java中的IO流
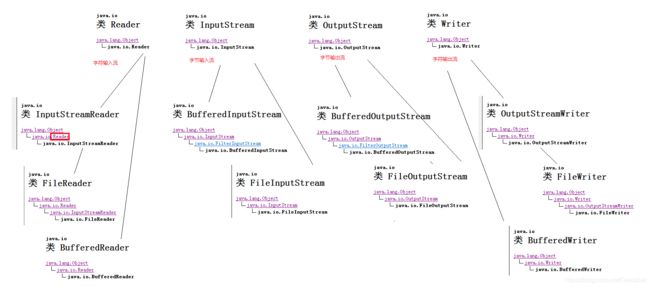
java中的IO流
IO流主要分为input 流和output 流,对于不同的操作方式分为字节流操作和字符流操作,以下为java中主要用来IO流操作的类

1.输出流
OutputStream(字节流)
- 基本信息:
- 包:java.io
- 类型:抽象类
- 子类:FileOutputStream
- 子类构造方法:
- 传入一个File类型进行输出
FileOutputStream(File file)(默认都是将流覆盖原始的文件) - 传入一个String类型进行输出
FileOutputStream(String name)(默认都是将流覆盖原始的文件) - 将append设置为true,不覆盖原始文件,将流写入文件后
FileOutputStream(File file, boolean append) FileOutputStream(String name, boolean append)
- 传入一个File类型进行输出
- 常用方法:
关闭此输出流并释放与此流有关的所有系统资源。close()
刷新此输出流并强制写出所有缓冲的输出字节flush()
将 b.length 个字节从指定的 byte 数组写入此输出流。write(byte[] b)
将指定 byte 数组中从偏移量 off 开始的 len 个字节写入此输出流。write(byte[] b, int off, int len) - 代码示例:
在文件夹下创建并写入a.txt文件内容为helloworld
String string = "helloworld";
OutputStream os=null;
try {
os = new FileOutputStream("D:\\0XYZ\\a.txt");
byte [] buffer = string.getBytes();
os.write(buffer,0,string.length());
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
os.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
2.输入流
InputStream(字节流)
- 基本信息:
- 包:java.io
- 类型:抽象类
- 子类:FileInputStream
- 子类构造方法:传入一个File类型
FileInputStream(File file)传入一个String类型FileInputStream(String name)
- 常用方法:
- 关闭此输入流并释放与该流关联的所有系统资源。
close() - 将输入流中最多 len 个数据字节读入 byte 数组。
read(byte[] b, int off, int len)返回的是一个读取的长度,当最后读完后再进行读取时返回-1
3.利用二进制字符流进行文件的复制操作
InputStream is = null;
OutputStream os = null;
try {
is = new FileInputStream("C:\\a.txt");
os = new FileOutputStream("D:\\a.txt");
byte [] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while ((len = is.read(bytes,0,bytes.length))!=-1){
os.write(bytes,0,len);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
is.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
os.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
4.缓冲流
基本思想就是减少磁盘的访问次数,一次性的先从磁盘中获取一部分数据到内存中。程序后续如果能从
缓存中获取数据,就不会真正访问磁盘,以提高读取效率。

用到的两个类BufferedInputStream和BufferedOutputStream
构造方法:
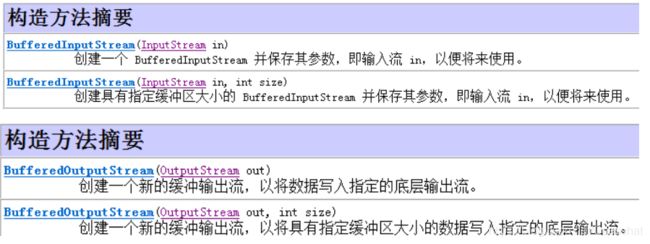
可以指定缓存区大小,如果不指定就是8192=8kb
关闭流,直接关闭缓存流,内部的资源流也会关闭
具体使用:
InputStream is = null;
OutputStream os = null;
BufferedInputStream bis = null;
BufferedOutputStream bos = null;
try {
is = new FileInputStream("C:\\a.txt");
os = new FileOutputStream("D:\\a.txt");
bis = new BufferedInputStream(is);
bos = new BufferedOutputStream(os);
byte [] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len = -1;
while((len = bis.read(bytes,0,bytes.length))!=-1){
bos.write(bytes,0,len);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
bis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
bos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
5.字符流
因为读取和写入的编码格式不一致,如果采用字节流进行文件操作,在打开后会存在乱码问题
常见的字符编码:
- ASCII 英文的最古老的字符集 (a-97 、 A-65、 0-48)
- GB2312: 以前的简体中文的方案
- GBK: 简体中文
- ISO-8859-1 : 网络传输编码
- Gig 5 : 繁体中文
- UTF 8 : 主流的全球通用的编码格式。
用到的两个类:
InputStreamReader和OutputStreamWriter
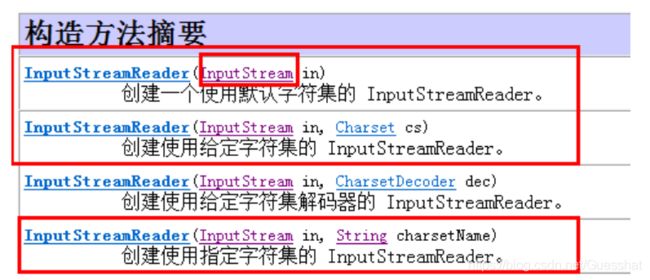
1.InputStreamReader
传入的类型都是InputStream类型,也支持传入缓冲流,在构造方法中支持传入字符编码格式
使用第四种构造方法中文编码格式:GB2311 GBK utf8 都可以作为字符串传入
读取方法:
read(char[] cbuf, int offset, int length)可以自动按照文字的字节读取,不会乱码
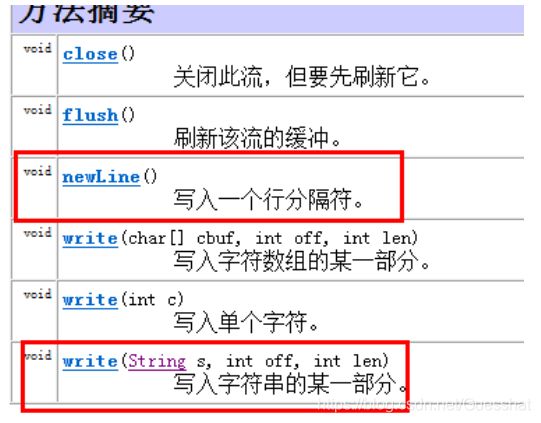
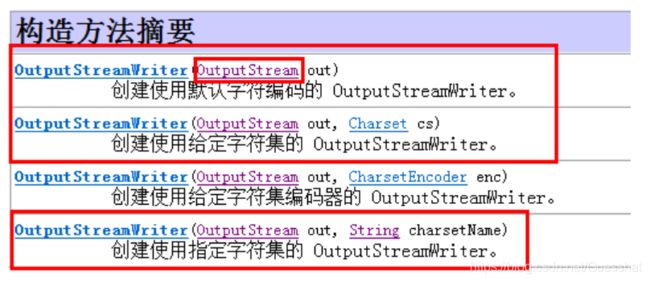
2.OutputStreamWriter
类似InputStreamReader
写入方法:
write(char[] cbuf, int off, int len)
3.综合案例
将C盘下以GBK编码的a.txt文件复制到D盘下,并以utf8格式写入,原理是利用了二进制流加缓存流然后转换成字符流进行操作
InputStream is = null;
OutputStream os = null;
BufferedInputStream bis = null;
BufferedOutputStream bos = null;
InputStreamReader isr = null;
OutputStreamWriter osw = null;
try {
is = new FileInputStream("C:\\a.txt");
os = new FileOutputStream("D:\\a.txt");
bis = new BufferedInputStream(is);
bos = new BufferedOutputStream(os);
isr = new InputStreamReader(bis,"GBK");
osw = new OutputStreamWriter(bos,"utf8");
char [] buffer = new char[1024];
int len = -1;
while((len = isr.read(buffer,0,buffer.length))!=-1){
osw.write(buffer,0,len);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
isr.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
osw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
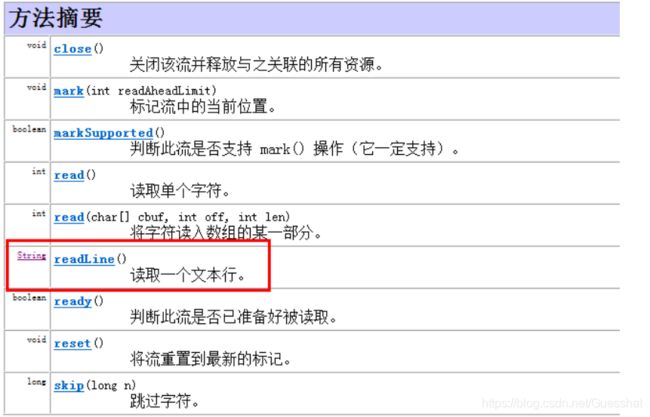
6.字符缓存流
重要方法是存在读取和写入一行的操作,可以先将字节流转换成字符流,然后加入缓存机制,优势是可以进行读一行和写一行的操作,在写入和读取的时候更灵活。
1.BufferedReader
2.BufferedWriter
3.具体代码实现
将C盘下的一个以gbk编码的aaa.txt文件以utf8格式写入到D盘下的bbb.txt文件
InputStream is = null;
OutputStream os = null;
InputStreamReader isr = null;
OutputStreamWriter osw = null;
BufferedReader br = null;
BufferedWriter bw = null;
try {
is = new FileInputStream("C:\\aaa.txt");
os = new FileOutputStream("D:\\bbb.txt");
isr = new InputStreamReader(is,"gbk");
osw = new OutputStreamWriter(os,"utf8");
br =new BufferedReader(isr);
bw = new BufferedWriter(osw);
String str = null;
//这里使用!=而不用equals,是因为当str最后为null时会报空指针异常,程序崩溃
while ((str = br.readLine())!=null){
System.out.println(str);
bw.write(str);
bw.newLine();
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
br.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
bw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
7.转换流简写
- 只用于字符文件的操作,不用于视频图片的处理
- 默认是utf8编码格式,如果源文件编码格式不是utf8的不建议使用,会造成乱码
- 其实是将字节流转换成字符流处理并加入缓存机制的另一种操作
1.FileReader
相当于:
- FileInputStream
- BufferedInputStream
- InputStreamReader
- utf-8 编码
2.FileWriter
相当于:
- FileOutputStream
- BufferedOutputStream
- OutputStreamWriter
- utf-8 编码
3.具体代码实现
FileReader fr = null;
FileWriter fw = null;
try {
fr = new FileReader("C:\\b.txt");
fw = new FileWriter("D:\\b.txt");
char[] buffer = new char[1024];
int len = -1;
while ((len = fr.read(buffer,0,buffer.length))!=-1){
fw.write(buffer,0,len);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
fr.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
fw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
8.总结:
- 二进制流可以适用任何文件的操作(字符文件、视频文件、图像文件、音频文件)
1.1 InputStream/OutputStream用于二进制操作流
1.2 为解决内存占用效率不高的情况,引入二进制缓存流BufferedInputStream/BufferedOutputStream - 为解决字符文件源文件和写入时的编码格式问题引入字符流处理操作
2.1 InputStreamReader/OutputStreamWriter用于字符流的文件操作,构造方法中可以设置编码格式,解决乱码问题
2.2 对应的也有缓存流机制 BUfferedReader/BufferedWriter
2.3 为了将这一系列字符流操作简化,引入FileReader/FileWriter,相当于既设置了缓存流,也设置了字符流,并且默认编码方式为utf8格式