UIView
+ (Class)layerClass;
每个UIView对象都有一个隐式层(underlying layer),即一个 CALayer对象。该方法返回隐式层所属的类。通常为CALayer类型。不建议创建CALayer的子类,如确实需要CALayer子类。需实现该方法,并返回子类的class。
- (id)initWithFrame:(CGRect)frame;
默认的初始化方法。
@property(nonatomic,getter=isUserInteractionEnabled) BOOL userInteractionEnabled;
可以通过[self isUserInteractionEnabled];获取 userInteractionEnabled的值。
默认为yes,表示可以响应事件。设置为no,表示把对象移出响应链,对象不能接受事件,交给下一响应对象。
@property(nonatomic) NSInteger tag;
视图的一个标志。
ps:中介者模式中,可以根据小按钮的tag值来开启/关闭响应的视图。
@property(nonatomic,readonly,retain) CALayer *layer;
每个UIView对象都有一个隐式层,该属性指向隐式层。
----------------------------------------------------------<UIViewGeometry>------------------------------------------------------
@property(nonatomic) CGRect frame;
相对坐标,origin的值是相对于父视图(bounds)而言的。
@property(nonatomic) CGRect bounds;
默认origin的值为0,以视图本身为原点,size和frame相同。
@property(nonatomic) CGPoint center;
相对于父类的中心点。
@property(nonatomic) CGAffineTransform transform;
仿射变换,用来对视图进行2D的转换,如(平移,旋转,缩放)。
比较庆幸的是,使用这个属性并不需要熟悉的理解仿射变换这个数学概念,因为CoreGraphics.framework里的CGAffineTransform.h对几种常用变换进行了封装,可以直接调用。
例如:
image.transform = CGAffineTransformMakeRotation(M_PI);
可使image视图旋转180度。
另,高级的3d旋转,请参见核心动画。
@property(nonatomic) CGFloat contentScaleFactor
据说是“修改contentScaleFactor可以让UIView的渲染精度提高”
实际测试,UIImageView的这个属性值越小,image就被放的越大。
@property(nonatomic,getter=isMultipleTouchEnabled) BOOL multipleTouchEnabled;
默认不实现多点触控,设置为yes开启多点触控。
@property(nonatomic,getter=isExclusiveTouch) BOOL exclusiveTouch;
独占touch事件。视图成为第一响应对象后,得等全部手指离开,否则别的视图不会接受touch事件。(手指不受此影响)
- (UIView *)hitTest:(CGPoint)point withEvent:(UIEvent *)event; // recursively calls -pointInside:withEvent:. point is in the receiver's coordinate system
- (BOOL)pointInside:(CGPoint)point withEvent:(UIEvent *)event; // default returns YES if point is in bounds
关于这几个方法,没有比这篇文章更好的介绍了。
链接如下:
- (CGPoint)convertPoint:(CGPoint)point toView:(UIView *)view;
把本地视图(调用者)下的point(第一参数)转换为指定view(第二参数)的point(返回值);
- (CGPoint)convertPoint:(CGPoint)point fromView:(UIView *)view;
把指定view(第二参数)下的point(第一参数)转化为本地视图(调用者)的point(返回值);
- (CGRect)convertRect:(CGRect)rect toView:(UIView *)view;
- (CGRect)convertRect:(CGRect)rect fromView:(UIView *)view;
道理同上。
@property(nonatomic) BOOL autoresizesSubviews;
是否开启子视图自动布局。默认返回yes,返回no关闭自动布局。
@property(nonatomic) UIViewAutoresizing autoresizingMask;
该属性相对于是父视图而言,即设置该属性并不会影响该视图的子视图。
固,想要设置某个子视图的自动布局,需要修改子视图的UIViewAutoresizing属性。
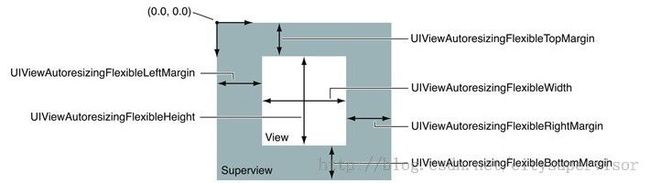
该属性为枚举类型。具体内容如下:
typedef NS_OPTIONS(NSUInteger, UIViewAutoresizing) {
UIViewAutoresizingNone = 0,
UIViewAutoresizingFlexibleLeftMargin = 1 << 0,
UIViewAutoresizingFlexibleWidth = 1 << 1,
UIViewAutoresizingFlexibleRightMargin = 1 << 2,
UIViewAutoresizingFlexibleTopMargin = 1 << 3,
UIViewAutoresizingFlexibleHeight = 1 << 4,
UIViewAutoresizingFlexibleBottomMargin = 1 << 5
};
UIViewAutoresizingNone :这个常量如果被设置,视图将不进行自动尺寸调整。
UIViewAutoresizingFlexibleHeight这个常量如果被设置,视图的高度将和父视图的高度一起成比例变化。否则,视图的高度将保持不变。
UIViewAutoresizingFlexibleWidth这个常量如果被设置,视图的宽度将和父视图的宽度一起成比例变化。否则,视图的宽度将保持不变。
UIViewAutoresizingFlexibleLeftMargin这个常量如果被设置,视图的左边界将随着父视图宽度的变化而按比例进行调整。否则,视图和其父视图的左边界的相对位置将保持不变。
UIViewAutoresizingFlexibleRightMargin这个常量如果被设置,视图的右边界将随着父视图宽度的变化而按比例进行调整。否则,视图和其父视图的右边界的相对位置将保持不变。
UIViewAutoresizingFlexibleBottomMargin这个常量如果被设置,视图的底边界将随着父视图高度的变化而按比例进行调整。否则,视图和其父视图的底边界的相对位置将保持不变。
UIViewAutoresizingFlexibleTopMargin这个常量如果被设置,视图的上边界将随着父视图高度的变化而按比例进行调整。否则,视图和其父视图的上边界的相对位置将保持不变。
该图很直观的表达了枚举的用法
- (CGSize)sizeThatFits:(CGSize)size;
返回最佳尺寸,默认返回self.frame.size。
可以把指定的求最佳尺寸的算法写进该方法,并调用- (void)sizeToFit; 来调该方法。
例如,lable可以用把自文字长度作为返回值,来修改lable的长度。
- (void)sizeToFit;
会调用- (CGSize)sizeThatFits:(CGSize)size; 方法。
-----------------------------------------------------<UIViewHierarchy>---------------------------------------------
@property(nonatomic,readonly) UIView *superview;
指向父视图。
@property(nonatomic,readonly,copy) NSArray *subviews;
存放子视图。
@property(nonatomic,readonly) UIWindow *window;
指向当前窗口。可以用来判断视图是否在窗体中,不在返回nil;
- (void)removeFromSuperview;
从父视图中移出。
- (void)insertSubview:(UIView *)view atIndex:(NSInteger)index;
插入子视图到指定的位置。(就是subviews数组)。
- (void)exchangeSubviewAtIndex:(NSInteger)index1 withSubviewAtIndex:(NSInteger)index2;
交换指定位置的两个视图。
- (void)addSubview:(UIView *)view;
插入子视图。比较常用。
- (void)insertSubview:(UIView *)view belowSubview:(UIView *)siblingSubview;
在siblingSubview下插入视图。
- (void)insertSubview:(UIView *)view aboveSubview:(UIView *)siblingSubview;
在siblingSubview上插入视图。
- (void)bringSubviewToFront:(UIView *)view;
把视图放到最前。
- (void)sendSubviewToBack:(UIView *)view;
把视图放到最后。
ps:子视图本来是并列的关系,那么这个前后关系是什么意思呢?按index插入又有什么意义呢?
答案是,自视图的前后关系体现在显示上,当frame重叠的时候,“前面”的视图会覆盖住“后面”的视图,代码里这个关系表现为,subviews[1]在subviews[0]前面,subviews[0]被subviews[1]覆盖。
- (void)didAddSubview:(UIView *)subview;
- (void)willRemoveSubview:(UIView *)subview;
- (void)willMoveToSuperview:(UIView *)newSuperview;
- (void)didMoveToSuperview;
- (void)willMoveToWindow:(UIWindow *)newWindow;
- (void)didMoveToWindow;
以上方法都会在指定的事件(方法名)发生时被UIKit框架调用。。。
可以通过实现这几个方法,在事件发生的时候执行自己的代码。。。
- (BOOL)isDescendantOfView:(UIView *)view;
是否为某视图的后裔(就是子视图的子视图.......)自己做参数,返回yes。
- (UIView *)viewWithTag:(NSInteger)tag; // recursive search. includes self
查找指定tag的view。
// Allows you to perform layout before the drawing cycle happens. -layoutIfNeeded forces layout early
- (void)setNeedsLayout;
标记视图需要重新布局,会调用layoutSubviews。
- (void)layoutIfNeeded;
看了下外国的博客,大体意思是,有时候,当调用了并不会马上调用layoutSubviews,这时候调用该方法,可以强制发生重新布局。
- (void)layoutSubviews;
子视图布局。
需要子类去实现这个方法。
很多地方会调用这个方法。
-----------------------------------------------------------<UIViewRendering>------------
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect;
重绘。在里定制代码。
- (void)setNeedsDisplay;
- (void)setNeedsDisplayInRect:(CGRect)rect;
调用重绘。
可以参考这篇文章,写的不错。
Phone重绘机制drawRect
@property(nonatomic) BOOL clipsToBounds;
默认返回no,表示视图不会被边框剪切,如果希望视图被边框剪切。可以返回yes;
@property(nonatomic,copy) UIColor *backgroundColor;
背景颜色。
@property(nonatomic) CGFloat alpha;
透明度。在0到1之间,0表示完全透明,1表示完全不透明。透明后移出响应链。
@property(nonatomic,getter=isOpaque) BOOL opaque;
算是一个开关,不准备透明,就用默认值“yes”,会开启系统的优化,提高性能。设置为no,则不会开启优化。
另外, opaque为no的时候,alpha应该设置为1.0。否则结果未定义。
@property(nonatomic) BOOL clearsContextBeforeDrawing;
是否在画图前清除绘图上下文。默认是清除。
在滚动的时候,会进行大量清除操作,会影响效率。一般设置为no;
@property(nonatomic,getter=isHidden) BOOL hidden;
是否隐藏,默认不隐藏返回no,返回yes表示隐藏,不接受事件,不显示。
@property(nonatomic) UIViewContentMode contentMode;
感觉这个属性多用在UIImageView里,有几种显示方式,需不需要拉伸,或填充,自行判断。
@property(nonatomic) CGRect contentStretch NS_DEPRECATED_IOS(3_0,6_0);
6.0被废弃。建议用这个 -[UIImage resizableImageWithCapInsets:] 。主要是做那种能拉长,收缩的图片,类似温度计一样的东西。
---------------------------------------------<。。。。。>------------------
先写这些,剩下的,过些日子再做整理。