【JavaEE进阶】Spring 使用注解存储获取bean对象及安装配置环境介绍
目录
一、Spring创建项目的环境配置
二、添加注解存储 Bean 对象
2.1 类注解的种类
2.2 方法注解@Bean
三、取出Bean对象
3.1 属性注入操作演示
3.2、@Resource的用法
一、Spring创建项目的环境配置
在创建Spring项目可以分为三个步骤:1. 创建⼀个普通 Maven 项⽬ 2. 添加 Spring 框架⽀持(spring-context、spring-beans) 3. 添加启动类。
1. 创建⼀个普通 Maven 项⽬
打开IDEA软件,选择Maven创建,进入项目界面后首先检查自己的IDEA是否配置了国内的镜像源
settings.xml文件下载地址:
https://gitee.com/xu-zhongfa/javacode/blob/f66cfb55fee1184c640717a050e76a0bb745b10f/settings.xml/settings.xml
2、完成以上操作在Spring项目中找到pom.xml并导入依赖,添加以下相关内容到pom.xml文件中
org.springframework
spring-context
5.2.3.RELEASE
org.springframework
spring-beans
5.2.3.RELEASE
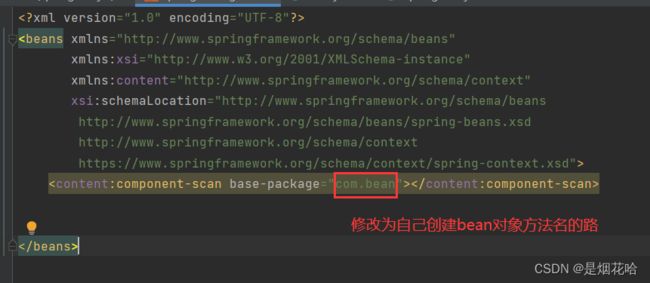
3、创建spring配置文件:spring-config.xml (此处配置类注解的xml文件)
4、添加注解存储 Bean 对象
以我自己为例,在src-main-java下面创建一个包名为com.bean来存储bean对象,在包中建立一个类名为User
二、添加注解存储 Bean 对象
将Bean对象存储在Spring容器中,注解类有两种:
(1) 类注解:@Controller @Service @Repository @Configuration @Component
(2) 方法注解:@Bean
注意:使用类注解来存储Bean对象,其中类注解当中传入的参数,就是这一个类对象的名称。
这里使用@Service 为例来存储Bean对象,见如下代码
package com.bean;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service //使用类注解
public class User {//此时User作为参数传入
public void sayHi(String name){
System.out.println("你的名字:"+name);
}
}
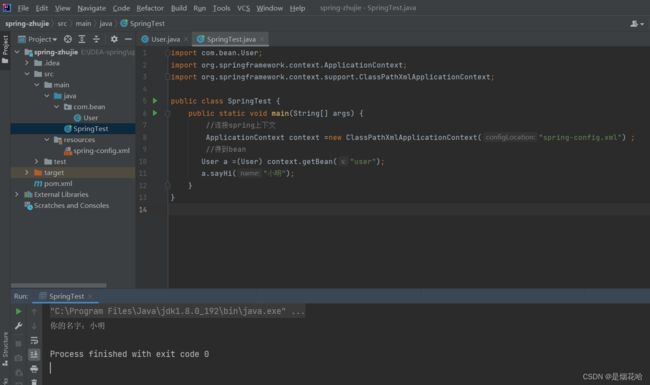
读取bean的代码为
import com.bean.User;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpringTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//连接spring上下文
ApplicationContext context =new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-config.xml") ;
//得到bean
User a =(User) context.getBean("user");
a.sayHi("小明");
}
}
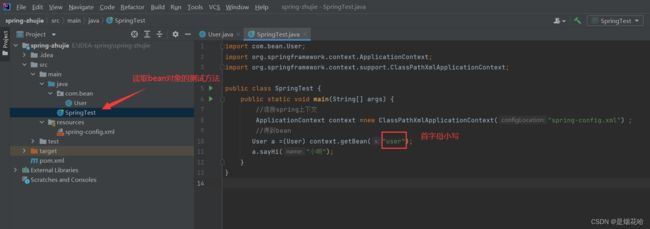
在使用类注解存储bean对象的时候,使用存储bean对象的类名作为参数传递,在读取bean对象的时候,此时bean对象的类名的首字母需要小写。
2.1 类注解的种类
类注解有五种,它们的使用方法和功能都是相同的,但为何还需要这么多的类注解,是因为每个类注解有不同的含义,当程序员看到不同的注解时就就能直接了解当前类的⽤途
- @Controller 业务逻辑层
- @Service 服务层
- @Repository 持久层
- @Configuration 配置层
2.2 方法注解@Bean
在使用方法注解时,就可以想到方法注解是放在方法上使用的。类注解是添加到某个类上的,⽽ 方法注解是放到某个⽅法上的
重点: 方法注解在使用的时候需要配合类注解去使用的。
举例代码如下:
储存bean对象代码
package com.bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class User {
@Bean
public User user1() {
User user = new User();
user.setId(1);
user.setName("Java");
return user;
}
private void setName(String java) {
System.out.println(java);
}
private void setId(int i) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}取出bean对象代码:
import com.bean.User;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpringTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-config.xml");
// 2.得到某个 bean
User user = (User) context.getBean("user1");
// 3.调⽤ bean ⽅法
System.out.println(user);
}
}
运行结果:
2.2.1 Bean重命名操作
使用方法注解时,可以通过设置 name 属性给 Bean 对象进⾏重命名操作
操作方式:@Bean (name={"n1","n2",.....})
三、取出Bean对象
3.1 属性注入操作演示
在属性注入时,使用关键字@Autowired 或者@Resource
使用@Service中注入到@Controller
package com.bean;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class UserService {
public User getUser(Integer id) {
// 伪代码,不连接数据库
User user = new User();
user.setId(id);
user.setName("Java-" );
return user;
}
private void setId(Integer id) {
System.out.println(id);
}
private void setName(String s) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}Controller类的实现代码:
package com.bean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
@Controller
public class User1 {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
public user sayHi(String name){
return userService.sayHi(name);
}
}import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class UserControllerTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-config.xml");
User1 user1 = context.getBean(User1.class);
System.out.println(user1.sayHi(小白).toString());
}
}在使用将Service属性注入到Controller时,需要注意下面代码核心实现
3.2、@Resource的用法
@Resource的使用操作方法与@Autowired 相同,但他们两者也有不同之处。
(1)Autowird是Spring提供的,而Resource 是JDK提供的
(2)Resource 可以根据设置更多参数,例如name属性@Resource(name="user1")
(3) @Autowired 可⽤于 Setter 注⼊、构造函数注⼊和属性注⼊,⽽ @Resource 只能⽤于 Setter 注⼊和属性注⼊,不能⽤于构造函数注⼊。