【嵌入式Linux】嵌入式Linux驱动开发基础知识之驱动程序基石
文章目录
- 前言
- 1、休眠唤醒功能
-
- 1.1、使用场景
- 1.2、使用函数
- 1.3、使用程序
-
- 1.3.1、驱动框架
- 1.3.2、程序源码
- 1.4、使用实验
- 2、POLL机制
-
- 2.1、使用流程
- 2.2、使用程序
- 2.3、使用实验
- 2.4、系统函数
- 3、异步通知
-
- 3.1、使用流程
- 3.2、使用程序
- 3.3、使用实验
- 3.4、系统函数
- 4、阻塞和非阻塞
-
- 3.1、使用流程
- 3.2、使用程序
- 3.3、使用实验
- 5、定时器
-
- 5.1、使用流程
- 5.2、使用程序
- 5.3、使用实验
- 5.4、深入研究:定时器的内部机制
- 6、中断的下半部分tasklet
-
- 6.1、内核函数
- 6.2、使用流程
- 6.3、使用程序
- 6.6、使用实验
- 6.7、tasklet内部机制
- 7、工作队列
-
- 7.1、内核函数
- 7.2、使用程序
- 7.3、使用实验
- 7.4、工作机制
- 8、中断线程化处理
-
- 8.1、内核函数
- 8.2、内核机制
- 8.2、使用程序
- 8.3、使用实验
- 9、mmap
前言
韦东山嵌入式Linux驱动开发基础知识学习笔记
文章中大多内容来自韦东山老师的文档,还有部分个人根据自己需求补充的内容
视频教程地址:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV14f4y1Q7ti
▲APP访问硬件的四种方式
1、休眠唤醒功能
1.1、使用场景
关于用户态、内核态、上下文,参考下面的文章:
用户态与内核态
linux 用户态和内核态以及进程上下文、中断上下文 内核空间用户空间理解
当应用程序必须等待某个事件发生,比如必须等待按键被按下时,可以使用“休眠-唤醒”机制:
① APP调用read等函数试图读取数据,比如读取按键;
② APP进入内核态,也就是调用驱动中的对应函数,发现有数据则复制到用户空间并马上返回;
③ 如果APP在内核态,也就是在驱动程序中发现没有数据,则APP休眠;
④ 当有数据时,比如当按下按键时,驱动程序的中断服务程序被调用,它会记录数据、唤醒APP;
⑤ APP继续运行它的内核态代码,也就是驱动程序中的函数,复制数据到用户空间并马上返回。
▲APP读取--有数据
▲APP读取--无数据
在APP1的“上下文”,也就是在APP1的执行过程中,它是可以休眠的。
在中断的处理过程中,也就是gpio_key_irq的执行过程中,它不能休眠:“中断”怎么能休眠?“中断”休眠了,谁来调度其他APP啊?
所以,请记住:在中断处理函数中,不能休眠,也就不能调用会导致休眠的函数。
1.2、使用函数
▲休眠函数
注:wait_event_timeout(wq, condition, timeout)退出条件不仅仅为condition为真,超时也会返回
wait_event_interruptible(wq, condition)
wait_event(wq, condition)
wait_event_interruptible_timeout(wq, condition, timeout)
wait_event_timeout(wq, condition, timeout)
比较重要的参数就是:
① wq:waitqueue,等待队列
休眠时除了把程序状态改为非RUNNING之外,还要把进程/进程放入wq中,以后中断服务程序要从wq中把它取出来唤醒。
没有wq的话,茫茫人海中,中断服务程序去哪里找到你?
② condition
这可以是一个变量,也可以是任何表达式。表示“一直等待,直到condition为真”。
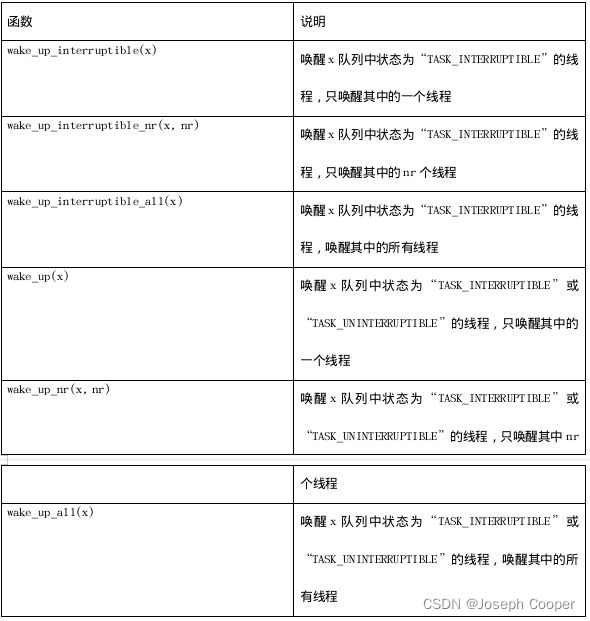
▲唤醒函数
wake_up_interruptible(x)
wake_up_interruptible_nr(x, nr)
wake_up_interruptible_all(x)
wake_up(x)
wake_up_nr(x, nr)
wake_up_all(x)
1.3、使用程序
1.3.1、驱动框架
▲驱动框架
要休眠的线程,放在wq队列里,中断处理函数从wq队列里把它取出来唤醒。
所以,我们要做这几件事:
① 初始化wq队列
② 在驱动的read函数中,调用wait_event_interruptible:
它本身会判断event是否为FALSE,如果为FASLE表示无数据,则休眠。
当从wait_event_interruptible返回后,把数据复制回用户空间。
③ 在中断服务程序里:
设置event为TRUE,并调用wake_up_interruptible唤醒线程。
对应程序:
static DECLARE_WAIT_QUEUE_HEAD(gpio_key_wait);
/* 实现对应的open/read/write等函数,填入file_operations结构体 */
static ssize_t gpio_key_drv_read (struct file *file, char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *offset)
{
//printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
int err;
int key;
/* 如果环形缓冲区中没有数据则休眠,把线程放到wq:gpio_key_wait 中,直到有数据后,中断服务程序中可将其唤醒 */
wait_event_interruptible(gpio_key_wait, !is_key_buf_empty());
key = get_key();
err = copy_to_user(buf, &key, 4);
return 4;
}
/* 定义自己的file_operations结构体 */
static struct file_operations gpio_key_drv = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.read = gpio_key_drv_read,
};
static irqreturn_t gpio_key_isr(int irq, void *dev_id)
{
struct gpio_key *gpio_key = dev_id;
int val;
int key;
val = gpiod_get_value(gpio_key->gpiod);
printk("key %d %d\n", gpio_key->gpio, val);
key = (gpio_key->gpio << 8) | val;
put_key(key);
/* 唤醒wq:gpio_key_wait中的一个线程 */
wake_up_interruptible(&gpio_key_wait);
return IRQ_HANDLED;
}
1.3.2、程序源码
gpio_key_drv.c
#include button_test.c
#include \n" , argv[0]);
return -1;
}
/* 2. 打开文件 */
fd = open(argv[1], O_RDWR);
if (fd == -1)
{
printf("can not open file %s\n", argv[1]);
return -1;
}
while (1)
{
/* 3. 读文件 */
read(fd, &val, 4);
printf("get button : 0x%x\n", val);
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}
1.4、使用实验
▲实验
2、POLL机制
POLL机制相关的APP操作见下文
【嵌入式Linux】嵌入式Linux应用开发基础知识之输入系统应用编程
2.1、使用流程
假设APP使用poll机制试图获取按键键值,在时间内中断发生获得了键值,那么函数调用关系将是下面的流程

▲POLL机制工作流程
2.2、使用程序
APP中的核心源码
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int fd;
int val;
struct pollfd fds[1];
int timeout_ms = 5000;
int ret;
/* 1. 判断参数 */
if (argc != 2)
{
printf("Usage: %s \n" , argv[0]);
return -1;
}
/* 2. 打开文件 */
fd = open(argv[1], O_RDWR);
if (fd == -1)
{
printf("can not open file %s\n", argv[1]);
return -1;
}
fds[0].fd = fd;
fds[0].events = POLLIN;
while (1)
{
/* 3. 读文件 */
ret = poll(fds, 1, timeout_ms);
if ((ret == 1) && (fds[0].revents & POLLIN))
{
read(fd, &val, 4);
printf("get button : 0x%x\n", val);
}
else
{
printf("timeout\n");
}
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}
驱动中的核心源码
/* 将线程放入wq,返回event状态 */
static unsigned int gpio_key_drv_poll(struct file *fp, poll_table * wait)
{
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
poll_wait(fp, &gpio_key_wait, wait);
return is_key_buf_empty() ? 0 : POLLIN | POLLRDNORM;
}
/* 定义自己的file_operations结构体 */
static struct file_operations gpio_key_drv = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.read = gpio_key_drv_read,
.poll = gpio_key_drv_poll,
};
static irqreturn_t gpio_key_isr(int irq, void *dev_id)
{
struct gpio_key *gpio_key = dev_id;
int val;
int key;
val = gpiod_get_value(gpio_key->gpiod);
printk("key %d %d\n", gpio_key->gpio, val);
key = (gpio_key->gpio << 8) | val;
put_key(key);
wake_up_interruptible(&gpio_key_wait);
return IRQ_HANDLED;
}
2.3、使用实验
▲实验--console
对比dmesg和console可以发现每次timeout在内核中调用了两次gpio_key_drv_poll程序
▲实验--dmesg
2.4、系统函数
…待写
3、异步通知
异步通知机制相关的APP操作见下文
【嵌入式Linux】嵌入式Linux应用开发基础知识之输入系统应用编程
3.1、使用流程
▲异步通知机制使用流程
3.2、使用程序
APP核心程序
/* 存放驱动设备文件 */
static int fd;
/* SGIO信号对应函数 */
static void sig_func(int sig)
{
int val;
read(fd, &val, 4);
printf("get button : 0x%x\n", val);
}
/*
* ./button_test /dev/100ask_button0
*
*/
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int val;
struct pollfd fds[1];
int timeout_ms = 5000;
int ret;
int flags;
/* 1. 判断参数 */
if (argc != 2)
{
printf("Usage: %s \n" , argv[0]);
return -1;
}
/* 给信号注册函数,当线程收到SIGIO信号时执行sig_func函数 */
signal(SIGIO, sig_func);
/* 2. 打开文件 */
fd = open(argv[1], O_RDWR);
if (fd == -1)
{
printf("can not open file %s\n", argv[1]);
return -1;
}
/* 向内核的文件系统层次传递PID */
fcntl(fd, F_SETOWN, getpid());
/* 读取驱动程序中的flag */
flags = fcntl(fd, F_GETFL);
/* 设置驱动flag中FASYNC位为1,此操作会导致驱动中fasync函数被调用 */
fcntl(fd, F_SETFL, flags | FASYNC);
while (1)
{
printf("www.100ask.net \n");
sleep(2);
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}
驱动核心程序
static int gpio_key_drv_fasync(int fd, struct file *file, int on)
{
/* 调用faync_helper,它会根据FAYSNC的值决定是否设置button_async->fa_file=驱动文件filp */
if (fasync_helper(fd, file, on, &button_fasync) >= 0)
return 0;
else
return -EIO;
}
/* 定义自己的file_operations结构体 */
static struct file_operations gpio_key_drv = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.read = gpio_key_drv_read,
.poll = gpio_key_drv_poll,
.fasync = gpio_key_drv_fasync,
};
static irqreturn_t gpio_key_isr(int irq, void *dev_id)
{
struct gpio_key *gpio_key = dev_id;
int val;
int key;
val = gpiod_get_value(gpio_key->gpiod);
printk("key %d %d\n", gpio_key->gpio, val);
key = (gpio_key->gpio << 8) | val;
put_key(key);
wake_up_interruptible(&gpio_key_wait);
/* 向button_fasync记录PID对应的线程发送SIGIO信号 */
kill_fasync(&button_fasync, SIGIO, POLL_IN);
return IRQ_HANDLED;
}
3.3、使用实验
▲实验
3.4、系统函数
…韦东山老师还没写,后面有空打算自己写
4、阻塞和非阻塞
3.1、使用流程
所谓阻塞,就是等待某件事情发生。比如调用read读取按键时,如果没有按键数据则read函数不会返回,它会让线程休眠等待。
使用poll时,如果传入的超时时间不为0,这种访问方法也是阻塞的。
使用poll时,可以设置超时时间为0,这样即使没有数据它也会立刻返回,这就是非阻塞方式。能不能让read函数既能工作于阻塞方式,也可以工作于非阻塞方式?可以!
APP调用open函数时,传入O_NONBLOCK,就表示要使用非阻塞方式;默认是阻塞方式。
注意:对于普通文件、块设备文件,O_NONBLOCK不起作用。
注意:对于字符设备文件,O_NONBLOCK起作用的前提是驱动程序针对O_NONBLOCK做了处理。
只能在open时表明O_NONBLOCK吗?在open之后,也可以通过fcntl修改为阻塞或非阻塞。
3.2、使用程序
APP核心源码
static int fd;
/*
* ./button_test /dev/100ask_button0
*
*/
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int val;
struct pollfd fds[1];
int timeout_ms = 5000;
int ret;
int flags;
int i;
/* 1. 判断参数 */
if (argc != 2)
{
printf("Usage: %s \n" , argv[0]);
return -1;
}
/* 2. 打开文件 */
/* 非阻塞方式 */
fd = open(argv[1], O_RDWR | O_NONBLOCK);
if (fd == -1)
{
printf("can not open file %s\n", argv[1]);
return -1;
}
/* 非阻塞方式读取数据 */
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
if (read(fd, &val, 4) == 4)
printf("get button: 0x%x\n", val);
else
printf("get button: -1\n");
}
/* 设定阻塞方式 */
flags = fcntl(fd, F_GETFL);
fcntl(fd, F_SETFL, flags & ~O_NONBLOCK);
while (1)
{
if (read(fd, &val, 4) == 4)
printf("get button: 0x%x\n", val);
else
printf("while get button: -1\n");
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}
驱动核心源码
static ssize_t gpio_key_drv_read (struct file *file, char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *offset)
{
//printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
int err;
int key;
/* 如果环形缓冲区为空且读取方式为非阻塞则返回err */
if (is_key_buf_empty() && (file->f_flags & O_NONBLOCK))
return -EAGAIN;
wait_event_interruptible(gpio_key_wait, !is_key_buf_empty());
key = get_key();
err = copy_to_user(buf, &key, 4);
return 4;
}
3.3、使用实验
▲实验
5、定时器
注:这里介绍的定时器是一个软件概念是指Linux系统借助硬件滴答定时器实现的一个软件定时器
5.1、使用流程
内核函数
① timer_setup(timer, callback, flags):
设置定时器,主要是初始化timer_list结构体,设置其中的函数、flags(一般设为0)。
② void add_timer(struct timer_list *timer):
向内核添加定时器。timer->expires表示超时时间。
当超时时间到达,内核就会调用这个函数:timer->function(timer->data)。
③ int mod_timer(struct timer_list *timer, unsigned long expires):
修改定时器的超时时间,
它等同于:del_timer(timer); timer->expires = expires; add_timer(timer);
但是更加高效。
④ int del_timer(struct timer_list *timer):
删除定时器。
定时器时间单位
通过在.config文件可以指定滴答定时器的中断频率进而指定软件定时器的时间单位
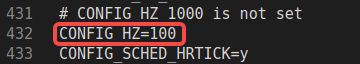
▲.config
上面的栗子中滴答定时器触发一次中断的时间即软件定时器的时间单位就是1s/100 = 10ms
如何修改超时时间?
① 在add_timer之前,直接修改:
timer.expires = jiffies + xxx; // xxx表示多少个滴答后超时,也就是xxx*10ms
timer.expires = jiffies + 2*HZ; // HZ等于CONFIG_HZ,2*HZ就相当于2秒
② 在add_timer之后,使用mod_timer修改:
mod_timer(&timer, jiffies + xxx); // xxx表示多少个滴答后超时,也就是xxx*10ms
mod_timer(&timer, jiffies + 2*HZ); // HZ等于CONFIG_HZ,2*HZ就相当于2秒
5.2、使用程序
实验程序所实现的功能:对按键进行消抖,防止一次按键按下触发多次中断的情况
APP核心源码
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int val;
struct pollfd fds[1];
int timeout_ms = 5000;
int ret;
int flags;
int i;
/* 1. 判断参数 */
if (argc != 2)
{
printf("Usage: %s \n" , argv[0]);
return -1;
}
/* 2. 打开文件 */
fd = open(argv[1], O_RDWR );
if (fd == -1)
{
printf("can not open file %s\n", argv[1]);
return -1;
}
while (1)
{
if (read(fd, &val, 4) == 4)
printf("get button: 0x%x\n", val);
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}
驱动核心源码
struct gpio_key{
int gpio;
struct gpio_desc *gpiod;
int flag;
int irq;
struct timer_list key_timer;
} ;
static irqreturn_t gpio_key_isr(int irq, void *dev_id)
{
struct gpio_key *gpio_key = dev_id;
printk("gpio_key_isr key %d irq happened\n", gpio_key->gpio);
//如果中断被重复触发即按键状态不稳定时会在每次中断被触发时增加timer的超时时间
/* 修改定时器的超时时间 */
mod_timer(&gpio_key->key_timer, jiffies + HZ/50);
return IRQ_HANDLED;
}
static int gpio_key_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
int err;
struct device_node *node = pdev->dev.of_node;
int count;
int i;
enum of_gpio_flags flag;
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
count = of_gpio_count(node);
if (!count)
{
printk("%s %s line %d, there isn't any gpio available\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
return -1;
}
gpio_keys_100ask = kzalloc(sizeof(struct gpio_key) * count, GFP_KERNEL);
for (i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
gpio_keys_100ask[i].gpio = of_get_gpio_flags(node, i, &flag);
if (gpio_keys_100ask[i].gpio < 0)
{
printk("%s %s line %d, of_get_gpio_flags fail\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
return -1;
}
gpio_keys_100ask[i].gpiod = gpio_to_desc(gpio_keys_100ask[i].gpio);
gpio_keys_100ask[i].flag = flag & OF_GPIO_ACTIVE_LOW;
gpio_keys_100ask[i].irq = gpio_to_irq(gpio_keys_100ask[i].gpio);
//setup_timer(&gpio_keys_100ask[i].key_timer, key_timer_expire, &gpio_keys_100ask[i]);
/* 设定每个按键对应定时器,设定回调函数key_timer_expire */
timer_setup(&gpio_keys_100ask[i].key_timer, key_timer_expire, 0);
gpio_keys_100ask[i].key_timer.expires = ~0;
/* 向内核添加定时器,timer->expires表示超时时间,这里超时时间设定为unsigned long型最大值 */
add_timer(&gpio_keys_100ask[i].key_timer);
}
for (i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
err = request_irq(gpio_keys_100ask[i].irq, gpio_key_isr, IRQF_TRIGGER_RISING | IRQF_TRIGGER_FALLING, "100ask_gpio_key", &gpio_keys_100ask[i]);
}
/* 注册file_operations */
major = register_chrdev(0, "100ask_gpio_key", &gpio_key_drv); /* /dev/gpio_key */
gpio_key_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "100ask_gpio_key_class");
if (IS_ERR(gpio_key_class)) {
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
unregister_chrdev(major, "100ask_gpio_key");
return PTR_ERR(gpio_key_class);
}
device_create(gpio_key_class, NULL, MKDEV(major, 0), NULL, "100ask_gpio_key"); /* /dev/100ask_gpio_key */
return 0;
}
static int gpio_key_remove(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
//int err;
struct device_node *node = pdev->dev.of_node;
int count;
int i;
device_destroy(gpio_key_class, MKDEV(major, 0));
class_destroy(gpio_key_class);
unregister_chrdev(major, "100ask_gpio_key");
count = of_gpio_count(node);
for (i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
free_irq(gpio_keys_100ask[i].irq, &gpio_keys_100ask[i]);
/* 删除定时器 */
del_timer(&gpio_keys_100ask[i].key_timer);
}
kfree(gpio_keys_100ask);
return 0;
}
5.3、使用实验
由于 开发板上的按键质量较好,所以没有抖动,但是也能看出程序生效
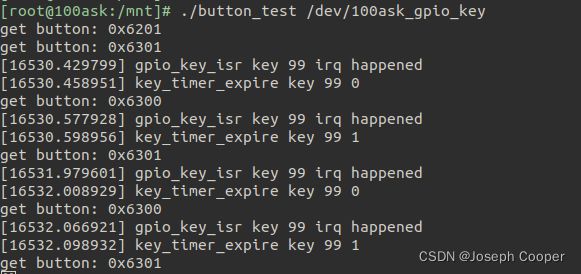
▲使用实验
5.4、深入研究:定时器的内部机制
…待写
6、中断的下半部分tasklet
关于tasklet的基础知识见下面文章的2.2节,这里不做赘述:
【嵌入式Linux】嵌入式Linux驱动开发基础知识之Linux中断系统简介及按键中断设备树驱动编写
6.1、内核函数
数据结构:tasklet_struct
struct tasklet_struct
{
struct tasklet_struct *next;
unsigned long state;
atomic_t count;
void (*func)(unsigned long);
unsigned long data;
};
其中的state有2位:
1、bit0表示TASKLET_STATE_SCHED
等于1时表示已经执行了tasklet_schedule把该tasklet放入队列了;tasklet_schedule会判断该位,如果已经等于1那么它就不会再次把tasklet放入队列。
2、 bit1表示TASKLET_STATE_RUN
等于1时,表示正在运行tasklet中的func函数;函数执行完后内核会把该位清0。
3、其中的count表示该tasklet是否使能:等于0表示使能了,非0表示被禁止了。对于count非0的tasklet,里面的func函数不会被执行。
创建和初始化tasklet_struct
//定义一个tasklet_struct并使能
#define DECLARE_TASKLET(name, func, data) \
struct tasklet_struct name = { NULL, 0, ATOMIC_INIT(0), func, data }
//定义一个tasklet_struct并禁止
#define DECLARE_TASKLET_DISABLED(name, func, data) \
struct tasklet_struct name = { NULL, 0, ATOMIC_INIT(1), func, data }
//定义一个tasklet_struct
struct tasklet_struct name;
extern void tasklet_init(struct tasklet_struct *t,
void (*func)(unsigned long), unsigned long data);
//tasklet_enable把count增加1;tasklet_disable把count减1。
static inline void tasklet_enable(struct tasklet_struct *t);
static inline void tasklet_disable(struct tasklet_struct *t);
//调度tasklet
//把tasklet放入链表,并且设置它的TASKLET_STATE_SCHED状态为1。
static inline void tasklet_schedule(struct tasklet_struct *t);
//kill tasklet
/*
* 如果一个tasklet未被调度,tasklet_kill会把它的TASKLET_STATE_SCHED状态清0;
* 如果一个tasklet已被调度,tasklet_kill会等待它执行完华,再把它的TASKLET_STATE_SCHED状态清0。
* 通常在卸载驱动程序时调用tasklet_kill。
*/
extern void tasklet_kill(struct tasklet_struct *t);
6.2、使用流程
先定义tasklet
需要使用时调用tasklet_schedule
驱动卸载前调用tasklet_kill。
tasklet_schedule只是把tasklet放入内核队列,它的func函数会在软件中断的执行过程中被调用。
6.3、使用程序
APP核心程序
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int val;
struct pollfd fds[1];
int timeout_ms = 5000;
int ret;
int flags;
int i;
/* 1. 判断参数 */
if (argc != 2)
{
printf("Usage: %s \n" , argv[0]);
return -1;
}
/* 2. 打开文件 */
fd = open(argv[1], O_RDWR | O_NONBLOCK);
if (fd == -1)
{
printf("can not open file %s\n", argv[1]);
return -1;
}
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
if (read(fd, &val, 4) == 4)
printf("get button: 0x%x\n", val);
else
printf("get button: -1\n");
}
flags = fcntl(fd, F_GETFL);
fcntl(fd, F_SETFL, flags & ~O_NONBLOCK);
while (1)
{
if (read(fd, &val, 4) == 4)
printf("get button: 0x%x\n", val);
else
printf("while get button: -1\n");
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}
驱动核心程序
struct gpio_key{
int gpio;
struct gpio_desc *gpiod;
int flag;
int irq;
struct timer_list key_timer;
struct tasklet_struct tasklet;
} ;
static void key_tasklet_func(unsigned long data)
{
/* data ==> gpio */
struct gpio_key *gpio_key = (struct gpio_key *)data;
int val;
val = gpiod_get_value(gpio_key->gpiod);
printk("key_tasklet_func key %d %d\n", gpio_key->gpio, val);
}
static irqreturn_t gpio_key_isr(int irq, void *dev_id)
{
struct gpio_key *gpio_key = dev_id;
//printk("gpio_key_isr key %d irq happened\n", gpio_key->gpio);
tasklet_schedule(&gpio_key->tasklet);
mod_timer(&gpio_key->key_timer, jiffies + HZ/50);
return IRQ_HANDLED;
}
/* 1. 从platform_device获得GPIO
* 2. gpio=>irq
* 3. request_irq
*/
static int gpio_key_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
int err;
struct device_node *node = pdev->dev.of_node;
int count;
int i;
enum of_gpio_flags flag;
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
count = of_gpio_count(node);
if (!count)
{
printk("%s %s line %d, there isn't any gpio available\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
return -1;
}
gpio_keys_100ask = kzalloc(sizeof(struct gpio_key) * count, GFP_KERNEL);
for (i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
gpio_keys_100ask[i].gpio = of_get_gpio_flags(node, i, &flag);
if (gpio_keys_100ask[i].gpio < 0)
{
printk("%s %s line %d, of_get_gpio_flags fail\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
return -1;
}
gpio_keys_100ask[i].gpiod = gpio_to_desc(gpio_keys_100ask[i].gpio);
gpio_keys_100ask[i].flag = flag & OF_GPIO_ACTIVE_LOW;
gpio_keys_100ask[i].irq = gpio_to_irq(gpio_keys_100ask[i].gpio);
//setup_timer(&gpio_keys_100ask[i].key_timer, key_timer_expire, &gpio_keys_100ask[i]);
timer_setup(&gpio_keys_100ask[i].key_timer, key_timer_expire, 0);
gpio_keys_100ask[i].key_timer.expires = ~0;
add_timer(&gpio_keys_100ask[i].key_timer);
tasklet_init(&gpio_keys_100ask[i].tasklet, key_tasklet_func, (unsigned long)(&(gpio_keys_100ask[i])));
}
for (i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
err = request_irq(gpio_keys_100ask[i].irq, gpio_key_isr, IRQF_TRIGGER_RISING | IRQF_TRIGGER_FALLING, "100ask_gpio_key", &gpio_keys_100ask[i]);
}
/* 注册file_operations */
major = register_chrdev(0, "100ask_gpio_key", &gpio_key_drv); /* /dev/gpio_key */
gpio_key_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "100ask_gpio_key_class");
if (IS_ERR(gpio_key_class)) {
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
unregister_chrdev(major, "100ask_gpio_key");
return PTR_ERR(gpio_key_class);
}
device_create(gpio_key_class, NULL, MKDEV(major, 0), NULL, "100ask_gpio_key"); /* /dev/100ask_gpio_key */
return 0;
}
static int gpio_key_remove(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
//int err;
struct device_node *node = pdev->dev.of_node;
int count;
int i;
device_destroy(gpio_key_class, MKDEV(major, 0));
class_destroy(gpio_key_class);
unregister_chrdev(major, "100ask_gpio_key");
count = of_gpio_count(node);
for (i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
free_irq(gpio_keys_100ask[i].irq, &gpio_keys_100ask[i]);
del_timer(&gpio_keys_100ask[i].key_timer);
tasklet_kill(&gpio_keys_100ask[i].tasklet);
}
kfree(gpio_keys_100ask);
return 0;
}
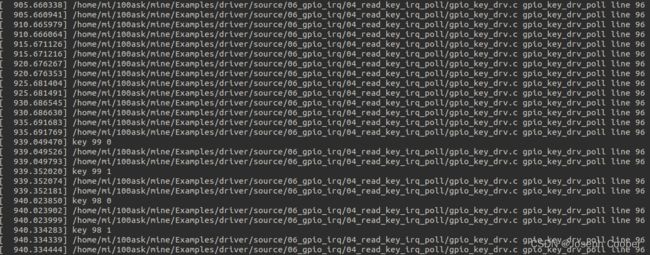
6.6、使用实验
▲实验
从[73720.317024] key_tasklet_func key 99 0可以看出内核中的tasklet_func已被调用
6.7、tasklet内部机制
待写
7、工作队列
关于工作队列的基础知识见下面文章的2.2节,这里不做赘述:
【嵌入式Linux】嵌入式Linux驱动开发基础知识之Linux中断系统简介及按键中断设备树驱动编写
7.1、内核函数
▲struct work_struct
工作队列的使用步骤:
① 构造一个work_struct结构体,里面有函数;
② 把这个work_struct结构体放入工作队列,内核线程就会运行work中的函数。
定义、初始化、挂载work
1、用来定义一个work_struct结构体,要指定它的函数。
#define DECLARE_WORK(n, f) \
struct work_struct n = __WORK_INITIALIZER(n, f)
2、用来定义一个delayed_work结构体,也要指定它的函数。所以“delayed”,意思就是说要让它运行时,可以指定:某段时间之后你再执行。
#define DECLARE_DELAYED_WORK(n, f) \
struct delayed_work n = __DELAYED_WORK_INITIALIZER(n, f, 0)
3、如果要在代码中初始化work_struct结构体,可以使用下面的宏:
#define INIT_WORK(_work, _func)
4、调用schedule_work时,就会把work_struct结构体放入队列中,并唤醒对应的内核线程。内核线程就会从队列里把work_struct结构体取出来,执行里面的函数。
static inline bool schedule_work(struct work_struct *work)
{
return queue_work(system_wq, work);
}
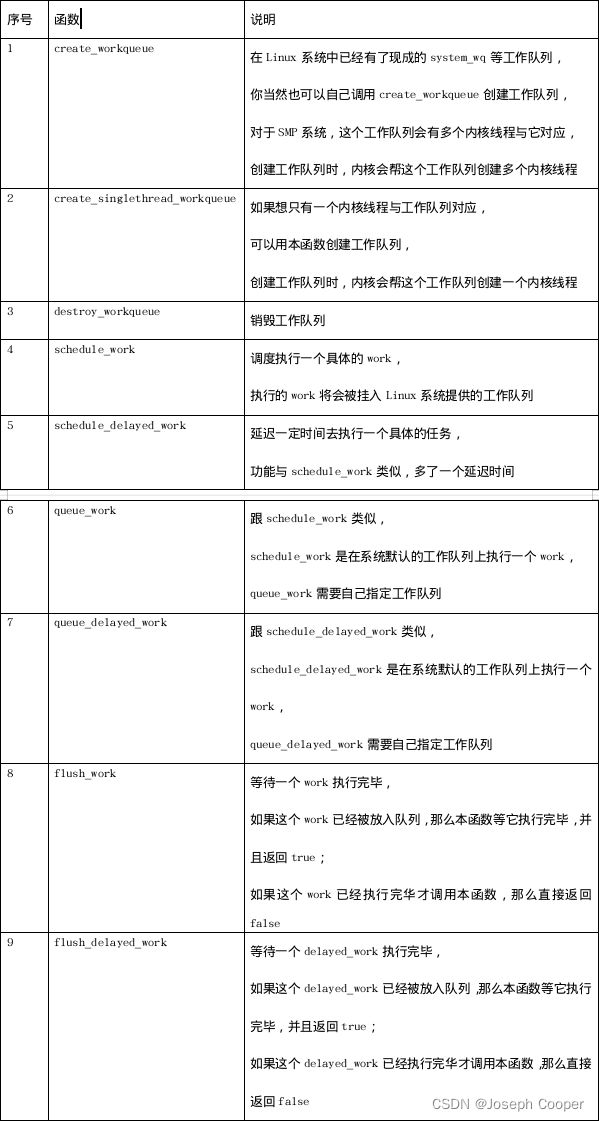
▲其他函数
create_workqueue
create_singlethread_workqueue
destroy_workqueue
schedule_work
schedule_delayed_work
queue_work
queue_delayed_work
flush_work
flush_delayed_work
7.2、使用程序
驱动核心程序
struct gpio_key{
int gpio;
struct gpio_desc *gpiod;
int flag;
int irq;
struct timer_list key_timer;
struct tasklet_struct tasklet;
struct work_struct work;
} ;
/* 工作函数 */
static void key_work_func(struct work_struct *work)
{
/* container_of可以根据结构体成员返回结构体(首)地址 */
struct gpio_key *gpio_key = container_of(work, struct gpio_key, work);
int val;
val = gpiod_get_value(gpio_key->gpiod);
printk("key_work_func: the process is %s pid %d\n",current->comm, current->pid);
printk("key_work_func key %d %d\n", gpio_key->gpio, val);
}
static irqreturn_t gpio_key_isr(int irq, void *dev_id)
{
struct gpio_key *gpio_key = dev_id;
//printk("gpio_key_isr key %d irq happened\n", gpio_key->gpio);
tasklet_schedule(&gpio_key->tasklet);
mod_timer(&gpio_key->key_timer, jiffies + HZ/50);
/* 将工作挂载到工作队列并唤醒kworker线程执行工作 */
schedule_work(&gpio_key->work);
return IRQ_HANDLED;
}
/* 1. 从platform_device获得GPIO
* 2. gpio=>irq
* 3. request_irq
*/
static int gpio_key_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
int err;
struct device_node *node = pdev->dev.of_node;
int count;
int i;
enum of_gpio_flags flag;
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
count = of_gpio_count(node);
if (!count)
{
printk("%s %s line %d, there isn't any gpio available\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
return -1;
}
gpio_keys_100ask = kzalloc(sizeof(struct gpio_key) * count, GFP_KERNEL);
for (i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
gpio_keys_100ask[i].gpio = of_get_gpio_flags(node, i, &flag);
if (gpio_keys_100ask[i].gpio < 0)
{
printk("%s %s line %d, of_get_gpio_flags fail\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
return -1;
}
gpio_keys_100ask[i].gpiod = gpio_to_desc(gpio_keys_100ask[i].gpio);
gpio_keys_100ask[i].flag = flag & OF_GPIO_ACTIVE_LOW;
gpio_keys_100ask[i].irq = gpio_to_irq(gpio_keys_100ask[i].gpio);
//setup_timer(&gpio_keys_100ask[i].key_timer, key_timer_expire, &gpio_keys_100ask[i]);
timer_setup(&gpio_keys_100ask[i].key_timer, key_timer_expire, 0);
gpio_keys_100ask[i].key_timer.expires = ~0;
add_timer(&gpio_keys_100ask[i].key_timer);
tasklet_init(&gpio_keys_100ask[i].tasklet, key_tasklet_func, (unsigned long)(&gpio_keys_100ask[i]));
/* 将工作函数和工作绑定 */
INIT_WORK(&gpio_keys_100ask[i].work, key_work_func);
}
for (i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
err = request_irq(gpio_keys_100ask[i].irq, gpio_key_isr, IRQF_TRIGGER_RISING | IRQF_TRIGGER_FALLING, "100ask_gpio_key", &gpio_keys_100ask[i]);
}
/* 注册file_operations */
major = register_chrdev(0, "100ask_gpio_key", &gpio_key_drv); /* /dev/gpio_key */
gpio_key_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "100ask_gpio_key_class");
if (IS_ERR(gpio_key_class)) {
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
unregister_chrdev(major, "100ask_gpio_key");
return PTR_ERR(gpio_key_class);
}
device_create(gpio_key_class, NULL, MKDEV(major, 0), NULL, "100ask_gpio_key"); /* /dev/100ask_gpio_key */
return 0;
}
7.3、使用实验
▲使用实验
7.4、工作机制
…待写
8、中断线程化处理
关于中断线程化的基础知识见下面文章的2.2节,这里不做赘述:
【嵌入式Linux】嵌入式Linux驱动开发基础知识之Linux中断系统简介及按键中断设备树驱动编写
8.1、内核函数
/**
* @brief: 中断线程化申请函数
* @irq: 中断号
* @handler: 中断的上半部函数
* @thread_fn: 线程中运行的函数
* @irqflags: 中断触发方式标志位
* @devname: 设备名称
* @dev_id: 传入数据,该数据会被传入线程运行函数
*
*/
int request_threaded_irq(unsigned int irq, irq_handler_t handler,
irq_handler_t thread_fn, unsigned long irqflags,
const char *devname, void *dev_id)
中断线程化的使用很简单,只用到这一个内核函数,所以其使用流程直接在程序中体现
8.2、内核机制
…待写
8.2、使用程序
驱动核心代码
/* 中断线程处理函数 */
static irqreturn_t gpio_key_thread_func(int irq, void *data)
{
struct gpio_key *gpio_key = data;
int val;
val = gpiod_get_value(gpio_key->gpiod);
printk("gpio_key_thread_func: the process is %s pid %d\n",current->comm, current->pid);
printk("gpio_key_thread_func key %d %d\n", gpio_key->gpio, val);
return IRQ_HANDLED;
}
/* 1. 从platform_device获得GPIO
* 2. gpio=>irq
* 3. request_irq
*/
static int gpio_key_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
int err;
struct device_node *node = pdev->dev.of_node;
int count;
int i;
enum of_gpio_flags flag;
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
count = of_gpio_count(node);
if (!count)
{
printk("%s %s line %d, there isn't any gpio available\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
return -1;
}
gpio_keys_100ask = kzalloc(sizeof(struct gpio_key) * count, GFP_KERNEL);
for (i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
gpio_keys_100ask[i].gpio = of_get_gpio_flags(node, i, &flag);
if (gpio_keys_100ask[i].gpio < 0)
{
printk("%s %s line %d, of_get_gpio_flags fail\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
return -1;
}
gpio_keys_100ask[i].gpiod = gpio_to_desc(gpio_keys_100ask[i].gpio);
gpio_keys_100ask[i].flag = flag & OF_GPIO_ACTIVE_LOW;
gpio_keys_100ask[i].irq = gpio_to_irq(gpio_keys_100ask[i].gpio);
//setup_timer(&gpio_keys_100ask[i].key_timer, key_timer_expire, &gpio_keys_100ask[i]);
timer_setup(&gpio_keys_100ask[i].key_timer, key_timer_expire, 0);
gpio_keys_100ask[i].key_timer.expires = ~0;
add_timer(&gpio_keys_100ask[i].key_timer);
tasklet_init(&gpio_keys_100ask[i].tasklet, key_tasklet_func, (unsigned long)(&gpio_keys_100ask[i]));
INIT_WORK(&gpio_keys_100ask[i].work, key_work_func);
}
for (i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
//err = request_irq(gpio_keys_100ask[i].irq, gpio_key_isr, IRQF_TRIGGER_RISING | IRQF_TRIGGER_FALLING, "100ask_gpio_key", &gpio_keys_100ask[i]);
/* 为每个设备申请中断线程 */
err = request_threaded_irq(gpio_keys_100ask[i].irq, gpio_key_isr, gpio_key_thread_func, IRQF_TRIGGER_RISING | IRQF_TRIGGER_FALLING, "100ask_gpio_key", &gpio_keys_100ask[i]);
}
/* 注册file_operations */
major = register_chrdev(0, "100ask_gpio_key", &gpio_key_drv); /* /dev/gpio_key */
gpio_key_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "100ask_gpio_key_class");
if (IS_ERR(gpio_key_class)) {
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
unregister_chrdev(major, "100ask_gpio_key");
return PTR_ERR(gpio_key_class);
}
device_create(gpio_key_class, NULL, MKDEV(major, 0), NULL, "100ask_gpio_key"); /* /dev/100ask_gpio_key */
return 0;
}
8.3、使用实验
▲实验
9、mmap
…待写
▲
#pic_center