【Java数据结构】链表OJ提交小记
目录
1.删除链表中所有值为val的节点
2.反转单链表
3.返回链表的中间节点
4.返回链表倒数第k个节点
5.按次序合并链表
6.按值分割链表
7.判断链表是否为回文
1.删除链表中所有值为val的节点
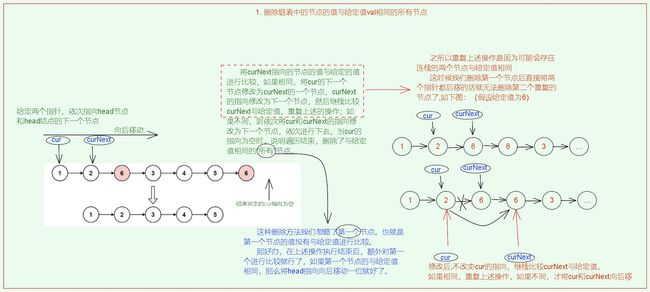
1. 删除链表中所有值为val的节点![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-linked-list-elements/description/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-linked-list-elements/description/
解题思路:
解题代码:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
if(head == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode prev = head;
ListNode cur = head.next;
//从cur开始,进行节点的比较
while(cur != null) {
//比较节点与给定值
if(cur.val == val) {
//相等
prev.next = cur.next; //从cur的下一个节点开始继续与val的值进行比较,如果相同,继续向后移动cur
cur = cur.next;
} else {
//不相等
prev = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
if(head.val == val) {
head = head.next;
}
return head;
}
}2.反转单链表
2.反转单链表![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-linked-list/description/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-linked-list/description/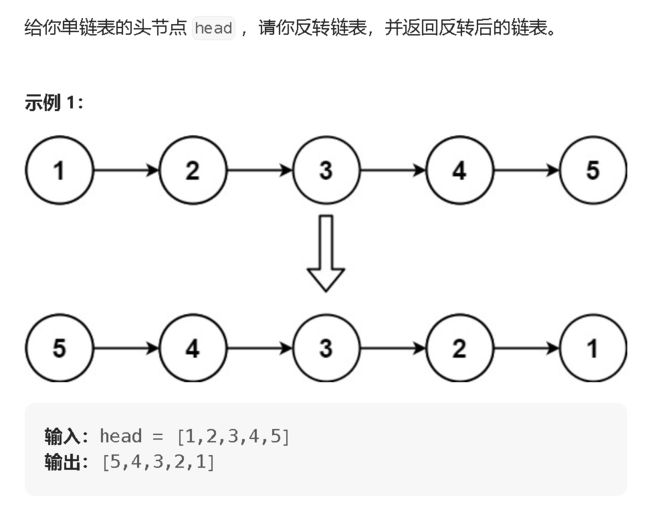
j解题思路:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
//原地反转
if(head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode cur = head.next;
head.next = null; //反转后现在头结点指向节点的next域应为空
while(cur != null) {
ListNode curNext = cur.next;
//将cur指向的节点的next域指向当前的头结点
cur.next = head;
//将头结点的指向修改为cur节点
head = cur;
//将cur指向修改为curNext的指向
cur = curNext;
//重复上述操作
}
//反转结束
return head;
}
}3.返回链表的中间节点
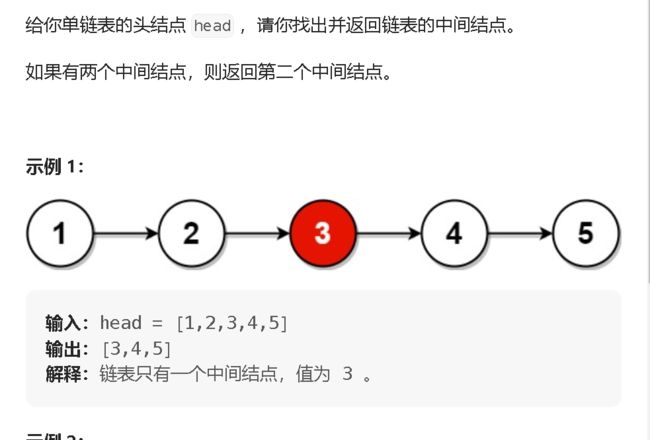
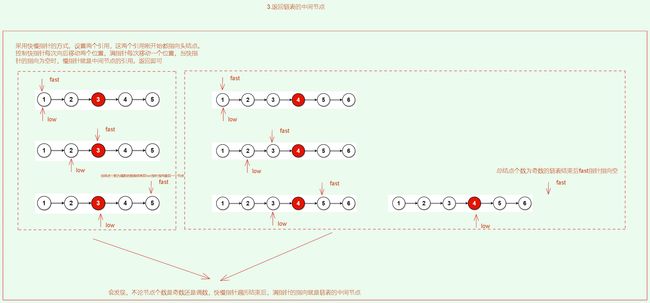
3. 返回链表的中间节点![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/middle-of-the-linked-list/description/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/middle-of-the-linked-list/description/
解题思路:
解题代码:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
//定义快慢引用,初始化为引用head节点
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null) {
//fast向后移动两次
fast = fast.next.next;
//slow向后移动一次
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
}4.返回链表倒数第k个节点
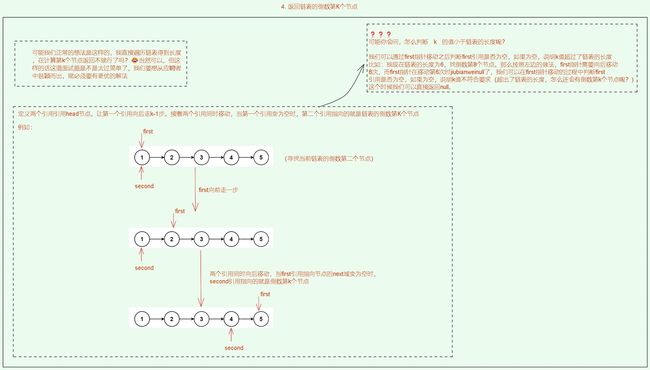
4. 返回链表倒数第K个节点![]() https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/529d3ae5a407492994ad2a246518148a?tpId=13&&tqId=11167&rp=2&ru=/activity/oj&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking
https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/529d3ae5a407492994ad2a246518148a?tpId=13&&tqId=11167&rp=2&ru=/activity/oj&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking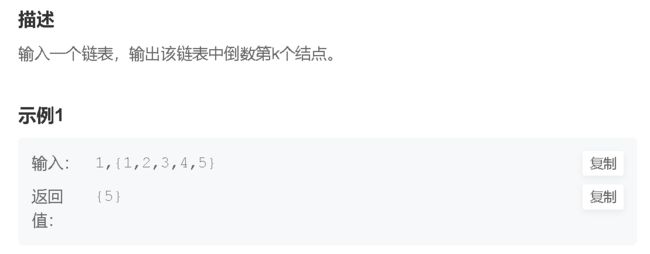
解题思路:
解题代码:
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode FindKthToTail(ListNode head,int k) {
if(head == null || k <= 0) {
return null;
}
ListNode first = head;
ListNode second = head;
for(int i=0;i5.按次序合并链表
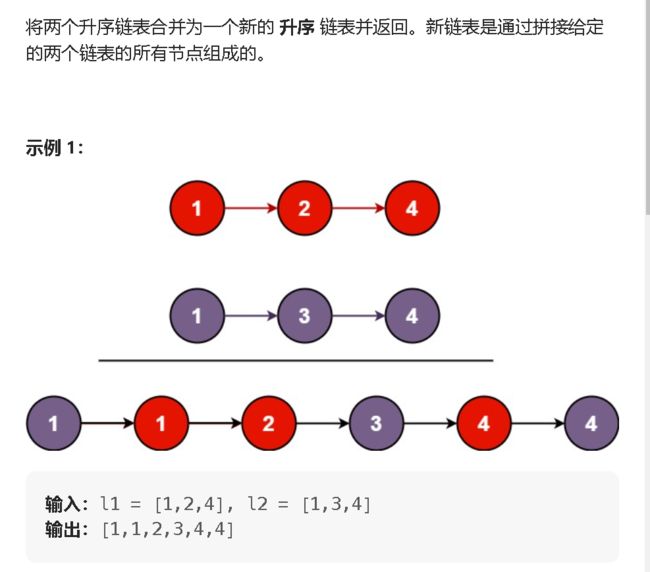
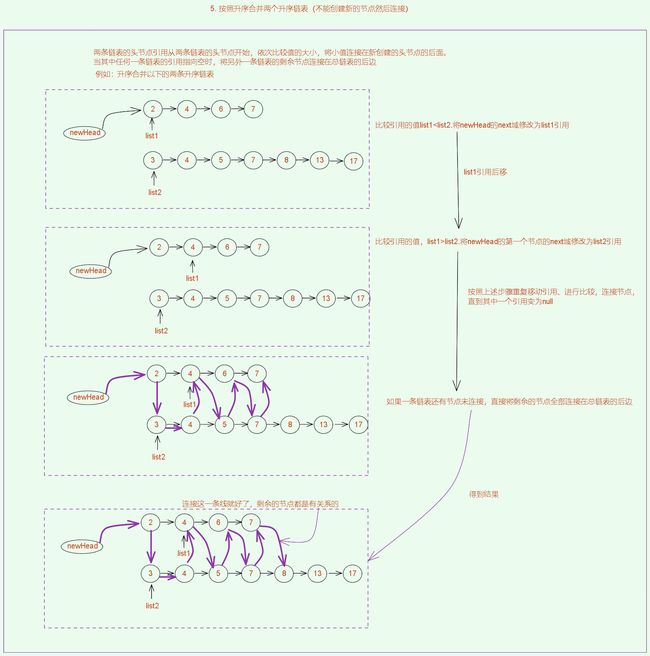
5. 按照升序合并两个升序链表(不能创建新的节点)![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/merge-two-sorted-lists/description/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/merge-two-sorted-lists/description/
解题思路:
解题代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
if(list1 == null) {
return list2;
}
if(list2 == null) {
return list1;
}
//定义一个新的头节点。组装链表
ListNode newHead = new ListNode();
ListNode cur = newHead;
while(list1 != null && list2 != null) {
if(list1.val > list2.val) {
cur.next = list2;
list2 = list2.next;
} else {
cur.next = list1;
list1 = list1.next;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
if(list1 != null) {
cur.next = list1;
} else if(list2 != null) {
cur.next = list2;
}
return newHead.next;
}
}6.按值分割链表
6. 编写代码,以给定值x为基准将链表分割成两部分,所有小于x的结点排在大于或等于x的结点之前![]() https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/0e27e0b064de4eacac178676ef9c9d70?tpId=8&&tqId=11004&rp=2&ru=/activity/oj&qru=/ta/cracking-the-coding-interview/question-ranking
https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/0e27e0b064de4eacac178676ef9c9d70?tpId=8&&tqId=11004&rp=2&ru=/activity/oj&qru=/ta/cracking-the-coding-interview/question-ranking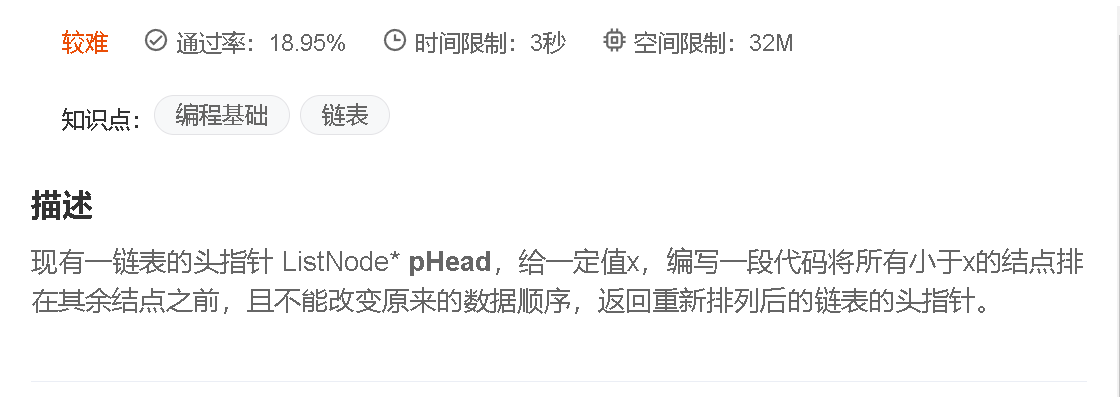
解题思路:
解题代码:
import java.util.*;
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
public class Partition {
public ListNode partition(ListNode pHead, int x) {
if (pHead == null || pHead.next == null) {
return pHead;
}
ListNode smallHead = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode bigHead = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode curSamll = smallHead;
ListNode curBig = bigHead;
//进行值的比较,节点的连接
while(pHead != null) {
if(pHead.val < x) {
curSamll.next = pHead;
curSamll = pHead;
} else {
curBig.next = pHead;
curBig = pHead;
}
pHead = pHead.next;
}
//连接结束后,应当将bigHead这条链表的尾节点的next域置为空。防止出现死循环
curBig.next = null;
//连接smallHead和bigHead这两条链表
curSamll.next = bigHead.next;
return smallHead.next;
}
}7.判断链表是否为回文
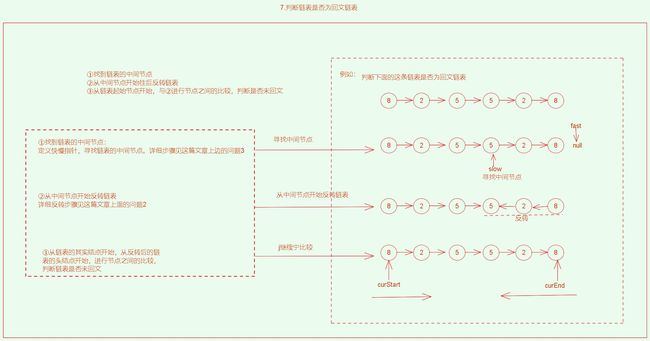
7.判断链表是否为回文链表![]() http:// https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/d281619e4b3e4a60a2cc66ea32855bfa?tpId=49&&tqId=29370&rp=1&ru=/activity/oj&qru=/ta/2016test/question-ranking
http:// https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/d281619e4b3e4a60a2cc66ea32855bfa?tpId=49&&tqId=29370&rp=1&ru=/activity/oj&qru=/ta/2016test/question-ranking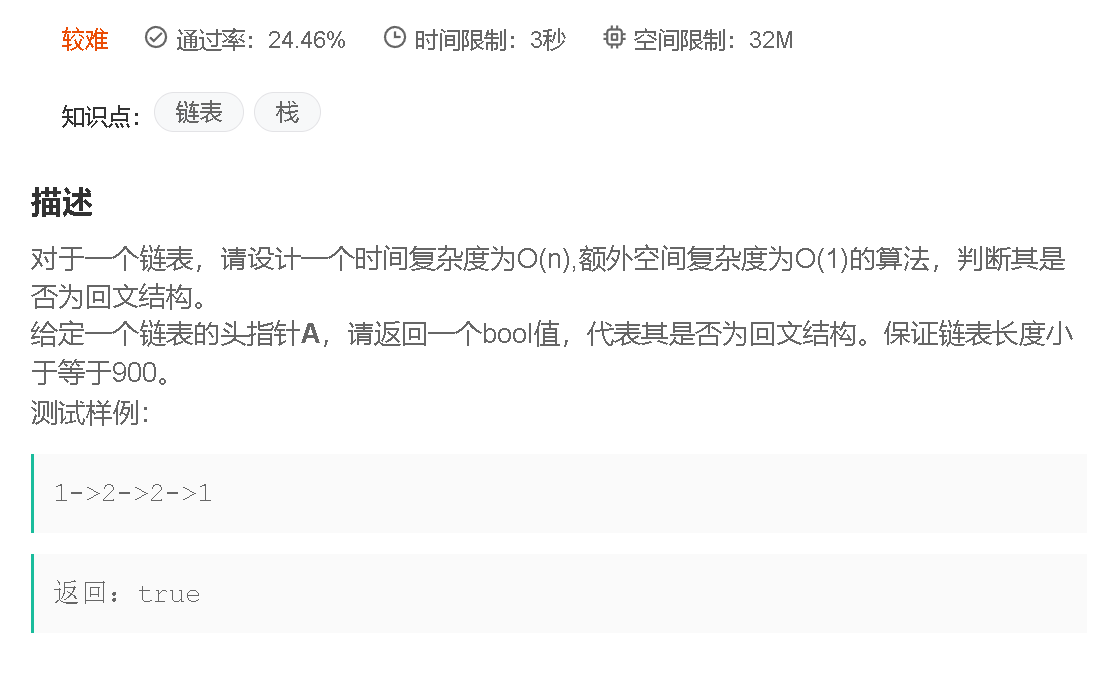
解题思路:
解题代码:
import java.util.*;
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {2
this.val = val;
}
}*/
public class PalindromeList {
public boolean chkPalindrome(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return true;
}
//寻找链表的中间节点
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
//slow即为中间节点
//从中间节点开始反转链表
ListNode cur = slow.next;
while(cur != null) {
ListNode curNext = cur.next;
cur.next = slow;
slow = cur;
cur = curNext;
}
//反转链表结束
//从首个节点开始与从反转后的中间节点开始进行比较,判断是否为回文
while(head.next != slow.next) {
if(head.next == slow) {
return true;
}
if(head.val != slow.val) {
return false;
}
head = head.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return true;
}
}