host_mem }}"
- "{{ host_ver }}"
- name: Reboot Server
file:
path: /root/web0102.txt
state: touch
when: ansible_distribution == "CentOS" or ansible_fqdn == "web02"
(7) 修改Nginx配置文件 把Nginx从ansible服务器拷贝到web服务器
拷贝过去需要启动或者重启 如果Nginx配置文件不对 不让加载
1. 安装Nginx
2. 拷贝文件到Nginx.conf 判断文件是否正确 ngixn -t 变量注册接收结果
3. 启动
4. 重新加载 在重新加载的地方进行when判断
[root@m01 when]# cat nginx.yml
- hosts: web02
tasks:
- name: Install Nginx
yum:
name: nginx
state: present
- name: scp configure Nginx
copy:
src: ./nginx.j2
dest: /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
- name: Check Nginx Configure
command: /usr/sbin/nginx -t
register: result
ignore_errors: yes # 忽略错误继续执行
- name: print result
debug:
msg: "{{ result.rc }}"
- name: Reload Nginx
systemd:
name: nginx
state: reloaded
when: result.rc == 0 # 判断nginx -t执行结果 是否为0 通过变量注册获取的
-----------------------------
- name: Reload Nginx
systemd:
name: nginx
state: reloaded
when: result.rc is match "0"
(8)rsync服务进行主机名的判断(rsync的优化)
[root@m01 rsync]# cat rsync.yml
- hosts: rsyncall
tasks:
- name: Install Rsyncd Server
yum:
name: rsync
state: present
- name: Create www Group
group:
name: www
gid: 666
- name: Create User www
user:
name: www
uid: 666
group: www
create_home: false
shell: /sbin/nologin
- name: Configure Rsync Server
copy:
src: rsync.j2
dest: /etc/rsyncd.conf
when: ansible_hostname == "backup"
- name: Auth Password
copy:
content: rsync_backup:123456
dest: /etc/rsync.passwd
mode: 0600
when: ansible_hostname == "backup"
- name: Create Dir /backup
file:
path: /backup
state: directory
owner: www
group: www
recurse: yes
when: ansible_hostname == "backup"
- name: Start Rsyncd Server
systemd:
name: rsyncd
state: started
enabled: yes
when: ansible_hostname == "backup"
- name: clinet Auth Password
copy:
content: 123456
dest: /etc/rsync.passwd
mode: 0600
when: ansible_hostname == "web01" or ansible_hostname == "web02"
(9)判断http是否存活
- hosts: web02
tasks:
- name: Install Nginx
yum:
name: nginx
state: present
- name: scp configure Nginx
copy:
src: ./nginx.j2
dest: /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
- name: Check Nginx Configure
command: /usr/sbin/nginx -t
register: result
ignore_errors: yes
- name: Check HTTP Server
command: systemctl is-active httpd
register: result_http
ignore_errors: yes
- name: print result
debug: var=result_http
- name: Reload Nginx
systemd:
name: nginx
state: reloaded
when: result.rc == 0
2. playbook循环语句
有时候我们写playbook得时候发现了很多task都要重复引用某个模块,比如一次启动10个服务,或者一次拷贝10个文件,如果按照传统得写法最少要写10次,这样会显得playbook很臃肿。如果使用循环得方式来编写playbook,这样可以减少重复使用某个模块。
实践案例一、使用循环启动多个服务
[root@m01 project2]# cat with.yml
- hosts: webservers
tasks:
- name: Start httpd mariadb
systemd: name={{ item }} state=started
with_items:
- httpd
- mariadb
1.案例二、使用定义变量方式循环安装软件包。
- hosts: webservers
tasks:
- name: ensure a list of packages installed
yum: name= "{{ packages }}" state=present
vars:
packages:
- httpd
- httpd-tools
#弃用的方式
- hosts: webservers
tasks:
- name: ensure a list of packages installed
yum: name= "{{ item }}" state=present
with_items:
- httpd
- httpd-tools
实践案例三、使用字典循环方式创建用户和批量拷贝文件
[root@manager ~]# cat loop-user.yml
- hosts: webservers
tasks:
- name: Add Users
user: name={{ item.name }} groups={{ item.groups }} state=present
with_items:
- { name: 'testuser1', groups: 'bin' }
- { name: 'testuser2', groups: 'root' }
[root@m01 project2]# cat with4.yml
- hosts: webservers
tasks:
- name: Copy Rsync configure and Rsync passwd
copy: src={{ item.src }} dest={{ item.dest }} mode={{ item.mode }}
with_items:
- { src: "./rsyncd.conf", dest: "/etc/rsyncd.conf", mode: "0644" }
- { src: "./rsync.passwd", dest: "/tmp/rsync.passwd", mode: "0600" }
===============================================
官方推荐写法:
[root@m01 when]# vim when.yml
- hosts: web
tasks:
- name: Started Server
yum: # systemd 起不来
name: "{{ packages }}"
state: started
vars:
packages:
- httpd
- mariadb
也可以这样写:
[root@m01 when]# vim when.yml
- hosts: web
tasks:
- name: Started Server
yum: # systemd 起不来
name: "{{ item }}"
state: started
with_items:
- httpd
- mariadb
(1)使用with_item循环列表
[root@m01 file]# cat create_file.yml
- hosts: web
tasks:
- name: Create file
file:
path: "{{ item }}"
state: touch
with_items:
- file1.txt
- file2.txt
(2)使用loop方式进行循环列表
[root@m01 file]# cat create_file.yml
- hosts: web
tasks:
- name: Create file
file:
path: "{{ item }}"
state: touch
loop:
- file1.txt
- file2.txt
(3)循环启动列表 一次启动多个服务
[root@m01 file]# cat start.yml
- hosts: web
tasks:
- name: Install HTTPD Nginx Mariadb Server
yum:
name: "{{ item }}"
state: present
loop:
- nginx
- mariadb-server
- name: Start HTTP Nginx Mariadb Sever
systemd:
name: "{{ item }}"
state: started
loop:
- nginx
- mariadb
(4)拷贝两个文件到目标
1.txt 到目标主机为600
2.txt 到目标主机为644
[root@m01 file]# cat scp.yml
- hosts: web
tasks:
- name: scp file dest web01 web02
copy:
src: "{{ item }}"
dest: /root/
loop:
- 1.txt
- 2.txt
(5)scp多个文件到目标主机 权限不同
[root@m01 file]# cat scp.yml
- hosts: web
tasks:
- name: scp file dest web01 web02
copy:
src: "{{ item.src }}"
dest: "{{ item.dest }}"
owner: "{{ item.owner }}"
group: "{{ item.group }}"
mode: "{{ item.mode }}"
loop:
- { src: 1.txt,dest: /root/,mode: '0600',owner: www,group: root }
- { src: 2.txt,dest: /opt/,mode: '0000',owner: root,group: www }
(6)rsync拷贝文件(rsync优化)
[root@m01 rsync]# vim rsync.yml
[root@m01 rsync]# cat rsync.yml
- hosts: rsyncall
tasks:
- name: Install Rsyncd Server
yum:
name: rsync
state: present
- name: Create www Group
group:
name: www
gid: 666
- name: Create User www
user:
name: www
uid: 666
group: www
create_home: false
shell: /sbin/nologin
- name: Configure Rsync Server
copy:
src: "{{ item.src }}"
dest: "{{ item.dest }}"
mode: "{{ item.mode }}"
loop:
- { src: rsync.j2, dest: /etc/rsyncd.conf,mode: '0644' }
- { src: rsync_pass.j2, dest: /etc/rsync.passwd,mode: '0600' }
when: ansible_hostname == "backup"
- name: Create Dir /backup
file:
path: /backup
state: directory
owner: www
group: www
recurse: yes
when: ansible_hostname == "backup"
- name: Start Rsyncd Server
systemd:
name: rsyncd
state: started
enabled: yes
when: ansible_hostname == "backup"
- name: clinet Auth Password
copy:
content: 123456
dest: /etc/rsync.passwd
mode: 0600
when: ansible_hostname == "web01" or ansible_hostname == "web02"
3. playbook handlers
handler用来执行某些条件下的任务,比如当配置文件发生变化的时候,通过notify触发handler去重启服务。
在saltstack中也有类似的触发器,写法相对Ansible简单,只需要watch,配置文件即可。
[root@m01 project2]# cat han.yml
- hosts: webservers
vars:
- http_port: 8083
tasks:
- name: Install Http Server
yum: name=httpd state=present
- name: configure httpd server
template: src=./httpd.conf.j2 dest=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
notify:
- Restart Httpd Server
- Restart PHP Server
- name: start httpd server
service: name=httpd state=started enabled=yes
handlers:
- name: Restart Httpd Server
systemd: name=httpd state=restarted
- name: Restart PHP Server
systemd: name=php-fpm state=restarted
3.handlers注意事项
1.无论多少个task通知了相同的handlers,handlers仅会在所有tasks结束后运行一次。
2.只有task发生改变了才会通知handlers,没有改变则不会触发handlers
3.不能使用handlers替代tasks
====================================================
handle注意事项:
1.无论多少个task通知了相同的handlers,handlers仅会在所有tasks结束后运行一次。
2.只有task发生改变了才会通知handlers,没有改变则不会触发handlers
3.不能使用handlers替代tasks
(1)handlers触发修改
[root@m01 handlers]# cat handlers.yml
- hosts: web01
vars:
- http_port: 82
tasks:
- name: Install Nginx
yum:
name: nginx
state: present
- name: Configure Nginx Server
template: # 在剧本中可以使用变量,可以使用系统的变量,也可以使用自己定义的变量
src: nginx_conf.j2
dest: /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
notify: Reload Nginx
- name: Start Nginx Server
systemd:
name: nginx
state: started
enabled: yes
handlers:
- name: Reload Nginx
systemd:
name: nginx
state: reloaded
(2)触发后重启nginx和mariadb
[root@m01 handlers]# cat handlers.yml
- hosts: web01
vars:
- http_port: 83
tasks:
- name: Install Nginx
yum:
name: nginx
state: present
- name: Configure Nginx Server
template:
src: nginx_conf.j2
dest: /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
notify: Reload Nginx
- name: Start Nginx Server
systemd:
name: nginx
state: started
enabled: yes
handlers:
- name: Reload Nginx
systemd:
name: "{{ item }}"
state: restarted
loop:
- nginx
- mariadb
(2)handlers触发nginx和mariadb重启 并且when判断nginx文件是否正确
[root@m01 handlers]# cat handlers.yml
- hosts: web01
vars:
- http_port: 85
tasks:
- name: Install Nginx
yum:
name: nginx
state: present
- name: Configure Nginx Server
template:
src: nginx_conf.j2
dest: /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
notify: Reload Nginx
- name: Check Nginx Configuer
command: /usr/sbin/nginx -t
ignore_errors: yes
register: result
- name: Start Nginx Server
systemd:
name: nginx
state: started
enabled: yes
handlers:
- name: Reload Nginx
systemd:
name: "{{ item }}"
state: restarted
loop:
- nginx
- mariadb
when: result.rc == 0
4. Playbook任务标签
默认情况下,Ansible在执行一个playbook时,会执行playbook中定义得多有任务。Ansible的标签(tags)功能可以给单独任务甚至整个playbook打上标签,然后利用这些标签来指定要运行playbook中的个别任务,或不执行指定的任务。(可以进行调试)
1. 打标签的方式有几种,比如:
对一个task打一个标签、对一个task打多个标签、对多个task打一个标签
2. 对task打完标签应该如何使用
-t : 执行指定的tag标签任务
--skip-tags : 执行--skip-tags之外的标签任务
ansible-playbook tag.yml --list-tags 查看有多少个tags
tag标记(用于调试的场景下)
[root@m01 project2]# cat tag.yml
- hosts: webservers
vars:
- http_port: 8083
tasks:
- name: Install Http Server
yum: name=httpd state=present
tags:
- install_httpd
- httpd_server
- name: configure httpd server
template: src=./httpd.conf.j2 dest=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
notify: Restart Httpd Server
tags:
- confiure_httpd
- httpd_server
- name: start httpd server
service: name=httpd state=started enabled=yes
tags: service_httpd
handlers:
- name: Restart Httpd Server
systemd: name=httpd state=restarted
[root@m01 project2]# ansible-playbook tag.yml --list-tags
[root@m01 project2]# ansible-playbook tag.yml -t httpd_server
[root@m01 project2]# ansible-playbook tag.yml -t install_httpd,confiure_httpd
[root@m01 project2]# ansible-playbook tag.yml --skip-tags httpd_server
5. Playbook文件复用
include用来动态额包含tasks任务列表include——tasks新版/include老版

Include包含
include(import_playbook)
include_tasks
[root@m01 project2]# cat task.yml
- hosts: webservers
vars:
- http_port: 801
tasks:
- include_tasks: task_install.yml
- include_tasks: task_configure.yml
- include_tasks: task_start.yml
handlers:
- name: Restart Httpd Server
systemd: name=httpd state=restarted
[root@m01 project2]# cat task_install.yml
- name: Install Http Server
yum: name=httpd state=present
[root@m01 project2]# cat task_configure.yml
- name: configure httpd server
template: src=./httpd.conf.j2 dest=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
notify: Restart Httpd Server
[root@m01 project2]# cat task_start.yml
- name: start httpd server
service: name=httpd state=started enabled=yes
6. Playbook忽略错误
默认playbook会检查tasks执行的返回状态,如遇到错误则会立即种植playbook的后续的tasks执行。然而有些时候playbook即使执行错误了也要让其继续执行
加入参数:ignore_error:yes 忽略错误
- 编写playbook,当有task执行失败则会立即终止后续task运行
忽略错误ignore_errors
[root@manager ~]# cat f9.yml
---
- hosts: webservers
tasks:
- name: Ignore False
command: /bin/false
ignore_errors: yes
- name: touch new file
file: path=/tmp/bgx_ignore state=touch
7. Playbook异常处理
通常情况下,当task失败后,play将会终止,任何在前面已经被tasks notify的handlers都不会被执行。如果你在play中设置了force_handlers: yes参数,被通知的handlers就会被强制执行。(有些特殊场景可能会使用到)
案例一: task执行失败强制调用handlers
案例二:控制task报告的状态,不一定必须时"changed"
异常处理
force_handlers: yes 强制调用handlers
changed_when: false 被管理主机没有发生变化,可以使用参数将change状态改为ok
changed_when: httpd_check.stdout.find('OK') #查看变量中的某个字符串
[root@m01 project2]# cat changed_when.yml
- hosts: webservers
vars:
- http_port: 8083
tasks:
- name: configure httpd server
template: src=./httpd.conf.j2 dest=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
notify: Restart Httpd Server
- name: Check HTTPD
shell: /usr/sbin/httpd -t
register: httpd_check
changed_when:
- httpd_check.stdout.find('OK')
- false
- name: start httpd server
service: name=httpd state=started enabled=yes
handlers:
- name: Restart Httpd Server
systemd: name=httpd state=restarted
failed_when
命令不依赖返回状态码来判定是否执行失败,而是要查看命令返回内容来决定,比如返回内容中包括 failed 字符串,则判定为失败。示例如下:
- name: this command prints FAILED when it fails
command: /usr/bin/example-command -x -y -z
register: command_result
failed_when: "'FAILED' in command_result.stderr"
小总结:
-------tasl任务处理相关流程与控制参数
when 判断
item 循环
handlers 触发器(需要task使用notify通知)
tags 标签(调试使用)
include_tasks 包含task任务
ignore_errors 忽略错误
错误处理
force_handlers #扩展
changed_when false 抑制改变的状态为ok(获取系统的状态信息时)
------------------------------重要(检查服务的配置是否正常,正常则不处理,不正常则中断)
register: httpd_check
changed_when:
- httpd_check.stdout.find('OK')
- false
8. Ansible Valut概述
Ansible Vault作为ansible的一项新功能可将例如passwords,keys等敏感数据文件进行加密,而非存放在明文的playbooks或roles中
8.1 Ansible Valut实践
ansible加密模块
[root@m01 project2]# ansible-vault --help
Usage: ansible-vault [create|decrypt|edit|encrypt|encrypt_string|rekey|view] [options] [vaultfile.yml]
加密一个文件
ansible-vault encrypt include.yml
查看一个文件
[root@m01 project2]# ansible-vault view include.yml
Vault password:
- import_playbook: han.yml
- import_playbook: when2.yml
修改加密的文件内容
[root@m01 project2]# ansible-vault edit include.yml
rekey 修改密码
[root@m01 project2]# ansible-vault rekey include.yml
Vault password:
New Vault password:
Confirm New Vault password:
Rekey successful
执行加密的playbook
echo "1" >pass
chmod 600 pass
ansible-playbook include.yml --vault-password-file=pass
9. Ansible Jinja2模板
jinja模板
2.jinja 模板逻辑关系
{% for i in EXPR %}...{% endfor%} 作为循环表达式
{% if EXPR %}...{% elif EXPR %}...{% endif%} 作为条件判断
--------------------------------------nginx
[root@m01 project2]# cat jinja_nginx.yml
- hosts: webservers
vars:
- http_port: 80
- server_name: www.oldboyedu.com
tasks:
- name: Copy Nginx COnfigure
template: src=./oldboyedu.conf.j2 dest=/etc/nginx/conf.d/oldboyedu_proxy.conf
[root@m01 project2]# cat oldboyedu.conf.j2
upstream {{ server_name }} {
{% for i in range(1,20) %}
server 172.16.1.{{i}}:{{http_port}};
{%endfor%}
}
server {
listen {{ http_port }};
server_name {{ server_name }};
location / {
proxy_pass http://{{ server_name }};
proxy_set_header Host $http_host;
}
}
--------------------------------------keepalived
[root@m01 project2]# cat jinja_keepalived.yml
- hosts: webservers
tasks:
- name: Copy Keepalived Configure
template: src=./kee.conf.j2 dest=/tmp/keepalived.conf
[root@m01 project2]# cat kee.conf.j2
global_defs {
router_id {{ ansible_hostname }}
}
vrrp_instance VI_1 {
{%if ansible_hostname =="web01" %}
state MASTER
priority 150
{%elif ansible_hostname == "web02" %}
state BACKUP
priority 100
{%endif%}
interface eth0
virtual_router_id 50
advert_int 1
authentication {
auth_type PASS
auth_pass 1111
}
virtual_ipaddress {
10.0.0.3
}
}
使用Ansible jinja IF 生成不同的mysql配置文件 (自定义变量)
[root@m01 project2]# cat jinja_mysql.yml
- hosts: webservers
gather_facts: no
vars:
PORT: 13306
# PORT: false #相当于开关
tasks:
- name: Copy MySQL Configure
template: src=./my.cnf.j2 dest=/tmp/my.cnf
[root@m01 project2]# cat my.cnf.j2
{% if PORT %}
bind-address=0.0.0.0:{{ PORT }}
{% else %}
bind-address=0.0.0.0:3306
{%endif%}
10. Ansible Roles
role角色
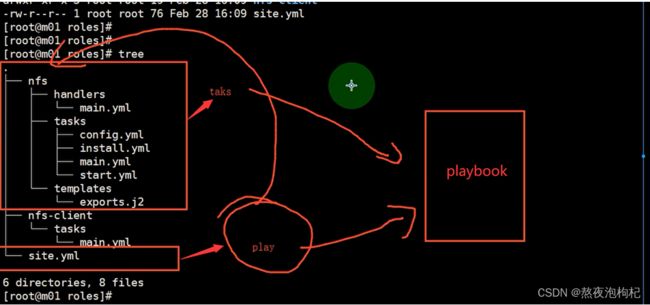
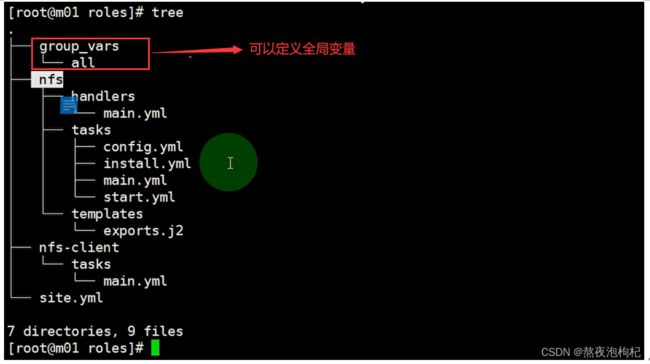
[root@m01 ~]# cd /etc/ansible/roles/
[root@m01 roles]# mkdir nfs/{tasks,handlers,templates} -pv
mkdir: created directory ‘nfs’
mkdir: created directory ‘nfs/tasks’
mkdir: created directory ‘nfs/handlers’
mkdir: created directory ‘nfs/templates’
[root@m01 roles]# cat nfs/tasks/install.yml
- name: Install NFS-utils Server
yum: name=nfs-utils state=present
[root@m01 roles]# cat nfs/tasks/config.yml
- name: Configure Nfs-utils Server
template: src=./exports.j2 dest=/etc/exports owner=root group=root mode=0644
notify: Restart NFS Server
[root@m01 roles]# cat nfs/tasks/start.yml
- name: Start NFS Server
systemd: name=nfs state=started enabled=yes
[root@m01 roles]# cat nfs/tasks/main.yml
- include_tasks: install.yml
- include_tasks: config.yml
- include_tasks: start.yml
[root@m01 roles]# cat nfs-client/tasks/main.yml
- name: Mount NFS Server
mount: path=/opt src=172.16.1.7:/data fstype=nfs opts=defaults state=mounted
[root@m01 roles]#
[root@m01 roles]#
[root@m01 roles]# cat site.yml
- hosts: web01
roles:
- nfs
- hosts: web02
roles:
- nfs-client
----------------------------安装memcached
[root@m01 roles]# mkdir memcached/{tasks,handlers,templates} -pv
mkdir: created directory ‘memcached’
mkdir: created directory ‘memcached/tasks’
mkdir: created directory ‘memcached/handlers’
mkdir: created directory ‘memcached/templates’
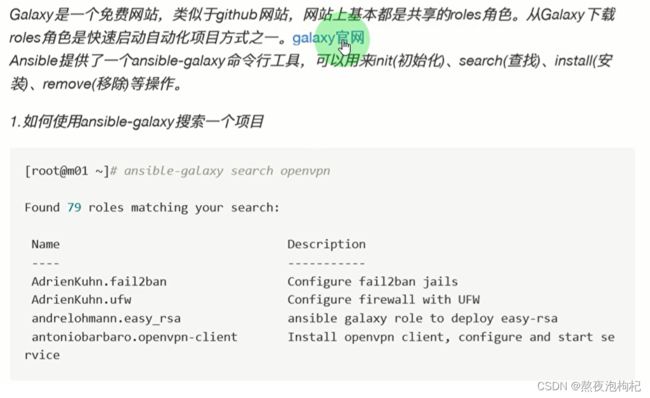
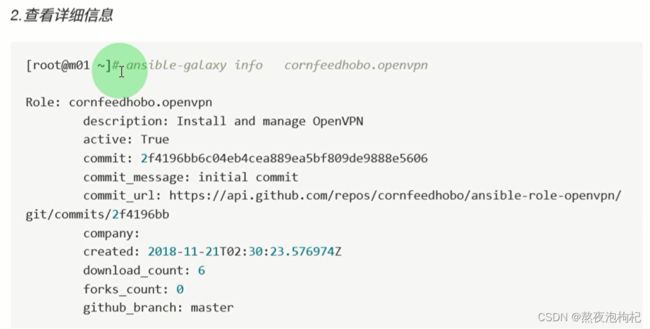
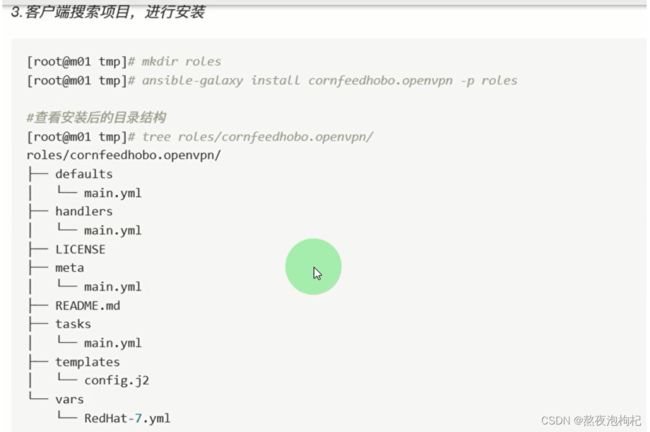
11. AnsibleGalaxy
12. 自我总结
条件语句:
1. 一个条件的简单判断
(1)根据主机判断(when、match)
when ansible_distribution == "Ubuntu"
根据主机判断-->match
when (ansible_hostname is match ("web")) or (ansible_hostname is natch("lb"))
(2)根据主机名进行判断
when ansible_fqdn =="web02"
(3)根据不同的ip地址进行判断
when ansible_default_ipv4.address == "10.0.0.7"
(4)根据内存值来进行大小判断
when ansible_memtotal_mb | int < "2000"
(5)判断nginx -t执行结果 是否为0,如果result.rc == 0 则执行正确(这个需要用到注册变量)
when result.rc == 0
result.rc is match "0"
2. 多个条件的判断
(1)列表方式判断 and并且关系(或者两个关系用列表进行表示)
when:
- ansible_distribution == "CentOS"
- ansible_fqdn == "web01"
when: ansible_default_ipv4.address == "10.0.0.7" and ansible_fqdn == "web1"
(2)或者or 关系判断
when:ansible_distribution == "CentOS" or ansible_fqdn == "web02"
循环语句:
1. with_item循环列表的写法
file:
path: "{{ item }}"
state: touch
with_items:
- file1.txt
- file2.txt
2. 使用loop方式进行循环列表
file:
path: "{{ item }}"
state: touch
loop:
- file1.txt
- file2.txt
3. 字典的方式(一个循环可以写多个条件)
copy:
src: "{{ item.src }}"
dest: "{{ item.dest }}"
owner: "{{ item.owner }}"
group: "{{ item.mode }}"
mode: "{{ item.mode }}"
loop:
- { src: 1.txt , dest:/root/ , mode: '0600' , owner: www , group: root }
- { src: 2.txt , dest: /opt/ , mode: '0000' , owner: root , group: www}
playbook handlers
1. 需要监控的地方
notify: Reload Nginx
2. 触发监控
handlers:
- name Reload Nginx
systemd:
name: "{{ item }}"
state: restarted
loop:
- nginx
- mariadb
when: result.rc == 0 # 检查语法进行判断