第八章小结
第八章小结
1. 借助JDK文档, 选取String与StringBuffer 、StringBuilder的常用API,并编写实例测试API的功能。
String:
- charAt(int index): 得到字符串中指定位置的一个字符
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args){
String w=new String("hello,nice to meet you");
System.out.println(w);
int i;
for(i=0;i<w.length();++i)
System.out.print(w.charAt(i)+"#");
}
}
//运行结果
hello,nice to meet you
h#e#l#l#o#,#n#i#c#e# #t#o# #m#e#e#t# #y#o#u#
- length()返货string的长度
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args){
String w=new String("hello,nice to meet you");
System.out.println(w。length());
}
}
//运行结果
22
- toLowerCase/toUpperCase 将字符串的所有字符转换为小写/大写
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args){
String w=new String("Hello,Nice to Meet You!");
System.out.println(w);//Hello,Nice to Meet You!
String s=w.toLowerCase();
System.out.println(w);//Hello,Nice to Meet You!
System.out.println(s);//hello,nice to meet you!
s = w.toUpperCase();
System.out.println(w);//Hello,Nice to Meet You!
System.out.println(s);//HELLO,NICE TO MEET YOU!
}
}
StringBuffer:
- append(char[] str) 将括号里的字符串加到原字符串后面
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args){
StringBuffer w=new StringBuffer("Hello,Nice to Meet You!");
System.out.println(w);
System.out.println("#"+w.append("\n I am happy")+"#");
System.out.println("$"+w+"$");
}
}
//运行结果
Hello,Nice to Meet You!
#Hello,Nice to Meet You!
I am happy#
$Hello,Nice to Meet You!
I am happy$
- deleteCharAt(int index) 删除此序列中指定位置的字符
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args){
StringBuffer w=new StringBuffer("Hello,Nice to Meet You!");
System.out.println(w);
System.out.println("#"+w.deleteCharAt(4)+"#");
System.out.println("$"+w+"$");
}
}
//运行结果
Hello,Nice to Meet You!
#Hell,Nice to Meet You!#
$Hell,Nice to Meet You!$
StringBuilder:
- append(char[] str) 和StringBuffer的append(char[] str)
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args){
StringBuilder w=new StringBuilder("Hello,Nice to Meet You!");
System.out.println(w);
System.out.println("#"+w.append("\n I am happy")+"#");
System.out.println("$"+w+"$");
}
}
//运行结果
Hello,Nice to Meet You!
#Hello,Nice to Meet You!
I am happy#
$Hello,Nice to Meet You!
I am happy$
- delete(int start,int end) 删除原字符串中下标为start(包含)到下标为end(不包含) 的子串
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args){
StringBuilder w=new StringBuilder("Hello,Nice to Meet You!");
System.out.println(w);
System.out.println("#"+w.delete(1,4)+"#");
//0 1 2 3 4
//H e l l o
// y y y
//删除了下标为1,2,3的字符
System.out.println("$"+w+"$");
}
}
//运行结果
Hello,Nice to Meet You!
#Ho,Nice to Meet You!#
$Ho,Nice to Meet You!$
attention:由上面的例子可以看出,String中的API 并不会在原对象上进行修改,而是创建一个新的对象,类存储新的值,即String对象是不可变的,在String类中每一个看起来会修改String对象内容的方法,实质都是创建了一个全新的String对象。
而StringBuffer 和StringBuilder 则是在原对象的本事进行的修改。
String源码
public final class String implements java.io.Serializable, Comparable<String>, CharSequence {
/** The value is used for character storage. */
private final char value[];
AbstractStringBuilder源码
abstract class AbstractStringBuilder implements Appendable, CharSequence {
/**
* The value is used for character storage.
*/
char[] value; //常量字符数组,被StringBuffer继承
StringBuffer源码
public final class StringBuffer extends AbstractStringBuilder
implements java.io.Serializable, CharSequence {
2. 请简述String,StringBuffer,StringBuilder三者之间的共同点与区别,应该分别在何种场景下使用?
相同点:
1.内部实现基于字符数组,封装了对字符串处理的各种操作
2.可自动检测数组越界等运行时异常
不同之处:
- String内部实现基础常量字符数组(private final char value[];),其内容在一次赋值后,无法进行修改;而StringBuffer 、StringBuilder基于普通字符数组(char[] value; )数组大小可根据字符串的实际长度自动扩容,内容可以发生改变
- 性能方面对于字符串的出路,相对来说
StringBuilder > StringBuffer > String - StringBuffer 线程安全,而StringBuilder非线程安全
使用场景:
- string: 对安全要求高
- StringBuffer 线程安全
- StringBuilder 非线程安全
为什么String被设计成不可变性(immutable)?
兼顾效率 & 安全
-
String多线程安全
-
String常作为参数传递(网络、数据库、安全性)
3. 为什么不建议在for循环中使用“+”进行字符串拼接?
字符串拼接方式: 使用+ 、使用concat方法、使用StringBuilder、使用StringBuffer 以及使用StringUtils.join
萍姐速度从块到慢的对比:StringBuilder > StringBuffer>concat>+>StringUtils.join
StringBuffer与String字符串拼接的比较
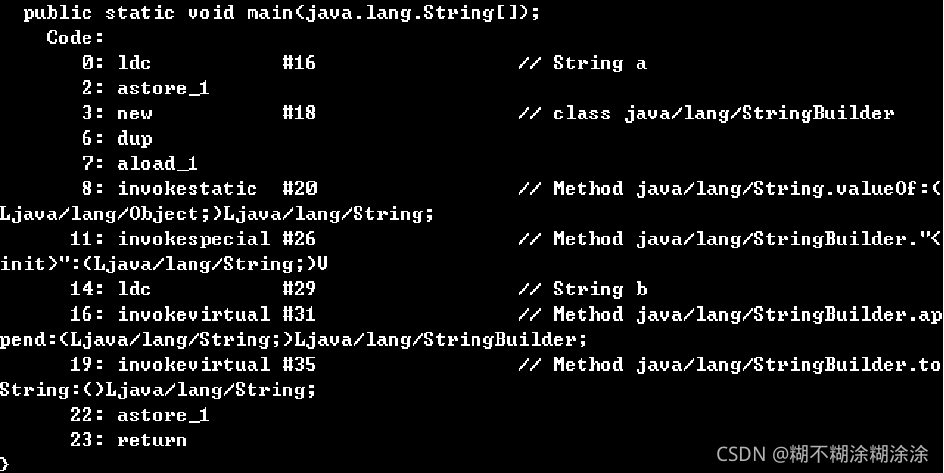
String s = “a”; s = s + “b”; // 编译器会转化为下述语句
String st = new StringBuilder("a").append("b").toString();
String字符串拼接:
String s = "a";
for(int i=0; i<10000;i++){
s = s + “b” ; //编译器会进行优化,但此种写法仍然效率低下,循环体内每次需要产生StringBuilder对象
由于字符串拼接过程中会创建新的对象,所以如果要在一个循环提中进行字符串拼接,就要考虑内存问题和效率问题。而“+” 反编译后的代码,在for循环中,每次都是new了一个StringBuilder,然后再把String转成StringBuilder,在进行append 而频繁的新建对象要消耗很多时间,还会造成内存资料浪费
建议用一下代码进行拼接
//StringBuilder字符串拼接:
StringBuilder st = new StringBuilder("a"); //效率较高,只需新建一个对象
for(int i=0; i<10000;i++){
st.append(“b");
}