【云原生】k8s 一键部署(ansible)
一、概述
前面我写了关于k8s环境部署的几篇文章,k8s部署还是比较麻烦的,所以是有必要考虑一键部署的方案,这里借助ansible playbook来实现k8s环境的一键部署,实现快速部署的目的。
节点信息
k8s 架构图:
基于ansible部署k8s流程图:
二、Ansible 部署
yum -y install epel-release
yum -y install ansible
ansible --version
1)开启记录日志
配置文件:/etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
vi /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
# 去掉前面的'#'号
#log_path = /var/log/ansible.log ==> log_path = /var/log/ansible.log
2)去掉第一次连接ssh ask确认
vi /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
# 其实就是把#去掉
# host_key_checking = False ==> host_key_checking = False
3)配置hosts
配置文件:/etc/ansible/hosts
[master1]
192.168.182.110
[master2]
192.168.182.111
192.168.182.112
[node]
192.168.182.113
[k8s:children]
master1
master2
node
[k8s:vars]
ansible_ssh_user=root
ansible_ssh_pass=1331301116
ansible_ssh_port=22
# k8s 版本
k8s_version=1.23.6
测试连通性
ansible k8s -m ping
 三、开始编排 ansible playbook
三、开始编排 ansible playbook
1)创建目录
mkdir -pv ./install-k8s/{init,install-docker,install-k8s,master-init,install-cni,install-ipvs,master-join,node-join,install-ingress-nginx,install-nfs-provisioner,install-harbor,install-metrics-server,uninstall-k8s}/{files,templates,vars,tasks,handlers,meta,default}
2)节点初始化
准备install-k8s/init/files/hosts文件
192.168.182.110 local-168-182-110
192.168.182.111 local-168-182-111
192.168.182.112 local-168-182-112
192.168.182.113 local-168-182-113
准备脚本install-k8s/init/templates/init.sh,内容如下:
#!/usr/bin/env bash
### 【第一步】修改主机名
# 获取主机名
hostnamectl set-hostname $(grep `hostname -i` /tmp/hosts|awk '{print $2}')
### 【第二步】配置hosts
# 先删除
for line in `cat /tmp/hosts`
do
sed -i "/$line/d" /etc/hosts
done
# 追加
cat /tmp/hosts >> /etc/hosts
### 【第三步】添加互信
# 先创建秘钥对
ssh-keygen -f ~/.ssh/id_rsa -P '' -q
# 安装expect
yum -y install expect -y
# 批量推送公钥
for line in `cat /tmp/hosts`
do
ip=`echo $line|awk '{print $1}'`
password={{ ansible_ssh_pass }}
expect <<-EOF
spawn ssh-copy-id -i /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub $ip
expect {
"(yes/no)?"
{
send "yes\n"
expect "*assword:" { send "$password\n"}
}
"*assword:"
{
send "$password\n"
}
}
expect eof
EOF
done
### 【第四步】时间同步
yum install chrony -y
systemctl start chronyd
systemctl enable chronyd
chronyc sources
### 【第五步】关闭防火墙
systemctl stop firewalld
systemctl disable firewalld
### 【第六步】关闭swap
# 临时关闭;关闭swap主要是为了性能考虑
swapoff -a
# 永久关闭
sed -ri 's/.*swap.*/#&/' /etc/fstab
### 【第七步】禁用SELinux
# 临时关闭
setenforce 0
# 永久禁用
sed -i 's/^SELINUX=enforcing$/SELINUX=disabled/' /etc/selinux/config
### 【第八步】允许 iptables 检查桥接流量
sudo modprobe br_netfilter
lsmod | grep br_netfilter
# 先删
rm -rf /etc/modules-load.d/k8s.conf
cat <<EOF | sudo tee /etc/modules-load.d/k8s.conf
overlay
br_netfilter
EOF
sudo modprobe overlay
sudo modprobe br_netfilter
rm -rf /etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf
# 设置所需的 sysctl 参数,参数在重新启动后保持不变
cat <<EOF | sudo tee /etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
EOF
# 应用 sysctl 参数而不重新启动
sudo sysctl --system
任务编排 install-k8s/init/tasks/main.yml
- name: cp hosts
copy: src=hosts dest=/tmp/hosts
- name: init cp
template: src=init.sh dest=/tmp/init.sh
- name: init install
shell: sh /tmp/init.sh
3)安装 docker
install-k8s/install-docker/files/install-docker.sh
#!/usr/bin/env bash
### 安装docker
# 配置yum源
cd /etc/yum.repos.d ; mkdir bak; mv CentOS-Linux-* bak/
# centos7
wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/Centos-7.repo
# centos8
# wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/Centos-8.repo
# 安装yum-config-manager配置工具
yum -y install yum-utils
# 设置yum源
yum-config-manager --add-repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/docker-ce/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
# 安装docker-ce版本
yum install -y docker-ce
# 启动并开机自启
systemctl enable --now docker
# Docker镜像源设置
# 修改文件 /etc/docker/daemon.json,没有这个文件就创建
# 添加以下内容后,重启docker服务:
cat >/etc/docker/daemon.json<<EOF
{
"registry-mirrors": ["http://hub-mirror.c.163.com"],
"exec-opts": ["native.cgroupdriver=systemd"]
}
EOF
# 重启
systemctl restart docker
# 查看
systemctl status docker containerd
任务编排 install-k8s/install-docker/tasks/main.yml
- name: install docker cp
copy: src=install-docker.sh dest=/tmp/install-docker.sh
- name: install docker
shell: sh /tmp/install-docker.sh
4)安装 k8s 相关组件
install-k8s/install-k8s/templates/install-k8s.sh
#!/usr/bin/env bash
# 检查是否已经安装
yum list installed kubelet
if [ $? -eq 0 ];then
exit 0
fi
cat > /etc/yum.repos.d/kubernetes.repo << EOF
[k8s]
name=k8s
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0
baseurl=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/repos/kubernetes-el7-x86_64/
EOF
# disableexcludes=kubernetes:禁掉除了这个kubernetes之外的别的仓库
yum install -y kubelet-{{ k8s_version }} kubeadm-{{ k8s_version }} kubectl-{{ k8s_version }} --disableexcludes=kubernetes
# 设置为开机自启并现在立刻启动服务 --now:立刻启动服务
systemctl enable --now kubelet
# 查看状态,这里需要等待一段时间再查看服务状态,启动会有点慢
systemctl status kubelet
# 提前下载好
docker pull registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/kube-apiserver:v{{ k8s_version }}
docker pull registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/kube-controller-manager:v{{ k8s_version }}
docker pull registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/kube-scheduler:v{{ k8s_version }}
docker pull registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/kube-proxy:v{{ k8s_version }}
docker pull registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/pause:3.6
docker pull registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/etcd:3.5.1-0
docker pull registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/coredns:v1.8.6
任务编排 install-k8s/install-k8s/tasks/main.yml
- name: install k8s cp
template: src=install-k8s.sh dest=/tmp/install-k8s.sh
- name: install k8s
shell: sh /tmp/install-k8s.sh
5)k8s master节点初始化
install-k8s/master-init/templates/master-init.sh
#!/usr/bin/env bash
# 判断是否已经初始化了
kubectl get nodes |grep -q `hostname` 1>&2 >/dev/null
if [ $? -eq 0 ];then
exit 0
fi
ip=`hostname -i`
kubeadm init \
--apiserver-advertise-address=$ip \
--image-repository registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers \
--kubernetes-version v{{ k8s_version }} \
--control-plane-endpoint=$ip \
--service-cidr=10.1.0.0/16 \
--pod-network-cidr=10.244.0.0/16 \
--v=5
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
rm -rf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
任务编排 install-k8s/master-init/tasks/main.yml
- name: k8s master init cp
template: src=master-init.sh dest=/tmp/master-init.sh
- name: k8s master init
shell: sh /tmp/master-init.sh
6)安装 CNI(flannel)
install-k8s/install-cni/files/install-flannel.sh
#!/usr/bin/env bash
# 去掉master污点
kubectl taint nodes `hostname` node-role.kubernetes.io/master:NoSchedule- 2>/dev/null
kubectl taint nodes `hostname` node.kubernetes.io/not-ready:NoSchedule- 2>/dev/null
# For Kubernetes v1.17+
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/flannel-io/flannel/v0.20.2/Documentation/kube-flannel.yml
# 查看
kubectl get all -n kube-flannel
# 持续检查
while true
do
kubectl get pods -n kube-flannel|grep -q '0/1'
if [ $? -ne 0 ];then
echo "flannel started"
break
else
echo "flannel starting..."
fi
sleep 1
done
任务编排 install-k8s/install-cni/tasks/main.yml
- name: install cni flannel cp
copy: src=install-flannel.sh dest=/tmp/install-flannel.sh
- name: install cni flannel
shell: sh /tmp/install-flannel.sh
7)master 节点加入k8s集群
install-k8s/master-join/files/master-join.sh
#!/usr/bin/env bash
# 获取master ip,假设都是第一个节点为master
# 证如果过期了,可以使用下面命令生成新证书上传,这里会打印出certificate key,后面会用到
maser_ip=`head -1 /tmp/hosts |awk '{print $1}'`
# 判断节点是否加入
ssh $maser_ip "kubectl get nodes|grep -q `hostname`"
if [ $? -eq 0 ];then
exit 0
fi
CERT_KEY=`ssh $maser_ip "kubeadm init phase upload-certs --upload-certs|tail -1"`
join_str=`ssh $maser_ip kubeadm token create --print-join-command`
$( echo $join_str " --control-plane --certificate-key $CERT_KEY --v=5")
# 拿到上面打印的命令在需要添加的节点上执行
# --control-plane 标志通知 kubeadm join 创建一个新的控制平面。加入master必须加这个标记
# --certificate-key ... 将导致从集群中的 kubeadm-certs Secret 下载控制平面证书并使用给定的密钥进行解密。这里的值就是上面这个命令(kubeadm init phase upload-certs --upload-certs)打印出的key。
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
# 去掉master污点
kubectl taint nodes `hostname` node-role.kubernetes.io/master:NoSchedule- 2>/dev/null
kubectl taint nodes `hostname` node.kubernetes.io/not-ready:NoSchedule- 2>/dev/null
任务编排 install-k8s/master-join/tasks/main.yml
- name: master join cp
copy: src=master-join.sh dest=/tmp/master-join.sh
- name: master join
shell: sh /tmp/master-join.sh
8)node 节点加入k8s集群
install-k8s/node-join/files/node-join.sh
#!/usr/bin/env bash
# 获取master ip,假设都是第一个节点为master
maser_ip=`head -1 /tmp/hosts |awk '{print $1}'`
# 判断节点是否加入
ssh $maser_ip "kubectl get nodes|grep -q `hostname`"
if [ $? -eq 0 ];then
exit 0
fi
CERT_KEY=`ssh $maser_ip "kubeadm init phase upload-certs --upload-certs|tail -1"`
join_str=`ssh $maser_ip kubeadm token create --print-join-command`
$( echo $join_str " --certificate-key $CERT_KEY --v=5")
任务编排 install-k8s/node-join/tasks/main.yml
- name: node join cp
copy: src=node-join.yaml dest=/tmp/node-join.yaml
- name: node join
shell: sh /tmp/node-join.yaml
9)安装 ingress-nginx
install-k8s/install-ingress-nginx/files/ingress-nginx.sh
#!/usr/bin/env bash
# wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/ingress-nginx/controller-v1.2.0/deploy/static/provider/cloud/deploy.yaml -O /tmp/deploy.yaml
# 可以先把镜像下载,再安装
docker pull registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/nginx-ingress-controller:v1.2.0
docker pull registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/kube-webhook-certgen:v1.1.1
kubectl apply -f /tmp/deploy.yaml
任务编排 install-k8s/install-ingress-nginx/tasks/main.yml
- name: ingress-nginx deploy cp
copy: src=deploy.yaml dest=/tmp/deploy.yaml
- name: install ingress-nginx cp
copy: src=ingress-nginx.sh dest=/tmp/ingress-nginx.sh
- name: install ingress-nginx
shell: sh /tmp/ingress-nginx.sh
10)安装 nfs 共享存储
install-k8s/install-nfs-provisioner/files/nfs-provisioner.sh
#!/usr/bin/env bash
### 安装helm
# 下载包
wget https://get.helm.sh/helm-v3.7.1-linux-amd64.tar.gz -O /tmp/helm-v3.7.1-linux-amd64.tar.gz
# 解压压缩包
tar -xf /tmp/helm-v3.7.1-linux-amd64.tar.gz -C /root/
# 制作软连接
rm -rf /usr/local/bin/helm
ln -s /root/linux-amd64/helm /usr/local/bin/helm
# 判断是否已经部署
helm list -n nfs-provisioner|grep -q nfs-provisioner
if [ $? -eq 0 ];then
exit 0
fi
### 开始安装nfs-provisioner
# 添加helm仓库源
helm repo add nfs-subdir-external-provisioner https://kubernetes-sigs.github.io/nfs-subdir-external-provisioner/
#### 安装nfs
yum -y install nfs-utils rpcbind
# 服务端
mkdir -p /opt/nfsdata
# 授权共享目录
chmod 666 /opt/nfsdata
cat > /etc/exports<<EOF
/opt/nfsdata *(rw,no_root_squash,no_all_squash,sync)
EOF
# 配置生效
exportfs -r
systemctl enable --now rpcbind
systemctl enable --now nfs-server
# 客户端
for line in `cat /tmp/hosts`
do
ip=`echo $line|awk '{print $1}'`
master_ip=`head -1 /tmp/hosts|awk '{print $1}'`
if [ "$ip" != "$master_ip" ];then
ssh $ip "yum -y install rpcbind"
ssh $ip "systemctl enable --now rpcbind"
fi
done
### helm安装nfs provisioner
ip=`hostname -i`
helm install nfs-subdir-external-provisioner nfs-subdir-external-provisioner/nfs-subdir-external-provisioner \
--namespace=nfs-provisioner \
--create-namespace \
--set image.repository=willdockerhub/nfs-subdir-external-provisioner \
--set image.tag=v4.0.2 \
--set replicaCount=2 \
--set storageClass.name=nfs-client \
--set storageClass.defaultClass=true \
--set nfs.server=${ip} \
--set nfs.path=/opt/nfsdata
# 查看
kubectl get pods,deploy,sc -n nfs-provisioner
# 持续检查
while true
do
kubectl get pods -n nfs-provisioner|grep -q '0/1'
if [ $? -ne 0 ];then
echo "nfs-provisioner started"
break
else
echo "nfs-provisioner starting..."
fi
sleep 1
done
任务编排 install-k8s/install-nfs-provisioner/tasks/main.yml
- name: install nfs-provisioner cp
copy: src=nfs-provisioner.sh dest=/tmp/nfs-provisioner.sh
- name: install nfs-provisioner
shell: sh /tmp/nfs-provisioner.sh
11)k8s 环境安装编排 roles
install-k8s.yaml
- hosts: k8s
remote_user: root
roles:
- init
- hosts: k8s
remote_user: root
roles:
- install-docker
- hosts: k8s
remote_user: root
roles:
- install-k8s
- hosts: master1
remote_user: root
roles:
- master-init
- hosts: master1
remote_user: root
roles:
- install-cni
- hosts: master2
remote_user: root
roles:
- master-join
- hosts: node
remote_user: root
roles:
- node-join
- hosts: master1
remote_user: root
roles:
- install-ingress-nginx
- hosts: master1
remote_user: root
roles:
- install-nfs-provisioner
【云原生】k8s 一键部署(ansible)
原创2023-01-17 00:26·大数据老司机
一、概述
前面我写了关于k8s环境部署的几篇文章,k8s部署还是比较麻烦的,所以是有必要考虑一键部署的方案,这里借助ansible playbook来实现k8s环境的一键部署,实现快速部署的目的。关于k8s传统部署详细过程可以参考我以下几篇文章:
Kubernetes(k8s)安装以及搭建k8s-Dashboard详解
「云原生」Kubernetes(k8s)最完整版环境部署(V1.24.1)
关于Ansible的介绍可以参考我以下几篇文章:
Ansible 介绍与实战操作演示
Ansible playbook 讲解与实战操作
节点信息
主机名
IP
角色
操作系统
local-168-182-110
192.168.182.110
master,ansible
centos7
local-168-182-111
192.168.182.110
master
centos7
local-168-182-112
192.168.182.110
master
centos7
local-168-182-113
192.168.182.110
node
centos7
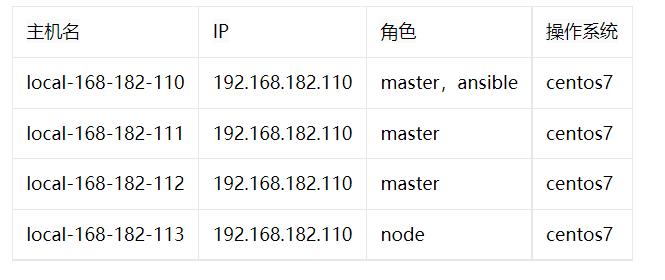
k8s 架构图:
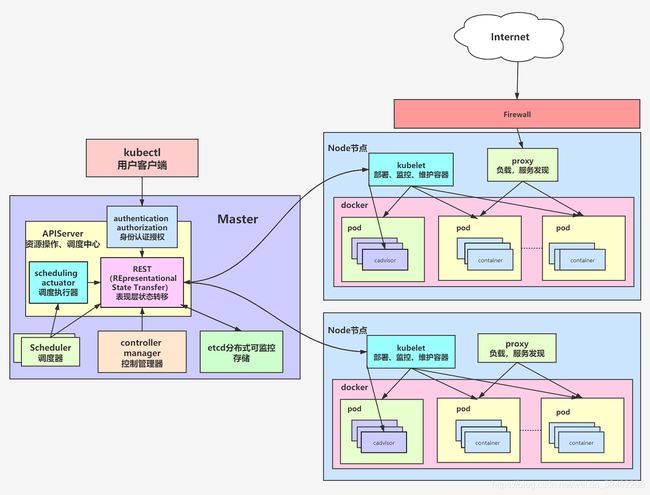
基于ansible部署k8s流程图:
二、Ansible 部署
yum -y install epel-release
yum -y install ansible
ansible --version
1)开启记录日志
配置文件:/etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
vi /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
去掉前面的’#'号
#log_path = /var/log/ansible.log ==> log_path = /var/log/ansible.log
2)去掉第一次连接ssh ask确认
vi /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
其实就是把#去掉
host_key_checking = False ==> host_key_checking = False
3)配置hosts
配置文件:/etc/ansible/hosts
[master1]
192.168.182.110
[master2]
192.168.182.111
192.168.182.112
[node]
192.168.182.113
[k8s:children]
master1
master2
node
[k8s:vars]
ansible_ssh_user=root
ansible_ssh_pass=1331301116
ansible_ssh_port=22
k8s 版本
k8s_version=1.23.6
测试连通性
ansible k8s -m ping
三、开始编排 ansible playbook
1)创建目录
mkdir -pv ./install-k8s/{init,install-docker,install-k8s,master-init,install-cni,install-ipvs,master-join,node-join,install-ingress-nginx,install-nfs-provisioner,install-harbor,install-metrics-server,uninstall-k8s}/{files,templates,vars,tasks,handlers,meta,default}
2)节点初始化
准备install-k8s/init/files/hosts文件
192.168.182.110 local-168-182-110
192.168.182.111 local-168-182-111
192.168.182.112 local-168-182-112
192.168.182.113 local-168-182-113
准备脚本install-k8s/init/templates/init.sh,内容如下:
#!/usr/bin/env bash
【第一步】修改主机名
获取主机名
hostnamectl set-hostname $(grep hostname -i /tmp/hosts|awk ‘{print $2}’)
【第二步】配置hosts
先删除
for line in cat /tmp/hosts
do
sed -i “/$line/d” /etc/hosts
done
追加
cat /tmp/hosts >> /etc/hosts
【第三步】添加互信
先创建秘钥对
ssh-keygen -f ~/.ssh/id_rsa -P ‘’ -q
安装expect
yum -y install expect -y
批量推送公钥
for line in cat /tmp/hosts
do
ip=echo $line|awk '{print $1}'
password={{ ansible_ssh_pass }}
expect <<-EOF
spawn ssh-copy-id -i /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub KaTeX parse error: Undefined control sequence: \n at position 52: … send "yes\̲n̲" expec…password\n"}
}
“*assword:”
{
send “$password\n”
}
}
expect eof
EOF
done
【第四步】时间同步
yum install chrony -y
systemctl start chronyd
systemctl enable chronyd
chronyc sources
【第五步】关闭防火墙
systemctl stop firewalld
systemctl disable firewalld
【第六步】关闭swap
临时关闭;关闭swap主要是为了性能考虑
swapoff -a
永久关闭
sed -ri ‘s/.swap./#&/’ /etc/fstab
【第七步】禁用SELinux
临时关闭
setenforce 0
永久禁用
sed -i ‘s/^SELINUX=enforcing$/SELINUX=disabled/’ /etc/selinux/config
【第八步】允许 iptables 检查桥接流量
sudo modprobe br_netfilter
lsmod | grep br_netfilter
先删
rm -rf /etc/modules-load.d/k8s.conf
cat <
br_netfilter
EOF
sudo modprobe overlay
sudo modprobe br_netfilter
rm -rf /etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf
设置所需的 sysctl 参数,参数在重新启动后保持不变
cat <
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
EOF
应用 sysctl 参数而不重新启动
sudo sysctl --system
任务编排 install-k8s/init/tasks/main.yml
- name: cp hosts
copy: src=hosts dest=/tmp/hosts - name: init cp
template: src=init.sh dest=/tmp/init.sh - name: init install
shell: sh /tmp/init.sh
3)安装 docker
install-k8s/install-docker/files/install-docker.sh
#!/usr/bin/env bash
安装docker
配置yum源
cd /etc/yum.repos.d ; mkdir bak; mv CentOS-Linux-* bak/
centos7
wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/Centos-7.repo
centos8
wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/Centos-8.repo
安装yum-config-manager配置工具
yum -y install yum-utils
设置yum源
yum-config-manager --add-repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/docker-ce/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
安装docker-ce版本
yum install -y docker-ce
启动并开机自启
systemctl enable --now docker
Docker镜像源设置
修改文件 /etc/docker/daemon.json,没有这个文件就创建
添加以下内容后,重启docker服务:
cat >/etc/docker/daemon.json<
“registry-mirrors”: [“http://hub-mirror.c.163.com”],
“exec-opts”: [“native.cgroupdriver=systemd”]
}
EOF
重启
systemctl restart docker
查看
systemctl status docker containerd
任务编排 install-k8s/install-docker/tasks/main.yml
- name: install docker cp
copy: src=install-docker.sh dest=/tmp/install-docker.sh - name: install docker
shell: sh /tmp/install-docker.sh
4)安装 k8s 相关组件
install-k8s/install-k8s/templates/install-k8s.sh
#!/usr/bin/env bash
检查是否已经安装
yum list installed kubelet
if [ $? -eq 0 ];then
exit 0
fi
cat > /etc/yum.repos.d/kubernetes.repo << EOF
[k8s]
name=k8s
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0
baseurl=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/repos/kubernetes-el7-x86_64/
EOF
disableexcludes=kubernetes:禁掉除了这个kubernetes之外的别的仓库
yum install -y kubelet-{{ k8s_version }} kubeadm-{{ k8s_version }} kubectl-{{ k8s_version }} --disableexcludes=kubernetes
设置为开机自启并现在立刻启动服务 --now:立刻启动服务
systemctl enable --now kubelet
查看状态,这里需要等待一段时间再查看服务状态,启动会有点慢
systemctl status kubelet
提前下载好
docker pull registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/kube-apiserver:v{{ k8s_version }}
docker pull registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/kube-controller-manager:v{{ k8s_version }}
docker pull registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/kube-scheduler:v{{ k8s_version }}
docker pull registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/kube-proxy:v{{ k8s_version }}
docker pull registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/pause:3.6
docker pull registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/etcd:3.5.1-0
docker pull registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/coredns:v1.8.6
任务编排 install-k8s/install-k8s/tasks/main.yml
- name: install k8s cp
template: src=install-k8s.sh dest=/tmp/install-k8s.sh - name: install k8s
shell: sh /tmp/install-k8s.sh
5)k8s master节点初始化
install-k8s/master-init/templates/master-init.sh
#!/usr/bin/env bash
判断是否已经初始化了
kubectl get nodes |grep -q hostname 1>&2 >/dev/null
if [ $? -eq 0 ];then
exit 0
fi
ip=hostname -i
kubeadm init
–apiserver-advertise-address= i p − − i m a g e − r e p o s i t o r y r e g i s t r y . a l i y u n c s . c o m / g o o g l e c o n t a i n e r s − − k u b e r n e t e s − v e r s i o n v k 8 s v e r s i o n − − c o n t r o l − p l a n e − e n d p o i n t = ip \ --image-repository registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers \ --kubernetes-version v{{ k8s_version }} \ --control-plane-endpoint= ip −−image−repositoryregistry.aliyuncs.com/googlecontainers −−kubernetes−versionvk8sversion −−control−plane−endpoint=ip
–service-cidr=10.1.0.0/16
–pod-network-cidr=10.244.0.0/16
–v=5
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
rm -rf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown ( i d − u ) : (id -u): (id−u):(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
任务编排 install-k8s/master-init/tasks/main.yml
- name: k8s master init cp
template: src=master-init.sh dest=/tmp/master-init.sh - name: k8s master init
shell: sh /tmp/master-init.sh
6)安装 CNI(flannel)
install-k8s/install-cni/files/install-flannel.sh
#!/usr/bin/env bash
去掉master污点
kubectl taint nodes hostname node-role.kubernetes.io/master:NoSchedule- 2>/dev/null
kubectl taint nodes hostname node.kubernetes.io/not-ready:NoSchedule- 2>/dev/null
For Kubernetes v1.17+
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/flannel-io/flannel/v0.20.2/Documentation/kube-flannel.yml
查看
kubectl get all -n kube-flannel
持续检查
while true
do
kubectl get pods -n kube-flannel|grep -q ‘0/1’
if [ $? -ne 0 ];then
echo “flannel started”
break
else
echo “flannel starting…”
fi
sleep 1
done
任务编排 install-k8s/install-cni/tasks/main.yml
- name: install cni flannel cp
copy: src=install-flannel.sh dest=/tmp/install-flannel.sh - name: install cni flannel
shell: sh /tmp/install-flannel.sh
7)master 节点加入k8s集群
install-k8s/master-join/files/master-join.sh
#!/usr/bin/env bash
获取master ip,假设都是第一个节点为master
证如果过期了,可以使用下面命令生成新证书上传,这里会打印出certificate key,后面会用到
maser_ip=head -1 /tmp/hosts |awk '{print $1}'
判断节点是否加入
ssh $maser_ip “kubectl get nodes|grep -q hostname”
if [ $? -eq 0 ];then
exit 0
fi
CERT_KEY=ssh $maser_ip "kubeadm init phase upload-certs --upload-certs|tail -1"
join_str=ssh $maser_ip kubeadm token create --print-join-command
$( echo $join_str " --control-plane --certificate-key $CERT_KEY --v=5")
拿到上面打印的命令在需要添加的节点上执行
–control-plane 标志通知 kubeadm join 创建一个新的控制平面。加入master必须加这个标记
–certificate-key … 将导致从集群中的 kubeadm-certs Secret 下载控制平面证书并使用给定的密钥进行解密。这里的值就是上面这个命令(kubeadm init phase upload-certs --upload-certs)打印出的key。
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown ( i d − u ) : (id -u): (id−u):(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
去掉master污点
kubectl taint nodes hostname node-role.kubernetes.io/master:NoSchedule- 2>/dev/null
kubectl taint nodes hostname node.kubernetes.io/not-ready:NoSchedule- 2>/dev/null
任务编排 install-k8s/master-join/tasks/main.yml
- name: master join cp
copy: src=master-join.sh dest=/tmp/master-join.sh - name: master join
shell: sh /tmp/master-join.sh
8)node 节点加入k8s集群
install-k8s/node-join/files/node-join.sh
#!/usr/bin/env bash
获取master ip,假设都是第一个节点为master
maser_ip=head -1 /tmp/hosts |awk '{print $1}'
判断节点是否加入
ssh $maser_ip “kubectl get nodes|grep -q hostname”
if [ $? -eq 0 ];then
exit 0
fi
CERT_KEY=ssh $maser_ip "kubeadm init phase upload-certs --upload-certs|tail -1"
join_str=ssh $maser_ip kubeadm token create --print-join-command
$( echo $join_str " --certificate-key $CERT_KEY --v=5")
任务编排 install-k8s/node-join/tasks/main.yml
- name: node join cp
copy: src=node-join.yaml dest=/tmp/node-join.yaml - name: node join
shell: sh /tmp/node-join.yaml
9)安装 ingress-nginx
install-k8s/install-ingress-nginx/files/ingress-nginx.sh
#!/usr/bin/env bash
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/ingress-nginx/controller-v1.2.0/deploy/static/provider/cloud/deploy.yaml -O /tmp/deploy.yaml
可以先把镜像下载,再安装
docker pull registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/nginx-ingress-controller:v1.2.0
docker pull registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/kube-webhook-certgen:v1.1.1
kubectl apply -f /tmp/deploy.yaml
任务编排 install-k8s/install-ingress-nginx/tasks/main.yml
- name: ingress-nginx deploy cp
copy: src=deploy.yaml dest=/tmp/deploy.yaml - name: install ingress-nginx cp
copy: src=ingress-nginx.sh dest=/tmp/ingress-nginx.sh - name: install ingress-nginx
shell: sh /tmp/ingress-nginx.sh
10)安装 nfs 共享存储
install-k8s/install-nfs-provisioner/files/nfs-provisioner.sh
#!/usr/bin/env bash
安装helm
下载包
wget https://get.helm.sh/helm-v3.7.1-linux-amd64.tar.gz -O /tmp/helm-v3.7.1-linux-amd64.tar.gz
解压压缩包
tar -xf /tmp/helm-v3.7.1-linux-amd64.tar.gz -C /root/
制作软连接
rm -rf /usr/local/bin/helm
ln -s /root/linux-amd64/helm /usr/local/bin/helm
判断是否已经部署
helm list -n nfs-provisioner|grep -q nfs-provisioner
if [ $? -eq 0 ];then
exit 0
fi
开始安装nfs-provisioner
添加helm仓库源
helm repo add nfs-subdir-external-provisioner https://kubernetes-sigs.github.io/nfs-subdir-external-provisioner/
安装nfs
yum -y install nfs-utils rpcbind
服务端
mkdir -p /opt/nfsdata
授权共享目录
chmod 666 /opt/nfsdata
cat > /etc/exports<
EOF
配置生效
exportfs -r
systemctl enable --now rpcbind
systemctl enable --now nfs-server
客户端
for line in cat /tmp/hosts
do
ip=echo $line|awk '{print $1}'
master_ip=head -1 /tmp/hosts|awk '{print $1}'
if [ “ i p " ! = " ip" != " ip"!="master_ip” ];then
ssh $ip “yum -y install rpcbind”
ssh $ip “systemctl enable --now rpcbind”
fi
done
helm安装nfs provisioner
ip=hostname -i
helm install nfs-subdir-external-provisioner nfs-subdir-external-provisioner/nfs-subdir-external-provisioner
–namespace=nfs-provisioner
–create-namespace
–set image.repository=willdockerhub/nfs-subdir-external-provisioner
–set image.tag=v4.0.2
–set replicaCount=2
–set storageClass.name=nfs-client
–set storageClass.defaultClass=true
–set nfs.server=${ip}
–set nfs.path=/opt/nfsdata
查看
kubectl get pods,deploy,sc -n nfs-provisioner
持续检查
while true
do
kubectl get pods -n nfs-provisioner|grep -q ‘0/1’
if [ $? -ne 0 ];then
echo “nfs-provisioner started”
break
else
echo “nfs-provisioner starting…”
fi
sleep 1
done
任务编排 install-k8s/install-nfs-provisioner/tasks/main.yml
- name: install nfs-provisioner cp
copy: src=nfs-provisioner.sh dest=/tmp/nfs-provisioner.sh - name: install nfs-provisioner
shell: sh /tmp/nfs-provisioner.sh
11)k8s 环境安装编排 roles
install-k8s.yaml - hosts: k8s
remote_user: root
roles:- init
- hosts: k8s
remote_user: root
roles:- install-docker
- hosts: k8s
remote_user: root
roles:- install-k8s
- hosts: master1
remote_user: root
roles:- master-init
- hosts: master1
remote_user: root
roles:- install-cni
- hosts: master2
remote_user: root
roles:- master-join
- hosts: node
remote_user: root
roles:- node-join
- hosts: master1
remote_user: root
roles:- install-ingress-nginx
- hosts: master1
remote_user: root
roles:- install-nfs-provisioner
执行安装
- install-nfs-provisioner
# 可以加上-vvv显示更多信息
ansible-playbook install-k8s.yaml
kubectl get nodes
kubectl get pods -A

12)k8s 环境卸载
install-k8s/uninstall-k8s/files/uninstall-k8s.sh
#!/usr/bin/env bash
expect <<-EOF
spawn kubeadm reset
expect "*y/N*"
send "y\n"
expect eof
EOF
rm -rf /etc/kubernetes/*
rm -fr ~/.kube
rm -fr /var/lib/etcd
任务编排 install-k8s/uninstall-k8s/tasks/main.yaml
- name: uninstall k8s cp
copy: src=uninstall-k8s.sh dest=/tmp/uninstall-k8s.sh
- name: uninstall k8s
shell: sh /tmp/uninstall-k8s.sh
13)k8s 环境卸载编排 roles
uninstall-k8s.yaml
- hosts: k8s
remote_user: root
roles:
- uninstall-k8s
执行卸载
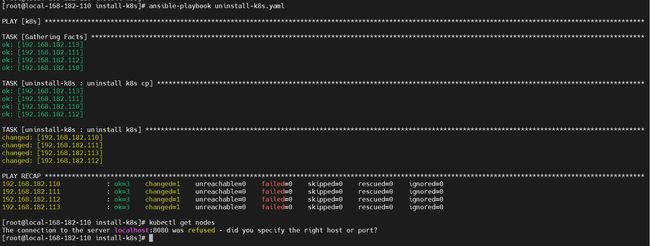
ansible-playbook uninstall-k8s.yaml
其实创建目录结构可以通过ansible-galaxy工具,也可以通过这个工具安装在线别人编排好的包,非常方便的。
这里只是验证了k8s V1.23.6版本的,其它高版本和低版本后续会继续完善验证,还有就是如果执行脚本的话,可以将copy和shell模块并用一个script模块,编排就会变更更简洁,其实script内部也是先copy文件,执行完后会清理。
k8s 一键部署(ansible)就先到这里了,后续会继续完善,增加其它组件和验证其它版本,让部署k8s环境变得更简单方便