第九章:Java集合
第九章:Java集合
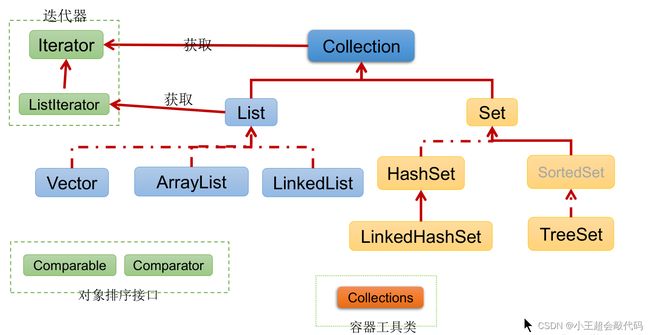
9.1:Java集合框架概述
数组、集合都是对多个数据进行存储(内存层面,不涉及持久化)操作的结构,简称Java容器。
-
数组存储多个数据方面的特点
- 一旦初始化以后,其长度就确定了。
- 数组一旦定义好,其元素的类型也就确定了。我们也就只能操作指定类型的数据了。
-
数组在存储多个数据方面的缺点
- 一旦初始化以后,其长度就不可修改。
- 数组中提供的方法非常有限,对于添加、删除、插入数据等操作,非常不便,同时效率不搞。
- 获取数据中实际元素的个数的需求,数组没有现成的属性或方法可用。
- 数组存储数据的特点:有序、可重复。对于无序、不可重复的需求,不能满足。
-
Java集合可分为Collection和Map两种体系
9.2:Collection接口方法
-
add(Object obj):将元素obj添加到集合中。 -
addAll(Collection coll):将coll集合中的元素添加到当前的集合中。 -
int size():获取添加的元素的个数。 -
void clear():清空集合元素。 -
isEmpty():判断当前集合是否为空。Collection coll = new ArrayList(); coll.add("AA"); coll.add("BB"); coll.add(123);//自动装箱 coll.add(new Date()); System.out.println(coll.size());//4 Collection coll1 = new ArrayList(); coll1.add(456); coll1.add("CC"); coll.addAll(coll1); System.out.println(coll.size());//6 coll.clear(); System.out.println(coll.isEmpty());// true -
boolean contains(Object obj):判断当前集合是否包含obj。 -
boolean containsAll(Collection c):判断形参c中的所有元素是否都存在于当前集合中。Collection coll = new ArrayList(); coll.add(123); coll.add(456); coll.add(new String("Tom")); coll.add(false); boolean contains = coll.contains(123); System.out.println(contains); // true System.out.println(coll.contains(new String("Tom"))); // true Collection coll1 = Arrays.asList(123,4567); System.out.println(coll.containsAll(coll1)); // false注意:如果判断的对象是自定义类,则需要重写
equals()方法。 -
boolean remove(Object obj):从当前集合中移除obj元素。 -
boolean removeAll(Collection coll):从当前集合中移除coll中所有的元素。Collection coll = new ArrayList(); coll.add(123); coll.add(456); coll.add(new String("Tom")); coll.add(false); coll.remove(1234); System.out.println(coll); // [123, 456, Tom, false] Collection coll1 = Arrays.asList(123,456); coll.removeAll(coll1); System.out.println(coll); // [Tom, false] -
boolean retainAll(Collection c):获取当前集合和C集合的交集,并返回给当前集合。Collection coll = new ArrayList(); coll.add(123); coll.add(456); coll.add(new String("Tom")); coll.add(false); Collection coll1 = Arrays.asList(123,456,789); coll.retainAll(coll1); System.out.println(coll); // [123, 456] -
boolean equals(Object obj):想要返回true,需要当前集合和形参集合的元素的相同。Collection coll = new ArrayList(); coll.add(123); coll.add(456); coll.add(new Person("Jerry",20)); coll.add(new String("Tom")); coll.add(false); Collection coll1 = new ArrayList(); coll1.add(456); coll1.add(123); coll1.add(new Person("Jerry",20)); coll1.add(new String("Tom")); coll1.add(false); System.out.println(coll.equals(coll1)); // false -
Object[] toAttay():转成对象数组。 -
hashCode():返回对象的哈希值。 -
iterator():返回Iterator接口的实例,用于遍历集合。Collection coll = new ArrayList(); coll.add(123); coll.add(456); coll.add(new String("Tom")); coll.add(false); System.out.println(coll.hashCode()); // -1579892151 Object[] arr = coll.toArray(); for(int i = 0;i < arr.length;i++){ System.out.print(arr[i] + "\t"); // 123 456 Tom false }
9.3:Iterator迭代器接口
Iterator对象称为迭代器(设计模式的一种),主要用于遍历Collection集合中的元素。
GOF给迭代器模式的定义为:提供一种方法访问一个容器(container)对象中各个元素,而有不需暴露该对象的内部细节。迭代器模式,就是为容器而生。
-
内部方法
-
hasNext():判断是否还有下一个元素。 -
next():指针下移,将下移以后集合位置上的元素返回。Collection coll = new ArrayList(); coll.add(123); coll.add(456); coll.add(new String("Tom")); coll.add(false); Iterator iterator = coll.iterator(); while(iterator.hasNext()){ System.out.print(iterator.next() + "\t"); // 123 456 Tom false }说明:
Iterator仅用于遍历集合,Iterator本身并不提供承装对象的能力。如果需要创建Itertor对象,则必须有一个被迭代的集合。- 集合对象每次调用
iterator()方法到得到一个全新的迭代器对象,默认游标都在集合的第一个元素之前。 - 在调用
next()方法之前必须要调用hasNext()进行检测。若不调用,且下一条记录记录无效,直接调用next()会抛出NoSuchElementException异常。
-
remove():可以在遍历的时候,删除集合中的元素。此方法不同于集合直接调用remove()。Collection coll = new ArrayList(); coll.add(123); coll.add(456); coll.add(new String("Tom")); coll.add(false); Iterator iterator = coll.iterator(); while(iterator.hasNext()) { Object obj = iterator.next(); if("Tom".equals(obj)) { iterator.remove(); } } iterator = coll.iterator(); while(iterator.hasNext()) { System.out.print(iterator.next() + "\t"); // 123 456 false }说明:
Iterator可以删除集合的元素,但是是遍历过程中通过迭代器对象的remove方法,不是集合对象的remove方法。- 如果还为调用
next()或在上一次调用next方法之后已经调用remove方法,再调用remove都会报IllegalStateException。
-
-
使用
foreach循环遍历集合元素Java 5.0提供了foreach循环迭代访问Collection和数组。- 遍历操作不需要获取
Collection或数组的长度,无需使用索引访问元素。 - 遍历集合的底层调用
Iterator完成操作。 foreach还可以用来遍历数组。
Collection coll = new ArrayList(); coll.add(123); coll.add(456); coll.add(new Person("Jerry", 20)); coll.add(new String("Tom")); coll.add(false); //for(集合元素的类型 局部变量 : 集合对象) for(Object obj: coll) { System.out.println(obj); }
9.4:List接口
List集合类中元素有序,且可重复,集合中的每个元素都有其对应的顺序索引。JDK API中List接口的实现类常用的有:ArrayList、LinkedList、Vector。
-
ArrayList源码分析作为
List接口的主要实现类,线程不安全的,效率高,底层使用Object[]存储。-
JDK 7情况下// 空参构造器,底层创建了长度是10的Object[]数组 public ArrayList() { this(10); } // 添加操作 public boolean add(E e) { ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); elementData[size++] = e; return true; } // 判断索引是否超出Object[]的长度 private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) { modCount++; if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0) grow(minCapacity); } // 超出长度进行扩容,且扩容为原来容量的1.5倍,同时需要将原有数组中的数据复制到新的数组中 private void grow(int minCapacity) { int oldCapacity = elementData.length; int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1); if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0) newCapacity = minCapacity; if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity); elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); }说明:建议开发中使用带参的构造器:
ArrayList list = new ArrayList(int capacity) -
JDK 8情况下private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; // 空参构造器,对Object[] 进行初始化 public ArrayList() { this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; } // 添加操作 public boolean add(E e) { ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); elementData[size++] = e; return true; } // 判断是不是第一次进行添加操作 private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) { if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) { minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity); } ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity); } // 判断索引是否超出Object[]的长度 private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) { modCount++; if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0) grow(minCapacity); } // 超出长度进行扩容,且扩容为原来容量的1.5倍,同时需要将原有数组中的数据复制到新的数组中 private void grow(int minCapacity) { int oldCapacity = elementData.length; int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1); if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0) newCapacity = minCapacity; if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity); elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); }
总结:
jdk7中的ArrayList的对象创建类似于单例的饿汉式,而jdk8中的ArrayList的对象创建类似于单例的懒汉式,延迟了数组的创建,节省内存。 -
-
LinkedList的源码分析对于频繁的插入、删除操作,使用此类效率比
ArrayList高,底层使用双向链表存储。transient Node<E> first; transient Node<E> last; // Node定义,体现了LinkedList的双向链表的说法 private static class Node<E> { E item; Node<E> next; Node<E> prev; Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) { this.item = element; this.next = next; this.prev = prev; } } -
Vector源码分析作为
List接口的古老实现类,线程安全的,效率低,底层使用Object[]数组存储。// 空参构造器,底层创建了长度是10的Object[]数组 public Vector() { this(10); } // 添加操作 public synchronized boolean add(E e) { modCount++; ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1); elementData[elementCount++] = e; return true; } // 判断索引是否超出Object[]的长度 private void ensureCapacityHelper(int minCapacity) { if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0) grow(minCapacity); } // 超出长度进行扩容,且扩容为原来容量的2倍,同时需要将原有数组中的数据复制到新的数组中 private void grow(int minCapacity) { int oldCapacity = elementData.length; int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((capacityIncrement > 0) ? capacityIncrement : oldCapacity); if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0) newCapacity = minCapacity; if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity); elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); } -
List接口方法void add(int index, Object ele):在index位置插入ele元素。boolean addAll(int index, Collection eles):从index位置开始将eles中的素有元素添加进来。Object get(int index):获取指定index位置的元素。
ArrayList list = new ArrayList(); list.add(123); list.add(456); list.add("AA"); list.add(new Person("Tom", 12)); list.add(456); System.out.println(list); // [123, 456, AA, Person{name='Tom', age=12}, 456] list.add(1, "BB"); System.out.println(list); // [123, BB, 456, AA, Person{name='Tom', age=12}, 456] List list1 = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3); list.addAll(list1); System.out.println(list.size()); // 9 System.out.println(list.get(0)); // 123int indexOf(Object obj):返回obj在集合中首次出现的位置,集合中没有则返回-1。int lastIndexOf(Object obj):返回obj在当前集合中末次出现的位置,集合中没有则返回-1。Object remove(int index):移除指定的index位置的元素,并返回此元素。Object set(int index, Object ele):设置指定index位置的元素为ele。List subList(int formIndex, int toIndex):返回从fromIndex到toIndex位置的子集合。
ArrayList list = new ArrayList(); list.add(123); list.add(456); list.add("AA"); list.add(new Person("Tom", 12)); list.add(456); int index = list.indexOf(4567); System.out.println(index); // -1 System.out.println(list.lastIndexOf(456)); // 4 Object obj = list.remove(0); System.out.println(obj); // 123 System.out.println(list); // [456, AA, Person{name='Tom', age=12}, 456] list.set(1, "CC"); System.out.println(list); // [456, CC, Person{name='Tom', age=12}, 456] List subList = list.subList(2, 4); System.out.println(subList); // [Person{name='Tom', age=12}, 456] System.out.println(list); // [456, CC, Person{name='Tom', age=12}, 456]
9.5:Set接口
Set接口存储无序的、不可重复的数据。set接口没有提供额外的方法。JDK API中Set接口的实现类常用的有:HashSet、LinkedHashSet、TreeSet。
无序性:不等于随机性。存储的数据在底层数组中并非按照数组索引的顺序添加,而是根据数据的哈希值决定的。
不可重复性:保证添加的元素按照equals()判断时,不能返回true。即:相同的元素只能添加一个。
-
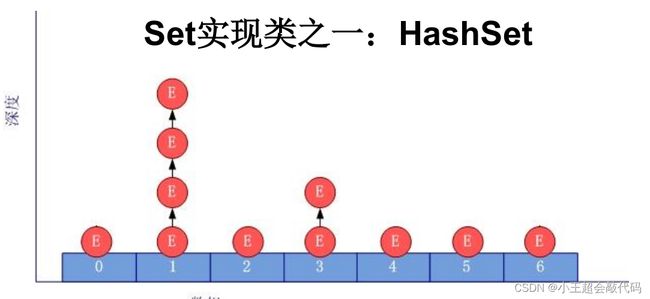
HashSet作为
Set接口的主要实现类:线程不安全的,可以存储null值。-
添加元素的过程
- 我们向
HashSet中添加元素a,首先调用元素a所在类的hashCode()方法,计算机元素a的哈希值,此哈希值接着通过某种算法计算出HashSet底层数组中的存放位置(即为:索引位置)。 - 判断数组此位置上是否已经有元素。
- 如果此位置上没有其他元素,则元素a添加成功。
- 如果此位置上有其他元素b(或以链表形式存在的多个元素),则比较元素a与元素b的
hash值。 - 如果
hash值不相同,则元素a添加成功, - 如果
hash值相同,进而需要调用元素a所在类的equals()方法。 equals()返回true,元素a添加失败。equals()返回false,则元素a添加成功。
注意:对于索引位置已有元素然后还添加成功的而已,元素a与已经存在指定索引位置上数据以链表的方式存储。
- 我们向
-
-
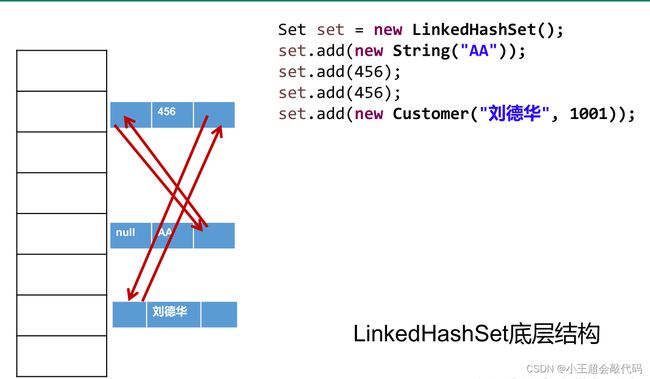
LinkedHashSet 作为
HashSet的子类,遍历其内部数据时,可以按照添加的顺序遍历。在添加数据还维护了两个引用,记录此数据前一个数据和后一个数据,对于频繁的遍历操作,LinkedHashSet效率高于HashSet。
-
TreeSet-
TreeSet底层使用红黑树结构存储数据。 -
向
TreeSet中添加的数据,要求是相同的对象。 -
TreeSet可以确保集合元素处于排序状态。就必须得实现Comparable或者Comparator。 -
在比较两个对象是否相同的标准为:
compareTo()或者compare()返回0,不再是equals()。
-
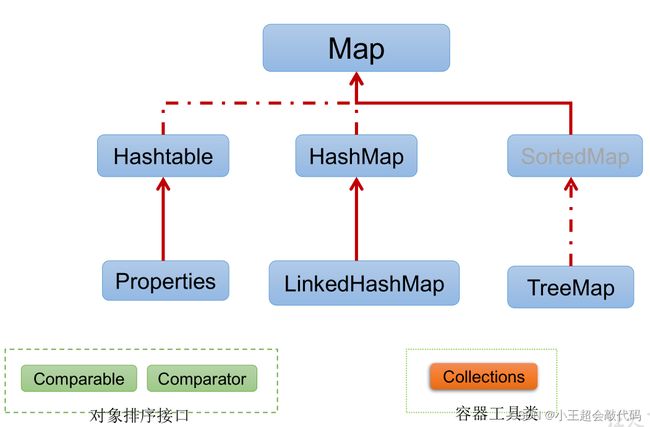
9.6:Map接口
map与Collection并列存在。用于保存具有映射关系的数据。Map存储的是双列数据,存储key-value对的数据。Map中的**key用Set来存放,不允许重复**,即同一个Map对象所对应的类,须重写hashCode()和equals()方法。Map接口的常用实现类:HashMap、TreeMap、LinkedHashMap和Properties。
-
HashMap作为
Map的主要实现类:线程不安全,效率高,能存储null的key和value。-
Map结构的理解Map中的key:无序的、不可重复的,使用Set存储所有的key。Map中的value:无序的、可重复的,使用Collection存储所有的value。Map中的entry:key-value构成了一个Entry对象。无序的,不可重复的,使用Set存储所有的entry。
-
HashMap的底层实现原理-
jdk 7HashMap map = new HashMap(); // 实例化以后,底层创建了长度是16的一维数组Entry[] table map.put(key1, value1);- 首先,调用
key1所在类的hashCode()计算key1哈希值,此哈希值经过某种算法计算以后,得到在Entry数组中的存在位置。 - 如果此位置上的数据为空,此时的
key1-value添加成功。 - 如果此位置上的数据不为空,比较
key1和已经存在的一个或多个数据的哈希值。 - 如果
key1的哈希值与已经存在的数据的哈希值都不相同,此时key1-value1添加成功。 - 如果
key1的哈希值和已经存在的某一个数据key2-value2的哈希值相同,继续比较,调用key1所在类类的equals(key2)方法。 - 如果
equals()返回false,此时key-value添加成功。 - 如果
equals()返回true,使用value1替换value2。
// HashMap的默认容量 static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16; // HashMap的默认加载因子 static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f; // 扩容的临界值(容量 * 加载因子) final float loadFactor; // 空参构造器 public HashMap() { this(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR); } // 初始化数组 public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) { // 不执行此处3个if if (initialCapacity < 0) // 最大容量是不是小于0 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: "+initialCapacity); if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) // 最大容量是不是超出范围 initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY; if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor)) // 扩容临界值是不是小于0,或者没有初始化 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " + loadFactor); int capacity = 1; // capacity循环完为16 while (capacity < initialCapacity) capacity <<= 1; // this.loadFactor = 0.75 this.loadFactor = loadFactor; // threshold = 12 threshold = (int)Math.min(capacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1); // 初始化Entry数组的长度为16 table = new Entry[capacity]; useAltHashing = sun.misc.VM.isBooted() && (capacity >= Holder.ALTERNATIVE_HASHING_THRESHOLD); init(); } // 添加数据方法 public V put(K key, V value) { // 判断key是否为null if (key == null) return putForNullKey(value); // 获取key的哈希值 int hash = hash(key); // 获取在table数组中存放的位置 int i = indexFor(hash, table.length); // 看table数组位置上是否有数据 for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) { Object k; // 判断哈希值是否相等,如果相等判断equals是否为true if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) { V oldValue = e.value; e.value = value; e.recordAccess(this); return oldValue; } } modCount++; addEntry(hash, key, value, i); return null; } // 判断table是否需要扩容,如果需要扩容,则长度扩容2倍 void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) { if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) { resize(2 * table.length); hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0; bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length); } createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex); } // 把数据添加到HashMap中 void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) { Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex]; table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e); size++; } - 首先,调用
-
jdk 8new HashMap():底层没有创建一个长度为16的数组。jdk 8底层的数组是:Node[],而非Entry[]。- 首次调用
put()方法时,底层创建长度为16的数组。 jdk 8中底层结构:数组+链表(七上八下)+红黑树。- 当数组中的某一个索引位置上的元素以链表形式存在的数据个数 > 8 且当前数组的长度 < 64时,此时此索引位置上的数据改为使用红黑树存储。
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f; tatic final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // Bucket中链表长度大于该默认值,转为红黑树 static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8; // 桶中的Node被数化时最小的hash表容量 static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64; // 空参构造器 public HashMap() { this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR; } // 添加数据方法 public V put(K key, V value) { return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true); } final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent, boolean evict) { Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i; // 判断是否为第一次添加数据 if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) n = (tab = resize()).length; // 判断添加数据在数组的位置是否为空 if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null) tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null); else { Node<K,V> e; K k; // 判断数组不为空的位置第一个元素与添加元素哈希值是否相等,如果相等判断equals是否为true if (p.hash == hash && ((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) e = p; else if (p instanceof TreeNode) // 判断数据是否为红黑树的方式存储 e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value); else { for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) { // 判断数组不为空的位置后面是否还有元素 if ((e = p.next) == null) { p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null); if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // 把链表变为红黑树存储 treeifyBin(tab, hash); break; } // 判断数组不为空的位置里的元素与添加元素哈希值是否相等 // 如果相等判断equals是否为true if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) break; p = e; } } // 看是否有元素的哈希值一样与equals方法也为true if (e != null) { V oldValue = e.value; if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null) e.value = value; afterNodeAccess(e); return oldValue; } } ++modCount; if (++size > threshold) resize(); afterNodeInsertion(evict); return null; } // 第一次添加数据或者扩容 final Node<K,V>[] resize() { Node<K,V>[] oldTab = table; int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length; int oldThr = threshold; int newCap, newThr = 0; // 此if执行else if (oldCap > 0) { ..... } else if (oldThr > 0){ ..... } else { // newCap = 16, newThr = 12 newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY; newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY); } // 此if不执行 if (newThr == 0) { .... } // threshold = 12 threshold = newThr; // 初始化table数组,长度为16 @SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"}) Node<K,V>[] newTab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[newCap]; table = newTab; // 此if不执行 if (oldTab != null) { ..... } return newTab; } final void treeifyBin(Node<K,V>[] tab, int hash) { int n, index; Node<K,V> e; // 链表长度大于8并且小于64 if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) < MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY) resize(); else if ((e = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) { TreeNode<K,V> hd = null, tl = null; do { TreeNode<K,V> p = replacementTreeNode(e, null); if (tl == null) hd = p; else { p.prev = tl; tl.next = p; } tl = p; } while ((e = e.next) != null); if ((tab[index] = hd) != null) hd.treeify(tab); } }
-
-
-
LinkedHashMap
LinkedHashMap是HashMap的子类。 保证在遍历
map元素时,可以按照添加的顺序实现遍历。在原有的HashMap底层结构基础上,添加了一对指针,指向前一个和后一个元素。对于频繁的遍历操作,此类执行效率高于HashMap。final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent, boolean evict) { if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null) // LinkedHashMap重写了newNode方法 tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null); else { ... } } // 重写的newNode方法 Node<K,V> newNode(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> e) { LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p = new LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>(hash, key, value, e); linkNodeLast(p); return p; } // LinkedHashMap中的Entry static class Entry<K,V> extends HashMap.Node<K,V> { Entry<K,V> before, after; Entry(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) { super(hash, key, value, next); } } -
Map接口的常用方法Object put(Object key, Object value):将指定key-value添加到(或修改)当前map对象中。void putAll(Map m):将m中的所有key-value对存放到当前map中。Object remove(Object key):移除指定key的key-value对,并返回value。void clear():清空当前map中的所有数据。
Map map = new HashMap(); map.put("AA", 123); map.put(45, 123); map.put("BB", 56); map.put("AA", 87); System.out.println(map); // {AA=87, BB=56, 45=123} Map map1 = new HashMap(); map1.put("CC", 123); map.put("DD", 123); map.putAll(map1); System.out.println(map); // {AA=87, BB=56, DD=123, CC=123, 45=123} Object value = map.remove("CC"); System.out.println(value); // 123 System.out.println(map); // {AA=87, BB=56, DD=123, 45=123} map.clear(); System.out.println(map.size()); // 0 System.out.println(map); // {}Object get(Object key):获取指定key对应的value。boolean containsKey(Object key):是否包含指定的key。boolean containsValue(Object value):是否包含指定的value。int size():返回map中key-value对的个数。boolean isEmpty():判断当前map是否为空、boolean equals(Object obj):判断当前map和参数对象Object是否相等。
Map map = new HashMap(); map.put("AA", 123); map.put(45, 123); map.put("BB", 56); System.out.println(map.get(45)); // 123 boolean isExist = map.containsKey("BB"); System.out.println(isExist); // true isExist = map.containsValue(123); System.out.println(isExist); // true map.clear(); System.out.println(map.isEmpty()); // trueSet keySet():返回所有key构成的Set集合。Collection values():返回所有value构成的Collection集合。Set entrySet():返回所有key-value对构成的Set集合。
Map map = new HashMap(); map.put("AA", 123); map.put(45, 1234); map.put("BB", 56); Set set = map.keySet(); Iterator iterator = set.iterator(); while(iterator.hasNext()) { System.out.print(iterator.next() + "\t"); // AA BB 45 } System.out.println(); Collection values= map.values(); for(Object obj: values) { System.out.print(obj + "\t"); // 123 56 1234 } System.out.println(); Set entrySet = map.entrySet(); Iterator iterator1 = entrySet.iterator(); while(iterator1.hasNext()) { Object obj = iterator1.next(); Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry) obj; System.out.print(entry.getKey() + "-" + entry.getValue() + "\t"); // AA-123 BB-56 45-1234 } System.out.println(); Set keySet = map.keySet(); Iterator iterator2 = keySet.iterator(); while(iterator2.hasNext()) { Object key = iterator2.next(); Object value = map.get(key); System.out.print(key + "=" + value + "\t"); // AA=123 BB=56 45=1234 } -
TreeMap-
保证按照添加的
key-value对进行排序,实现排序遍历。此时考虑key的自然排序或定制排序。 -
TreeSet底层使用红黑树结构存储数据。‘ -
TreeMap的key必须实现Comparable或者Comparator接口。 -
TreeMap判断两个key相等的标准:两个key通过compareTo()方法或者compare()方法返回0。
-
-
PropertiesProperties的父类是Hashtable,是古老的实现类,线程安全的,效率低,不能存储null的key和value。Properties常用来处理配置文件。key和value都是String类型。Properties pros = new Properties(); pros.load(new FileInputStream("jdbc.properties")); String user = pros.getProperty("user"); System.out.println(user);
9.7:Collections工具类
Collections是一个操作Set、List、Map等集合的工具类。
-
排序操作
reverse(List):反转List中元素的顺序。shuffle(List):对List集合元素进行随机排序。sort(List):根据元素的自然顺序对指定List集合元素按升序排序。sort(List, Comparator):根据指定的Comparator产生的顺序对List集合元素进行排序。swap(List, int, int):将指定list集合中的i处元素和j处元素进行交换。
-
查找、替换
-
Object max(Collection):根据元素的自然顺序,返回给定集合中的最大元素。 -
Object max(Collection, Comparator):根据Comparator指定的顺序,返回给定集合中的最大元素。 -
Object min(Collection):根据元素的自然顺序,返回给定集合中的最小元素。 -
Object min(Collection, Comparator):根据Comparator指定的顺序,返回给定集合中的最小元素。 -
int frequency(Collection, Object):返回指定集合中指定元素的出现次数。 -
void copy(List dest, List src):将src中的内容复制到dest中。注意:
dest的长度要大于等于src的长度,不然会报错。 -
boolean replaceAll(List list, Object oldVal, Object newVal):使用新值替换List对象的所有旧值。
Collections类中提供了多个synchronizedXxx()方法,该方法可使将指定集合包装成线程同步的集合,从而可以解决多线程并发访问集合时的线程安全问题。 -
-
EnumerationEnumeration接口是Iterator迭代器的"古老版本"。Enumeration stringEnum = new StringTokenizer("a-b*c-d-e-g", "-"); while(stringEnum.hasMoreElements()){ Object obj = stringEnum.nextElement(); System.out.print(obj + "\t"); // a b*c d e g }