Dubbo 入门学习
Dubbo 入门学习
-
-
- 1. 概述
- 2. 注解配置
-
- 2.1 user-rpc-service-api-02
-
- 2.1.1 自定义实现拓展点
- 2.2 user-rpc-service-provider-02
- 2.3 user-rpc-service-consumer-02
-
1. 概述
Apache Dubbo:一款高性能、轻量级的开源服务框架。提供了六大核心能力:
- 面向接口代理的高性能 RPC 调用(提供高性能的基于代理的远程调用能力,服务以接口为粒度,为开发者屏蔽远程调用底层细节);
- 智能容错和负载均衡(内置多种负载均衡策略,智能感知下游节点健康状况,显著减少调用延迟,提高系统吞吐量);
- 服务自动注册和发现(支持多种注册中心服务,服务实例上下线实时感知);
- 高度可扩展能力(遵循微内核 + 插件的设计原则,所有核心能力如 Protocol、Transport、Srialization 被设计为扩展点,平等对待内置实现和第三方实现);
- 运行期流量调度(内置条件、脚本等路由策略,通过配置不同的路由规则,轻松实现灰度发布,同机房优先等功能);
- 可视化的服务治理与运维(提供丰富服务治理、运维工具:随时查询服务元数据、服务健康状态及调用统计,实时下发路由策略、调整参数配置)。
Apache Dubbo 的 RPC 通信和微服务治理是它的两大关键能力。这意味着:使用 dubbo 开发的微服务,将具备相互之间的远程发现和通信能力,同时利用 Dubbo 提供的丰富服务治理能力,可以实现诸如服务发现、负载均衡、流量调度等服务治理诉求。同时,它也是高度可拓展的。
Dubbo 提供了从服务定义、服务发现、服务通信到流量监控等几乎所有的服务治理能力,并且从使用上对用户屏蔽底层细节,以提供更好的易用性。
定义服务在 Dubbo 中非常简单与直观,可以选择使用与某种语言绑定的方式(如Java 中可以直接定义 interface,我们下面就是这样实现的)
点对点的服务通信是 Dubbo 提供的另一项基本能力,Dubbo 以 RPC 的方式将请求数据(Request)发送给后端服务,并接收服务端返回的计算结果(Response)。RPC 通信对用户来说是完全透明的,使用者无需关心请求是如何发出去的、发到了哪里,每次调用只需要拿到正确的调用结果就行。同步的 Request-Response 是默认的通信模型,简单但却不能覆盖全部的场景。因此,dubbo 提供了更丰富的通信模型:
- 消费端异步请求(Client Side Asynchronous Request-Response)
- 提供端异步执行(Server Side Asynchronous Request-Response)
- 消费端请求流
- 提供端响应流
- 双向流式通信
Dubbo 的服务发现:即消费端自动发现服务地址列表的能力,是微服务框架需要具备的关键能力,借助于自动化的服务发现,微服务之间可以在无需感知对端部署位置与 IP 地址的情况下实现通信。
Dubbo 提供的是一种 Client-Based 的服务发现机制,使用者可以有多种方式启用服务发现:通常需要部署额外的第三方注册中心组件来协调服务发现过程,如常用的 Nacos、Consul、Zookeeper 等,Dubbo 自身也提供了对许多注册中心组件的对接,用户可以灵活选择。
透明地址发现让 Dubbo 请求可以发送到任意 IP 实例上,这个过程流量被随机分配。当需要对流量进行更丰富、更细粒度的管控时,就可以用到 Dubbo 的流量管控策略,Dubbo 提供了包括负载均衡、流量路由、请求超时、流量降级、重试策略等。更酷的是,Dubbo 支持流控策略在运行态动态生效,无需重新部署。
Dubbo 基于消费端的自动服务发现能力,其基本工作原理如下图:
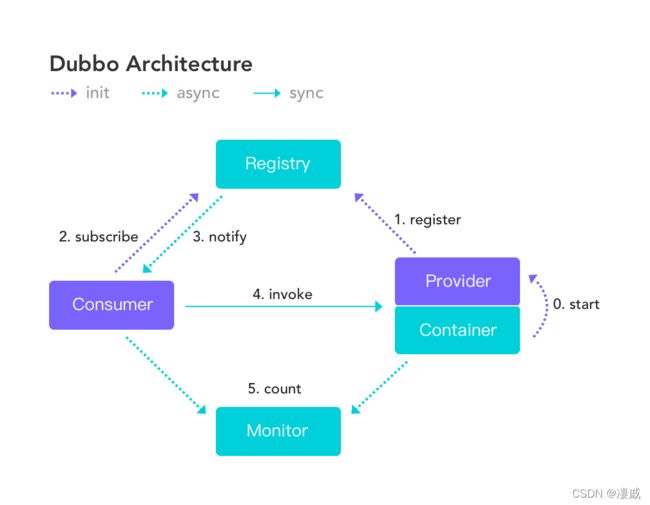
服务发现的一个核心组件是注册中心,Provider 注册地址到注册中心,Consumer 从注册中心读取和订阅 Provider 地址列表。因此,要启用服务发现,就需要为 Dubbo 增加注册中心配置:
Dubbo2 与 Dubbo3 的服务发现配置是完全一致的,但是实现原理上,Dubbo 3 引入了全新的服务发现模型-应用级服务发现(Dubbo 2.x 版本中是基于接口粒度的服务发现机制以接口粒度组织地址数据,3.x 引入了全新的基于应用粒度的服务发现机制以应用粒度组织地址数据,带来了极大优势)
2. 注解配置
需要创建三个 maven 项目:
user-rpc-service-api-02:服务接口,定义 Dubbo Service API 接口
user-rpc-service-provider-02:服务提供者,实现 user-rpc-service-api-02 中定义的接口,提供相应的服务。
user-rpc-service-consumer-02:服务消费者,会调用 user-rpc-service-provider-02暴露的的接口服务。
2.1 user-rpc-service-api-02
pom.xml 配置如下:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starterartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.validationgroupId>
<artifactId>validation-apiartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate.validatorgroupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-validatorartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.glassfishgroupId>
<artifactId>javax.elartifactId>
<version>3.0.1-b12version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtoolsartifactId>
<scope>runtimescope>
<optional>trueoptional>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId>
<artifactId>lombokartifactId>
<optional>trueoptional>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-testartifactId>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>
在这个项目下创建 api,core,dto 包
在 dto 下创建类:
@Data
public class UserDTO implements Serializable {
/**
* id
*/
private Integer id;
/**
* 姓名
*/
@NotEmpty(message = "昵称不能为空")
@Length(min = 5, max = 16, message = "账号长度为 5-16 位")
private String name;
/**
* 性别
*/
@NotNull(message = "性别不能为 Null")
private Integer gender;
}
@Data
public class UserAddDTO implements Serializable {
/**
* 昵称
*/
@Length(min = 6, max = 16, message = "昵称长度限制在 6-16 位")
@NotEmpty(message = "昵称不能为空")
private String name;
/**
* 性别
*/
@NotNull(message = "性别不能位 null")
private Integer gender;
}
参数校验,对于提供 API 调用的服务来说是必不可少的。
public interface UserRpcService {
/**
* 根据用户编号,获得用户信息
*
* @param id 用户编号
* @return 用户信息
*/
UserDTO getUser(@NotNull(message = "用户编号不能为 null") Integer id) throws ConstraintDeclarationException;
/**
* 添加用户
* @param userAddDTO 新建用户
* @return 用户编号
*/
Integer addUser(UserAddDTO userAddDTO) throws ConstraintDeclarationException;
}
在 getUser()上,添加@NotNull 注解,校验用户 id 不允许传 null。这里的参数是平铺开的(就是指参数可以直接校验),所以无需添加 @Valid注解。
在addUser()上,我们没有做校验,是因为 UserAddDTO 内部已经做了校验,这里要加校验的话是这样:Integer addUser(@Valid UserAddDTO userAddDTO)这个叫嵌套校验。
2.1.1 自定义实现拓展点
在参数校验的时候,我们入门了 Dubbo 提供的参数校验的功能,它是由 ValidationFilter 过滤器通过拦截请求,并按照我们添加的校验规则校验参数是否正确的。在 Dubbo 中,还提供了 AccessLogFilter、ExceptionFilter 等过滤器,它们都属于 Dubbo Filter接口的实现类。
而实际上,Filter 是 Dubbo 定义的调用拦截扩展点,除此之外,还有协议、路由、注册中心等等拓展点。
而这些 Dubbo 拓展点,通过 ==Dubbo SPI ==机制进行加载。
Dubbo 中的扩展能力是从 JDK 标准的 SPI 扩展点发现机制加强而来的,它改进了 JDK 标准的 SPI 以下问题:
- JDK 标准的 SPI 会一次性实例化扩展点所有实现,如果有扩展实现初始化很耗时,但如果没用上也会加载,很浪费资源。
- 如果扩展点加载失败,连扩展点的名称都拿不到了。如:JDK 标准的 Script Engine ,如果所依赖的包 jruby.jar 不存在,会导致失败原因被吃掉,不显示真实原因。
用户能够基于 Dubbo 提供的扩展能力,很方便基于自身需求扩展其他协议、过滤器、路由等。
Dubbo SPI 的特性如下: - 按需加载;
- 增加扩展类的 IOC 能力。Dubbo 的扩展能力并不仅仅只是发现扩展服务实现类,而是在此基础上更进一步:**如果该扩展类的属性依赖其他对象,则 Dubbo 会自动完成该对象的注入功能。
- 增加扩展类的 AOP 能力。Dubbo 会自动发现扩展类的包装类,完成包装类的构造,增强扩展类的功能。
- 具备动态选择扩展实现的能力。
- 可以对扩展进行排序。能够基于用户的需求,制定扩展实现的顺序。
- 提供扩展点的 Adaptive 能力。该能力可以使得一些扩展类在 consumer 端生效,一些扩展类在 provider 端生效。
Dubbo 扩展加载顺序如下:
主要步骤为 4 个:
- 读取并解析配置文件
- 缓存所有扩展实现
- 基于用户执行的扩展名,实例化对应的扩展实现
- 进行扩展实例属性的 IOC 注入以及实例化扩展的包装类,实现 AOP 特性。
在yaml中配置:
dubbo:
application:
name: user-service-provider02
registry:
address: zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181
protocol:
port: -1
name: dubbo
provider:
timeout: 1000
UserRpcService:
version: 1.0.0
filter:
-exception
scan:
base-packages: com.gui.userrpcserviceprovider02.service
在 core 包下:
@Getter
public enum ServiceExceptionEnum {
SUCCESS(0, "成功"),
SYS_ERROR(2021001000, "服务端发生异常"),
MISSING_REQUEST_PARAM_ERROR(2021001001, "参数缺失"),
INVALID_REQUEST_PARAM_ERROR(2001001002, "请求参数不合法"),
// ======= 用户模块 =======
USER_NOT_FOUND(1001002000, "用户不存在"),
USER_EXISTS(1001002001, "用户已存在");
// ======= 订单模块 =======
// ======= 。。。。 =======
private final int code;
private final String message;
ServiceExceptionEnum(int code, String message) {
this.code = code;
this.message = message;
}
}
错误码是全局的,可以按照模块来分。如上:一共10位。第一段,1位,代表类型:业务级别类型和系统级别类型。第二段,3位,代表系统类型:001-用户系统,002-商品系统。。。第三段,3位,代表模块:不限制,每个系统中可能有多个模块。第四段,3位,错误码:不限制
继续创建 ServiceException 类:
@Getter
public final class ServiceException extends RuntimeException{
private Integer code;
public ServiceException() {
}
public ServiceException(ServiceExceptionEnum exceptionEnum) {
// 使用父类的 message 字段
super(exceptionEnum.getMessage());
// 设置错误码
this.code = exceptionEnum.getCode();
}
public ServiceException(ServiceExceptionEnum exceptionEnum, String message) {
// 使用父类的 message 字段
super(message);
// 设置错误码
this.code = exceptionEnum.getCode();
}
}
到此,api 这个包里的就完成了,实现会在 provider 项目中完成。
2.2 user-rpc-service-provider-02
在此项目下,创建 filter、service 包,filter 下创建 DubboExceptionFilter 类:
package com.gui.userrpcserviceprovider02.filter;
import com.gui.userrpcserviceapi02.core.ServiceException;
import com.gui.userrpcserviceapi02.core.ServiceExceptionEnum;
import org.apache.dubbo.common.constants.CommonConstants;
import org.apache.dubbo.common.extension.Activate;
import org.apache.dubbo.common.utils.ReflectUtils;
import org.apache.dubbo.common.utils.StringUtils;
import org.apache.dubbo.rpc.*;
import org.apache.dubbo.rpc.service.GenericService;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import javax.validation.ConstraintViolation;
import javax.validation.ConstraintViolationException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
@Activate(group = CommonConstants.PROVIDER)
public class DubboExceptionFilter extends ListenableFilter {
public DubboExceptionFilter() {
super.listener = new ExceptionListenerX();
}
@Override
public Result invoke(Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
return invoker.invoke(invocation);
}
static class ExceptionListenerX extends ExceptionListener {
@Override
public void onResponse(Result appResponse, Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) {
//发生异常,并且非泛化调用
if (appResponse.hasException() && GenericService.class != invoker.getInterface()) {
Throwable exception = appResponse.getException();
// 如果是 ServiceException ,直接返回
if (exception instanceof ServiceException) {
return;
}
// 如果是参数校验的异常,则调用 handleConstraintViolationException 封装返回
if (exception instanceof ConstraintViolationException) {
appResponse.setException(this.handleConstraintViolationException((ConstraintViolationException) exception));
return;
}
}
// 其他情况,继续使用父类处理
super.onResponse(appResponse, invoker, invocation);
}
private ServiceException handleConstraintViolationException(ConstraintViolationException ex) {
// 凭借错误报告
StringBuilder detailMessages = new StringBuilder();
for (ConstraintViolation<?> constraint : ex.getConstraintViolations()) {
// 使用 ;分割
if (detailMessages.length() > 0) {
detailMessages.append(";");
}
// 拼接
detailMessages.append(constraint.getMessage());
}
return new ServiceException(ServiceExceptionEnum.INVALID_REQUEST_PARAM_ERROR, detailMessages.toString());
}
}
static class ExceptionListener implements Listener {
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ExceptionListener.class);
@Override
public void onResponse(Result appResponse, Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) {
//
if (appResponse.hasException() && GenericService.class != invoker.getInterface()) {
try {
Throwable exception = appResponse.getException();
// 检测到异常直接返回
if (!(exception instanceof ServiceException) && (exception instanceof Exception)) {
return;
}
// 如果异常匹配则返回
try {
Method method = invoker.getInterface()
.getMethod(invocation.getMethodName(), invocation.getParameterTypes());
Class<?>[] exceptionClasses = method.getExceptionTypes();
for (Class<?> exceptionClass : exceptionClasses) {
if (exception.getClass().equals(exceptionClass)) {
return;
}
}
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
return;
}
// 对于没有匹配的异常,通过错误日志抛出
logger.error("Got unchecked and undeclared exception which called by "
+ RpcContext.getContext().getRemoteHost()
+ ".service"
+ invoker.getInterface().getName()
+ ",method" + invocation.getMethodName()
+ ",exception:" + exception.getClass().getName() + ": " + exception.getMessage(),
exception);
// 如果异常类和接口在相同的jar包下,直接抛出
String serviceFile = ReflectUtils.getCodeBase(invoker.getInterface());
String exceptionFile = ReflectUtils.getCodeBase(exception.getClass());
if (serviceFile == null || exceptionFile == null || serviceFile.equals(exceptionFile)) {
return;
}
//如果 jdk 异常直接抛出
String className = exception.getClass().getName();
if (className.startsWith("java.") || className.startsWith("javax.")) {
return;
}
// 否则,打包运行时异常并抛给客户端
appResponse.setException(new RuntimeException(StringUtils.toString(exception)));
} catch (Throwable e) {
logger.warn("Fail to ExceptionFilter when called by " +
RpcContext.getContext() + ". service: " + invoker.getInterface().getName() +
", method: " + invocation.getMethodName() +
", exception: " + e.getClass().getName() + ": " + e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
}
@Override
public void onError(Throwable e, Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) {
logger.error("Got unchecked and undeclared exception which called by "+
RpcContext.getContext() + ". service: " + invoker.getInterface().getName() +
", method: " + invocation.getMethodName() +
", exception: " + e.getClass().getName() + ": " + e.getMessage(), e);
}
// 测试用
public void setLogger(Logger logger) {
this.logger = logger;
}
}
}
在类上,添加@Activate注解,并设置group = CommonConstants.PROVIDER属性,使得过滤器仅在服务提供者生效。
在构造方法中,我们创建了 ExceptionFilterX 类,作为 listener 监听器。且 ExceptionFilterX 继承自 ExceptionFilter 类,是直接从 Dubbo ExceptionFilter.ExceptionListener 复制过来的逻辑,为了保持 ExceptionFilter 原有逻辑不变。
处理完成后,需要制定配置文件,在 resources 目录下,创建 META-INF/dubbo/ 目录,然后创建 org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Filter 配置文件,里边直接写:dubboExceptionFilter=com.gui.userrpcserviceprovider02.filter.DubboExceptionFilter
- org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Filter 配置文件名,不能乱创建,就是 DubboExceptionFilter 对应的 Dubbo 扩展点 Filter。
- 配置文件里的内容:格式为
${扩展名}=${扩展类全名}
继续在 service 下创建:
@Service(version="${dubbo.provider.UserRpcService.version}",validation = "true",filter = "-exception")
public class UserRpcServiceImpl implements UserRpcService {
@Override
public UserDTO getUser(Integer id) {
UserDTO userDTO = new UserDTO();
userDTO.setId(1);
userDTO.setName("获取到用户:"+id);
userDTO.setGender(id % 2 + 1);
return userDTO;
}
@Override
public Integer addUser(UserAddDTO userAddDTO) throws ConstraintDeclarationException {
if ("user02".equals(userAddDTO.getName())) {
throw new ServiceException(ServiceExceptionEnum.USER_EXISTS);
}
return Math.toIntExact(System.currentTimeMillis() / 10000);
}
}
这里,我们将 version 使用配置的版本,并且开启 validation 。如果想把 Dubbo 服务消费者的所有 Service 的校验都开启,可以修改 application.yml 文件,增加dubbo.provider.validation = true配置。
filter=-exception代表去掉服务提供者的 ExceptionFilter 过滤器,一般情况下可以采用全局配置,即dubbo.provider.filter=-exception.
2.3 user-rpc-service-consumer-02
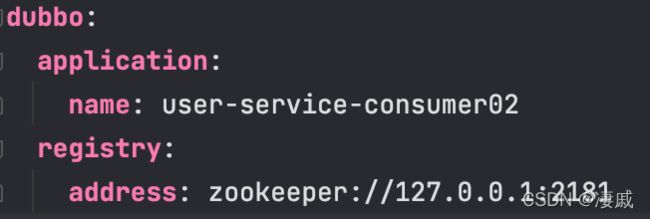
在这个项目下,yml 配置:
dubbo:
application:
name: user-service-consumer02
registry:
address: zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181
consumer:
timeout: 1000
UserRpcService:
version: 1.0.0
将对服务调用直接写在启动类中:
@SpringBootApplication
public class UserRpcServiceConsumer02Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext run = SpringApplication.run(UserRpcServiceConsumer02Application.class, args);
}
@Component
public class UserRpcServiceTest implements CommandLineRunner {
private final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(getClass());
@Reference(version = "${dubbo.consumer.UserRpcService.version}")
private UserRpcService userRpcService;
@Override
public void run(String... args) {
//获得用户
try {
UserDTO user = userRpcService.getUser(null);
logger.info("[run][发起一次 Dubbo RPC 请求,获得用户为({})", user);
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
logger.error("[run][获得用户发生异常:({})",e.getMessage());
}
//添加用户
try {
UserAddDTO userAddDTO = new UserAddDTO();
userAddDTO.setName("user02");
userAddDTO.setGender(1);
userRpcService.addUser(userAddDTO);
logger.info("[run][发起一次 Dubbo RPC 请求,添加用户为:({})]", userAddDTO);
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
logger.error("[run][添加用户发生异常:({}),信息为:({})]", e.getClass().getSimpleName(), e.getMessage());
}
}
}
}