2023年第三届陕西省大学生网络安全技能大赛--本科高校组 Reverse题解
文章目录
- 一. 我的upx -d怎么坏了
-
- 1. 查看节区信息
- 2. 动态调试脱壳
- 3.输出迷宫图
- 4.走迷宫
- 二. babypython
-
- 1.字节码简单分析
- 2. gpt分析
- 3. 程序逻辑
- 4.解题脚本
- 三. BadCoffee
-
- 1. 相关文章
- 2.解混淆
- 3.解题脚本
- 四. Web&Assembly(暂时没复现出来,提供一些相关文章)
- 总结
这次比赛做出来三道题,Web&Assembly找到了工具和相关文章,但是时间不太够了hhh,收获还是不少的
一. 我的upx -d怎么坏了
1. 查看节区信息
可以看到节区被修改了,本来应该是UPX被改成了HOEY,试着修改了一下还是不能upx -d,遂选择动调

2. 动态调试脱壳
这里推荐使用吾爱破解专用OD打开,可以很快找到popad这个关键码,x32dbg和ollydbg都不行(不知道是不是指令集的问题或者是什么插件的问题)
打开程序后向上翻大概四五行就可以看到popad,而且这个下面有个调整栈的循环,还有个jmp 0x004012D0的远跳转,所以很可能是oep

脱壳后的文件打开分析,shift+f12查看字符串,可以看到第一行有一串可疑字符串,然后跟进,再对函数按x交叉引用往上面找就可以找到主函数,可以看到是迷宫,并且能看出迷宫是每行15个元素
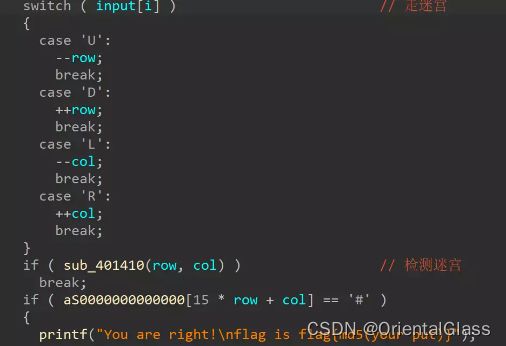
3.输出迷宫图
#include 得到迷宫图:
***************
*S000*0000000**
*0**000*****0**
*0*00*0*000*0**
*000**0*0*0*0**
*0***00*0*0*00*
*0***0**0*0**0*
*000*0*00*00*0*
***0*0******0#*
***0*00000000**
*000********0**
*0***00000*00**
*0*0*****0**0**
*0000000*00000*
***************
4.走迷宫
我以前写过一个走迷宫脚本,稍微修改一下就可以解这题的路径了
C语言实现自动走迷宫 自动输出迷宫路径
修改后:
#include 得到路径:RRRDRRURRRRRRDDDDRDDD,32位小写md5后得到flag
flag{ae2de0be8285f69db701d4dba8721a40}
二. babypython
这题一开始想着能不能将txt里的字节码转成pyc文件的二进制字节码,询问gpt得到的脚本并不行,只能老老实实生啃字节码了(还好有gpt)
使用gpt辅助分析,但是要注意有一部分混淆代码没有实际作用,可以跳过,保留关键代码然后让gpt整合分析
1.字节码简单分析
可以搜索flag快速定位关键代码,关键代码上方有一些初始化操作
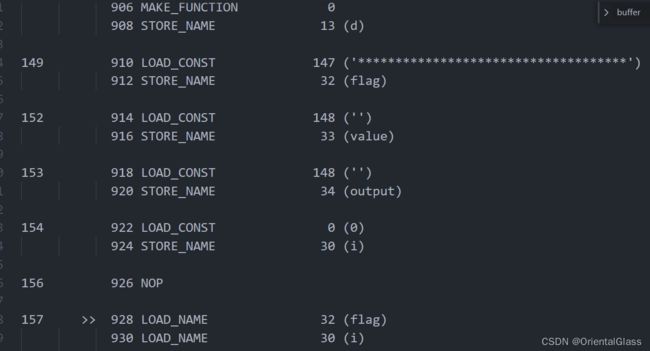
遍历flag,元素异或8保存到value数组

垃圾代码,后面还提示了"This line will never be executed"
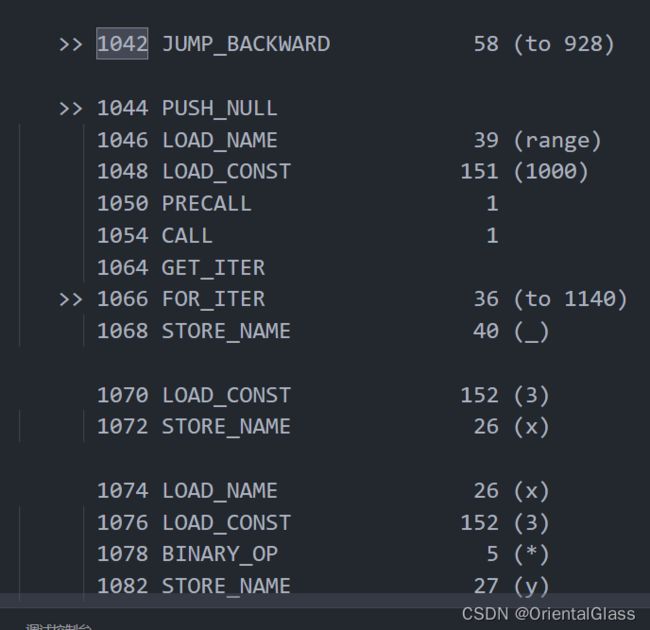
遍历value数组,元素+3
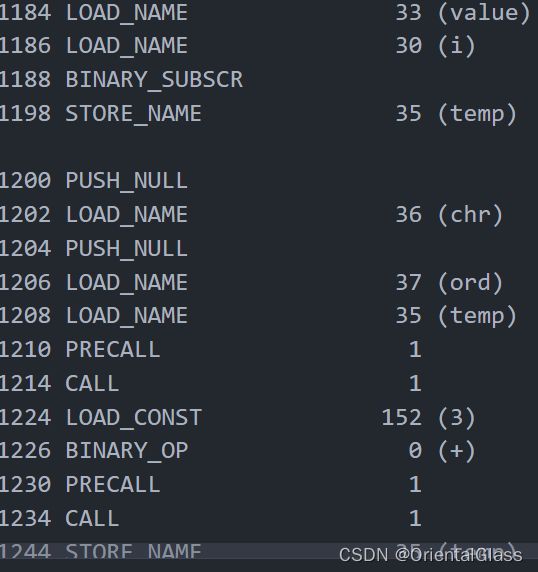
后面还有一些垃圾代码,是无用的操作和一些跳转,像这里是跳转到1362

跳转到最后有base64编码处理(处理完之后字符串还要倒序)

替换字符处理

文件末尾可以看到输出的值
2. gpt分析
这里将字节码中有用的部分截取出来给gpt分析,然后让他给出python代码,再将各个代码段整合就可以得到程序逻辑的结果了

3. 程序逻辑
总之,主要逻辑如下:
- 遍历flag,每个元素和8异或后保存到value中
- 遍历value,每个元素+3后保存到output中
- 对output进行base64编码,然后进行逆序得到obfuscated_output
- 对obfuscated_output中部分字符进行替换
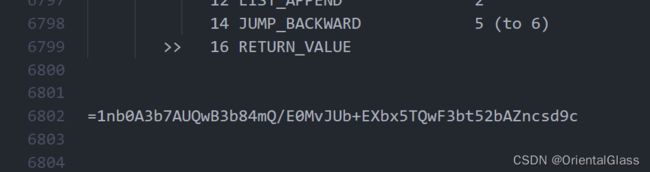
最后输出 =1nb0A3b7AUQwB3b84mQ/E0MvJUb+EXbx5TQwF3bt52bAZncsd9c
import base64
flag = '************************************'
value = ''
output = ''
i = 0
while i < len(flag):
temp = ord(flag[i]) ^ 8
value += chr(temp)
i += 1
for j in range(len(flag)):
temp = ord(value[j]) + 3
output += chr(temp)
obfuscated_output = base64.b64encode(output.encode()).decode()[::-1]
obfuscated_output = obfuscated_output.replace('g', '1').replace('H', '3').replace('W', '9')
print(obfuscated_output)
4.解题脚本
import base64
Encoded= '=1nb0A3b7AUQwB3b84mQ/E0MvJUb+EXbx5TQwF3bt52bAZncsd9c'
Encoded= Encoded.replace('1', 'g').replace('3', 'H').replace('9', 'W')
decoded = base64.b64decode(Encoded[::-1])
for i in decoded:
print(chr((i- 3)^8),end='')
flag{5dcbafe63fbf3b7d8647c1aee650ae9c}
三. BadCoffee
1. 相关文章
这题最开始也看不出是怎么做,然后就到网上查了下js逆向的混淆方法
找到几篇文章:
- 【JavaScript 逆向】AST 技术反混淆
- 使用javascript-obfuscator对js文件进行混淆
不过文章只是简单介绍了一下,并没有给出反混淆的解决方法
2.解混淆
后来找到了工具:
function xxx(_0x53b7bb, _0x590286) {
return _0x53b7bb ^ _0x590286;
}
function enc(_0x4bda4c) {
var _0x8ff1dd = [],
_0x6aca75 = [233, 129, 127, 238, 145, 144, 11, 43, 87, 134, 243, 158, 197, 216, 111, 136, 152, 29, 204, 31, 26, 228, 39, 148, 215, 220, 90, 76, 251, 57, 183, 184, 150, 157, 156, 176, 13, 41, 30, 86, 244, 8];
for (let _0x7bc200 = 0; _0x7bc200 < 42; _0x7bc200++) {
_0x8ff1dd[_0x7bc200] = xxx(_0x6aca75['at'](_0x7bc200), _0x4bda4c["charAt"](_0x7bc200)['charCodeAt']());
}
for (let _0x4f674a = 0; _0x4f674a < 42; _0x4f674a++) {
_0x8ff1dd[_0x4f674a] = xxx(_0x8ff1dd['at'](_0x4f674a), _0x6aca75['at'](41 - _0x4f674a));
}
console["log"](_0x8ff1dd);
return _0x8ff1dd;
}
function fff() {
var _0xe4960c = "flag{xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx}",
_0x55dae6 = enc(_0xe4960c),
_0xbb5ecd = [135, 25, 72, 151, 195, 212, 228, 212, 250, 101, 39, 77, 163, 77, 70, 167, 119, 184, 7, 77, 144, 154, 93, 10, 185, 48, 179, 77, 71, 163, 67, 61, 113, 156, 196, 136, 239, 241, 128, 93, 84, 156];
for (let _0x37df9d = 0; _0x37df9d < 42; _0x37df9d++) {
if (_0x55dae6['at'](_0x37df9d) != _0xbb5ecd['at'](_0x37df9d)) {
console["log"]("Error");
return;
}
}
console["log"]("YES");
return;
}
fff();
3.解题脚本
手动修改变量名和函数美化后的代码:
function xor(a, b) {
return a ^ b;
}
function enc(data) {
var result = [],
buffer = [233, 129, 127, 238, 145, 144, 11, 43, 87, 134, 243, 158, 197, 216, 111, 136, 152, 29, 204, 31, 26, 228, 39, 148, 215, 220, 90, 76, 251, 57, 183, 184, 150, 157, 156, 176, 13, 41, 30, 86, 244, 8];
for (let j = 0; j < 42; j++) {
result[j] =xor(buffer['at'](j), data["charAt"](j)['charCodeAt']());
}
for (let k = 0; k < 42; k++) {
result[k] =xor(result['at'](k), buffer['at'](41 - k));
}
console["log"](result);
return result;
}
function main() {
var flag = "flag{xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx}",
encodeFlag = enc(flag),
data = [135, 25, 72, 151, 195, 212, 228, 212, 250, 101, 39, 77, 163, 77, 70, 167, 119, 184, 7, 77, 144, 154, 93, 10, 185, 48, 179, 77, 71, 163, 67, 61, 113, 156, 196, 136, 239, 241, 128, 93, 84, 156];
for (let i = 0; i < 42; i++) {
if (encodeFlag['at'](i) != data['at'](i)) {
console["log"]("Error");
return;
}
}
console["log"]("YES");
return;
}
main();
很容易看出来是简单的异或和比较操作,解题脚本也很简单:
Encoded = [135, 25, 72, 151, 195, 212, 228, 212, 250, 101, 39, 77, 163, 77, 70, 167, 119, 184, 7, 77, 144, 154, 93, 10, 185, 48, 179, 77, 71, 163, 67, 61, 113, 156, 196, 136, 239, 241, 128, 93, 84, 156]
array = [233, 129, 127, 238, 145, 144, 11, 43, 87, 134, 243, 158, 197, 216, 111, 136, 152, 29, 204, 31, 26, 228, 39, 148, 215, 220, 90, 76, 251, 57, 183, 184, 150, 157, 156, 176, 13, 41, 30, 86, 244, 8]
for i in range(42):
print(chr(Encoded[i]^array[41-i]^array[i]),end='')
flag{I_c0uld_neu3r_undeRstand_jvaVs3rIpt!}
四. Web&Assembly(暂时没复现出来,提供一些相关文章)
- 一步步学习Webassembly逆向分析方法
- WebAssembly/wabt
- WASM逆向分析
- WASM反编译,WASM逆向
- js遇到的wasm的加密
- 一种Wasm逆向静态分析方法
- 1.2.1 生成wasm
总结
- 这次比赛总体感觉很好,比前几天黑盾杯和国赛坐牢要好太多,虽然一些题目没见过,但是在网上查一下就能找到相关文章和工具
- 还要重视理论知识水平,不能做脚本小子,这些题目虽然有现成的工具做,但还是要了解一下相关原理,不然下次变一下就呆住了.例如这个的babypython,以前都是用工具或者脚本直接干pyc文件,这次只能生啃字节码(还好有gpt强大的分析能力),甚至还有很多混淆和跳转代码,也是锻炼到了啃字节码的能力
- 另一方面,个人的经验还是不足,还要继续多做题,多比赛,多复现,勤能补拙


