Set集合的基本使用
Set集合
Set接口:存储无序的,不可重复的数据 ---->高中讲的“集合”
Set接口是Collection的子接口,set接口没有提供额外的方法。但是比Collection接口更加严格了。
Set 集合不允许包含相同的元素,如果试把两个相同的元素加入同一个 Set 集合中,则添加操作失败。
Set集合支持的遍历方式和Collection集合一样:foreach和Iterator。
Set的常用实现类有:HashSet、TreeSet、LinkedHashSet。
* HashSet: 作为Set接口的主要实现类 线程是不安全的 可以存储null值
* LinkedHashSet:作为HashSet子类 遍历其内部数据是 可以按照添加的顺序遍历
* TreeSet:可以按照添加对象的指定属性 进行排序
*
* Set 存储无序的 不可重复的数据
* 无序性:不等于随机性 存储的数据在底层数组中并非按照数组索引的顺序添加 而是根据数据的哈希值添加的
* 不可重复性: 加了重复相同的元素也没办法被获取到 保证添加的元素按照equals()判断是 不能返回true 相同元素只能添加一个
* HashSet底层是以数组加链表的形式存在 通过特定的哈希值决定储存位置的
* 向Set中添加的数据 其所在的类一定要重写hashCode()和equals()方法
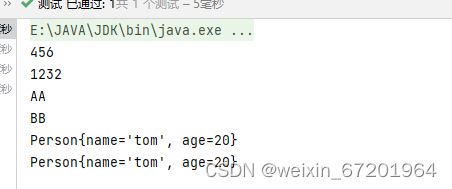
代码测试:
@Test
public void test(){
Set set = new HashSet();
set.add(456);
set.add(1232);
set.add("AA");
set.add("BB");
set.add(new Person("tom",20));
set.add(new Person("tom",20));
set.add(1232);
Iterator iterator = set.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
}
以及LinkedHashSet的测试:
//LinkedHashSet
@Test
public void test2(){
Set set = new LinkedHashSet();
set.add(456);
set.add(1232);
set.add("AA");
set.add("BB");
set.add(new Person("tom",20));
set.add(new Person("tom",20));
set.add(1232);
Iterator iterator = set.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
}
TreeSet
底层结构:里面维护了一个TreeMap,都是基于红黑树实现的!
特点:
1、不允许重复
2、实现排序
自然排序或定制排序 --------> 不能用equals()
(如果使用的是自然排序,则通过调用实现的compareTo方法
如果使用的是定制排序,则通过调用比较器的compare方法)
- 1
@Test
public void test1(){
TreeSet treeSet = new TreeSet();
treeSet.add(123);
treeSet.add(32);
treeSet.add(43);
Iterator iterator = treeSet.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
}
如果加的不是相同类的话无法通过运行 可以通过编译
运行结果:
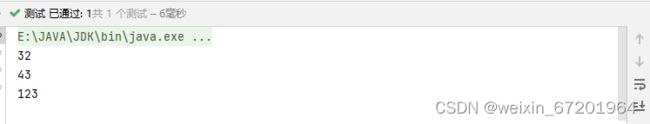
自然顺序
如果试图把一个对象添加到 TreeSet 时,则该对象的类必须实现 Comparable 接口。实现 Comparable 的类必须实现 compareTo(Object obj) 方法,两个对象即通过 compareTo(Object obj) 方法的返回值来比较大小。对于 TreeSet 集合而言,它判断两个对象是否相等的唯一标准是:两个对象通过 compareTo(Object obj) 方法比较返回值为0。
自然排序代码格式:
@Override
public int compareTo(java.lang.Object o) {
if (o instanceof Person){
Person p = (Person) o;
// return this.name.compareTo(p.name);
if (this.name.equals(p.name)){
// return Integer.compare(this.age,p.age);
if (this.age>p.age){
return 1;
}else if (this.age<p.age){
return -1;
}else if (this.age==p.age){
return 0;
}
}else
return this.name.compareTo(p.name);
}
throw new RuntimeException("数据异常错误");
}
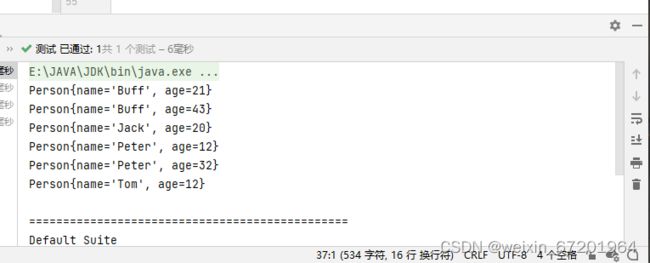
使用TreeSet测试:
@Test
public void test2(){
TreeSet treeSet = new TreeSet();
treeSet.add(new Person("Jack",20));
treeSet.add(new Person("Peter",32));
treeSet.add(new Person("Peter",12));
treeSet.add(new Person("Tom",12));
treeSet.add(new Person("Tom",12));
treeSet.add(new Person("Buff",43));
treeSet.add(new Person("Buff",21));
Iterator iterator = treeSet.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
}
定制排序
如果放到TreeSet中的元素的自然排序(Comparable)规则不符合当前排序需求时,或者元素的类型没有实现Comparable接口。那么在创建TreeSet时,可以单独指定一个Comparator的对象。使用定制排序判断两个元素相等的标准是:通过Comparator比较两个元素返回了0。
示范如比较各人的生日的年月日来比较的话从大到小:
- 1 先写好两个类:
public class Employee implements Comparable {
private String name;
private int age;
private MyDate birthday;
public Employee() {
}
public Employee(MyDate birthday) {
this.birthday = birthday;
}
public Employee(String name, int age, MyDate birthday) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.birthday = birthday;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public MyDate getBirthday() {
return birthday;
}
public void setBirthday(MyDate birthday) {
this.birthday = birthday;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Employee{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", birthday=" + birthday +
'}';
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Object o) {
if ( o instanceof Employee){
Employee e = (Employee) o;
return this.name.compareTo(e.name);
}
throw new RuntimeException("数据异常");
}
}
public class MyDate {
private int year;
private int month;
private int day;
public MyDate() {
}
public MyDate(int year, int month, int day) {
this.year = year;
this.month = month;
this.day = day;
}
public int getYear() {
return year;
}
public void setYear(int year) {
this.year = year;
}
public int getMonth() {
return month;
}
public void setMonth(int month) {
this.month = month;
}
public int getDay() {
return day;
}
public void setDay(int day) {
this.day = day;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "MyDate{" +
"year=" + year +
", month=" + month +
", day=" + day +
'}';
}
}
- 2 使用定制方法:
@Test
public void test1(){
TreeSet set = new TreeSet(new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
if (o1 instanceof Employee && o2 instanceof Employee){
Employee e1 = (Employee) o1;
Employee e2 = (Employee) o2;
MyDate m1 = e1.getBirthday();
MyDate m2 = e2.getBirthday();
int minusYear = m1.getYear() - m2.getYear();
if (minusYear != 0){
if (minusYear > 0){
return 1;}
else return -1;
}
int minusMonth = m1.getMonth()-m2.getMonth();
if (minusMonth != 0){
if (minusMonth >0){
return 1;}
else return -1;
}
int minusDay = m1.getDay()-m2.getDay();
if (minusDay != 0){
if (minusDay>0){
return 1;
}else return -1;
}
return 0;
}
throw new RuntimeException("数据异常");
}
});
Employee employee = new Employee("Tom", 21, new MyDate(2002, 9, 26));
Employee employee1 = new Employee("Jack",54,new MyDate(1996,2,8));
Employee employee2 = new Employee("Ross",12,new MyDate(1988,4,3));
Employee employee3 = new Employee("Peter",68,new MyDate(2004,9,12));
Employee employee4 = new Employee("Tonny",34,new MyDate(2012,11,21));
Employee employee5 = new Employee("XXX",34,new MyDate(1988,11,21));
Employee employee6 = new Employee("YYYY",34,new MyDate(2002,9,21));
Employee employee7 = new Employee("MMM",34,new MyDate(2002,9,21));
set.add(employee);
set.add(employee1);
set.add(employee2);
set.add(employee3);
set.add(employee4);
set.add(employee5);
set.add(employee6);
set.add(employee7);
Iterator iterator = set.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
}
运行结果如下: