C语言函数大全-- j 开头的函数
C语言函数大全
本篇介绍C语言函数大全– j 开头的函数
1. j0,j0f
1.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
double j0 (double x); |
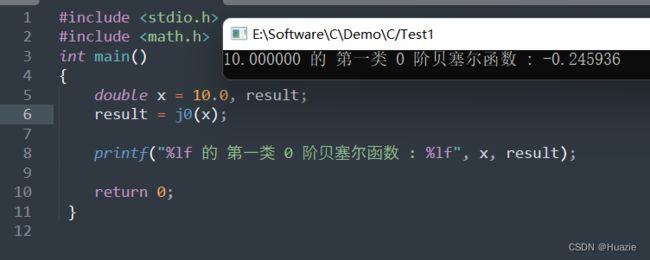
计算 x 的 第一类 0 阶贝塞尔函数(double) |
float j0f (float x); |
计算 x 的 第一类 0 阶贝塞尔函数(float)【笔者本地windows环境,无此函数】 |
注意: 如果操作成功,则返回 x 的 第一类 0 阶贝塞尔函数;如果 x 是 NaN 值,则返回 NaN 值;如果 x 太大或发生溢出范围错误,则返回 0 并将 errno 设置为 ERANGE。
1.2 演示示例
#include 1.3 运行结果
2. j1,j1f
2.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
double j1 (double x); |
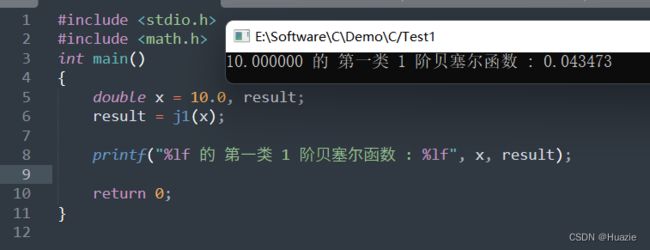
计算 x 的 第一类 1 阶贝塞尔函数(double) |
float j1f (float x); |
计算 x 的 第一类 1 阶贝塞尔函数(float)【笔者本地windows环境,无此函数】 |
注意: 如果操作成功,则返回 x 的 第一类 1 阶贝塞尔函数;如果 x 是 NaN 值,则返回 NaN 值;如果 x 太大或发生溢出范围错误,则返回 0 并将 errno 设置为 ERANGE。
2.2 演示示例
#include 2.3 运行结果
3. jn,jnf
3.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
double jn (int n, double x); |
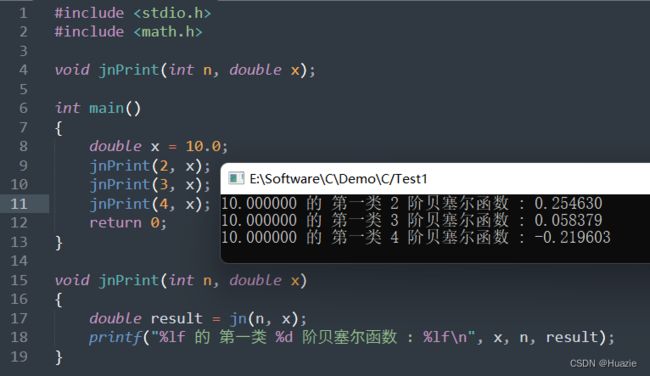
计算 x 的 第一类 n 阶贝塞尔函数(double) |
float jnf (int n, float x); |
计算 x 的 第一类 n 阶贝塞尔函数(float)【笔者本地windows环境,无此函数】 |
注意: 如果操作成功,则返回 x 的 第一类 n 阶贝塞尔函数;如果 x 是 NaN 值,则返回 NaN 值;如果 x 太大或发生溢出范围错误,则返回 0 并将 errno 设置为 ERANGE。
3.2 演示示例
#include 3.3 运行结果
4. jrand48
4.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
double jrand48(); |
生成伪随机数序列 |
jrand48 函数是一个生成伪随机数序列的函数,并且它是可重入的,即可以在多个线程中同时调用而不会出现冲突。
4.2 演示示例
#include 上述程序首先通过 srand48 函数初始化随机数生成器的种子,这里使用了当前系统时间作为种子。然后循环调用 jrand48 函数 5 次,每次输出一个伪随机数。注意,由于 jrand48 函数返回的是一个双精度浮点数(范围在 [0, 1) 内),因此输出时需要使用 %f 格式化符号。
5. join
5.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
int join(pthread_t thread, void **retval); |
等待线程退出并回收资源 |
在 C 语言中,join 函数不是标准库函数,也不是 POSIX 标准的函数。然而,一些操作系统(如 UNIX/Linux)提供了 join 函数用于等待线程退出并回收资源。在 POSIX 线程中,相应的函数是 pthread_join。
5.2 演示示例
#include 上述程序创建了一个新线程,并且主线程等待新线程退出后才继续执行。在新线程中,打印一条消息并调用 pthread_exit 函数退出线程。在主线程中,调用 join 函数等待新线程退出,并通过 NULL 参数指示不需要返回值。最终输出一条消息表示新线程已经退出。
6. jmp_buf
6.1 类型说明
| 类型定义 | 描述 |
|---|---|
typedef _JBTYPE jmp_buf[_JBLEN]; |
它是一个数组类型,保存跳转目标地址的缓冲区。通常与 setjmp 和 longjmp 函数一起使用,用于实现非局部跳转 |
6.2 演示示例
#include 上述程序定义了一个名为 env 的 jmp_buf 类型变量,用于保存当前执行状态。在主函数中,通过调用 setjmp 函数将当前状态保存到 env 中,并返回 0。然后调用 func 函数,该函数打印一条消息并调用 longjmp 函数恢复之前保存的状态,这里传入参数值为 1。由于 longjmp 函数会导致程序跳转到 setjmp 函数继续执行,因此后面的 printf 语句会输出 "Returning from longjmp with value 1"。
需要注意的是,在使用 jmp_buf、setjmp 和 longjmp 函数时需要遵循特定的使用规范,否则可能会导致未定义行为或错误。
参考
- [MATH-标准C库]