webpack打包原理--webapck-cli及Tapable
一、webpack-cli
(1)作用
- 引入 yargs,对命令行进行定制
- 分析命令行参数,对各个参数进行转换,组成编译配置项
- 引用webpack,根据配置项进行编译和构建
(2) 命令行工具包 yargs
- 提供命令和分组参数
- 动态生成 help 帮助信息
(3)webpack-cli 使用 args 分析
参数分组 (config/config-args.js),将命令划分为9类:
- Config options: 配置相关参数(文件名称、运行环境等)
- Basic options: 基础参数(entry设置、debug模式设置、watch监听设置、devtool设置)
- Module options: 模块参数,给 loader 设置扩展
- Output options: 输出参数(输出路径、输出文件名称)
- Advanced options: 高级用法(记录设置、缓存设置、监听频率、bail等)
- Resolving options: 解析参数(alias 和 解析的文件后缀设置)
- Optimizing options: 优化参数
- Stats options: 统计参数
- options: 通用参数(帮助命令、版本信息等)
(4) webpack-cli 执行的结果
1、webpack-cli对配置文件和命令行参数进行转换最终生成配置选项参数 options
2、最终会根据配置参数实例化 webpack 对象,然后执行构建流程
二、Tapable
(1)意义
Tapable 是一个类似于 Node.js 的 EventEmitter 的库, 主要是控制钩子函数的发布与订阅,控制着 webpack 的插件系统。
(2)Tapable库暴露了很多 Hook(钩子)类,为插件提供挂载的钩子
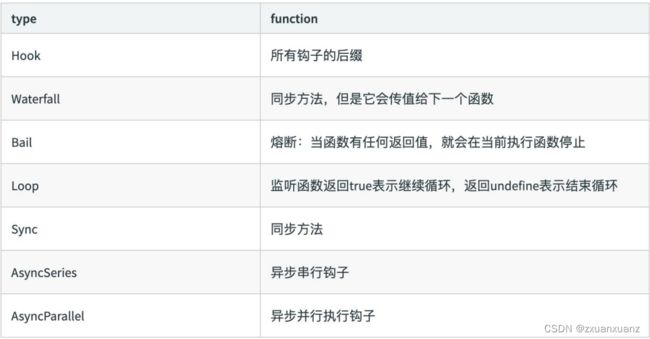
(3)Tapable hooks 类型
1、Tapable 暴露出来的都是类方法,new 一个类方法获得我们需要的钩子
2、class 接受数组参数 options ,非必传。类方法会根据传参,接受同样数量的参数。
const hook1 = new SyncHook(["arg1", "arg2", "arg3"]);(5)Tapable 的使用-钩子的绑定与执行
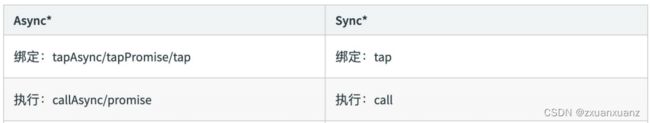
Tapable 提供了同步&异步绑定钩子的方法,并且他们都有绑定事件和执行事件对 应的方法。
(6)Tapable 的使用-hook 基本用法示例
const hook1 = new SyncHook(["arg1", "arg2", "arg3"]);
//绑定事件到webapck事件流
hook1.tap('hook1', (arg1, arg2, arg3) => console.log(arg1, arg2, arg3)) //1,2,3
//执行绑定的事件
hook1.call(1,2,3)(7)Tapable 的使用-实际例子演示
1、定义一个 Car 方法,在内部 hooks 上新建钩子。
2、分别是同步钩子 accelerate、 brake( accelerate 接受一个参数)、异步钩子 calculateRoutes
3、使用钩子对应的绑定和执行方法 calculateRoutes
4、使用 tapPromise 可以返回一个 promise 对象
const {
SyncHook,
AsyncSeriesHook
} = require('tapable');
class Car {
constructor() {
this.hooks = {
accelerate: new SyncHook(['newspeed']),
brake: new SyncHook(),
calculateRoutes: new AsyncSeriesHook(["source", "target", "routesList"])
}
}
}
const myCar = new Car();
//绑定同步钩子
myCar.hooks.brake.tap("WarningLampPlugin", () => console.log('WarningLampPlugin'));
//绑定同步钩子 并传参
myCar.hooks.accelerate.tap("LoggerPlugin", newSpeed => console.log(`Accelerating to ${newSpeed}`));
//绑定一个异步Promise钩子
myCar.hooks.calculateRoutes.tapPromise("calculateRoutes tapPromise", (source, target, routesList, callback) => {
// return a promise
return new Promise((resolve,reject)=>{
setTimeout(()=>{
console.log(`tapPromise to ${source} ${target} ${routesList}`)
resolve();
},1000)
})
});
myCar.hooks.brake.call();
myCar.hooks.accelerate.call(10);
console.time('cost');
//执行异步钩子
myCar.hooks.calculateRoutes.promise('Async', 'hook', 'demo').then(() => {
console.timeEnd('cost');
}, err => {
console.error(err);
console.timeEnd('cost');
});
(8)Tapable 是如何和 webpack 联系起来的
1、核心对象 Compiler 继承 Tapable
2、核心对象 Compilation 继承 Tapable
3、node_modules/webpack/lib/webpack.js
const webpack = (options, callback) => {
const webpackOptionsValidationErrors = validateSchema(
webpackOptionsSchema,
options
);
if (webpackOptionsValidationErrors.length) {
throw new WebpackOptionsValidationError(webpackOptionsValidationErrors);
}
let compiler;
if (Array.isArray(options)) {
compiler = new MultiCompiler(
Array.from(options).map(options => webpack(options))
);
} else if (typeof options === "object") {
//初始化默认配置等
options = new WebpackOptionsDefaulter().process(options);
compiler = new Compiler(options.context);
compiler.options = options;
//内部插件(插件必须有个aplly,传入参数compiler)
new NodeEnvironmentPlugin({
infrastructureLogging: options.infrastructureLogging
}).apply(compiler);
//配置或命令行的插件组装成的options(通过webpack-cli生成)
if (options.plugins && Array.isArray(options.plugins)) {
//遍历将compiler传递给每个插件,插件监听compiler里的hooks事件,
//一旦触发事件,插件就会执行相应方法
for (const plugin of options.plugins) {
if (typeof plugin === "function") {
plugin.call(compiler, compiler);
} else {
plugin.apply(compiler);
}
}
}
compiler.hooks.environment.call();
compiler.hooks.afterEnvironment.call();
//加入内置插件
compiler.options = new WebpackOptionsApply().process(options, compiler);
} else {
throw new Error("Invalid argument: options");
}
if (callback) {
if (typeof callback !== "function") {
throw new Error("Invalid argument: callback");
}
if (
options.watch === true ||
(Array.isArray(options) && options.some(o => o.watch))
) {
const watchOptions = Array.isArray(options)
? options.map(o => o.watchOptions || {})
: options.watchOptions || {};
return compiler.watch(watchOptions, callback);
}
compiler.run(callback);
}
return compiler;
};(9)模拟 Compiler.js
const {
SyncHook,
AsyncSeriesHook
} = require('tapable');
module.exports = class Compiler {
constructor() {
this.hooks = {
accelerate: new SyncHook(['newspeed']),
brake: new SyncHook(),
calculateRoutes: new AsyncSeriesHook(["source", "target", "routesList"])
}
}
run(){
this.accelerate(10)
this.break()
this.calculateRoutes('Async', 'hook', 'demo')
}
accelerate(speed) {
this.hooks.accelerate.call(speed);
}
break() {
this.hooks.brake.call();
}
calculateRoutes() {
this.hooks.calculateRoutes.promise(...arguments).then(() => {
}, err => {
console.error(err);
});
}
}(10)插件 my-plugin.js
const Compiler = require('./Compiler')
class MyPlugin{
constructor() {
}
apply(compiler){
compiler.hooks.brake.tap("WarningLampPlugin", () => console.log('WarningLampPlugin'));
compiler.hooks.accelerate.tap("LoggerPlugin", newSpeed => console.log(`Accelerating to ${newSpeed}`));
compiler.hooks.calculateRoutes.tapPromise("calculateRoutes tapAsync", (source, target, routesList) => {
return new Promise((resolve,reject)=>{
setTimeout(()=>{
console.log(`tapPromise to ${source} ${target} ${routesList}`)
resolve();
},1000)
});
});
}
}
(11)模拟插件执行
const Compiler = require('./Compiler')
const myPlugin = new MyPlugin();
const options = {
plugins: [myPlugin]
}
const compiler = new Compiler();
for (const plugin of options.plugins) {
if (typeof plugin === "function") {
plugin.call(compiler, compiler);
} else {
plugin.apply(compiler);
}
}
compiler.run();