k8s编程operator实战之云编码平台——③Code-Server Pod访问实现
文章目录
-
- 1、openresty介绍和安装
- 2、实现code-server的反向代理
- 3、动态反向代理实现
-
- 启动多个code-server访问
k8s编程operator系列:
k8s编程operator——(1) client-go基础部分
k8s编程operator——(2) client-go中的informer
k8s编程operator——(3) 自定义资源CRD
k8s编程operator——(4) kubebuilder & controller-runtime
k8s编程operator实战之云编码平台——①架构设计
k8s编程operator实战之云编码平台——②controller初步实现
k8s编程operator实战之云编码平台——③Code-Server Pod访问实现
k8s编程operator实战之云编码平台——④web后端实现
k8s编程operator实战之云编码平台——⑤项目完成、部署
在上一节中实现了controller的逻辑,可以通过grpc来创建、删除工作空间以及查询信息。接下来要实现的就是如何访问到工作空间,我们就采用反向代理的方式,反向代理服务器就使用nginx。
openresty是一个基于nginx和luajit的web平台,我们可以通过它来实现动态的反向代理。接下来将会逐步实现。
1、openresty介绍和安装
openresty官网:http://openresty.org/cn/
openresty安装参考:http://openresty.org/cn/linux-packages.html
2、实现code-server的反向代理
首先我们只使用配置文件来实现固定的code-server的反向代理并测试功能是否正常,然后再通过lua脚本来配置动态的反向代理。
openresty安装后一般在/usr/local/openresty中,下面有一个nginx文件夹,里面就和nginx是一样的了。
1、启动上一节中实现的controller,先来启动一个code-server的pod
# 直接运行
make run
# 或者 先编译,再运行
make build
./bin/manager
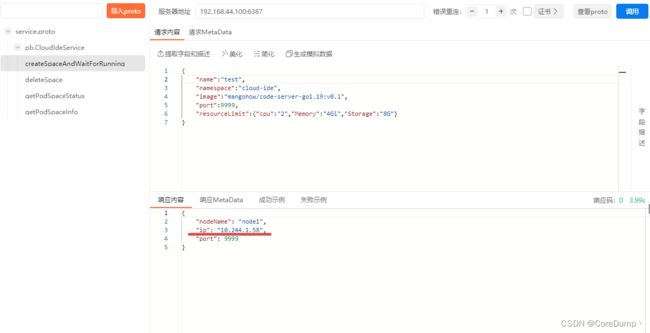
2、使用apiPost来调用grpc创建pod,下面的ip等下要在nginx配置中使用
3、修改nginx的配置文件nginx.conf来配置反向代理:
一定要配置下面的几个header,因为code-server使用了wesocket,如果不配置将会使用不了websocket
#user nobody;
worker_processes 1;
error_log logs/error.log;
# error_log logs/error.log notice;
# error_log logs/error.log info;
#pid logs/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
server {
listen 80;
# 使用ws作为访问的prefix
location /ws/ {
# 反向代理到code-server所在pod中
proxy_pass http://10.244.1.58:9999/;
# 一定要设置这几个header
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection upgrade;
proxy_set_header Accept-Encoding gzip;
}
}
}
4、启动nginx
./nginx
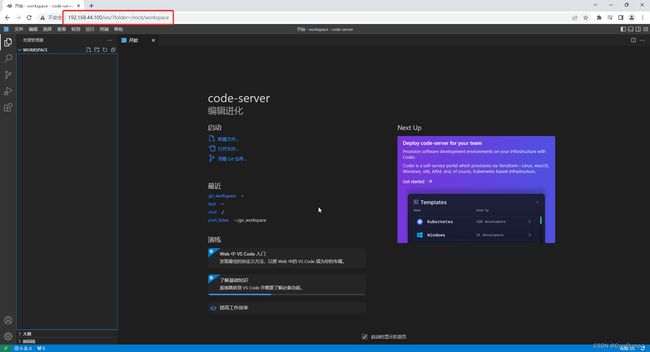
5、在浏览器中访问,地址:http://yourip/ws/
可以看到已经可以成功访问到code-server了,但是目前是将ip地址写死了,接下来将实现动态的反向代理。
3、动态反向代理实现
动态反向代理,即根据不同的用户将他的请求代理到他的code-server中,要实现这个,我们可以在启动code-server时获取到pod的ip地址,然后生成一个UID,然后将UID和ip地址保存到redis中。当用户在访问时在路径中带上UID,nginx获取到UID,然后从redis中查询出ip,再根据这个ip来反向代理。
那么就需要通过lua脚本来实现,openresty中内置了lua,我们可以直接使用,关于lua的语法在此就不展开介绍了,网上很多资料。
1、修改nginx.conf
#user nobody;
worker_processes 1;
error_log logs/error.log;
# error_log logs/error.log notice;
# error_log logs/error.log info;
#pid logs/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
server {
listen 80;
# 路径以/ws/开头的请求都会通过这里
location ^~ /ws/ {
# 声明变量,等下在lua脚本中可以修改
set $backend '';
set $pth '';
# 调用lua脚本
rewrite_by_lua_file 'lua/proxy.lua';
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection upgrade;
proxy_set_header Accept-Encoding gzip;
# 设置反向代理的后端url
proxy_pass http://$backend/$pth;
}
}
}
我们在nginx.conf中声明了两个变量,分别是backend、pth
backend:是反向代理的ip和portpth:为路径中的其它参数,比如当路径为http://ip:port/ws/uid/?folder=/root/workspace时,需要将uid后面的路径添加到proxy_pass的路径后面,添加后为http://podip:podport/?folder=/root/workspace
2、在/usr/loacl/openresty/nignx/目录下创建一个lua目录
lua脚本就存放在这个目录中,接下来创建proxy.lua文件:
local function split(str,reps)
local resultStrList = {}
string.gsub(str,'[^'..reps..']+',function (w)
table.insert(resultStrList,w)
end)
return resultStrList
end
--[[
1、解析出路径中的uid和其它路径
--]]
-- 获取请求的路径
local request_uri = ngx.var.request_uri
-- 分割路径
local data = split(request_uri, '/')
-- 请求路径为 /ws/uid/... , 因此至少为2个
if #data < 2 then
return
end
-- lua中数组下标从1开始,uid为第二个
local uid = data[2]
local uid_index = string.find(request_uri, uid)
local other_path_indx = uid_index + string.len(uid)
-- 获取到uid后面的路径
local other_path = string.sub(request_uri, other_path_indx + 1)
if other_path == '/' then
other_path = ''
end
-- 设置nginx.conf中的变量
ngx.var.pth = other_path
--[[
2、从redis中根据uid查询后端ip和端口
注意:在跳转网页时 一定是 http://ip:port/ws/uid/ 最后面一定要有'/'
--]]
-- 连接redis
local redis = require "resty.redis"
local red = redis:new()
red:set_timeouts(1000, 1000, 1000) -- 1 sec
-- 在这里修改你的redis地址
local ok, err = red:connect("10.99.252.66", 6379)
if not ok then
ngx.log(ngx.ERR, "failed to connect to redis")
return ngx.exit(ngx.HTTP_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR)
end
-- 根据uid从redis中获取ip和port
local res, err = red:hget('hosts', uid)
if not res then
ngx.log(ngx.ERR, "failed get host, uid:"..uid, err)
return ngx.exit(ngx.HTTP_BAD_REQUEST)
end
if res == ngx.null then
ngx.log(ngx.ERR, 'failed get host, uid:'..uid)
return ngx.exit(ngx.HTTP_BAD_REQUEST)
end
ngx.log(ngx.INFO, 'uid:'..uid..', host:'..res)
-- 设置backend
ngx.var.backend = res
ngx.log(ngx.NOTICE, "other_path: "..other_path)
在上面的lua脚本中分为两个步骤:
(1)从请求路径中解析出uid和uid后面的其它路径
(2)根据uid从redis中查询后端ip和port
3、重启nginx
nginx -s reload
4、接下来在redis中设置一个哈希值
# 修改成你的code-server的podip
hset hosts abcd123 10.244.1.58:9999
5、在浏览器中访问:http://yourip/ws/abcd123/ 路径最后面一定要有'/'
可以看到成功访问到了。
启动多个code-server访问
接下来再启动一个pod,看是否可以同时访问两个
再次调用grpc创建pod,记得修改name:
再向nginx中添加一个映射
hset hosts qwer456 10.244.1.59:9999
在浏览器中访问http://yourip/ws/qwer456/:
都是可以访问到的。
虽然看似很轻松的配置成功了,但是因为nginx使用的不熟,我经过了很多次的失败和调试,搞了很久才配置成功的。
到此后端pod的访问问题已经解决了,接下来就是web服务器的开发了。