Robot Framework 自动化框架 - 定制自己的library
Robot 自动化框架内置提供了一些library,如OperatingSystem(包含一些常用的的文件操作关键字,如copy文件,创建目录),Telent,Screenshot,String,另外还有一些第三提供的library ,比较常用的如SeleniumLibrary,用于Web自动化测试。但如何定制适合自己项目需求的library呢?
- 支持的编程语言
支持的语言包括:Python & Java. Robot框架本身就是有Python开发,理所当然支持Python来实现library。当运行时,选择了Jybot,那么你也可以用Java来实现library。
- Robot框架提供了三种不同的实现library的API
- Static API
这是最简单的方式,实现一个python module,在这个module里面有一些functions,或则在module里面有个python 的类,里面有一些方法。通过Java来实现的话,提供一个Class,里面有些public 的method。当import 这个python module, python class或java class这些method就会自动映射为keyword。
有一点需要注意的是,如何判断一个keyword的状态,当执行这个keyword时,是Pass,还是Fail呢?如果在方法里面抛出了异常,那么这个keyword的状态就是Fail.
下面先来看看之前写的一个library,截取了一段代码:
class RemoveSMDLibrary(RuntimeError):
'''A test library providing keyword for SMLD uninstallation related tasks.
'''
#Test library scope
ROBOT_LIBRARY_SCOPE = 'GLOBAL'
#specifiying library version
ROBOT_LIBRARY_VERSION = '0.2'
ROBOT_EXIT_ON_FAILURE = True
def __init__(self,is_windows=-1):
self._is_windows=is_windows
sys.path.append("MyConfigParser.py")
logger.console('Add MyConfigParser.py file into Python path!')
def get_smdsys_path(self,msg=None):
logger.console('Get smdsys.ini File...')
winsmdsysPath = os.path.expandvars('$systemroot\\smdsys.ini')
nonwinsmdsysPath = "/etc/smdsysV2.ini"
if os.path.isfile(winsmdsysPath):
self._is_windows = 1
self._smdsyspath = winsmdsysPath
elif os.path.isfile(nonwinsmdsysPath):
self._is_windows = 0
self._smdsyspath = nonwinsmdsysPath
if self._is_windows ==-1:
if not msg:
msg="File '%s' does not exist" %winsmdsysPath
raise AssertionError(msg)
def _get_windows_path(self,smdsysPath):
config = ConfigParser()
config.read(smdsysPath)
productPath = config.get("SMDConf","ProductPath")
notesiniPath = config.get("DomSvr0","DomSvr0NotesIniPath")
return productPath,notesiniPath
def _get_nonwindows_path(self,smdsysPath):
config = ConfigParser()
config.read(smdsysPath)
SMDInstanceList = config.get("SMDInstances","SMDInstanceList")
productPath = config.get(SMDInstanceList,"ProductPath")
DomSvr = config.get(SMDInstanceList,"DomSvrISMDSecs")
notesiniPath = config.get(SMDInstanceList,DomSvr)
return productPath,notesiniPath
def get_notesini_path(self):
if self._is_windows == 1:
return self._get_windows_path(self._smdsyspath)
else:
return self._get_nonwindows_path(self._smdsyspath)
当一个Pyhton class中,会忽略以_开头的function,不认为是keyword。
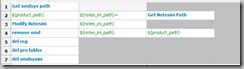
看一下实际应用在ride中如何导入:
因为Python module名和class的名字是一样的,所以可以直接用module名,如果不一样,就需要以这样的格式来导入mymodule.myclass来导入library。看下这个参数,这个参数是传递给构造函数的。
如果你的library导入成功了,那么这些library中的keyword颜色就会变成这样,把鼠标放上去,按ctrl就是出现提示。
2. Dynamic API
在keywords状态,logging和返回值方面,dynamic library API 和static library API是一样的。唯一的不同是Robot Framework如何判别导入的library里面的keywords。static library API是通过反射机制来实现的,dynamic library采用一种特别的方式。
就static library keywords而言,所有的keywords必须在一个class,或modules中。而dynamic library API,你的keywords可以分布在不同的class中。
Dynamic API中必须实现两个方法:run_keyword 和 get_keyword_names,Robot Framework通过这两个方法,得知在library实现了哪些keyword,怎么调用这些keyword.
有个第三方的库JavalibCore,实现了run_keyword和get_keyword_names,用户只需要实现自己的keyword就可以了。这里就不举例子了,建议看javalibcore的源码。
3. Hybrid API
Hybrid library API是间于static API, dynamic API之间的。
和dynamic library API 一样,你需要提供一个get_keyword_names方法,来返回这个library 可以提供的所有keywords的名字。还有一点,Hybrid library API 只适用于Python,对于Java不可以的。
下面之间看一个例子,这个library的实现就是采用的Hybrid API方式。
class Smdauto(RuntimeError):
'''A test library providing keywords for SMLD Automation
'''
ROBOT_LIBRARY_SCOPE = 'GLOBAL'
ROBOT_LIBRARY_VERSION = '0.1'
ROBOT_EXIT_ON_FAILURE = True
def __init__(self):
locator=KeywordsServiceLocator()
#kw={ 'tracefile' : sys.stdout, 'auth' : ( AUTH.httpbasic, 'test1', '111111' ) }
#self._port_type=locator.getKeywords(**kw)
self._port_type=locator.getKeywords()
self._notes_mail = None
self._lib_kws=self._notes_mail_kws=None
def get_keyword_names(self):
return self._get_library_keywords() + self._get_notes_mail_keywords()
def _get_library_keywords(self):
if self._lib_kws is None:
self._lib_kws = [ name for name in dir(self)
if not name.startswith('_') and name != 'get_keyword_names'
and inspect.ismethod(getattr(self, name)) ]
return self._lib_kws
def _get_notes_mail_keywords(self):
if self._notes_mail_kws is None:
notes_mail=self._get_notes_mail()
self._notes_mail_kws=[ name for name in dir(notes_mail)
if not name.startswith('_') and inspect.ismethod(getattr(notes_mail, name)) ]
return self._notes_mail_kws
def __getattr__(self,name):
if name not in self._get_notes_mail_keywords():
raise AttributeError(name)
notes_mail = self._notes_mail is None and self._get_notes_mail() or self._notes_mail
print dir(notes_mail)
return getattr(notes_mail,name)
def _get_notes_mail(self):
return NotesMail()
其实,Hybrid API的实质就是应用Python中委派机制,即__getattr__内置函数,当尝试调用一个不存在的方法时,Python会默认调用__getattr__。
首先,先来看get_keyword_names,这个方法返回了这个libray包含的所有的keywords,它调用了有两个method,第一个返回这个class中所有不是以_开头的方法名,另一个返回一个额外的class中的方法。当执行的method不在这个class中的时候,就会调用__getattr__,从而实现委派调用。