线性回归从零开始实现
文章目录
- 准备数据
-
- 数据生成
- 数据处理
- 模型
-
- 初始化模型参数
- 定义模型
- 定义损失函数
- 定义优化算法:小批量随机梯度下降优化器
- 训练过程
- 完整代码
-
- 总结
准备数据
根据带有噪声的线性模型构造一个人造数据集,线性模型参数=[2,−3.4]⊤,=4.2和噪声项生成数据集及其标签:
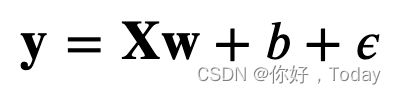
数据生成
def synthetic_data(w, b, num_examples):
"""生成 y = Xw + b + 噪声。"""
X = torch.normal(0, 1, (num_examples, len(w)))
y = torch.matmul(X, w) + b
y += torch.normal(0, 0.01, y.shape)
return X, y.reshape((-1, 1))
true_w = torch.tensor([2, -3.4])
true_b = 4.2
features, labels = synthetic_data(true_w, true_b, 1000)
数据解读:features 中的每一行都包含一个二维数据样本,labels 中的每一行都包含一维标签值(一个标量)
print('features:', features[0], '\nlabel:', labels[0])
features: tensor([-0.6612, -1.8215])
label: tensor([9.0842])
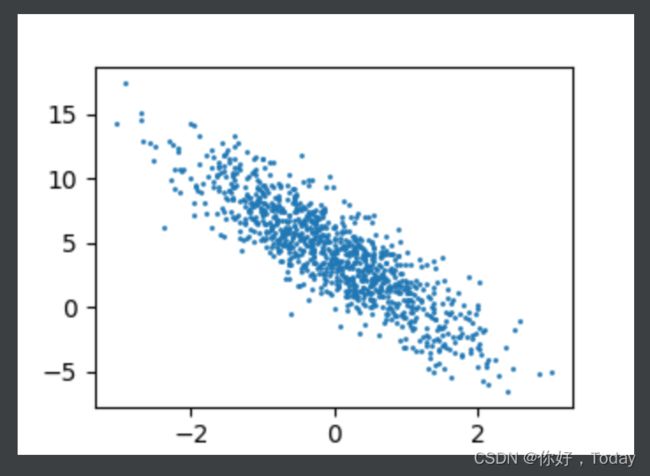
数据图示:
d2l.set_figsize()
d2l.plt.scatter(features[:, 1].detach().numpy(), labels.detach().numpy(), 1)
plt.show()
注:d2l是李沐动手学深度学习里面的一个包,可以通过pip install d2l直接安装
数据处理
定义一个data_iter 函数, 该函数接收批量大小、特征矩阵和标签向量作为输入,生成大小为batch_size的小批量
def data_iter(batch_size, features, labels):
num_examples = len(features)
indices = list(range(num_examples))
random.shuffle(indices)
for i in range(0, num_examples, batch_size):
batch_indices = torch.tensor(indices[i: min(i + batch_size, num_examples)])
yield features[batch_indices], labels[batch_indices]
模型
初始化模型参数
w = torch.normal(0, 0.01, size=(2, 1), requires_grad=True)
b = torch.zeros(1, requires_grad=True)
定义模型
def linreg(X, w, b):
"""线性回归模型。"""
return torch.matmul(X, w) + b
定义损失函数
def squared_loss(y_hat, y):
"""均方损失。"""
return (y_hat - y.reshape(y_hat.shape))**2 / 2
定义优化算法:小批量随机梯度下降优化器
def sgd(params, lr, batch_size):
"""小批量随机梯度下降。"""
with torch.no_grad():
for param in params:
param -= lr * param.grad / batch_size
param.grad.zero_()
训练过程
lr = 0.03
num_epochs = 3
net = linreg
loss = squared_loss
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
for X, y in data_iter(batch_size, features, labels):
l = loss(net(X, w, b), y)
l.sum().backward()
sgd([w, b], lr, batch_size)
with torch.no_grad():
train_l = loss(net(features, w, b), labels)
print(f'epoch {epoch + 1}, loss {float(train_l.mean()):f}')
比较真实参数和通过训练学到的参数来评估训练的成功程度
print(f'w的估计误差: {true_w - w.reshape(true_w.shape)}')
print(f'b的估计误差: {true_b - b}')
完整代码
# %matplotlib inline 注释掉此行
import random
import torch
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # 增加此行
from d2l import torch as d2l
# 生成人工数据集
def synthetic_data(w, b, num_examples):
"""生成 y = Xw + b + 噪声。"""
X = torch.normal(0, 1, (num_examples, len(w))) # 从均值为0,标准差为1的正太分布中,提取生成 num_examples * len(w)) 的Tensor
y = torch.matmul(X, w) + b # torch.matmul是tensor的乘法
y += torch.normal(0, 0.01, y.shape) # 加噪音
return X, y.reshape((-1, 1))
true_w = torch.tensor([2, -3.4])
true_b = 4.2
features, labels = synthetic_data(true_w, true_b, 1000)
print('features:', features[0], '\nlabel:', labels[0])
d2l.set_figsize()
d2l.plt.scatter(features[:, 1].detach().numpy(), labels.detach().numpy(), 1)
plt.show()
# 生成大小为batch_size的小批量
def data_iter(batch_size, features, labels):
num_examples = len(features)
indices = list(range(num_examples))
random.shuffle(indices)
for i in range(0, num_examples, batch_size):
batch_indices = torch.tensor(indices[i: min(i + batch_size, num_examples)])
yield features[batch_indices], labels[batch_indices]
batch_size = 10
#
# for X, y in data_iter(batch_size, features, labels):
# print(X, '\n', y)
# break
w = torch.normal(0, 0.01, size=(2, 1), requires_grad=True)
b = torch.zeros(1, requires_grad=True)
def linreg(X, w, b):
"""线性回归模型。"""
return torch.matmul(X, w) + b
def squared_loss(y_hat, y):
"""均方损失。"""
return (y_hat - y.reshape(y_hat.shape))**2 / 2
def sgd(params, lr, batch_size):
"""小批量随机梯度下降。"""
with torch.no_grad():
for param in params:
param -= lr * param.grad / batch_size
param.grad.zero_()
lr = 0.03
num_epochs = 3
net = linreg
loss = squared_loss
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
for X, y in data_iter(batch_size, features, labels):
l = loss(net(X, w, b), y)
l.sum().backward()
sgd([w, b], lr, batch_size)
with torch.no_grad():
train_l = loss(net(features, w, b), labels)
print(f'epoch {epoch + 1}, loss {float(train_l.mean()):f}')
总结
线性回归模型的从零开始实现