7-2 电路布线
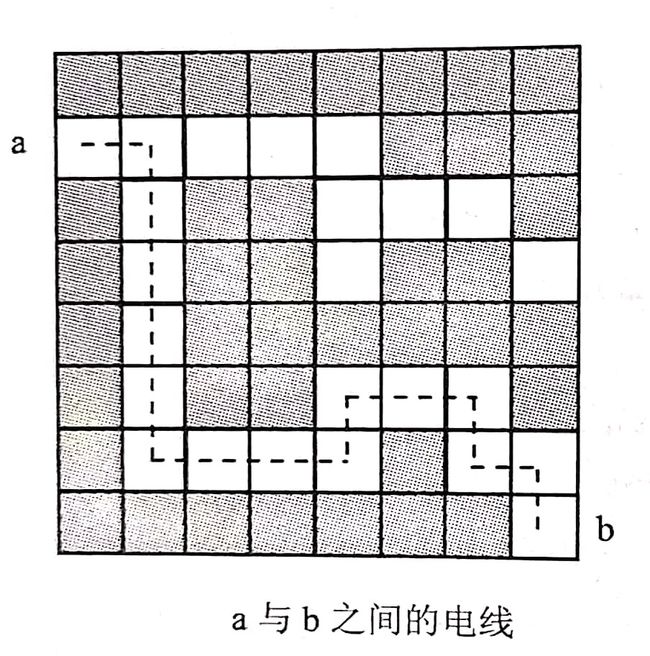
在解决电路布线问题时,一种很常用的方法就是在布线区域叠上一个网格,该网格把布线区域划分成m*n个方格,布线时,转弯处必须采用直角,如已经有某条线路经过一个方格时,则在该方格上不允许叠加布线。如下图所示,如从一个方格a(2,1)的中心点到另一个方格b(8,8)的中心点布线时, 每个方格布线时需要1个单位的电路材料,所需要最少的电路材料是16。
输入格式:
第一行输入网格的m和n
第二行开始输入网格中已经布线的情况,如果已经有布线时,用1表示,尚未布线时,用0表示。
接下来两行分别输入需要布线的起始位置a和结束位置b。
输出格式:
输出从起始位置a到结束位置b布线时所需要的最少电路材料。
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
8 8
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1
1 0 1 1 0 0 0 1
1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0
1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 0 1 1 0 0 0 1
1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0
2 1
8 8
输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
16对于求单一路径问题BFS效率远大于DFS
先提供BFS代码
#include
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 1000;
int N, M, x, y, X, Y;
int MAP[maxn][maxn];
//BFS
class ans
{
public:
int x;
int y;
int num;
ans(int A, int B, int C)
{
x = A;
y = B;
num = C;
}
};
void BFS(int x, int y)
{
queueQ;
ans* T = new ans(x,y, 1);
Q.emplace(T);
while (!Q.empty())
{
if (Q.front()->x == X && Q.front()->y == Y)
{
cout << Q.front()->num;
break;
}
int dx[4] = { 1,-1,0,0 };
int dy[4] = { 0,0,1,-1 };
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
int nx = Q.front()->x + dx[i], ny = Q.front()->y + dy[i];
if (nx >= 1 && nx <= N && ny >= 1 && ny <= M && MAP[nx][ny] == 0)
{
MAP[nx][ny] = 1;
ans* temp = new ans(nx, ny, Q.front()->num + 1);
Q.emplace(temp);
}
}
Q.pop();
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> N >> M;
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= M; j++)
{
cin >> MAP[i][j];
}
}
cin >> x >> y >> X >> Y;
BFS(x, y);
return 0;
} 2:DFS代码
#include
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 1000;
int N, M, x, y, X, Y;
int MAP[maxn][maxn];
bool vis[maxn][maxn];
int ans1 = 9999;
void DFS(int x, int y, int num)
{
if (x < 1 || x > N || y < 1 || y > M || MAP[x][y] == 1)
return;
if (x == X && y == Y) //只在终点更新答案
ans1 = min(ans1, num);
int dx[4] = { 0,0,1,-1 };
int dy[4] = { 1,-1,0,0 };
vis[x][y] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
int nx = x + dx[i], ny = y + dy[i];
if (nx >= 1 && nx <= N && ny >= 1 && ny <= M && MAP[nx][ny] == 0 && vis[nx][ny] == 0)
{
vis[nx][ny] = 1;
DFS(nx, ny, num + 1);
vis[nx][ny] = 0;
}
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> N >> M;
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= M; j++)
{
cin >> MAP[i][j];
}
}
cin >> x >> y >> X >> Y;
DFS(x, y, 1);
cout << ans1 << endl;
}