过去,我讨论过RandomAccessFile以及如何将其用于在Java中进行更快的IO,在本Java NIO教程中,我们将了解如何通过使用FileChannel和ByteBuffer来使用读/写数据。
Channel提供了一种从文件读取数据的替代方法,它提供了比InputStream或OutputStream更好的性能。 也可以在阻止和非阻止模式下打开它。 尽管FileChannles是读/写通道,但它们始终处于阻塞状态 ,不能将它们置于非阻塞模式。 RandomAccessFile类将文件视为字节数组。
您可以将数据写入Array的任何位置,也可以从任何位置读取。 为此,它使用保存当前位置的指针,并提供诸如seek()几种方法来移动该指针。 一旦定位正确,就可以从RandomAccessFile获取FileChannel并开始从文件中读取数据。 顺便说一下,JDK 7还引入了NIO 2,它使处理文件和目录变得更加容易。 阅读Anghel Leonard的Pro Java 7 NIO.2以了解更多信息。
如何使用FileChannel和ByteBuffer读取/写入文件
在开始编码之前,让我们修改Java NIO中Channel和Buffer的基本概念。 一言以蔽之,缓冲区与通道一起工作。 通道是传输数据的管道,缓冲区是这些数据传输的源和目标。 在写入的情况下,要写入的数据放置在缓冲区中,该缓冲区传递到通道,而不是通道从缓冲区读取该数据并写入文件。
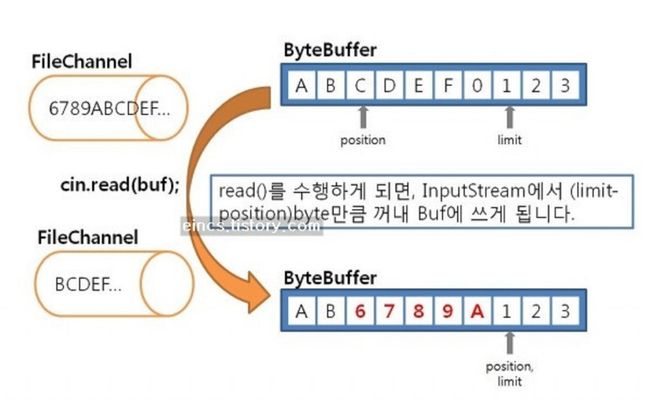
同样,在读取的情况下,通道会将数据放入您从文件 , 网络或任何其他来源提供的缓冲区中。 由于相同的缓冲区用于读取和写入,即您将数据写入缓冲区,而通道将其读取以写入文件,因此,一旦完成写入缓冲区,就必须调用flip()方法。 flip()方法更改指针,并允许您从缓冲区读取数据。 Java中的缓冲区有三种类型, 直接缓冲区,非直接缓冲区和映射缓冲区 。 在此示例中,我们将使用直接字节缓冲区。
使用FileChannel和Buffer读取/写入数据的步骤
这是逐步指南,开始使用RandomAccessFile , FileChannel和ByteBuffer从文件读取数据:
- 在读取/写入模式下使用RandomAccessFile打开要读取/写入的文件。
- 调用RandomAccessFile的
getChannel()方法以获取FileChannel。 返回的通道的位置将始终等于getFilePointer()方法返回的此对象的文件指针偏移量。 - 使用
ByteBuffer.allocate()方法创建一个ByteBuffer。 - 使用各种数据存储到字节缓冲区
put()方法例如putInt()putLong() - 翻转缓冲区,以便Channel可以从缓冲区读取数据并写入文件。 flip()方法更改指针,并允许您从缓冲区读取数据。
- 调用FileChannel的write()方法。
- 关闭文件通道
- 关闭RandomAccessFile。
要注意的另一个重要点是,您可以使用相同的缓冲区进行读写,但是需要翻转它。 现在,让我们看一个示例Java程序,该程序使用Java中的FileChannel和ByteBuffer从文件读取/写入数据。 在Memory Mapped File之后 ,这是从Java中读取和写入文件的第二快的方法。
Java程序,使用FileChannel和ByteBuffer从文件读取/写入
这是示例程序,以演示如何使用FileChannel和ByteBuffer类从文件(可以是二进制文件或文本文件)读取和写入数据。 我还使用抽象来创建一个名为Persistable的接口,该接口提供了两种方法persist()和recover() 。 任何实现此接口的对象都可以保存和加载,但是如何保存和加载它们则留给实现者,例如,可以像我们一样使用Chanel和Buffer,也可以使用旧方法在Java中读取/写入文件。 。
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.RandomAccessFile;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
/**
* Java Program to read and write on RandomAccessFile in Java
* using FileChannle and ByteBuffer.
*
* @author Javin
*/
public class FileChannelDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Tablet ipad = new Tablet("Apple", true, 1000);
System.out.println("Writing into RandomAcessFile : " + ipad);
write("tablet.store", ipad);
Tablet fromStore = new Tablet();
read("tablet.store", fromStore);
System.out.println("Object read from RandomAcessFile : " + fromStore);
}
/*
* Method to write data into File using FileChannel and ByteBuffeer
*/
public static void write(String filename, Persistable object) {
try {
// Creating RandomAccessFile for writing
RandomAccessFile store = new RandomAccessFile("tablet", "rw");
// getting FileChannel from file
FileChannel channel = store.getChannel();
// creating and initializing ByteBuffer for reading/writing data
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(2048);
// an instance of Persistable writing into ByteBuffer
object.persist(buffer);
// flip the buffer for writing into file
buffer.flip();
int numOfBytesWritten = channel.write(buffer); // writing into File
System.out.println("number of bytes written : " + numOfBytesWritten);
channel.close(); // closing file channel
store.close(); // closing RandomAccess file
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/*
* Method to read data from File using FileChannel and ByteBuffeer
*/
public static void read(String filename, Persistable object) {
try {
// Opening RandomAccessFile for reading data
RandomAccessFile store = new RandomAccessFile("tablet", "rw");
// getting file channel
FileChannel channel = store.getChannel();
// preparing buffer to read data from file
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
// reading data from file channel into buffer
int numOfBytesRead = channel.read(buffer);
System.out.println("number of bytes read : " + numOfBytesRead);
// You need to filp the byte buffer before reading
buffer.flip();
// Recovering object
object.recover(buffer);
channel.close();
store.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}我们的界面为抽象的读写机制。 这也是提供抽象的接口的实际用法 ,将要做的事情与要做的事情分开。 像这个界面,只说坚持并恢复,不说你怎么做。
interface Persistable {
public void persist(ByteBuffer buffer);
public void recover(ByteBuffer buffer);
}实现Persistable使其可读写的具体类:
class Tablet implements Persistable {
private String brand;
private boolean isCellular;
private long cost; // in US Dollars
public Tablet() {
brand = "";
}
public Tablet(String brand, boolean isCellular, long cost) {
this.brand = brand;
this.isCellular = isCellular;
this.cost = cost;
}
public final String getBrand() {
return brand;
}
public final boolean isCellular() {
return isCellular;
}
public final long getCost() {
return cost;
}
public final void setBrand(String brand) {
this.brand = brand;
}
public final void setCellular(boolean isCellular) {
this.isCellular = isCellular;
}
public final void setCost(long cost) {
this.cost = cost;
}
@Override
public void persist(ByteBuffer buffer) {
byte[] strBytes = brand.getBytes();
buffer.putInt(strBytes.length);
buffer.put(strBytes, 0, strBytes.length);
buffer.put(isCellular == true ? (byte) 1 : (byte) 0);
buffer.putLong(cost);
}
@Override
public void recover(ByteBuffer buffer) {
int size = buffer.getInt();
byte[] rawBytes = new byte[size];
buffer.get(rawBytes, 0, size);
this.brand = new String(rawBytes);
this.isCellular = buffer.get() == 1 ? true : false;
this.cost = buffer.getLong();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Tablet [brand=" + brand + ", isCellular=" + isCellular + ", cost=" + cost + "]";
}
}
Output:
Writing into RandomAcessFile : Tablet [brand=Apple, isCellular=true, cost=1000]
number of bytes written : 18
number of bytes read : 1024
Object read from RandomAcessFile : Tablet [brand=Apple, isCellular=true, cost=1000]警告
将对象的内容写入其中后,不要忘记翻转字节缓冲区,因为文件通道需要读取它才能将数据写入RandomAccessFile。 如果忘记在调用FileChannel.write()之前先调用flip()方法,那么最终将什么都没有写入文件中。
同样,将数据从文件读入缓冲区后,请再次翻转它,以便可以将数据从缓冲区读到对象的常用内容。 许多Java程序员都会犯这样的错误,即写后不会翻转,并最终导致调试时间过长,因为要么什么都没有写到文件中,要么什么都无法从文件中读取。
这就是如何在Java中使用FileChannel和ByteBuffer读取/写入文件的全部内容。 在本演示中,我向您展示了如何使用FileChannel和ByteBuffer读写RandomAccessFile,但是您可以应用相同的技术从Java程序读取任何其他文本或二进制文件。
翻译自: https://www.javacodegeeks.com/2016/01/readingwriting-tofrom-files-using-filechannel-bytebuffer-java.html