Java笔记_18(IO流)
Java笔记_18
- 一、IO流
-
- 1.1、IO流的概述
- 1.2、IO流的体系
- 1.3、字节输出流基本用法
- 1.4、字节输入流基本用法
- 1.5、文件拷贝
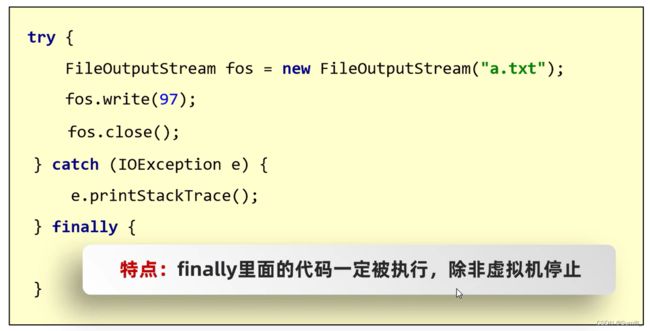
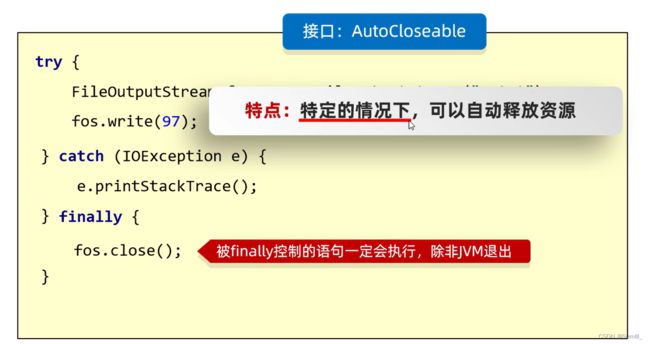
- 1.6、IO流中不同JDK版本捕获异常的方式
- 二、字符集
-
- 2.1、GBK、ASCII字符集
- 2.2、Unicode字符集
- 2.3、为什么会有乱码
- 2.4、Java中编码和解码的代码实现
- 2.5、字符输入流
- 2.5、字符输出流
- 2.6、字符流输入流原理解析
- 2.7、字符流输出流原理解析
- 三、字节流字符流综合案例
-
- 3.1、拷贝文件夹
- 3.2、文件加密
- 3.3、修改文件中的数据
- 四、缓冲流
-
- 4.1、字节缓冲流
- 4.2、字节缓冲流提升效率的原理
- 4.3、字符缓冲流
- 4.4、练习-四种拷问方式效率对比
- 4.5、练习-修改文本顺序
- 4.6、练习-软件运行的次数
- 五、转换流
-
- 5.1、转换流的基本用法
- 5.2、转换流练习
- 六、序列化流/对象操作输出流
-
- 6.1、序列化流/对象操作输出流
- 6.2、反序列化流/对象操作流
- 6.3、练习-读写多个对象
- 七、打印流
-
- 7.1、字节打印流
- 7.2、字符打印流
- 八、压缩流
-
- 8.1、解压缩流
- 8.2、压缩流
- 九、工具包
-
- 9.1、Commons-io
- 9.2、Hutool工具包
一、IO流
1.1、IO流的概述
IO流:存储和读取数据的解决方案
1.2、IO流的体系
1.3、字节输出流基本用法
- 操作本地文件的字节输出流,可以把程序中的数据写到本地文件中。
书写步骤:
- 创建字节输出流对象
- 细节1:参数是字符串表示的路径或者是File对象都是可以的
- 细节2:如果文件不存在会创建一个新的文件,但是要保证父级路径是存在的。
- 细节3:如果文件已经存在,则会清空文件
- 写数据
- 细节: write方法的参数是整数,但是实际上写到本地文件中的是整数在ASCII上对应的字符
- 释放资源
- 每次使用完流之后都要释放资源
FileOutputStream写数据的3种方式:
| 方法名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| void write(int b) | 一次写一个字节数据 |
| void write(byte[ ] b) | 一次写一个字节数组数据 |
| void write(byte[ ] b, int off, int len) | 一次写一个字节数组的部分数据 |
package IO;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Dome2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File f = new File("D:\\Java\\IDEA\\代码文件\\After_pintu_again\\a.txt");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(f);
//第一种写法
fos.write(97);
fos.write(98);
//第二种写法
byte[] bytes = {97,98,99,100,101,102,103};
fos.write(bytes);
//第三种写法
fos.write(bytes,0,6);
}
}
FileOutputStream写数据换行写和续写:
换行:
- Windows操作系用下,换行符是
\r\n - Linux操作系用下,换行符是
\n - Mac操作系统下,换行符是
\r
- 细节:
在windows操作系统当中,java对回车换行进行了优化。虽然完整的是\r\n,但是我们写其中一个\r或者\n,java也可以实现换行,因为java在底层会补全。 - 建议:
不要省略,还是写全了。
续写:
- 如果想要续写,打开续写开关即可开关
- 位置:创建对象的第二个参数
- 默认
false:表示关闭续写,此时创建对象会清空文件 - 手动传递
true:表示打开续写,此时创建对象不会清空文件
- 默认
package IO;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Dome3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*
* Windows操作系用下,换行符是\r\n
* Linux操作系用下,换行符是\n
* Mac操作系统下,换行符是\r
*
*细节:
在windows操作系统当中,java对回车换行进行了优化。虽然完整的是\r\n,
但是我们写其中一个\r或者\n,java也可以实现换行,因为java在底层会补全。
建议:
不要省略,还是写全了。
续写:
* 如果想要续写,打开续写开关即可开关
位置:创建对象的第二个参数
默认false:表示关闭续写,此时创建对象会清空文件
手动传递true:表示打开续写,此时创建对象不会清空文件
* */
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:\\Java\\IDEA\\代码文件\\After_pintu_again\\a.txt"
,true);
String str = "woshiyigeliangzai";
byte[] bytes1 = str.getBytes();
fos.write(bytes1);
String str2 = "\r\n";
byte[] bytes2 = str2.getBytes();
fos.write(bytes2);
String str3 = "666";
byte[] bytes3 = str3.getBytes();
fos.write(bytes3);
fos.close();
}
}
1.4、字节输入流基本用法
操作本地文件的字节输入流,可以把本地文件中的数据读取到程序中来。
书写步骤:
- 创建字节输入流对象
- 如果文件不存在,就直接报错
- 读数据
- 一次读一个字节,读出来的是数据在ASCIl上对应的数字
- 读到文件末尾了,read方法返回-1。
- 释放资源
- 每次使用完流之后都要释放资源
package IO;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Dome4 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("D:\\Java\\IDEA\\代码文件\\After_pintu_again\\a.txt");
//读取第一个数据
int read = fis.read();
System.out.println((char) read);
//读取第二数据
int read1 = fis.read();
System.out.println((char) read1);
//...
int read2 = fis.read();
System.out.println((char) read2);
int read3 = fis.read();
System.out.println((char) read3);
int read4 = fis.read();
System.out.println((char) read4);
//如果当前读取的数据不存在,则会返回-1
int read5 = fis.read();
System.out.println((char) read5);//-1
fis.close();
}
}
FileInputStream循环读取:
- 每执行一次
read()方法,就会移动一次指针
package IO;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Dome5 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("D:\\Java\\IDEA\\代码文件\\After_pintu_again\\a.txt");
while (true) {
//每执行一次read()方法,就会移动一次指针
//所以在代码里面只能进行一次read()方法
int read = fis.read();
if(read==-1){
break;
}
System.out.print((char) read);
}
fis.close();
}
}
1.5、文件拷贝
文件拷贝的基本用法
package IO;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Dome6 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:\\Java\\IDEA\\代码文件\\After_pintu_again\\copy.txt");
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("D:\\Java\\IDEA\\代码文件\\After_pintu_again\\a.txt");
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
while (true){
int read = fis.read();
if(read == -1){
break;
}
fos.write(read);
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
//获取程序运行的时间
System.out.println(endTime-startTime);
//后创建的对象,先结束
fis.close();
fos.close();
}
}
文件拷贝的弊端:
FileInputStream一次读多个字节
| 方法名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public int read() | 一次读一个字节数据 |
| public int read(byte[ ] buffer) | 一次读一个字节数组数据 |
注意: 一次读一个字节数组的数据,每次读取会尽可能把数组装满
package IO;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
//"""
public class Dome8 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("D:\\高数\\讲课视频\\2023-02-17 08-40-40.mkv");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:\\Java\\IDEA\\代码文件\\After_pintu_again\\copy.mkv");
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024*1024*5];
int len;
while ((len = fis.read(bytes))!=-1){
fos.write(bytes,0,len);
}
/*
while (true){
int read = fis.read(bytes);
if(read ==-1){
break;
}
fos.write(bytes,0,read);
}
*/
fos.close();
fis.close();
}
}
1.6、IO流中不同JDK版本捕获异常的方式
- JDK7方案必须要有
AutoCloseable接口
JDK7 抛出异常处理
package IO;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
//"""
public class Dome9_JDK7_try_catch {
public static void main(String[] args){
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024*1024*5];
try (FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("D:\\高数\\讲课视频\\2023-02-17 08-40-40.mkv");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:\\Java\\IDEA\\代码文件\\After_pintu_again\\copy.mkv");
){
int len;
while ((len = fis.read(bytes))!=-1){
fos.write(bytes,0,len);
}
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
JDK9 抛出异常处理
package IO;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
//JDK9 抛出异常练习
public class Dome10_JDK9_try_catch {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024*1024*5];
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("D:\\高数\\讲课视频\\2023-02-17 08-40-40.mkv");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:\\Java\\IDEA\\代码文件\\After_pintu_again\\copy.mkv");
try (fis;fos){
int len;
while ((len = fis.read(bytes))!=-1){
fos.write(bytes,0,len);
}
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
二、字符集
2.1、GBK、ASCII字符集
- GB2312字符集: 1980年发布,1981年5月1日实施的简体中文汉字编码国家标准。收录7445个图形字符,其中包括6763个简体汉字
- BIG5字符集: 台湾地区繁体中文标准字符集,共收录13053个中文字,1984年实施。
- GBK字符集: 2000年3月17日发布,收录21003个汉字。
包含国家标准GB13000-1中的全部中日韩汉字,和BIG5编码中的所有汉字。
Windows系统默认使用的就是GBK。系统显示:ANSI

4. Unicode字符集∶国际标准字符集,它将世界各种语言的每个字符定义一个唯一的编码,以满足跨语言、跨平台的文本信息转换。
计算机的储存规则(汉字)(GBK)
- 汉字两个字节存储
- 高位字节二进制一定以1开头,转成十进制之后是个负数
计算机的储存规则(英文)(GBK)
- 英文一个字节存储,兼容ASCII,二进制前面补0
2.2、Unicode字符集
- 研发方:统一码联盟(也叫Unicode组织)
- 总部位置:美国加州
- 研发时间:1990年
- 发布时间:1994年发布1.0版本,期间不断添加新的文字,
最新的版本是2022年9月13日发布的15.0版本。 - 联盟组成:世界各地主要的电脑制造商、软件开发商、数据库开发商、政府部门、研究机构、国际机构、及个人组成
UTF:Unicode Transfer Format
- UTF-16编码规则:用2~4个字节保存
- UTF-32编码规则:固定使用四个字节保存
- UTF-8编码规则:用1~4个字节保存
- 一个英文占一个字节,二进制第一位是0,转成十进制是正数
- 一个中文占三个字节,二进制第一位是1,第一个字节转成十进制是负数
2.3、为什么会有乱码
如何不产生乱码?
- 不要用字节流读取文本文件
- 编码解码时使用同一个码表,同一个编码方式
2.4、Java中编码和解码的代码实现
Java中编码的方法
| String类中的方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public byte[ ] getBytes() | 使用默认方式进行编码 |
| public byte[] getBytes(String charsetName) | 使用指定方式进行编码 |
Java中解码的方法
| String类中的方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| String(byte[ ] bytes) | 使用默认方式进行解码 |
| String(byte[ ] bytes, String charsetName) | 使用指定方式进行解码 |
package IO_charset;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Dome1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
//编码
String str = "this一行文字";
byte[] bytes1 = str.getBytes();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bytes1));//[116, 104, 105, 115, -28, -72, -128, -24, -95, -116, -26, -106, -121, -27, -83, -105]
byte[] bytes2 = str.getBytes("GBK");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bytes2));//[116, 104, 105, 115, -46, -69, -48, -48, -50, -60, -41, -42]
//解码
//采用相同的规则进行解码
String s1 = new String(bytes1);
System.out.println(s1);//this一行文字
//采用不用的规则进行解码
String s2 = new String(bytes1,"GBK");
System.out.println(s2);//this涓�琛屾枃瀛�
String s3 = new String(bytes2,"GBK");
System.out.println(s3);//this一行文字
}
}
2.5、字符输入流
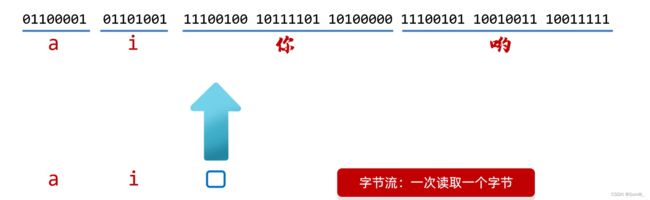
字符流底层其实就是字节流
字符流 = 字节流+字符集
特点:
- 输入流:一次读一个字节,遇到中文时,一次读多个字节
- 输出流:底层会把数据按照指定的编码方式进行编码,变成字节再写到文件中
使用场景
对于纯文本文件进行读写操作
- 创建字符输入流对象
| 构造方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public FileReader(File file) | 创建字符输入流关联本地文件 |
| public FileReader(string pathname) | 创建字符输入流关联本地文件 |
细节1:如果文件不存在,就直接报错
- 读取数据
| 成员方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public int read() | 读取数据,读到末尾返回-1 |
| public int read(char[ ] buffer) | 读取多个数据,读到末尾返回-1 |
细节1:按字节进行读取。遇到中文,一次读多个字节,读取后解码,返回一个整数
细节2:读到文件末尾了, read方法返回-1。
细节3:
- 如果遇到中文就会一次读取多个,GBK一次读两个字节,UTF-8一次读三个字节。
- 在读去之后,方法底层还会进行解码并转成十进制
- 释放资源
| 成员方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public int close() | 释放资源/关流 |
空参read()方法
package IO_charset;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Dome2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建对象
FileReader fr = new FileReader("a.txt");
//循环遍历出文件中的字符
int len;
while ((len=fr.read())!=-1){
System.out.print((char)len);
}
//关流
fr.close();
}
}
带参read()方法
package IO_charset;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Dome3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//定义一个数组,一次性查找3个元素
char[] chars = new char[3];
//定义一个变量来记录数组存储数据的长度
int ch;
FileReader fr = new FileReader("a.txt");
//循环遍历出每一个数据
//read(chars):读取数据,解码,强转三步合并了,把强转之后的字符放到数组当中
//空参的read +强转类型转换
while ((ch = fr.read(chars))!=-1){
//使用系统默认的编码规则
System.out.print(new String(chars,0,ch));
}
fr.close();
}
}
2.5、字符输出流
FileWriter构造方法
| 构造方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public Filewriter(File file) | 创建字符输出流关联本地文件 |
| public Filewriter(String pathname) | 创建字符输出流关联本地文件 |
| public Filewriter(File file,boolean append) | 创建字符输出流关联本地文件,续写 |
| public Filewriter(String pathname,boolean append) | 创建字符输出流关联本地文件,续写 |
成员方法
| 成员方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| void write(int c) | 写出一个字符 |
| void write(String str) | 写出一个字符串 |
| void write(string str, int off, int len) | 写出一个字符串的一部分 |
| void write(char[ ] cbuf) | 写出一个字符数组 |
| void write(char[ ] cbuf, int off, int len) | 写出字符数组的一部分 |
- 创建字符输出流对象
- 细节1:参数是字符串表示的路径或者File对象都是可以的
- 细节2:如果文件不存在会创建一个新的文件,但是要保证父级路径是存在的
- 细节3:如果文件已经存在,则会清空文件,如果不想清空可以打开续写开关
- 写数据
- 细节:如果write方法的参数是整数,但是实际上写到本地文件中的是整数在字符集上对应的字符
- 释放资源
- 每次使用完流之后都要释放资源
package IO_charset;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Dome4 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("a.txt",true);
fw.write("\n这是第六段中文");
char[] chars = {'\n','这','是','第','七','段','中','文'};
fw.write(chars);
fw.write(chars,0,3);
fw.write("\n这是第八段中文",4,4);
fw.write(97);
fw.close();
}
}
2.6、字符流输入流原理解析
-
创建字符输入流对象
底层:关联文件,并创建缓冲区(长度为8192的字节数组)
-
读取数据
底层:
1. 判断缓冲区中是否有数据可以读取
2. 缓冲区没有数据:就从文件中获取数据,装到缓冲区中,每次尽可能装满缓冲区,如果文件中也没有数据了,返回-1
3. 缓冲区有数据:就从缓冲区中读取。
空参的read方法:一次读取一个字节,遇到中文一次读多个字节,把字节解码并转成十进制返回
有参的read方法:把读取字节,解码,强转三步合并了,强转之后的字符放到数组中
2.7、字符流输出流原理解析
| 成员方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public void flush() | 将缓冲区中的数据,刷新到本地文件中 |
| public void close() | 释放资源/关流 |
- flush刷新:刷新之后,还可以继续在文件中写出数据
- close关流:断开通道,无法再往文件中写出数据
package IO_charset;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Dome4 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("a.txt",true);
fw.write("\n这是第六段中文");
char[] chars = {'\n','这','是','第','七','段','中','文'};
fw.write(chars);
fw.flush();
fw.write(chars,0,3);
fw.write("\n这是第八段中文",4,4);
fw.write(97);
fw.close();
}
}
三、字节流字符流综合案例
字节流和字符流的使用场景
- 字节流
- 拷贝任意类型的文件
- 字符流
- 读取纯文本文件中的数据
- 往纯文本文件中写出数据
3.1、拷贝文件夹
package IO_Test;
import java.io.*;
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// aaa
// aac
File f1 = new File("D:\\Java\\IDEA\\代码文件\\After_pintu_again\\aac");
File f2 = new File("D:\\Java\\IDEA\\代码文件\\After_pintu_again\\aad");
CopyFile(f1,f2);
}
public static void CopyFile(File f1,File f2) throws IOException {
f2.mkdirs();
//进入数据源
File[] files = f1.listFiles();
//遍历数组
for (File file : files) {
if (file.isFile()){
//判断文件,拷贝
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(f1);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File(f2,file.getName()));
byte[] bytes = new byte[2];
int len;
while ((len = fis.read(bytes)) != -1){
fos.write(bytes,0,len);
}
fos.close();
fis.close();
}else {
//判断文件夹,递归
CopyFile(file,new File(f2,file.getName()));
}
}
}
}
3.2、文件加密
package IO_Test;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建对象关联原始文件
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("D:\\Java\\IDEA\\代码文件\\After_pintu_again\\src\\IO_Test\\zxc.txt");
//创建对象关联加密文件
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:\\Java\\IDEA\\代码文件\\After_pintu_again\\src\\IO_Test\\asd.txt");
//加密处理
int b;
while ((b=fis.read())!=-1){
fos.write(b^2);
}
fos.close();
fis.close();
}
}
3.3、修改文件中的数据
package IO_Test;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Test3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("D:\\Java\\IDEA\\代码文件\\After_pintu_again\\src\\IO_Test\\aaab.txt");
FileReader fr = new FileReader("D:\\Java\\IDEA\\代码文件\\After_pintu_again\\src\\IO_Test\\aaaa.txt");
//提取出了aaaa里面的数据
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
int len;
while ((len = fr.read())!= -1){
sb.append((char) len);
}
fr.close();
System.out.println(sb);
//排序
Integer[] integers = Arrays.stream(sb.toString()
.split("-"))
.map(Integer::parseInt)
.sorted()
.toArray(Integer[]::new);
//写出
String s = Arrays.toString(integers).replace(", ","-");
String result = s.substring(1,s.length()-1);
System.out.println(result);//1-2-4-7-8-9
fw.write(result);
fw.close();
}
}
方法二:
package IO_Test;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Comparator;
public class Test4 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileReader fr = new FileReader("src\\IO_Test\\aaaa.txt");
//得到字符串
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
int len;
while ((len=fr.read())!=-1){
sb.append((char) len);
}
System.out.println(sb);
//排序
String s = sb.toString();
String[] str = s.split("-");
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (String s1 : str) {
int i = Integer.parseInt(s1);
list.add(i);
}
list.sort((o1,o2)->o1-o2);
System.out.println(list);
//写出
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("src\\IO_Test\\aaab.txt");
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
if (i==list.size()-1){
fw.write( list.get(i)+"");
}else {
fw.write(list.get(i)+"-");
}
}
fw.close();
fr.close();
}
}
四、缓冲流
4.1、字节缓冲流
| 方法名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public BufferedInputstream( InputStream is) | 把基本流包装成高级流,提高读取数据的性能 |
| public BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream os) | 把基本流包装成高级流,提高写出数据的性能 |
package IO.IO_BufferedStream;
import java.io.*;
public class Dome1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建两个缓冲流
BufferedInputStream bip = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("D:\\Java\\IDEA\\代码文件\\After_pintu_again\\src\\IO_Test\\aaaa.txt"));
BufferedOutputStream bop = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("D:\\Java\\IDEA\\代码文件\\After_pintu_again\\src\\IO_Test\\aaab.txt"));
//进行遍历数据
int len;
while ((len = bip.read())!=-1){
bop.write(len);
}
//关流
bop.close();
bip.close();
}
}
- 底层会创建一个8192大的字节数组
4.2、字节缓冲流提升效率的原理
- 缓冲流可以使两个缓冲区的数据来回交换,加快了两边缓冲区的交换速度
4.3、字符缓冲流
| 方法名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public BufferedReader(Reader r) | 把基本流变成高级流 |
| public BufferedWriter(Writer r) | 把基本流变成高级流 |
特有方法:
| 字符缓冲输入流特有方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public string readLine() | 读取一行数据,如果没有数据可读了,会返回null |
| 字符缓冲输出流特有方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public void newLine() | 跨平台的换行 |
package IO.IO_BufferedStream;
import java.io.*;
public class Dome2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("src\\IO_Test\\aaaa.txt"));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("src\\IO_Test\\aaab.txt"));
//一次性输入一行
//String s = br.readLine();
//System.out.println(s);
String s ;
while ((s = br.readLine())!=null){
//输出的时候需要打印换行
bw.write(s);
bw.newLine();
}
bw.close();
br.close();
}
}
4.4、练习-四种拷问方式效率对比
package IO_Test;
import java.io.*;
public class Text5 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
File f1 = new File("src\\IO_Test\\aaaa.txt");
File f2 = new File("src\\IO_Test\\aaab.txt");
method4(f1,f2);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("用了"+ (end - start)+"毫秒");
}
public static void method1(File f1, File f2) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(f1);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(f2);
int len;
while ((len= fis.read())!=-1){
fos.write((char)len);
}
fos.close();
fis.close();
}//用了9931毫秒
public static void method2(File f1,File f2) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(f1);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(f2);
byte[] b = new byte[8129];
int len;
while ((len= fis.read(b))!=-1){
fos.write(b,0,len);
}
fos.close();
fis.close();
}//用了19毫秒
public static void method3(File f1,File f2) throws IOException {
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(f1));
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(f2));
int len;
while ((len=bis.read())!=-1){
bos.write((char)len);
}
bos.close();
bis.close();
}//用了136毫秒
public static void method4(File f1,File f2) throws IOException{
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(f1));
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(f2));
int len;
byte[] b = new byte[8129];
while ((len = bis.read(b))!=-1){
bos.write(b,0,len);
}
bos.close();
bis.close();
}//用了8毫秒
}
4.5、练习-修改文本顺序
package IO_Test;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
public class Test6 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//先获取到文本数据
File f1 = new File("src\\IO_Test\\aaaa.txt");
File f2 = new File("src\\IO_Test\\aaab.txt");
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(f1));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(f2));
//将数据添加到集合中
String line;
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null){
list.add(line);
}
br.close();
//排序
Collections.sort(list, new Comparator<String>() {
@Override
public int compare(String o1, String o2) {
//获取o1和o2的序号
int i1 = Integer.parseInt(o1.split("\\.")[0]);
int i2 = Integer.parseInt(o2.split("\\.")[0]);
return i1-i2;
}
});
//写出来
for (String s : list) {
bw.write(s);
bw.newLine();
}
bw.close();
}
}
4.6、练习-软件运行的次数
- IO流原则:随用随创建,什么时候不用什么时候关闭
package IO_Test;
import java.io.*;
public class Test7 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//count需要声明到外部文件中,每次启用代码都会刷新count值
//引入文件
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("src\\IO_Test\\Test7.txt"));
String s = br.readLine();
int count = Integer.parseInt(s);
count++;
br.close();
//判断count
if (count<=3){
System.out.println("欢迎使用本软件,第"+count+"次使用免费!");
}else {
System.out.println("本软件只能免费试用3次,欢迎您注册会员后继续使用");
}
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("src\\IO_Test\\Test7.txt"));
bw.write(count+"");
bw.close();
}
}
五、转换流
5.1、转换流的基本用法
转换流的名字:
转换输出流:InputStreamReader
转换输入流:OutputStreamWriter
- 是字符流和字节流之间的桥梁
作用:
- 把GBK编码规则的文件在UTF-8的环境中打印出来
package IO.IO_ConverStream;
import java.io.*;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
public class Dome1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*
JDK11之后就淘汰了
把GBK编码规则的文件在UTF-8的环境中打印出来
//"C:\Users\20265\Desktop\ConverDome1.txt"
InputStreamReader isr =new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("C:\\Users\\20265\\Desktop\\ConverDome1.txt"),"GBK");
//得到里面的数据
int len;
while ((len = isr.read())!=-1){
System.out.print((char) len);
}
isr.close();
*/
//JDK11之后使用的方式
FileReader fr = new FileReader(new File("C:\\\\Users\\\\20265\\\\Desktop\\\\ConverDome1.txt"), Charset.forName("GBK"));
//得到里面的数据
int len;
while ((len = fr.read())!=-1){
System.out.print((char) len);
}
fr.close();
}
}
- 利用转换流按照指定字符编码写出
package IO.IO_ConverStream;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
public class Dome2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//利用转换流按照指定字符编码写出
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("C:\\\\Users\\\\20265\\\\Desktop\\\\ConverDome2.txt", Charset.forName("GBK"));
fw.write("你好你好");
fw.close();
}
}
- 将本地里的GBK文件转换成UTF-8文件
package IO.IO_ConverStream;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
public class Dome3 {
package IO.IO_ConverStream;
import java.io.*;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
public class Dome3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*
*
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("src\\IO\\IO_ConverStream\\a.txt"),"GBk");
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("src\\IO\\IO_ConverStream\\b.txt"),"UTF-8");
* */
FileReader fr = new FileReader("src\\IO\\IO_ConverStream\\a.txt", Charset.forName("GBK"));
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("src\\IO\\IO_ConverStream\\b.txt",Charset.forName("UTF-8"));
int len;
while ((len= fr.read())!=-1){
fw.write((char)len);
}
fw.close();
fr.close();
}
}
5.2、转换流练习
- 字节流在读取中文的时候,会出现乱码,但是字符流可以搞定
- 字节流里面是没有读一整行的方法的,只有字符缓冲流才可以搞定
package IO.IO_ConverStream;
import java.io.*;
public class Dome4 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("D:\\Java\\IDEA\\代码文件\\After_pintu_again\\src\\IO_Test\\aaab.txt"));
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr);
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("D:\\Java\\IDEA\\代码文件\\After_pintu_again\\src\\IO\\IO_ConverStream\\b.txt"));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(osw);
String len;
while ((len = br.readLine())!= null){
bw.write(len);
bw.newLine();
}
br.close();
bw.close();
}
}
六、序列化流/对象操作输出流
6.1、序列化流/对象操作输出流
可以把Java中的对象写到本地文件中
| 构造方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public objectoutputStream(Outputstream out) | 把基本流包装成高级流 |
| 成员方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public final void writeobject(object obj) | 把对象序列化(写出)到文件中去 |
- 使用对象输出流将对象保存到文件时会出现
NotSerializableException异常
解决方案: 需要让Javabean类实现Serializable接口
Serializable接口里面没有抽象方法,有标记型接口- 一旦实现了这个接口,那么就表示当前的类可以被序列化
- 相当于物品的合格证
package IO.ObjectStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
public class Dome1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("src\\IO\\ObjectStream\\Dome.txt"));
oos.writeObject(new Student());
oos.close();
}
}
package IO.ObjectStream;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Student implements Serializable {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String toString() {
return "Student{name = " + name + ", age = " + age + "}";
}
}
6.2、反序列化流/对象操作流
可以把序列化到本地文件为对象,读取到程序中来
| 构造方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public objectInputStream(InputStream out) | 把基本流变成高级流 |
| 成员方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public object readobject() | 把序列化到本地文件中的对象,读取到程序中来 |
package IO.ObjectStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
public class Dome2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("src\\IO\\ObjectStream\\Dome.txt"));
Object o = ois.readObject();
System.out.println(o);
ois.close();
}
}
-
固定版本号
- 每次修改JavaBean类时都会使得类的版本号发生改变
- 版本号改变以后反序列化时就会导致运行出错
- 需要在JavaBean类中添加
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
-
transient- 瞬态关键字
- 不会把当前属性序列化到本地文件当中
package IO.ObjectStream;
import java.io.Serial;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Student implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 2955674251672985750L;
private String name;
private int age;
//瞬态变量
//不会把该属性序列化到本地文件中
private transient int number;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age, int number) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.number = number;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public int getNumber() {
return number;
}
public void setNumber(int number) {
this.number = number;
}
public String toString() {
return "Student{name = " + name + ", age = " + age + ", number = " + number + "}";
}
}
6.3、练习-读写多个对象
package IO.ObjectStream;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
Student s1 = new Student("xiaoming",12,1);
Student s2 = new Student("xiaowang",13,2);
Student s3 = new Student("xiaozhang",18,3);
ArrayList<Student> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(s1);
list.add(s2);
list.add(s3);
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("src\\IO\\ObjectStream\\test1.txt"));
oos.writeObject(list);
oos.close();
}
}
package IO.ObjectStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("src\\IO\\ObjectStream\\test1.txt"));
ArrayList<Student> list = (ArrayList<Student>) ois.readObject();
for (Student student : list) {
System.out.println(student);
}
ois.close();
}
}
package IO.ObjectStream;
import java.io.Serial;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Student implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 2955674251672985750L;
private String name;
private int age;
//瞬态变量
//不会把该属性序列化到本地文件中
private transient int number;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age, int number) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.number = number;
}
/**
* 获取
* @return name
*/
public String getName() {
return name;
}
/**
* 设置
* @param name
*/
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
/**
* 获取
* @return age
*/
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
/**
* 设置
* @param age
*/
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
/**
* 获取
* @return number
*/
public int getNumber() {
return number;
}
/**
* 设置
* @param number
*/
public void setNumber(int number) {
this.number = number;
}
public String toString() {
return "Student{name = " + name + ", age = " + age + ", number = " + number + "}";
}
}
七、打印流
- 分类:
- 打印流一般是指: PrintStream,PrintWriter两个类
- 特点1:打印流只操作文件目的地,不操作数据源
- 特点2:特有的写出方法可以实现,数据原样写出
- 例如:
- 打印:97 文件中:97
- 打印: true 文件中: true
- 特点3:特有的写出方法,可以实现自动刷新,自动换行
打印一次数据 = 写出+换行+刷新
7.1、字节打印流
| 构造方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public PrintStream(outputStream/File/String) | 关联字节输出流/文件/文件路径 |
| public PrintStream(String fileName,Charset charset) | 指定字符编码 |
| public PrintStream(Outputstream out,boolean autoFlush) | 自动刷新 |
| public PrintStream(OutputStream out,boolean autoFlush,String encoding) | 指定字符编码且自动刷新 |
- 字节流底层没有缓冲区,开不开自动刷新都一样
| 成员方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public voidwrite(int b) | 常规方法:规则跟之前一样,将指定的字节写出 |
| public void println(Xxx xx) | 特有方法:打印任意数据,自动刷新,自动换行 |
| public void print(xxx xx) | 特有方法:打印任意数据,不换行 |
| public void printf(String format,0bject… args) | 特有方法:带有占位符的打印语句,不换行 |
package IO.IO_printStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintStream;
public class Dome1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream("D:\\Java\\IDEA\\代码文件\\After_pintu_again\\src\\IO\\IO_printStream\\dome1.txt"),true,"UTF-8");
ps.println("你好");
ps.println("world");
ps.print("sdasd");
ps.printf("%d+%d",1,2);
ps.close();
}
}
7.2、字符打印流
| 构造方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public Printwriter(lwlcite/File/string) | 关联字节输出流/文件/文件路径 |
| public Printwriter(String fileName,Charset charset) | 指定字符编码 |
| public Printwriter(write w, boolean autoFlush) | 自动刷新 |
| public Printwriter(oOutputStream out, boolean autoFlush,Charset charset) | 指定字符编码且自动刷新 |
| 成员方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public void write(…) | 常规方法:规则跟之前一样,写出字节或者字符串 |
| public void println(Xxx xx) | 特有方法:打印任意类型的数据并且换行 |
| public void print(Xxx xx) | 特有方法:打印任意类型的数据,不换行 |
| public void printf(String format,object… args) | 特有方法:带有占位符的打印语句 |
package IO.IO_printStream;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
public class Dome2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(new FileWriter("D:\\Java\\IDEA\\代码文件\\After_pintu_again\\src\\IO\\IO_printStream\\dome1.txt"),true);
pw.println("这是一段文字");
pw.print("这是一段文字");
pw.println("这是一段文字");
pw.close();
}
}
- 打印流不操作数据源,只能操作目的地
特殊的打印流:系统的标准输出流
package IO.IO_printStream;
import java.io.PrintStream;
public class Dome {
public static void main(String[] args) {
PrintStream ps = System.out;
ps.println("123");
//当系统打印流关闭时,则无法再次发生打印
ps.close();
ps.println("asdasd");
System.out.println("asdasd");
}
}
八、压缩流
8.1、解压缩流
解压本质: 把每一个ZipEntry按照层级拷贝到本地另一个文件夹中
package IO.IO_zipStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.zip.ZipEntry;
import java.util.zip.ZipInputStream;
public class Dome1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//D:\Java\IDEA\代码文件\After_pintu_again\src\02010110卢盛泽.zip
File f1 =new File("C:\\Users\\20265\\Desktop\\02010110卢盛泽.zip");
File f2 = new File("C:\\Users\\20265\\Desktop\\新建文件夹\\");
GetZip(f1,f2);
}
public static void GetZip(File f1,File f2) throws IOException{
//创建一个解压缩流文件
ZipInputStream zis = new ZipInputStream(new FileInputStream(f1));
ZipEntry n;
while ((n = zis.getNextEntry())!=null){
System.out.println(n);
if (!n.isDirectory()){
//如果是文件夹的处理办法
//需要在目的地创建一个相同的文件夹
File f = new File(f2,n.toString());
f.mkdirs();
}else {
//如果是文件的处理办法
//在目的地创建一个文件
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File(f2,n.toString()));
int b;
while ((b = zis.read())!=-1){
fos.write(b);
}
fos.close();
zis.closeEntry();
}
}
zis.close();
}
}
8.2、压缩流
压缩本质:把每一个(文件/文件夹)看成ZipEntry对象放在压缩包中
- 压缩单个文件
package IO.IO_zipStream;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.zip.ZipEntry;
import java.util.zip.ZipOutputStream;
public class Dome2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//要压缩的文件
File f1 = new File("D:\\Java\\IDEA\\代码文件\\After_pintu_again\\src\\IO\\IO_zipStream\\a.txt");
//压缩到的位置
File f2 = new File("D:\\Java\\IDEA\\代码文件\\After_pintu_again\\src\\IO\\IO_zipStream\\");
toZip(f1,f2);
}
public static void toZip(File f1, File f2) throws IOException {
//创建压缩流,关联压缩包
ZipOutputStream zos = new ZipOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(new File(f2,"a.zip")));
//创建ZipEntry对象,表示压缩包里面的每一个文件和文件夹
ZipEntry entry = new ZipEntry("a.txt");
//把zipEntry对象放到压缩包当中
zos.putNextEntry(entry);
//把f1文件中的数据写道压缩包中
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(f1);
int b;
while ((b = fis.read())!=-1){
zos.write(b);
}
zos.closeEntry();
zos.close();
}
}
- 压缩文件夹
package IO.IO_zipStream;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.zip.ZipEntry;
import java.util.zip.ZipInputStream;
import java.util.zip.ZipOutputStream;
public class Dome3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建一个File,获取想要压缩的文件夹
File src = new File("D:\\Java\\IDEA\\代码文件\\After_pintu_again\\src\\IO\\IO_zipStream\\newBag");
//创建File对象表示压缩包放在哪里(压缩包的父级路径)
File destParent = src.getParentFile();
//创建File对象表示压缩包的路径
File dest = new File(destParent,src.getName()+".zip");
//创建压缩流关联压缩包
ZipOutputStream zos = new ZipOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(dest));
//获取src里面的每一个文件,编程ZipeEntry对象,放入到压缩包中
tozip(src,zos, src.getName());
zos.close();
}
/*
* 作用:获取src里面的每一个文件,变成ZipEntry对象,插入到压缩流当中
* 参数一:数据源
* 参数二:压缩流
* 数据三:压缩包内部的路径
* */
public static void tozip(File src,ZipOutputStream zos,String name) throws IOException {
File[] files = src.listFiles();
for (File file : files) {
if (file.isFile()){
//当判断出是文件时
ZipEntry entry = new ZipEntry(name +"\\" +file.getName().toString());
ZipInputStream zis = new ZipInputStream(new FileInputStream(file));
zos.putNextEntry(entry);
int b;
while ((b=zis.read())!=-1){
zos.write((char)b);
}
zis.close();
zos.closeEntry();
}else {
//当判断出是文件夹时
tozip(file,zos,name+"\\"+file.getName());
}
}
}
}
九、工具包
9.1、Commons-io
Commons-io是apache开源基金组织提供的一组有关IO操作的开源工具包。
作用: 提高IO流的开发效率。
Apache
- 专门为支持开源软件项目而办的一个非盈利的组织
- 成立于1999年,总部设于美国马里兰州
Commons-io使用步骤
- 在项目中创建一个文件夹:lib
- 将jar包复制粘贴到lib文件夹
- 右键点击jar包,选择Add as Library ->点击OK
- 在类中导包使用
| FileUtils类(文件/文件夹相关) | 说明 |
|---|---|
| static void copyFile(File srcFile,File destFile) | 复制文件 |
| static void copyDirectory(File srcDir,File destDir) | 复制文件夹 |
| static void copyDirectoryToDirectory(File srcDir, File destDir) | 复制文件夹 |
| static void deleteDirectory( File directory) | 删除文件夹 |
| static void cleanDirectory(File directory) | 清空文件夹 |
| static String readFileToString(File file,Charset encoding) | 读取文件中的数据变成成字符串 |
| static void write(File file,CharSequence data,string encoding) | 写出数据 |
| IOUtils(流相关) | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public static intlcopy( InputStream input,outputStream output) | 复制文件 |
| public static int copyLarge( Reader input,writer output) | 复制大文件 |
| public static string readLines(Reader input) | 读取数据 |
| public static void write(String data,outputStream output) | 写出数据 |
package IO_Test;
import org.apache.commons.io.FileUtils;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
public class test8 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//复制文件
File f1= new File("a.txt");
File f2 = new File("b.txt");
FileUtils.copyFile(f1,f2);
//清空文件夹
File f3 = new File("D:\\Java\\IDEA\\代码文件\\After_pintu_again\\aac");
FileUtils.cleanDirectory(f3);
//删除文件夹
FileUtils.delete(f3);
//复制文件夹
File f4 = new File("D:\\Java\\IDEA\\代码文件\\After_pintu_again\\aad");
FileUtils.copyDirectory(f4,f3);
//复制带根目录的文件夹
FileUtils.copyDirectoryToDirectory(f4,f3);
}
}
9.2、Hutool工具包
| 相关类 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| IoUtil | 流操作工具类 |
| FileUtil | 文件读写和操作的工具类 |
| FileTypeUtil | 文件类型判断工具类 |
| WatchMonitor | 目录、文件监听 |
| ClassPathResource | 针对ClassPath中资源的访问封装 |
| FileReader | 封装文件读取 |
| FileWriter | 封装文件写入 |
FileUtil类相关方法
| 方法名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| file | 根据参数创建一个file对象 |
| touch | 根据参数创建文件 |
| writeLines | 把集合中的数据写出到文件中,覆盖模式。 |
| appendLines | 把集合中的数据写出到文件中,续写模式。 |
| readLines | 指定字符编码,把文件中的数据,读到集合中。 |
| readUtf8Lines | 按照UTF-8的形式,把文件中的数据,读到集合中 |
| copy | 拷贝文件或者文件夹 |
package IO.hutool;
import cn.hutool.core.io.FileUtil;
import cn.hutool.core.map.LinkedForestMap;
import java.io.File;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Dome1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File f1 = new File("D:\\Java\\IDEA\\代码文件\\After_pintu_again\\b.txt");
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("aaa");
list.add("aaa");
list.add("aaa");
list.add("aaa");
//将集合的数据传入到文件中去(不会覆盖原来的数据)
FileUtil.appendLines(list,f1,"UTF-8");
//将集合的数据写道文件中去(覆盖模式)
FileUtil.writeLines(list,f1,"UTF-8");
//将文件里面的数据按行传入到集合里面
List<String> strings = FileUtil.readLines(f1, "UTF-8");
System.out.println(strings);
//根据参数创建一个文件对象,并且该参数是可变参数,创建文件比较灵活
File f2 = FileUtil.file("D:\\", "Java\\IDEA\\代码文件\\", "After_pintu_again\\c.txt");
FileUtil.appendLines(list,f2,"UTF-8");
//可以直接根据参数创建文件,即便创建的这个文件没有文件夹,该包会自动创建一个文件夹
FileUtil.touch("D:\\Java\\IDEA\\代码文件\\After_pintu_again\\aaa\\ccc\\b.txt");
}
}