【C++】类和对象
文章目录
- 封装
-
- 访问权限控制
- 成员属性设置为私有
- 成员变量和成员函数分开存储
- struct和class的区别
- 对象的初始化和清理
-
- 构造函数与析构函数
- 拷贝构造函数
- 初始化列表
- 类作为类的成员
- 静态成员
- this指针
-
- this指针的使用
- 空指针可以调用成员函数
- const修饰成员函数和对象
- 友元
-
- 全局函数作为友元
- 类作为友元
- 成员函数作友元
- 继承
-
- 继承的基本语法
- 继承方式
- 继承中的对象模型
- 继承中的构造和析构顺序
- 继承中的同名成员处理
- 多态
-
- 虚函数
- 纯虚函数和抽象类
- 虚析构和纯虚析构
- 运算符重载
封装
访问权限控制
#include成员属性设置为私有
#include成员变量和成员函数分开存储
空对象占1个字节
#include只有非静态成员变量才属于对象
#includestruct和class的区别
#include对象的初始化和清理
构造函数与析构函数
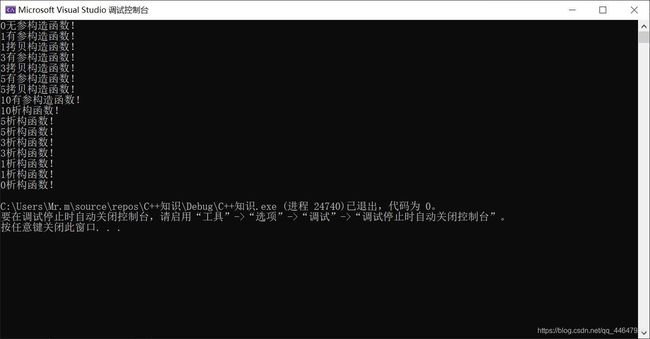
构造函数的分类
按参数分类
有参构造和无参构造
按类型分类
普通构造和拷贝构造
构造函数的调用方式
#include拷贝构造函数
调用规则
#include#include- 使用一个已经创建完毕的对象来初始化一个新对象
- 值传递的方式给函数参数传值
- 以值方式返回局部对象
初始化列表
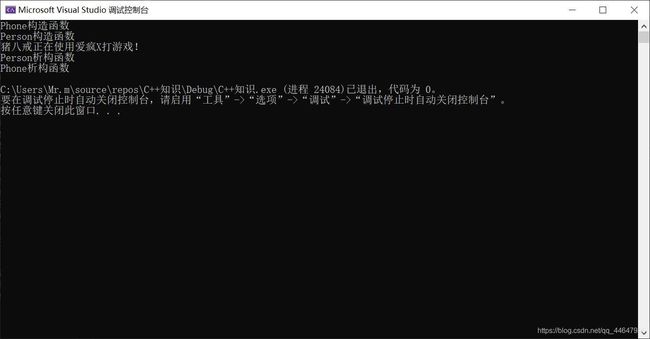
#include类作为类的成员
#include- 构造函数的执行顺序:先调用对象成员的构造,再调用本类构造
- 析构函数的执行顺序:与构造函数的执行顺序相反
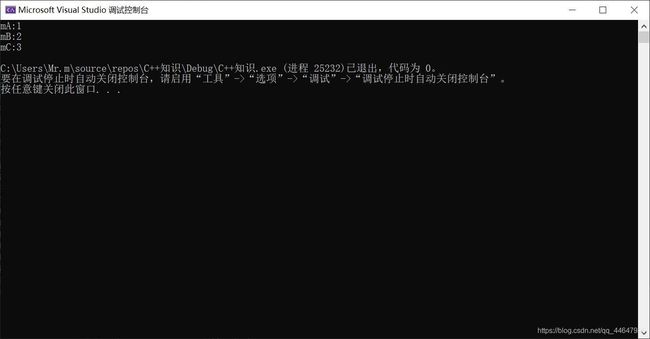
静态成员
静态成员变量
#include- 静态成员变量可以通过
类名::成员变量()和对象.成员变量()访问 - 私有的静态成员变量不可以在类外访问
静态成员函数
#include- 静态成员函数可以通过
类名::成员函数()和对象.成员函数()访问 私有静态成员函数不可以在类外访问
this指针
this指针的使用
#include- 解决形参和成员变量的命名冲突
- 实现链式编程
空指针可以调用成员函数
#include- 空指针可以访问不含成员变量的成员函数
- 空指针不能访问成员变量
const修饰成员函数和对象
#include- 常对象只能访问常函数和成员变量
- 常对象只能修改mutable修饰的成员变量
友元
全局函数作为友元
#include- 声明全局函数作为类的友元:
fiend 数据类型 函数名([参数列表])
类作为友元
#include- 声明一个类作为另一个类的友元:
friend class 类名
成员函数作友元
#include- 声明成员函数作为类的友元:
friend 数据类型 类名::函数名([参数列表]) - 声明友元的类需要先用
class 类名进行声明
继承
继承的基本语法
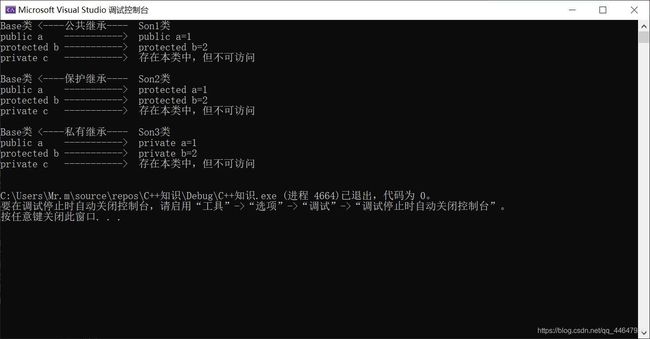
#include继承方式
#include- 继承的三种方式:
公共继承保护继承私有继承
继承中的对象模型
#include- 父类中私有成员也是被子类继承下去了,只是由编译器给隐藏后访问不到
继承中的构造和析构顺序
继承中的同名成员处理