数据结构之二叉树(Java)
在这里先说明一下,结点和节点其实一样的,无须关注这个。
一、树型结构
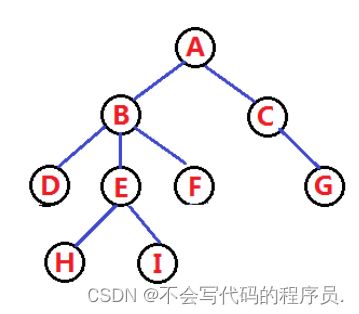
1. 概念:树是一种非线性的数据结构,它是由n个有限节点组成一个具有层次关系的集合。
如上图所示,把此种数据结构称作树是因为它看起来像一个倒挂的树。
2. 特点
- 有一个特殊的节点,称为根节点,它是唯一没有前驱节点的节点。
- 除根节点以外,其余节点被分为P个互不相交的集合;每一个集合又是一个与树类似的子树。每个子树只有一个前驱,可以任意个后继(有限个)。】
- 子树之间是不能有交集的,否则就不是树型结构。
- 树是递归定义的。
3. 基本重要概念
- 节点的度:一个节点含有子树的个数(其实就是一个节点下边连线的条数)。
- 树的度:一棵树中,所有节点度的最大值。
- 叶子节点(终端节点):度为0的节点(其实就是下边没连线的节点)。
- 双亲结点(父节点):若一个节点含有子节点,则这个节点称为子节点的父节点(就是某个节点它上边连线的节点)。
- 孩子节点(子节点):一个节点含有的子树的根节点就称为该节点的子节点(也就是一个节点下边连线的节点)。
- 根节点:一棵树中,没有双亲结点的节点(其实就是最上面的节点)。
- 节点的层次:从根开始定义,跟为第一层,根的子节点为第二层,以此类推。
- 树的高度(树的深度):树中节点的最大层次。
- 非终端节点(分支节点):度不为0的节点(也就是下边还有连线的节点)。
- 兄弟节点:具有相同父节点的节点(也就是某几个节点上边连线连到的是同一个节点,那么这几个节点就是兄弟节点)。
- 堂兄弟节点:双亲在同一层的节点。
- 节点的祖先:从根到该结点所经分支上的所有结点。
- 子孙:以某节点为根的子树中任一结点都称为该节点的子孙。
- 森林:有m棵互不相交的树组成的集合称为森林<注意m是大于等于0的>
二、二叉树
(1) 概念
一颗二叉树是节点的一个有限集合:该集合可能为空;可能是由一个根节点加上两棵分别称为左子树和右子树的二叉树组成
通过以上几张图片,可以看出二叉树的一些特点。
树的度不能超过2;树是有左树和右树之分的。
(2) 特殊树
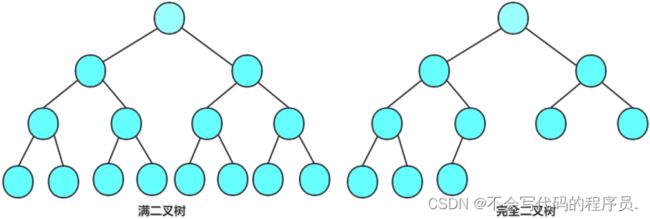
1. 满二叉树:一棵树中,每层次的结点都达到了最大值。
2. 完全二叉树:一棵树中,结点从最后一层最后一个开始依次减少就称为完全二叉树。
满二叉树是一种特殊的完全二叉树。
(3)性质
1. 若规定根节点的层数是1,则一棵树的结点总数是:(2的n次方)减1。
2. 若规定根节点的层数是1,则一棵树某层的结点书是:2的(n-1)次方。
3. 对任意一棵二叉树,如果其叶结点个数为n0,度为0的非叶节点个数为n2,则有n0 = n2 +1。
对上述结果进行推断:如果有一个二叉树,假设其结点的总数n,叶子节点的个数为n0,度为1的结点个数为n1,度为2的结点个数为n2,可得公式 n = n2 + n1 + n0
节点的总数为n,因此其边的数量就是n-1,根据二叉树的图想象一下,其叶子节点下边的连线数量是为0的,度为1的节点下边的连线数量是为1的,度为2的节点其下边的连线数量是为2的,因此可得公式 n - 1 = 2 * n2 + n1
根据上述公式就可得到结果。
4. 求对具有n个节点的完全二叉树的层次:log下以2为底,以n+1为真数向上取整。
5. 对于具有n个节点的完全二叉树,如果按照从上至下,从左至右的顺序对所有节点从0开始编号,那么对于序号为 i 的节点有:
- 对于 i 节点的左孩子是:2 i + 1,如果(2i+1)< n,那么无左孩子。
- 对于 i 节点的右孩子是:2 i + 2,如果(2i+2)< n,那么无右孩子。
- 对于 i = 0,那么其是根节点。
- 对于 i 节点的双亲结点是:(i - 1)/ 2。
6. 对于完全二叉树,如果其有奇数个节点:那么其度为1的节点不存在;如果其有偶数个节点,那么其度为1的节点有且只有一个。
7. 对于二叉树性质的一些题目:
- 某二叉树中共有399个节点,其中有199个度为2的节点,则该二叉树中的叶子节点数为() 此题直接根据公式 n0 = n2 + 1 直接可得:n0 = 200。
- 在具有2n个节点的完全二叉树中,叶子节点个数为() 此题也很简单,直接根据性质6可得:其度为1的节点是1,然后根据 n0 = n2 + 1 得出结论,其结果是 n + 1。
- 一个具有767个节点的完全二叉树,其叶子节点个数为() 根据题目得无度为1的节点,因此 n0 + n2 = n0 + n0 - 1 = 767,得结果是384。
- 一棵完全二叉树的节点个数为531个,那么这棵树的高度是() 直接根据公式就求出结论再向上取整可得:log 2 (531 + 1)= 10。
(4)二叉树存储
顺序存储和链表的链式存储都是二叉树的存储结构;下边的代码都以孩子表示法来写。
//孩子表示法中存储的是数据域,左孩子与右孩子的结点。
public class TreeNode {
int val; //数据域
TreeNode left; //左孩子的引用
TreeNode right; //右孩子的引用
}
//孩子双亲表示法中存储的是数据域,左孩子,右孩子与当前节点的根节点。
public class TreeNode {
int val; //数据域
TreeNode left; //左孩子的引用
TreeNode right; //右孩子的引用
TreeNode parent; //当前节点的根节点
}(5)二叉树的遍历
1. 前序遍历:根、左子树、右子树
2. 中序遍历:左子树、根、右子树
3. 后序遍历:左子树、右子树、根
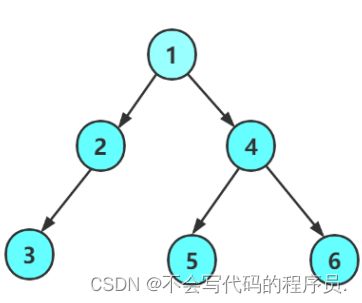
如图所示,当遍历完 1 ,也就是根之后;会向左子树走,也就是遍历 2 ,而 2 也是子树的根;经过子树的根之后,再往左子树走,遍历到 3 ,3 也是一棵子树的根;再往 3 的左树走,发现不存在;这时就会向右子树走;发现右子树不存在,就会返回到 3;而3相当于是 2 的左子树,因此会向 2 的右子树走,而右子树也不存在;这时就会返回 1 ;再向 1 的右子树走....
上述是前序遍历,对于中序和后序遍历就不过多赘述,接下来就是树中的一些基本操作。
(6)二叉树的基本操作
在这些基本操作之前,先构建一个节点以及一个模拟一棵树来测试数据
public class My_BinaryTree {
//构建一个节点
public static class TreeNode{
public int val;//数据域
public TreeNode left;//左孩子
public TreeNode right;//右孩子
public TreeNode(int val){
this.val = val;
}
}
//构建一棵树
public TreeNode createTree() {
TreeNode a = new TreeNode(1);
TreeNode b = new TreeNode(2);
TreeNode c = new TreeNode(3);
TreeNode d = new TreeNode(4);
TreeNode e = new TreeNode(5);
TreeNode f = new TreeNode(6);
TreeNode g = new TreeNode(7);
a.left = b;
a.right = c;
b.left = d;
b.right = e;
c.left = f;
c.right = g;
return a;
}
}-
前序遍历的递归操作和非递归操作
//递归的前序遍历
public void preOrder(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return ;
}
System.out.print(root.val + " ");
preOrder(root.left);
preOrder(root.right);
}
//非递归的前序遍历
public void preOrder(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return ;
}
//非递归的前序遍历利用栈来做,后进先出
Deque stack = new LinkedList<>();
TreeNode cur = root;
while(cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while(cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.val + " ");
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.left;
}
TreeNode top = stack.pop();
cur = top.right;
}
} -
中序遍历的递归操作和非递归操作
//递归的中序遍历
public void inorder(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return ;
}
inorder(root.left);
System.out.print(root.val + " ");
inorder(root.right);
}
//非递归的中序遍历
public void inorder(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return ;
}
Deque stack = new LinkedList<>();
TreeNode cur = root;
while(cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while(cur != null) {
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.left;
}
TreeNode top = stack.pop();
System.out.print(top.val + " ");
cur = top.right;
}
} -
后序遍历的递归与非递归操作
//递归的后序遍历
public void postOrder(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return ;
}
postOrder(root.left);
postOrder(root.right);
System.out.print(root.val + " ");
}
//非递归的后序遍历
public void postOrder(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return ;
}
Deque stack = new LinkedList<>();
TreeNode cur = root;
TreeNode pre = null;
while(cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while(cur != null) {
stack.push(cur);
cur =cur.left;
}
TreeNode top = stack.peek();
if(top.right == null || top.right == pre) {
System.out.print(top.val + " ");
stack.pop();
pre = top;
}else {
cur = top.right;
}
}
} -
层序遍历
//层序遍历
public void levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
Deque queue = new LinkedList<>();
if(root == null) {
return ;
}
queue.offer(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode cur = queue.poll();
System.out.print(cur.val +" ");
if(cur.left != null) {
queue.offer(cur.left);
}
if(cur.right != null) {
queue.offer(cur.right);
}
}
} -
获取树中结点的个数
//获取树中节点的个数
//第一种方法
public int size(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return 0;
}
int leftSize = size(root.left);
int rightSize = size(root.right);
return leftSize+rightSize+1;
}
//第二种方法
public int nodeSize = 0;
public void size(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return ;
}
nodeSize++;
size(root.left);
size(root.right);
}-
获取树中叶子节点的个数
// 获取叶子节点的个数
//第一种方法
public int getLeafNodeCount(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return 0;
}
if(root.left == null && root.right == null) {
return 1;
}
int leftLeaf = getLeafNodeCount(root.left);
int rightLeaf = getLeafNodeCount(root.right);
return leftLeaf + rightLeaf;
}
//第二种方法
private int leafNodeSize = 0;
public void getLeafNodeCount(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return ;
}
if(root.left == null || root.right == null) {
leafNodeSize++;
}
getLeafNodeCount(root.left);
getLeafNodeCount(root.right);
}-
获取第k层结点的个数
// 获取第K层节点的个数
public int getKLevelNodeCount(TreeNode root,int k) {
if(root == null) {
return 0;
}
if(k == 1) {
return 1;
}
int leftLeveNode = getKLevelNodeCount(root.left,k-1);
int rightLeveNode = getKLevelNodeCount(root.right,k-1);
return leftLeveNode + rightLeveNode;
}-
获取二叉树的高度
// 检测值为value的元素是否存在
TreeNode find(TreeNode root, int val) {
if(root == null) {
return null;
}
if(root.val == val) {
return root;
}
TreeNode leftFind = find(root.left,val);
if(leftFind != null) {
return leftFind;
}
TreeNode rightFind = find(root.right,val);
if(rightFind != null) {
return rightFind;
}
return null;
}-
判断一棵树是不是完全二叉树
// 判断一棵树是不是完全二叉树
public boolean isCompleteTree(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return true;
}
Deque queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode cur = queue.poll();
if(cur != null) {
queue.offer(cur.left);
queue.offer(cur.right);
}else {
break;
}
}
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode cur = queue.poll();
if(cur != null) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
} 三、oj题
1. 144. 二叉树的前序遍历 - 力扣(LeetCode)
public List preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List list = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null){
return list;
}
//非递归的前序遍历利用栈来做,后进先出
Deque stack = new LinkedList<>();
TreeNode cur = root;
while(cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while(cur != null) {
list.add(cur.val);
//System.out.print(cur.val + " ");
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.left;
}
TreeNode top = stack.pop();
cur = top.right;
}
return list;
} 2. 94. 二叉树的中序遍历 - 力扣(LeetCode)
public List inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List list = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null) {
return list;
}
Deque stack = new LinkedList<>();
TreeNode cur = root;
while(cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while(cur != null) {
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.left;
}
TreeNode top = stack.pop();
list.add(top.val);
//System.out.print(top.val + " ");
cur = top.right;
}
return list;
} 3. 145. 二叉树的后序遍历 - 力扣(LeetCode)
public List postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List list = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null) {
return list;
}
Deque stack = new LinkedList<>();
TreeNode cur = root;
TreeNode pre = null;
while(cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while(cur != null) {
stack.push(cur);
cur =cur.left;
}
TreeNode top = stack.peek();
if(top.right == null || top.right == pre) {
//System.out.print(top + " ");
list.add(top.val);
stack.pop();
pre = top;
}else {
cur = top.right;
}
}
return list;
} 4. 102. 二叉树的层序遍历 - 力扣(LeetCode)
//层序遍历()
public List> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
//先把需要返回的定义好
List> list = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null) {
return list;
}
Deque queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
//返回大数组中的小数组
List cur = new ArrayList<>();
while(size != 0) {
TreeNode top = queue.poll();
cur.add(top.val);
if(top.left != null) {
queue.offer(top.left);
}
if(top.right != null) {
queue.offer(top.right);
}
size--;
}
list.add(cur);
}
return list;
} 5. 100. 相同的树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
//判断两棵树是否相同
//条件:不仅两棵树的结构相同,其值也得相同
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
//首先判断是不是两棵树的结构是否不相同:不相同就返回false
if((p == null && q != null)||(p != null && q == null)) {
return false;
}
//结构相同,然后判断是否为空,空也算值相同
if(p == null && q == null) {
return true;
}
//再判断其值是否相同
if(p.val != q.val) {
return false;
}
return isSameTree(p.left,q.left) && isSameTree(p.right,q.right);
}6. 572. 另一棵树的子树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
//判断一棵树是不是另一棵树的子树
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
//首先判断是不是两棵树的结构是否不相同:不相同就返回false
if((p == null && q != null)||(p != null && q == null)) {
return false;
}
//结构相同,然后判断是否为空,空也算值相同
if(p == null && q == null) {
return true;
}
//再判断其值是否相同
if(p.val != q.val) {
return false;
}
return isSameTree(p.left,q.left) && isSameTree(p.right,q.right);
}
//判断q树是不是p树的子树
public boolean isSubtree(TreeNode root, TreeNode subRoot) {
//利用了两棵树是不是相同来做
if(isSameTree(root,subRoot)) {
return true;
}
if(root == null) {
return false;
}
if(isSubtree(root.left,subRoot)) {
return true;
}
if(isSubtree(root.right,subRoot)) {
return true;
}
return false;
}7. 226. 翻转二叉树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
//翻转二叉树
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return null;
}
TreeNode swap = root.left;
root.left = root.right;
root.right = swap;
invertTree(root.left);
invertTree(root.right);
return root;
}8. 110. 平衡二叉树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
// 获取二叉树的高度
public int getHeight(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return 0;
}
int leftHeight = getHeight(root.left);
int rightHeight = getHeight(root.right);
return (leftHeight > rightHeight) ? (leftHeight + 1) : (rightHeight + 1);
}
//求是不是平衡树,运用了求二叉树高度的方法
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return true;
}
int size = getHeight(root.left) - getHeight(root.right);
if(size > 1 || size < -1) {
return false;
}
boolean leftBalance = isBalanced(root.left);
boolean rightBalance = isBalanced(root.right);
return leftBalance && rightBalance;
}9. 101. 对称二叉树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
//对于对称二叉树的求解:其实归根结底就是先将二叉树的左右子树翻转
//判断左右子树是否相等即可
//不过需要使用到另外两个方法,因此需要对代码熟练掌握才可以将此题完整做出
//判断两棵树是否相同
//条件:不仅两棵树的结构相同,其值也得相同
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
//首先判断是不是两棵树的结构是否不相同:不相同就返回false
if((p == null && q != null)||(p != null && q == null)) {
return false;
}
//结构相同,然后判断是否为空,空也算值相同
if(p == null && q == null) {
return true;
}
//再判断其值是否相同
if(p.val != q.val) {
return false;
}
return isSameTree(p.left,q.left) && isSameTree(p.right,q.right);
}
//翻转二叉树
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return null;
}
TreeNode swap = root.left;
root.left = root.right;
root.right = swap;
invertTree(root.left);
invertTree(root.right);
return root;
}
//对称二叉树
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null || (root.left == null && root.right == null)) {
return true;
}
invertTree(root.right);
return isSameTree(root.left,root.right);
}10. 二叉树遍历_牛客题霸_牛客网 (nowcoder.com)
import java.util.Scanner;
// 注意类名必须为 Main, 不要有任何 package xxx 信息
//构建一棵树
class TreeNode {
public char val;
public TreeNode left;
public TreeNode right;
public TreeNode(char val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
public class Main {
//主函数
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
// 注意 hasNext 和 hasNextLine 的区别
while (in.hasNextLine()) { // 注意 while 处理多个 case
String s = in.nextLine();
TreeNode root = createTree(s);
inorder(root);
}
}
public static int i = 0;
//根据前序遍历创建一棵树
public static TreeNode createTree(String str) {
TreeNode root = null;
if(str.charAt(i) != '#') {
root = new TreeNode(str.charAt(i));
i++;
root.left = createTree(str);
root.right = createTree(str);
}else {
i++;
}
return root;
}
//中序遍历
public static void inorder(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return ;
}
inorder(root.left);
System.out.print(root.val + " ");
inorder(root.right);
}
}11. 236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先 - 力扣(LeetCode)
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(root == null) {
return null;
}
if(root == p || root == q) {
return root;
}
TreeNode leftRet = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q);
TreeNode rightRet = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q);
if(leftRet != null && rightRet != null) {
return root;
}else if(leftRet != null) {
return leftRet;
}else if(rightRet != null) {
return rightRet;
}
return null;
}