SpringMVC
SpringMVC
-
-
- SpringMVC
-
- 一、SpringMVC框架简介
- 二、SpringMVC入门案例
- 三、SpringMVC运行流程和配置详解`[重点]`
- 四、请求参数处理
- 五、数据的传递
-
- 5.1 在方法中使用HttpServlet相关对象
- 六、页面的跳转
-
- 6.1 页面`
`标签的作用
- 6.1 页面`
- 七、文件上传
-
- 7.1 文件查看和下载
- 7.2 图片修改
- 八、JSON处理
-
- 8.1 服务器返回JSON数据
- 8.2 客户端提交JSON数据
- 九、RESTful风格
- 十、异常处理
- 十一、拦截器
- 十二、国际化
-
SpringMVC
一、SpringMVC框架简介
使用Servlet遇到的问题:
- 参数的传递,封装成对象
- 类型的转换
- Servlet功能单一,往往需要很多个
- 编码处理
- 文件上传
- 异常处理
- 界面的跳转
- 数据的传递(作用域)
- json的处理
- 与spring框架的整合问题
SpringMVC框架是一个MVC模式的框架,用来实现MVC模式,并且简化了开发过程。
SpringMVC与Struts框架比较:
二、SpringMVC入门案例
POJO:plain object java object Java对象,狭义上指实体类
VO:value object 值对象,用来与界面交互的,接收页面提交的数据封装的对象,将数据传递到页面的封装对象
BO:business object 业务对象,用于service层对象
PO:persist object 持久化对象,用于DAO层
DAO:data access object 数据访问对象,一般就是指的数据库操作层
DTO:data transfer object 数据转换(传输)对象,VO与BO转换,BO与PO转换的类。
步骤:
1、导入依赖
2、编写entity、service、controller
3、编写spring-mvc.xml
4、编写web.xml配置
5、编写jsp文件
6、运行
<dependency>
<groupId>junitgroupId>
<artifactId>junitartifactId>
<version>4.12version>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvcartifactId>
<version>4.3.18.RELEASEversion>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId>
<artifactId>lombokartifactId>
<version>1.18.6version>
<scope>providedscope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servletgroupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-apiartifactId>
<version>3.1.0version>
<scope>providedscope>
dependency>
@Data
public class Users {
private String username;
private String password;
}
@Service
public class UserService {
public boolean login(Users users){
if (users.getUsername().equals("zhangsan") && users.getPassword().equals("123456")){
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
@Controller
public class UserController {
@Resource
private UserService userService;
@RequestMapping("/login") // 该方法的访问路径
@ResponseBody // 将返回的值直接显示在页面上(json)
public String login(Users users){
boolean isLogin = userService.login(users);
if (isLogin){
return "success";
}else{
return "fail";
}
}
}
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.qf.day3">context:component-scan>
<mvc:annotation-driven>mvc:annotation-driven>
<bean id="viewResolver" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/pages/">property>
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp">property>
bean>
beans>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>dispatcherServletservlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServletservlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocationparam-name>
<param-value>classpath:spring-mvc.xmlparam-value>
init-param>
servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>dispatcherServletservlet-name>
<url-pattern>/url-pattern>
servlet-mapping>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
Title
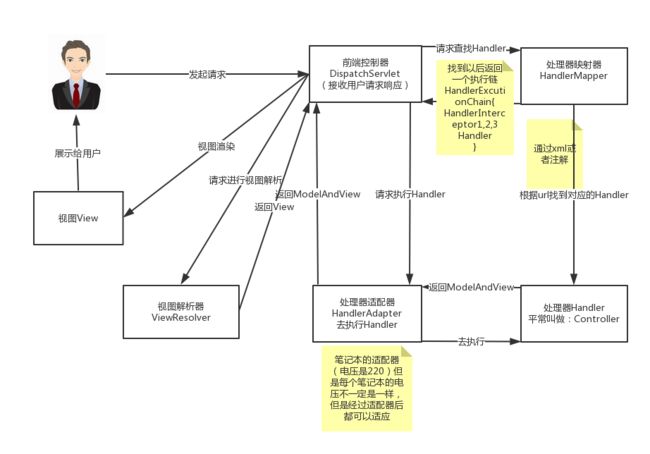
三、SpringMVC运行流程和配置详解[重点]
运行流程:
DispatcherServlet:(核心处理器<中央控制器>)分发,接收所有的用户请求,返回响应。(视图渲染:将数据传递到相应的页面)
HandlerMapping:根据请求路径查找相应的类(Controller)和相应的方法
HandlerAdapter:去执行Handler,调用相应的方法
ViewResolver:视图解析器,解析视图,根据视图名称查找到相应的页面
配置详解:
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.qf.day4">context:component-scan>
<mvc:annotation-driven>mvc:annotation-driven>
<mvc:default-servlet-handler>mvc:default-servlet-handler>
<bean id="viewResolver" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/pages/">property>
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp">property>
bean>
beans>
四、请求参数处理
@RequestMapping 定义请求的url,可以在类上使用,也可以在方法上使用,可以使用GET或POST
在方法上表示给方法添加url,在类上表示给当前类中的所有方法添加url前缀
如果没有写method属性,表示GET和POST都可以提交到该方法中
@GetMapping只能GET方法使用
@PostMapping只能POST方法使用
1、在方法中,使用HttpServletRequest类型的参数,也可以通过getParameter(“”)方法来获取参数,类似之前Servlet用法。
2、可以在方法中直接写参数,用来接收请求参数,要求变量名要与表单元素name属性一致。
3、方法的参数可以不写String类型,会根据情况自动转换类型,但是如果转换类型不成功会出现
400错误。4、实体类属性和方法的参数,如果有有基本数据类型,尽量使用包装类,这样可以接收null值。如果使用基本数据类型,当遇到null值时,会
400错误。5、如果参数类型是Date这类需要提供格式的类型,也无法直接转换,会出现
400错误,需要提供格式。6、可以直接使用实体类的对象来接收表单提交的所有参数,实体类属性的名称需要与表单元素的name一致,如果不能自动转换类型的(日期),需要设定格式。
@RequestMapping("/reg")
// 如果变量名与表单元素name属性一致,可以不写@RequestParam,
// value属性表示表单元素的名称,defaultValue设置默认值,required参数是否必须
public String reg(@RequestParam(value = "username", defaultValue = "1", required = false) String username, String age){
System.out.println(username);
System.out.println(age);
return "success";
}
public String reg(@RequestParam(value = "username", defaultValue = "1", required = false) String username,Integer age, @DateTimeFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd") Date birthday){
System.out.println(username);
System.out.println(age);
System.out.println(birthday);
return "success";
}
@Data
public class Users {
private String username;
private String password;
private Integer age;
@DateTimeFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd") //提交参数时将字符串转换程Date类型
private Date birthday;
}
@RequestMapping("/reg")
public String reg(Users users){
System.out.println(users);
return "success";
}
五、数据的传递
1、可以直接使用requset进行传递数据
@RequestMapping("/reg")
public String reg(Users users, HttpServletRequest request){
System.out.println(users);
request.setAttribute("u", users);
return "success";
}
2、使用Model来传递数据
在SpringMVC框架中,ModelAndView类用来处理视图和模型对象。视图主要用来封装视图名称,模型主要用来保存并传递数据。也可以分开用。
@RequestMapping("/reg")
public String reg(Users users, Model model){
System.out.println(users);
model.addAttribute("u", users);
return "success";
}
3、使用ModelAndView
@RequestMapping("/reg")
public ModelAndView reg(Users users){
ModelAndView mv = new ModelAndView("success"); // 封装视图名称
System.out.println(users);
mv.addObject("u", users); // 传递数据
return mv;
}
4、使用Map传值
@RequestMapping("/reg")
public String reg(Users users, Map<String, Object> map){
System.out.println(users);
map.put("u", users); // 传递数据
return "success";
}
5.1 在方法中使用HttpServlet相关对象
想用哪一个对象,就在方法参数中声明哪个对象。
@RequestMapping("/reg")
public String reg(Users users, HttpServletRequest request,
HttpSession session,
HttpServletResponse response,
PrintWriter out){
System.out.println(users);
return "/success";
}
不使用HttpSession来操作session作用域的办法:
当在类上面添加注解@SessionAttributes({“u”, “users”}),表示在方法中添加数据到request作用域时,会同时添加到session作用域,例如此处的u。
如果在方法中要取得session中的值,可以使用注解@SessionAttribute,如果在没有值的时候来取值,会出错,需要设置属性
required = false。
@SessionAttributes({"u", "users"})
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@RequestMapping("/reg")
public String reg(Users users, Model model){
System.out.println(users);
model.addAttribute("u", users);
return "/success";
}
@RequestMapping("/s")
public String show(@SessionAttribute(name = "u", required = false) Users u){
System.out.println("============" + u);
return "/show";
}
}
六、页面的跳转
1、使用String
@RequestMapping("/reg")
public String reg(Users users, Model model){
System.out.println(users);
model.addAttribute("u", users);
return "/success";
}
2、使用ModelAndView
@RequestMapping("/reg")
public ModelAndView reg(Users users){
ModelAndView mv = new ModelAndView("success"); // 封装视图名称
System.out.println(users);
mv.addObject("u", users); // 传递数据
return mv;
}
3、使用void,默认会将请求路径作为视图名称。例如下面的示例:会将user/s作为视图名称。(不推荐使用)
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@RequestMapping("/s")
public void show(@SessionAttribute(name = "u", required=false) Users u){
System.out.println("============" + u);
}
}
4、也可以使用重定向或请求转发来跳转页面,但是需要将页面的路径写详细,因为此时已经不会走视图解析器的步骤。
思考:通过视图解析器去跳转的路径,是请求转发,还是重定向?请求转发。
问题:在Controller中一个方法调用完毕后,如何继续调用其他方法?
可以在当前方法的返回值中写redirect:或者forward:后面加上需要访问其他的方法的url。流程上将本应该走视图解析器变成重新走一次SpringMVC的运行流程。
@RequestMapping("/s")
public String show(@SessionAttribute(name = "u", required=false) Users u){
System.out.println("============" + u);
return "redirect:/user/reg";
}
SSM整合:
1、以Spring和Mybatis整合为基础。
2、将SpringMVC框架使用加入。
3、在spring-mvc.xml中设置只扫描controller包。
4、在web.xml中添加spring.xml的加载配置信息。
6.1 页面
页面的base标签作用会让当前页面上所有本地静态路径(img、a、link、script)都会自动加上base中的地址,称为基地址。
当使用了base标签后,所有地址需要从根目录开始
[注意:]css和js的引入需要写在base标签的后面。
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
Title

欢迎
七、文件上传
步骤:
1、在form表单中设置enctype=“multipart/form-data”
2、添加相应的第三方库commons-fileupload,commons-io
3、添加相应的文件上传的配置信息,(文件大小、类型等)
4、使用流的形式接收文件(表单中文件的name要与接收时的变量名对应)
注意: spring中的配置bean标签的id必须为multipartResolver,不要随意改动
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-fileuploadgroupId>
<artifactId>commons-fileuploadartifactId>
<version>1.3.2version>
dependency>
<bean id="multipartResolver" class="org.springframework.web.multipart.commons.CommonsMultipartResolver">
<property name="maxUploadSize" value="100000000">property>
<property name="maxUploadSizePerFile" value="10000000">property>
bean>
// 1、使用MultipartHttpServletRequest
@RequestMapping("/add")
public String add(Books books, MultipartHttpServletRequest request){
MultipartFile file = request.getFile("file");
bookService.save(books);
return "redirect:/book/list";
}
// 2、使用MultipartRequest
@RequestMapping("/add")
public String add(Books books, MultipartRequest request){
MultipartFile file = request.getFile("file");
bookService.save(books);
return "redirect:/book/list";
}
// 3、直接使用MultipartFile
@RequestMapping("/add")
public String add(Books books, MultipartFile file) throws IOException {
// 接收了文件后,保存到服务器,并且将名称保存到数据库
if(file.getSize() > 0){
// 生成唯一的图片名称
String name = UUID.randomUUID().toString().replace("-", "");
// 保存到实体
books.setImgPath(name);
// 保存到服务器
file.transferTo(new File(filePath + name));
// 保存真实文件名称
books.setFileName(file.getOriginalFilename());
}
bookService.save(books);
return "redirect:/book/list";
}
7.1 文件查看和下载
@RequestMapping("/show")
public void show(String imgPath, HttpServletResponse response){
File file = new File(filePath + imgPath);
doFile(file, response);
}
@RequestMapping("/download")
public void download(Integer id, HttpServletResponse response){
Books books = bookService.findById(id); // 根据id查询数据
File file = new File(filePath + books.getImgPath()); //得到图片路径
// 通过文件名称设置下载格式
response.setHeader("Content-Disposition", "attachment;filename="+books.getFileName());
doFile(file, response);
}
private void doFile(File file, HttpServletResponse response){
try (
// 表示在finally时会自动判断是否为空并关闭
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
ServletOutputStream outputStream = response.getOutputStream();
){
byte [] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len = fileInputStream.read(buffer)) != -1){
outputStream.write(buffer, 0, len);
}
outputStream.flush();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
7.2 图片修改
一般情况下,如果不修改文件,则不需要上传文件,后台会使用动态sql判断用户是否上传文件来决定是否修改文件字段。
@RequestMapping("/update")
public String update(Books books, MultipartFile file) throws IOException {
// 接收了文件后,保存到服务器,并且将名称保存到数据库
// 如果没有上传图片,则不会执行括号中的代码,数据库操作使用的动态sql,就不会去修改图片相关内容
if(file.getSize() > 0){
// 生成唯一的图片名称
String name = UUID.randomUUID().toString().replace("-", "");
// 保存到实体
books.setImgPath(name);
// 保存到服务器
file.transferTo(new File(filePath + name));
// 保存真实文件名称
books.setFileName(file.getOriginalFilename());
}
bookService.update(books);
return "redirect:/book/list";
}
注意:如果要提交多个文件,可以在表单中写多个文件上传的元素,然后如果名称不同,controller中用多个名称接收(不推荐),如果名称相同,controller中MultipartFile使用数组或者List
格式接收。
八、JSON处理
1、服务器返回一段JSON数据。
2、客户端提交JSON数据给服务器。
8.1 服务器返回JSON数据
Servlet中一般采用out = response.getWrite(); out.write();
SpringMVC中处理办法如下:
1、导入json相关依赖
2、将方法的返回值类型设置为需要转换成JSON的数据类型。
3、在方法上添加@ResponseBody注解。
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.coregroupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databindartifactId>
<version>2.9.7version>
dependency>
@ResponseBody // 将当前方法的返回值转成JSON格式并返回
@RequestMapping(value = "/listJson", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public List<Books> listJson(){
List<Books> list = bookService.findAll();
return list;
}
8.2 客户端提交JSON数据
当客户端在使用AJAX提交数据时,如果没有设置格式为application/json,直接使用看似JSON格式的数据,其实都是application/x-www-form-urlencoded方式提交的,例如:
$(function () {
$.ajax({
"url":"add.do",
// 此处代码也可以写作:"data":"username=zhangsan&password=123456"},
"data":{"username":"zhangsan", "password":"123456"},
"success":function () {
}
});
});
这种写法后台应该使用String username = request.getParameter(“username”);接收数据。
正确的JSON格式传值是按如下方式:
$(function () {
var j = {"username":"zhangsan", "password":"123456"};
$.ajax({
"type":"POST",
"url":"add.do",
"contentType":"application/json",
"data":JSON.stringify(j), // 将json格式转换成字符串
"success":function () {
}
});
});
在servlet中的接收方式:
@WebServlet("/add.do")
public class AddServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
ServletInputStream inputStream = request.getInputStream();
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(inputStream));
String str = null;
StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer();
while ((str = reader.readLine()) != null){
stringBuffer.append(str);
}
System.out.println("stringBuffer:" + stringBuffer);
// 还需要使用JSON来转换成对象
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(req, resp);
}
}
在SpringMVC中接收的方式:使用@RequestBody注解
@PostMapping("/jsonAdd")
public String jsonAdd(@RequestBody Books books){
System.out.println(books);
return "redirect:/book/list";
}
九、RESTful风格
REST,Representational State Transfer,表述性状态传递,是一种软件架构风格(规范),可以降低开发的复杂性,提高系统的可伸缩性。
约定优于配置:在做项目之前进行一些约定,如果遵循约定,可以减少配置。
利用四种请求:GET(查询)、POST(添加)、PUT(修改)、DELETE(删除)
注意:springMVC框架中,使用POST模拟PUT和DELETE,因为表单默认没有PUT和DELETE请求
具体风格如下:比如操作product资源
查询所有: /products GET
根据ID查询:/products/1 GET
添加:/prodcts POST
修改:/prodcts/1 PUT
删除:/prodcts/1 DELETE
// 当项目遇到下面的异常: java.lang.IllegalStateException: No WebApplicationContext found: not in a DispatcherServlet request and no ContextLoaderListener registered? // 不在一个springmvc的标准请求中,并且没有ContextLoaderListener注册 // 错误原因:在页面上使用了spring的标签库,却没有使用springMVC的上下文 // 解决办法:使用springmvc的页面跳转方式跳转到该页面,或者使用ContextLoaderListener注册
<filter>
<filter-name>HiddenHttpMethodFilterfilter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.HiddenHttpMethodFilterfilter-class>
filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>HiddenHttpMethodFilterfilter-name>
<url-pattern>/*url-pattern>
filter-mapping>
@RestController // 表示所有的方法都自动添加@ResponseBody注解
public class ProductController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/products", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String list(){
return "list";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/products", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String add(){
return "add";
}
// 路径变量的特点:一定不能为空
@RequestMapping(value = "/products/{id}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String detail(@PathVariable("id") Integer id){
return "detail=" + id;
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/products/{id}", method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
public String delete(@PathVariable("id") Integer id){
return "delete=" + id;
}
// 路径变量的特点:一定不能为空
@RequestMapping(value = "/products/{id}", method = RequestMethod.PUT)
public String update(@PathVariable("id") Integer id){
return "update=" + id;
}
}
<%@ taglib prefix="form" uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags/form" %>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
Title
十、异常处理
在项目中异常处理原则:
1、如果是业务异常,应该使用自定义异常,并且将该异常从底层(DAO)抛出,然后在能够将信息传递给用户的层(Controller)进行处理(try),并且给用户提示。
2、如果不是业务异常,应该在出现异常的当前层直接处理,处理方式一般是写日志。
在业务层面异常应该有相关的定义:
@Service
public class ProductService {
public void save() throws Exception{
int i = 5;
if(i == 5){
// 消息编码
// 赋予相关的含义:
// 例如:异常级别:+模块编号+分层编号+方法顺序编号+异常编号
// 在业务异常(S)+用户模块(101),的controller层(01),的添加方法(01),的添加失败异常(01)
// S101010101
throw new BussinessExcetion("S101010101");
}
}
}
全局异常处理,Controller中也只需要直接抛出异常
@ControllerAdvice // 全局异常处理,会捕获所有的Controller中抛出的异常
public class AllExceptionHandler {
// 如果此方法在Controller类中,只会捕获当前类出现的异常
@ExceptionHandler
public String doException(Exception ex, Model model){
if (ex instanceof BussinessExcetion){ // 如果该异常是业务异常
model.addAttribute("msg", ex.getMessage());
return "/exception";
}else{
// 写日志
System.out.println("此处写日志");
model.addAttribute("msg", "E1000001");
return "/exception";
}
}
}
十一、拦截器
SpringMVC的拦截器与Servlet中的过滤器作用差不多。但是拦截器的粒度更细,在拦截器中,不仅可以在url对应的方法被调用之前拦截用户的请求,而且还可以在其他的时机来拦截。
<mvc:interceptors>
<mvc:interceptor>
<mvc:mapping path="/qf/**"/>
<bean class="com.qf.test.MyInterceptor">bean>
mvc:interceptor>
mvc:interceptors>
public class MyInterceper implements HandlerInterceptor{
// 在请求执行前拦截
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, Object o) throws Exception {
System.out.println("preHandle");
// 当返回false时,表示拦截请求,不继续执行
return true;
}
// controller中方法执行完毕后
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
Object o, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
System.out.println("postHandle");
}
// 在页面渲染完毕之后执行
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
Object o, Exception e) throws Exception {
System.out.println("afterCompletion");
}
}
十二、国际化
国际化,也叫i18n,指就是用户界面语言可以本地化。
原理:每个语言使用一个配置文件,根据不同的地区语言去加载不同的配置文件,界面所有的文字使用变量表示,该变量是由配置文件加载而来。
<bean id="messageSource" class="org.springframework.context.support.ResourceBundleMessageSource">
<property name="basename" value="locale">property>
bean>
新建相应的properties文件
msg_en.properties
msg.username=username
msg.password=password
msg.submit=login
msg_zh_CN.properties
msg.username=用户名
msg.password=密码
msg.submit=登录
msg_ja.properties
msg.username=ユーザ名
msg.password=パスワード
msg.submit=ログイン
<%@ taglib prefix="spring" uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags" %>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
Title
常见错误:
No WebApplicationContext found: not in a DispatcherServlet request and no ContextLoaderListener registered?
没有找到Spring的上下文:不是在一个SpringMVC流程请求中,并且也没有ContextLoaderListener注册。
出现上面错误的原因是:页面上使用spring的标签,而该标签需要找到配置的国际化文件的名称,该名称在spring-mvc.xml中配置,index.jsp页面的加载是通过web.xml中配置的welcome-file加载的,该加载并非一个SpringMVC的访问请求。
解决方案有两种:
1.将spring的配置文件写出来,通过ContextLoaderListener去加载,并且把国际化的配置配置到spring.xml中。
2.访问index.jsp时通过DispatcherServlet跳转,而不要使用web.xml中的直接加载。