Java初阶(异常)
文章目录
- 一、异常的结构体系
- 二、异常的处理
-
- 2.1 防御式编程
- 2.2 异常的抛出
- 2.4 异常的捕获(异常的具体处理方式)
-
- (1)异常声明 throws
- (2) 捕获处理 try-catch
- 2.4 异常的处理流程
- 三、自定义异常类
一、异常的结构体系
在Java中,将程序执行过程中发生的不正常行为称为异常,而java中不同类型的异常,都有与其对应的类来进行描述

- Throwable:是异常体系的顶层类,其派生出两个重要的子类, Error 和 Exception
- Error:指的是Java虚拟机无法解决的严重问题,比如:JVM的内部错误、资源耗尽等,典型代表:StackOverflowError和OutOfMemoryError,一旦发生回力乏术。
- Exception:异常产生后程序员可以通过代码进行处理,使程序继续执行。比如:感冒、发烧。我们平时所说的异常就是Exception
二、异常的处理
2.1 防御式编程
- 事前防御型(LBYL: Look Before You Leap.)
- 在操作之前就做充分的检查
- 事后认错型(EAFP: It’s Easier to Ask Forgiveness than Permission. ")
- 先操作, 遇到问题再处理
2.2 异常的抛出
- 概念
正常情况下,我们的异常都是交给了JVM ,JVM一旦去处理 直接就是异常的终止程序
而如果想要自定义地将异常抛出,我们就需要使用throw - 语法格式
throw new XXXException(“异常产生的原因”);
public static int getElement(int[] array, int index){
if(null == array){
throw new NullPointerException("传递的数组为null");
}
if(index < 0 || index >= array.length){
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("传递的数组下标越界");
}
return array[index];
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = {1,2,3};
getElement(array, 3);
}
- 注意事项
- throw必须写在方法体内部
- 抛出的对象必须是Exception 或者 Exception 的子类对象
- 如果抛出的是 RunTimeException 或者 RunTimeException 的子类,则可以不用处理,直接交给JVM来处理
- 如果抛出的是编译时异常,用户必须处理,否则无法通过编译
- 异常一旦抛出,其后的代码就不会执行
2.4 异常的捕获(异常的具体处理方式)
(1)异常声明 throws
使用场景:
处在方法声明时参数列表之后,当方法中抛出编译时异常,用户不想处理该异常,此时就可以借助throws将异常抛给方法的调用者来处理。即当前方法不处理异常,提醒方法的调用者处理异常。
语法格式:
修饰符 返回值类型 方法名(参数列表) throws 异常类型1,异常类型2…{}
class Person implements Cloneable{
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone(); //表示会有个编译时的CloneNotSupportedException异常,
} //但是这边并不想处理,于是只是用throws声明一下,异常的处理,交给方法的调用者(你要使用这个,就需要处理这个异常)
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException{
Person person1 = new Person(); //这边还是不想处理,所以再声明一下,这个异常最终会交给JVM处理,而一旦发生问题
Person person2 = (Person)person1.clone(); //JVM就会异常终止
}
}
- 注意事项
- throws必须跟在方法的参数列表之后
- 声明的异常必须是 Exception 或者 Exception 的子类
- 方法内部如果抛出了多个异常,throws之后必须跟多个异常类型,之间用逗号隔开,如果抛出多个异常类型
- 具有父子关系,直接声明父类即可
- 调用声明抛出异常的方法时,调用者必须对该异常进行处理,或者继续使用throws抛出(Alt + lnster 可以快速处理)
(2) 捕获处理 try-catch
使用场景:
throws 其实最终并没有自定义处理,只是将异常报告给抛出异常方法的调用者,还是交给了JVM处理,如果要实现自定义处理,需要使用 try-catch 进行捕获
语法格式:
try{
// 将可能出现异常的代码放在这里
}catch(要捕获的异常类型 e){
// 如果try中的代码抛出异常了,此处catch捕获时异常类型与try中抛出的异常类型一致时,或者是try中抛出异常的基类时,就会被捕获到
// 对异常就可以正常处理,处理完成后,跳出try-catch结构,继续执行后序代码
}[catch(异常类型 e){
// 对异常进行处理
}finally{
// 此处代码一定会被执行到
}]
// 后序代码
// 当异常被捕获到时,异常就被处理了,这里的后序代码一定会执行
// 如果捕获了,由于捕获时类型不对,那就没有捕获到,这里的代码就不会被执行
- 注意:
[]中表示可选项,可以添加,也可以不用添加
try中的代码可能会抛出异常,也可能不会
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("before");
try {
System.out.println(10/0);
int[] array = null;
System.out.println(array[2]);
System.out.println("fdsfsafdsdsafsafsa");
}/*catch (ArithmeticException | NullPointerException e) {
System.out.println(); //不建议写在一起,因为这样就看不出来是什么异常了,可读性差
}*/catch (ArithmeticException e) {
e.printStackTrace(); //给出异常所在的行数
System.out.println("捕获了ArithmeticException");
}catch (NullPointerException e) { //如果捕获了这个异常,就执行里面的语句
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("我捕获了空指针异常!");
}
}
//异常的处理方式
//System.out.println(e.getMessage()); // 只打印异常信息
//System.out.println(e); // 打印异常类型:异常信息
//e.printStackTrace(); // 打印信息最全面
}
- 注意事项
- try块内抛出异常位置之后的代码将不会被执行(只能捕获一个异常)
- 如果抛出异常类型与catch时异常类型不匹配,即异常不会被成功捕获,也就不会被处理,继续往外抛,直到JVM收到后中断程序----异常是按照类型来捕获的
- catch 进行类型匹配的时候, 不光会匹配相同类型的异常对象, 也会捕捉目标异常类型的子类对象
- 所以建议从下往上,先捕捉子类异常,再捕捉父类异常
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("before");
try {
System.out.println(10/0);
}catch (ArithmeticException e) {
//由于 Exception 类是所有异常类的父类.
//因此可以用这个类型表示捕捉所有异常,但那样就看不出来是因为什么异常了,不推荐
System.out.println("捕获了ArithmeticException");
}catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("我捕获到了:Exception!,这里一般处理异常");
}
System.out.println("after");
}
❤️finally:
使用场景:需要执行那些,即使出现了异常,也一定要执行的操作(eg.程序中打开的资源的需要回收的操作,异常会引发程序的跳转,可能导致有些语句执行不到)
语法格式:
try{
// 可能会发生异常的代码
}catch(异常类型 e){
// 对捕获到的异常进行处理
}finally{
// 此处的语句无论是否发生异常,都会被执行到
}
// 如果没有抛出异常,或者异常被捕获处理了,这里的代码也会执行
什么时候 try-catch-finally 中的代码不会执行???
当 try - catch 中有return的时候,如下面
public static int getData(){
Scanner sc = null;
try{
sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int data = sc.nextInt();
return data;
}catch (InputMismatchException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
System.out.println("finally中代码");
}
System.out.println("try-catch-finally之后代码");
//如果正常输入,成功接收输入后程序就返回了,那么这里的代码就不会执行即输入流就没有被释放,造成资源泄漏
if(null != sc){
sc.close(); //Scanner也是一种资源,需要释放,close方法可以释放Scanner
}
return 0;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int data = getData();
System.out.println(data);
}
- 总结
- 为了避免代码泄漏,我们可以利用finally中的代码一定会最后执行的这个特点,将资源清理的扫尾代码放在里面
两个 return 如何执行
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(func());
}
public static int func() {
try {
return 10;
} finally {
return 20;
}
}
//20
- 总结
- finally 执行的时机是在方法返回之前(try 或者 catch 中如果有 return 会在这个 return 之前执行 finally).
- 但是如果finally 中也存在 return 语句, 那么就会执行 finally 中的 return, 不会执行到 try 中原有的 return.
- 一般我们不建议在 finally 中写 return (被编译器当做一个警告).
2.4 异常的处理流程
关于 “调用栈”
方法之间是存在相互调用关系的, 这种调用关系我们可以用 “调用栈” 来描述. 在 JVM 中有一块内存空间称为"虚拟机栈" 专门存储方法之间的调用关系. 当代码中出现异常的时候, 我们就可以使用 e.printStackTrace(); 的方式查看出现异常代码的调用栈
执行流程总结
- 程序先执行 try 中的代码
- 如果 try 中的代码出现异常, 就会结束 try 中的代码, 看和 catch 中的异常类型是否匹配.
- 如果找到匹配的异常类型, 就会执行 catch 中的代码
- 如果没有找到匹配的异常类型, 就会将异常向上传递到上层调用者(如果本方法中没有合适的处理异常的方式, 就会沿着调用栈向上传递)
- 无论是否找到匹配的异常类型, finally 中的代码都会被执行到(在该方法结束之前执行).
- 如果上层调用者也没有处理的了异常, 就继续向上传递.
- 一直到 main 方法也没有合适的代码处理异常, 就会交给 JVM 来进行处理, 此时程序就会异常终止
三、自定义异常类
使用场景:Java 中提供的异常没有办法完全描述实际开发中所需要的异常,这时候就需要我们自定义异常类
实现方式:
自定义异常类,然后继承自Exception(默认是受查异常) 或者 RunTimeException(非受查异常)
实现一个带有String类型参数的构造方法,参数含义:出现异常的原因
❤️继承的是Exception
如果是继承了Exception,就默认是受查异常,需要 throws 处理或者 try-catch 的异常处理
class PasswordException extends Exception{
public PasswordException() {
}
public PasswordException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
class UserNameException extends Exception{
//自己写的类之所以说是异常类,是因为继承某个异常
public UserNameException() {
}
public UserNameException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
public class LogIn {
private String userName = "admin";
private String password = "123456";
public void loginInfo(String userName, String password)
throws UserNameException,PasswordException{
if (!this.userName.equals(userName)) {
throw new UserNameException(userName+" 用户名错误!");
//System.out.println("用户名错误!"); 单纯的打印,定位不到问题在哪里
//return;
}
System.out.println("登陆成功");
}
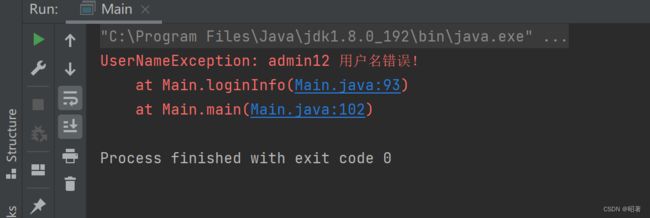
public static void main(String[] args) {
LogIn logIn = new LogIn();
try {
logIn.loginInfo("admin12", "123456111");
}catch (UserNameException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}catch (PasswordException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
❤️继承的是RunTimeException
class UserNameException extends RuntimeException{
public UserNameException() {
}
public UserNameException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
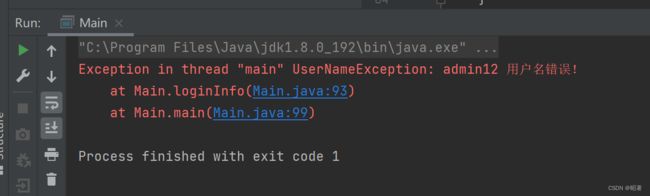
public class Main {
private String userName = "admin";
private String password = "123";
public void loginInfo(String userName, String password) {
if (!this.userName.equals(userName)) {
throw new UserNameException(userName+" 用户名错误!");
}
System.out.println("登陆成功");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main logIn = new Main();
logIn.loginInfo("admin12", "123456111");
}
}