Web前端学习之旅
目录
- JS/ES篇
-
- 数据类型
- 函数
- Object.setPrototypeOf设置原型对象
- Object.is方法
- Math方法
- Set方法
- Symbol
- rest参数
- 迭代器
- 生成器
- Class
- Class中的getter和setter
- Class类继承
- ES5构造函数继承
- Promise多文件读取
- Promise封装AJAX请求
- Vue篇
-
- 插槽
-
- 匿名插槽
- 具名插槽
- 作用域插槽
- VueX篇
-
- State
- Getters
- Mutations
- Actions
- Modules
- 微信小程序篇
-
- 加载效果
- 数据循环
- 设置页面头部名称
- 下拉刷新、上滑刷新
- 父子组件事件传递
- 设置导航栏购物车商品数量(角标)
- 左滑删除购物车商品
- 微信支付
- Uni-app篇
-
- MVVM模式
- 生命周期
- pages.json的一些配置
- 标签
- data-XXX
- 引入样式
- 导航栏上滑渐变显示
- 下拉刷新、上拉加载
- 数据缓存方法一览
- 图片上传预览方法
- 图片长按保存至本地
- 分享至微信好友
- 分享至微信朋友圈
- 跨端兼容(JS、CSS、HTML)
- 单视频播放暂停优化
- 多视频播放暂停优化
- createAnimation创建动画
- CSS篇
-
- flex
- React篇
-
- 路由模糊匹配和严格匹配
- 向路由组件传递params参数
- 向路由组件传递search参数
- 向路由组件传递state参数
- 编程式路由导航(通过JS代码跳转页面)
- withRouter方法(加工一般组件)
JS/ES篇
数据类型
总结:USONB(简单记忆:You are so NB)
U:undefined
S:string、symbol
O:object
N:null、number
B:boolean
- NaN不等于任何值,包括NaN
- null只会等于null和undefined
- undefined只会等于null和undefined
- 若两边有数字或布尔类型,都转换成数字类型进行比较(空数组[]等于0,空字符串‘’等于0,空对象{}等于0)
- 若一个是字符串,另一个是复杂类型,则复杂类型转换成字符串比较
- 若都是复杂类型,直接比较地址
函数
JS函数分为三类:命名函数、匿名函数、自执行函数。
function f1 () { ...... } // 命名函数
const f2 = function () { ...... } // 匿名函数
(function (n1, n2) { ...... })(10, 20) // 自执行函数(只执行一次)
Object.setPrototypeOf设置原型对象
const school = { name: 'new East' };
const cities = { xiaoqu: ['北京', '上海', '深圳'] };
Object.setPrototypeOf(school, cities);
Object.getPrototypeOf(school); // 此方法用于获取原型对象
Object.is方法
// Object.is方法判断两个值是否完全相等
Object.is(120, 120); // true
Object.is(NaN, NaN); // true
注意:NaN === NaN // false
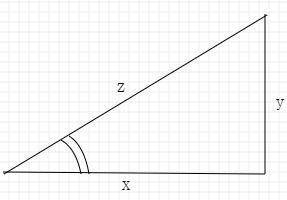
Math方法
// 开方
Math.sqrt(x * x + y * y);
// 反正弦(效果图如下)
Math.asin(y / z) / Math.PI * 180;
// 幂(注意:**为ES7的写法)
Math.pow(10, 3) == 10 * 10 * 10 == 10 ** 3;
// 去掉一个数的小数部分
Math.trunc(3.5); // 3
// 判断一个数是否为正数、零或负数
Math.sign(100); // 1
Math.sign(0); // 0
Math.sign(-200); // -1
Set方法
数组去重:
const rest = new Set([1, 2, 3, 4, 4]);
[...rest]; // [1, 2, 3, 4]
rest.size; // 4
rest.add(5); // 往集合中添加一项
rest.delete(3); // 删除集合中指定某一项
rest.has(2); // 判断集合中是否存在某一项
rest.clear(); // 清空集合
并集:
const a = new Set([1, 2, 3]);
const b = new Set([4, 2, 3]);
const union = [...new Set([...a, ...b])]; // [1, 2, 3, 4]
交集:
let interesct = new Set([...a].filter(item => b.has(item)));
interesct = [...interesct]; // [2, 3]
Symbol
const obj = {
[Symbol('name')]: '一斤代码',
age: 18,
title: 'engineer'
};
Object.keys(obj); // ['age', 'title']
Object.getOwnPropertySymbols(obj); // [Symbol('name')]
Reflect.ownKeys(obj); // ['age', 'title', Symbol('name')]
对象添加Symbol类型的属性:
// 方法一:
const game = {
name: "狼人杀",
[Symbol('say')]: function () { console.log('开始游戏吧'); },
[Symbol('zibao')]: function () { console.log('准备自爆啦'); }
}
// 方法二:
const obj = { ... } // 此处代码不可见
const methods = {
up: Symbol(),
down: Symbol()
}
obj[methods.up] = function () { ... }
obj[methods.down] = function () { ... }
rest参数
function fn (a, b, ...args) { // ...args参数一般放在最后
console.log(a, b, args);
}
fn (1, 2, 3, 4, 5); // 1, 2, [3, 4, 5]
迭代器
需求:采用面向对象的思想遍历对象中的数组的每一项值
const banji = {
name: '高三一班',
stus: ['小明', '小赵', '小李', '小钱'],
[Symbol.iterator]: function () {
let index = 0;
return {
next: () => {
if (index < this.stus.length) {
const result = { value: this.stus[index], done: false };
index++; // 下标自增
return result;
} else return { value: undefined, done: true };
}
}
}
};
for (let v of banji) {
console.log(v); // 小明小赵小李小钱
}
生成器
function *gen () {
console.log('111');
yield '字符串1';
console.log('222');
yield '字符串2';
console.log('333');
yield '字符串3';
console.log('444');
}
for (const v of gen()) {
console.log(v);
}
const iterator = gen();
console.log(iterator.next()); // 111(换行){ value: "字符串1", done: false }
// next方法可以传入实参
function *gen (arg) {
console.log(arg);
const one = yield 111;
console.log(one);
const two = yield 222;
console.log(two);
const three = yield 333;
console.log(three);
}
// 参数将作为上一个yield语句的整体返回结果
const iterator = gen('AAA');
console.log(iterator.next());
console.log(iterator.next('BBB'));
console.log(iterator.next('CCC'));
console.log(iterator.next('DDD'));
// 打印结果:
// AAA
// { value: 111, done: false }
// BBB
// { value: 222, done: false }
// CCC
// { value: 333, done: false }
// DDD
// { value: undefined, done: true }
// 生成器函数实例
function one () {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('111');
iterator.next();
}, 1000);
}
function two () {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('222');
iterator.next();
}, 1000);
}
function three () {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('333');
iterator.next();
}, 1000);
}
function *gen () {
yield one();
yield two();
yield three();
}
const iterator = gen();
iterator.next(); // 每隔一秒打印一个函数的值
function getUsers () {
setTimeout(() => {
iterator.next('用户数据');
}, 1000);
}
function getOrders () {
setTimeout(() => {
iterator.next('订单数据');
}, 1000);
}
function getGoods () {
setTimeout(() => {
iterator.next('商品数据');
}, 1000);
}
function *gen () {
const users = yield getUsers();
const orders = yield getOrders();
const goods = yield getGoods();
}
// 调用生成器函数
const iterator = gen();
iterator.next(); // { value: undefined, done: false }
Class
class Phone {
// 构造方法
constructor (brand, price) {
this.brand = brand;
this.price = price;
}
// 方法
call () { console.log('手机型号是', this.brand); }
}
const onePlus = new Phone('1+', 1999);
console.log(onePlus); // Phone { brand: "1+", price: 1999 }
onePlus.call(); // 手机型号是1+
Class中的getter和setter
class Phone {
get price () {
console.log('手机的价格是xxx');
return 'metoo';
}
set price (newVal) {
console.log('手机的价格修改了');
}
}
const s = new Phone();
console.log(s.price); // get函数的返回值是这个属性的值
s.price = 'free';
// 打印结果:手机的价格是xxx(换行)metoo(换行)手机的价格修改了(换行)"free"
Class类继承
class Phone {
// 构造方法
constructor (brand, price) {
this.brand = brand;
this.price = price;
}
// 父类成员属性
call () {
console.log('手机可以打电话');
}
}
class SmartPhone extends Phone {
// 构造方法
constructor (brand, price, color, size) {
super(brand, price);
this.color = color;
this.size = size;
}
photo () {
console.log('手机可以拍照');
}
}
const xiaomi = new SmartPhone('小米', 799, '黑色', '4.7inch');
xiaomi.call(); // 手机可以打电话
xiaomi.photo(); // 手机可以拍照
ES5构造函数继承
// 手机
function Phone (brand, price) {
this.brand = brand;
this.price = price;
}
Phone.prototype.call = function () {
console.log('这是一个方法');
}
// 智能手机
function SmartPhone (brand, price, color, size) {
Phone.call(this, brand, price);
this.color = color;
this.size = size;
}
// 设置子级构造函数的原型
SmartPhone.prototype = new Phone;
SmartPhone.prototype.constructor = SmartPhone; // 此行代码可省略
// 声明子类的方法
SmartPhone.prototype.photo = function () {
console.log('这是另外一个方法');
}
const chuizi = new SmartPhone('锤子', '2499', '黑色', '5.5inch');
console.log(chuizi); // { brand: "锤子", price: "2499", color: "黑色", size: "5.5inch" }
Promise多文件读取
// 引入fs模块
const fs = require('fs');
// 使用promise实现
const p = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
fs.readFile('文件1地址', (err, data) => {
resolve(data);
});
});
p.then(value => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
fs.readFile('文件2地址', (err, data) => {
resolve([value, data]);
});
});
}).then(value => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
fs.readFile('文件3地址', (err, data) => {
value.push(data);
resolve(value);
});
});
}).then(value => {
console.log(value);
});
Promise封装AJAX请求
const p = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.open('GET', '请求地址');
xhr.send();
xhr.onreadystatechange = function () {
if (xhr.readyState == 4) {
if (xhr.status >= 200 && xhr.status < 300) resolve(xhr.response);
else reject(xhr.status);
}
}
});
p.then(function (value) {
console.log(value);
}, function (reason) {
console.log(reason);
});
Vue篇
插槽
匿名插槽
<div><slot>后备内容slot>div>
<child1>这是一个匿名插槽child1>
具名插槽
<div>
<slot name="title">这里填写标题slot>
<slot name="subtitle">这里填写小标题slot>
div>
<child2>
<div slot="title">这是一个页面大标题div>
<div slot="subtitle">这是一个页面小标题div>
child2>
<div>
<slot name="title">这里填写标题slot>
<slot name="subtitle">这里填写小标题slot>
div>
<child3>
<template v-slot:title>这是一个页面大标题template>
<template v-slot:subtitle>这是一个页面小标题template>
child3>
作用域插槽
<div>
<slot :foo="foo">slot>
div>
<child4>
<template v-slot:default="scope">来自子组件数据:{{scope.foo}}template>
child4>
VueX篇
State
获取State中的数据(两种方法):
// 方法一
this.$store.state.params; // 注:params表示变量名
// 方法二
import { mapState } from 'vuex';
computed: {
...mapState(['params1', 'params2']) // 注:params1和params2均表示变量名
}
this.params1 // 使用时这样写
Getters
// 先定义
setStr (state) {
return state.params.slice(0, 2); // params表示在State中定义的变量
}
// 后使用(HTML代码和JS代码)
<div>{{setStr}}</div>
import { mapGetters } from 'vuex';
computed: {
...mapGetters(['setStr'])
}
Mutations
// HTML代码(此处省略v-for遍历代码)
<button @click="btn(item.name)"></button>
// JS代码(VueX代码)
state: { // 在State中定义变量
arr: [{ id: 1, name: '张三' }, { id: 2, name: '李四' }, { id: 3, name: '王五' }],
username: ''
},
mutations: { // 在Mutations中定义方法
setName (state, name) {
state.username = name;
}
}
// JS代码(使用VueX)
import { mapState, mapMutations } from 'vuex';
computed: {
...mapState(['arr', 'username'])
},
methods: {
...mapMutations(['setName'])
btn (name) {
this.setName(name); // 注意:传递多个值时,需要转化为object对象格式
}
}
注意:若需要进入某个页面就执行mutations中的方法,可在main.js中执行以下代码:
import store from './store';
store.commit('setName');
Actions
// JS代码(VueX代码)
state: { // 在State中定义变量
count: 0, // 购买数量
totalPrice: 0 // 总价
},
mutations: { // 在Mutations中定义方法
add (state) {
state.count++;
this.commit('total');
},
total (state) {
state.totalPrice = state.count * 10;
}
},
actions: { // 在Actions中提交mutation
addFn ({commit}) {
commit('add'); // 注意:传递多个值时,需要转化为object对象格式
}
}
注意:
1、action提交的是mutation,而不是直接变更状态
2、action可以包含任意异步操作
Modules
// VueX代码:假设category.js、shoppingCart.js和my.js均包含以下代码:
export default {
state: { ... },
getters: { ... },
mutations: { ... },
actions: { ... }
}
// VueX代码:将上述几个文件引入:
import category from './modules/category.js';
import shoppingCart from './modules/shoppingCart.js';
import my from './modules/my.js';
export default {
modules: {
category, shoppingCart, my
}
}
// HTML代码:
<div>{{count}}</div>
// JS代码:
import { mapState } from 'vuex';
export default {
computed: {
...mapState({ count: state => state.shoppingCart.count }) // 假设count变量在shoppingCart.js中已定义
}
}
微信小程序篇
加载效果
wx.showLoading({ title: '加载中...' });
wx.hideLoading();
数据循环
<view wx:for="{{arrList}}" wx:for-item="ite" wx:for-index="count"></view>
注意:在数据循环时,小程序内部已经封装好了item和index,可以直接使用。若需要更换名称,则需要使用wx:for-item="新变量"和wx:for-index=“新变量”。
设置页面头部名称
wx.setNavigationBarTitle({ title: "标题名称" });
下拉刷新、上滑刷新
// 首先需要配置json文件
"enablePullDownRefresh": true
"backgroundTextStyle": "dark" // 可选项,用于设置刷新时三个点的颜色
// 其次需要在js中编写如下代码
onPullDownRefresh () { // 下拉刷新
wx.showNavigationBarLoading(); // 可选项,开启头部刷新状态
wx.stopPullDownRefresh(); // 数据加载完毕,隐藏下拉刷新状态
wx.hideNavigationBarLoading(); // 可选项,隐藏头部刷新状态
}
onReachBottom () { ... } // 上滑刷新
父子组件事件传递
// 子组件child
this.triggerEvent('updateData', { data: 10 });
// 父组件
<child bind:updteData="update"></child>
设置导航栏购物车商品数量(角标)
// 设置角标
wx.setTabBarBadge({
index: 2, // 第几个tab
text: String(shoppingCartArr.length)
});
// 移除角标
wx.removeTabBarBadge({
index: 2
});
左滑删除购物车商品
// 定义变量
data: {
startX: 0,
startY: 0
},
// 定义方法
touchstart (e) { // 开始触摸时
this.data.shoppingCartArr.forEach(item => {
if (item.isTouchMove) item.isTouchMove = false;
// 开始触摸时将所有商品的删除按钮重置
this.setData({
startX: e.changedTouches[0].clientX,
startY: e.changedTouches[0].clientY
});
});
},
touchmove (e) { // 手指滑动时
const index = e.currentTarget.dataset.index;
// 开始的x和y坐标
const startX = this.data.startX;
const startY = this.data.startY;
// 移动的x和y坐标
const touchMoveX = e.changedTouches[0].clientX;
const touchMoveY = e.changedTouches[0].clientY;
// 调用计算角度方法
const angel = this.angel({ x: startX, y: startY }, { x: touchMoveX, y: touchMoveY });
// 遍历数组中的所有对象
this.data.shoppingCartArr.forEach((item, i) => {
item.isTouchMove = false;
// 滑动角度>30°则直接return
if (Math.abs(angel) > 30) return;
// 匹配
if (i == index) {
if (touchMoveX > startX) item.isTouchMove = false; // 右滑
else item.isTouchMove = true; // 左滑
}
});
},
angel (start, end) {
const _x = end.x - start.x;
const _y = end.y - start.y;
// 返回角度Math.atan()返回数字的反正切值
return 360 * (Math.atan(_y / _x) / (2 * Math.PI));
}
微信支付
// 步骤一:获取openid
wx.login({
success: (res) => {
const appid = '这是你的appid';
const secret = '这是你的secret';
wx.request({
url: '这里是你的请求地址',
success (res) {
const openid = res.data.openid;
this.wechatPay(openid);
}
});
}
});
// 步骤二:调用支付接口
wechatPay (openid) {
wx.request({ // 发起后端接口请求
url: '这里是你的请求地址',
methods: 'POST',
data: {
openid: openid // 这里填写后端需要的参数
},
success (res) {
wx.requestPayment({
appId: res.data.appId,
timeStamp: res.data.timeStamp,
nonceStr: res.data.nonceStr,
package: res.data.package,
signType: res.data.signType,
paySign: res.data.paySign,
success (res) {
wx.showToast({ title: '支付成功' });
},
fail () {
wx.showToast({ title: '支付失败' });
}
});
}
});
}
Uni-app篇
MVVM模式
View(页面HTML)
ViewModel(核心调度协调器)用于数据双向绑定
Model(单页面静态数据)
注意:三者之间是双向箭头
生命周期
应用生命周期:
onLaunch —— 初始化完成时触发(全局只触发一次)
onShow —— uni-app启动触发,或从后台进入前台(会多次触发)
onHide —— uni-app从前台进入后台(会多次触发)
onError —— uni-app报错时触发
页面生命周期:
onLoad —— 不会多次触发
onShow —— 多次触发
onReady —— 页面初次渲染完成时触发,不会多次触发
onHide —— 多次触发
onUnload —— 监听页面卸载
注意: tabBar页面展现过一次就保留在内存中,再次切换tabbar页面,只会触发每一个页面的onShow方法,不会再触发onLoad方法。
pages.json的一些配置
tabBar至多展示5个,至少展示2个。
"tabBar": {
"color": "文字默认颜色",
"selectedColor": "文字选中颜色",
"list": [{ "text": "标题", "pagePath": "页面路径" }, { ... }]
}
公用样式在globalStyle中配置。
"globalStyle": {
"navigationBarTextStyle": "导航栏标题颜色及状态栏前景颜色,仅支持black/white",
"navigationBarTitleText": "导航栏标题文字内容",
"navigationBarBackgroundColor": "导航栏背景颜色(同状态栏背景色)",
"backgroundColor": "下拉显示出来的窗口的背景色"
}
所有页面需要在pages中配置。
"pages": [
{ "path": "页面路径", "style": { "enablePullDownRefresh": true },
{ ... }
]
标签
<view></view>
// hover-class表示点击后加上指定的类
// hover-stop-propagation表示禁止事件冒泡
<button></button>
// size表示按钮大小
// plain表示按钮镂空(无背景颜色,只有描边)
// disabled表示禁用按钮
<image></image>
// mode="aspectFit"
// mode="aspectFill"
data-XXX
注意:无论XXX是否大小写,在js获取时均为小写。
// html代码
<view :data-userId="数值"></view>
// js代码
e.currentTarget.dataset.userid // 这里的userid每个字母均为小写
引入样式
@import url("css文件相对路径");
注意: 不能使用*选择器;字体引用推荐使用以~@开头的绝对路径
导航栏上滑渐变显示
// pages.json部分配置项
"path": "...",
"style": {
"app-plus": {
"titleNView": {
"type": "transparent",
"buttons": [{ "type": "share" }]
}
}
}
// js部分代码
uni.setNavigationBarColor({ // 通过代码设置导航栏
frontColor: '#fff',
backgroundColor: '#000'
});
下拉刷新、上拉加载
onPullDownRefresh () { ... }
// 该方法与data(){}等方法同级
// 当数据更新完成后,使用uni-stopPullDownRefresh()方法结束刷新
// 也可以使用uni-startPullDownRefresh()方法手动下拉刷新
onReachBottom () { ... }
// 该方法与data(){}等方法同级
// 可以使用onReachBottomDistance来设置距离页面底部还剩多少间距时触发该方法
数据缓存方法一览
uni.setStorage
uni.getStorage
uni.removeStorage
uni.setStorageSync
uni.getStorageSync
uni.removeStorageSync
图片上传预览方法
uni.chooseImage
uni.previewImage
图片长按保存至本地
// 1、HTML在标签上新增longpress事件
// 2、JS主要代码
uni.showActionSheet({
itemList: ['保存图片', '分享到微信'],
success: (res) => {
if (res.tapIndex == 0) {
uni.downLoadFile({
url: '图片地址',
success: (result) => {
const tempFilePath = result.tempFilePath; // 图片临时路径
uni.saveImageToPhotosAlbum({ // 保存图片至本地相册
filePath: tempFilePath,
success: () => {
uni.showToast({ title: '保存成功' });
}
});
}
});
}
}
});
分享至微信好友
小程序中用户点击分享后,在JS中定义onShareAppMessage处理函数,设置该页面的分享信息。
注意:此函数在微信小程序、百度小程序、字节跳动小程序和QQ小程序中生效。
onShareAppMessage (res) { // 此函数与onLoad()函数同级
return {
title: '标题',
path: '/pages/xxx/xxx?id=' + id //这里的参数根据需要添加即可
};
}
分享至微信朋友圈
// 首先需要设置appid和appsecret
mainfest.json -> App SDK配置 -> 分享微信消息及朋友圈 -> 填写appid和appsecret
// 监听导航栏的按钮
onNavigationBarButtonTap (e) { // 与onLoad()同级
const index = e.index;
if (index == 0) { // index为0则分享
uni.share({
provider: 'weixin',
scene: 'WXSenceTimeline',
type: 0,
href: '完整的url',
title: '这里填写标题',
summary: '简介',
imageUrl: '封面/图片url',
success: (res) => {}
});
}
}
跨端兼容(JS、CSS、HTML)
// #ifdef MP
console.log('这里的JS代码只在小程序中生效');
// #endif
/* #ifdef H5 */
.content { 这里的CSS代码只在H5中生效 }
/* #endif */
<!-- #ifdef MP -->
这里的HTML代码只在小程序中生效
<!-- #endif -->
<!-- #ifndef H5 -->
这里的HTML代码不在H5中生效
<!-- #endif -->
单视频播放暂停优化
// html代码
<video id="mymovie"></video>
// js代码
onReady () {
this.videoContext = uni.createVideoContext('mymovie');
}
onShow () {
if (this.videoContext) this.videoContext.play(); // 当页面展示时,播放视频(也可手动控制视频播放,就无需此行代码)
}
onHide () {
this.videoContext.pause();
}
多视频播放暂停优化
// html代码
<video
@playing="meIsPlaying"
v-for="item in hotTrailerArr"
:key="item.id"
:id="item.id"
:data-playingindex="item.id"
:src="item.src"
:poster="item.poster"></video>
// js代码(播放一个视频,需暂停其他视频)
meIsPlaying (e) {
let trailerId = '';
if (e) {
trailerId = e.currentTarget.dataset.playingindex;
this.videoContext = uni.createVideoContext(trailerId);
}
for (let i = 0; i < this.hotTrailerArr.length; i++) {
const temp = this.hotTrailerArr[i].id;
if (temp != trailerId) uni.createVideoContext(temp).pause();
}
}
createAnimation创建动画
// html代码
<view :animation="animationData" style="opacity: 0;"></view>
// js代码
data () {
animationData: {}
},
onLoad () {
this.animation = uni.createAnimation();
},
onUnload () {
this.animationData = {};
},
methods: {
// 创建点赞动画
praiseMe () {
// 构建动画数据,并通过step表示这组动画的完成
this.animation.translateY(-60).opacity(1).step({ duration: 400 });
// 导出动画数据到view数据,实现组件动画效果
this.animationData = this.animation.export();
// 还原动画
setTimeout(() => {
this.animation.translateY(0).opacity(0).step({ duration: 0 });
this.animationData = this.animation.export();
}, 500);
}
}
CSS篇
flex
order: 0;
flex-shrink: 0;
align-self: center;
React篇
路由模糊匹配和严格匹配
<NavLink to="/home" />
<NavLink to="/about" />
<Switch>
<Route exact path="/home" component={Home} />
<Route exact path="/about" component={About} />
<Redirect to="/home" />
Switch>
向路由组件传递params参数
<Link to={`/home/${item.id}/${item.name}`}>一个路由链接Link>
<Route path="/home/:id/:name" component={Home} />
const { id, name } = this.props.match.params
向路由组件传递search参数
一个路由链接Link>
<Route path="/home" component={Home} />
import qs from 'querystring'
const { search } = this.props.location
const { id, name } = qs.parse(search.slice(1))
向路由组件传递state参数
一个路由链接Link>
<Route path="/home" component={Home} />
const { id, name } = this.props.location.state
编程式路由导航(通过JS代码跳转页面)
// html代码
<button onClick={() => this.goPage(item.id, item.name)}>
// js代码
goPage = (id, name) => {
this.props.history.replace(`/home/${id}/${name}`) // params传参,这里的replace也可换成push方法
// this.props.history.replace(`/home?id=${id}&name=${name}`) // search传参
// this.props.history.replace(`/home`, { id, name }) // state传参
}
/*
提示:
1、后退一页this.props.history.goBack()
2、前进一页this.props.history.goForward()
3、指定跳转几页this.props.history.go(),小括号内填写正数表示前进几页,填写负数表示后退一页
*/
withRouter方法(加工一般组件)
import { withRouter } from 'react-router-dom'
class Header extends React.Component {
render () {} // 此处省略该组件里的代码
}
export default withRouter(Header)
// withRouter可以加工一般组件,使一般组件具备路由组件所特有的API。简言之,可以在该组件中使用this.props.history.xxx等一些方法
// withRouter的返回值是一个新组件