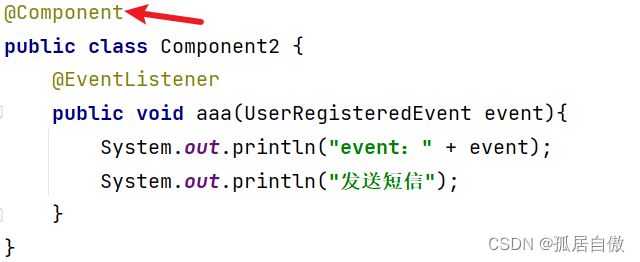
- 2025React岗位前端面试题180道及其答案解析,看完稳了,万字长文,持续更新....
祈澈菇凉
前端
1.什么是React?它的主要特点是什么?答案解析:React是一个用于构建用户界面的JavaScript库,主要用于构建单页应用。其主要特点包括:组件化:React应用由多个可重用的组件组成,便于管理和维护。虚拟DOM:React使用虚拟DOM提高性能,通过最小化实际DOM操作来优化渲染过程。单向数据流:数据在组件之间以单向流动的方式传递,简化了数据管理和调试。声明式编程:React允许开发者以
- 书籍-《优化基础:理论、工具及应用(论文版)》
机器学习人工智能
书籍:OptimizationEssentials:Theory,Tools,andApplications作者:FaizHamid出版:Springer编辑:陈萍萍的公主@一点人工一点智能下载:书籍下载-《优化基础:理论、工具及应用(论文版)》01书籍介绍本书探讨了运筹学和数学优化领域的最新发展和令人兴奋的挑战。它以统一且精心编排的方式呈现了以下内容:(a)现实生活中出现的新颖优化问题,并突出每
- numpy学习笔记10:arr *= 2向量化操作性能优化
宁宁可可
#机器学习#Python基础与进阶numpy学习笔记
numpy学习笔记10:arr*=2向量化操作性能优化在NumPy中,直接对整个数组进行向量化操作(如arr*=2)的效率远高于显式循环(如foriinrange(len(arr)):arr[i]*=2)。以下是详细的解释:1.性能差异的原理(1)底层实现不同显式循环(错误示范):Python的for循环是解释执行的,每次迭代需要动态解析变量类型、执行函数调用等操作。对每个元素的操作会触发多次Py
- Python前端开发
PITSU
正则表达式htmlcss3mysql
Python前端开发1.前端三剑客(HTML,CSS和JavaScript)1.1HTML1.1.1HTML简介HyperTextMark-upLanguage,指的是超文本标记语言;html是开发网页的语言;html中的标签大多数都是成对出现的,格式:1.1.2HTML结构第一行是文档声明部分HTML:分为页头,页身和页脚。标签大部分是成对出现1.1.3第一行文档声明部分HTML在vscode中
- java毕业设计,在线水果商城系统
爱编程的小哥
java毕设java课程设计springbootvue
天天生鲜在线商城系统技术解密|SpringBoot+Vue3企业级实战(附高并发场景解决方案)一、系统全景解读该系统是生鲜电商全流程解决方案,采用SpringBoot3+Vue3+ElementPlus技术栈,覆盖商品管理、智能分类、订单处理、用户画像等核心场景,通过RBAC权限控制+OSS图片存储+高并发库存管理三大技术亮点,日均支撑5000+商品、10万+订单的电商需求。系统以蓝白清新界面+实
- AIGC与教育行业的邂逅--其在数学领域的应用与实现
想成为高手499
AIGC
引言在数学教学中,教师往往需要大量的时间准备练习题和答案解析,而学生则需要定制化的练习来满足不同的学习需求。AIGC技术可以通过自动生成数学题目、定制化学习内容、即时反馈等方式,极大地提升数学学习的效率与质量。本文将深入探讨AIGC在数学领域的几种应用场景,并通过Python代码展示具体实现方式。1.自动生成数学题目与解析数学题目生成是AIGC在数学教学中的主要应用之一。通过生成不同难度和类型的题
- springboot整合mybatis分页插件不生效问题
潘 令
springbootmybatisjava后端
原因分析做项目时发现导入分页插件的场景启动器后,分页插件不生效,一直查询出所有数据上网搜索发现分页插件不生效主要有以下原因:1、没有导入分页插件的场景启动器,而是导入了普通的分页插件依赖com.github.pagehelperpagehelper5.1.10导入该依赖后还需要进行额外的配置1).在MyBatis配置xml中配置拦截器插件<propertyname="param1&
- 用LangChain构建自愈式生成式AI:颠覆传统知识库的智能问答系统实战
煜bart
机器人人工智能pythonAI编程
引言:当生成式AI遇到自进化架构ChatGPT的惊艳表现让企业意识到生成式AI的潜力,但传统问答系统仍面临数据孤岛、知识更新滞后等痛点。本文将揭秘如何通过LangChain框架构建具有自进化能力的智能问答系统,实现企业知识库的实时动态更新与智能推理。通过本文,您将掌握一套让AI系统在运行中持续学习、自主优化的创新架构。---##一、核心技术突破###1.1自愈式数据管道(Self-healingP
- Python在人工智能与机器人开发中的应用与实践
一键难忘
python人工智能机器人
Python在人工智能与机器人开发中的应用与实践Python已经成为人工智能和机器人开发的主要编程语言之一,凭借其简洁的语法、强大的库支持和广泛的社区资源,Python为开发者提供了一个高效且易于学习的平台。在这篇文章中,我们将深入探讨如何使用Python进行人工智能(AI)和机器人开发,并通过实际代码示例展示核心技术和应用。1.Python在人工智能中的应用人工智能(AI)领域的核心任务包括机器
- nginx性能优化有哪些方式?
企鹅侠客
linux面试nginx性能优化php
0.运维干货分享软考高级系统架构设计师备考学习资料软考高级网络规划设计师备考学习资料KubernetesCKA认证学习资料分享信息安全管理体系(ISMS)制度模板分享免费文档翻译工具(支持word、pdf、ppt、excel)PuTTY中文版安装包MobaXterm中文版安装包pinginfoview网络诊断工具中文版Nginx是一个高性能的HTTP服务器和反向代理服务器,但在高并发场景下,仍然有
- 疯狂python讲义学习日志06——异常处理
静笃归心方得平和心气
Python学习日志异常处理python学习python笔记python速成
疯狂python讲义学习日志06——异常处理引言1异常处理机制1.1使用try...except处理异常1.2异常类的继承体系1.3多异常捕获1.4访问异常信息1.5else块1.6使用finally回收资源2使用raise处理异常2.1引发异常2.2自定义异常类2.3except和raise同时使用3.python的异常传播轨迹4.异常处理规则4.1不要过度使用异常4.2不要忽略异常引言异常机制
- 计算机专业毕业设计题目推荐(新颖选题)本科计算机科学专业相关毕业设计选题大全✅
会写代码的羊
毕设选题课程设计计算机网络毕设选题毕设系统毕设题目计算机科学专业
文章目录前言最新毕设选题(建议收藏起来)本科计算机科学专业相关的毕业设计选题毕设作品推荐前言2025全新毕业设计项目博主介绍:✌全网粉丝10W+,CSDN全栈领域优质创作者,博客之星、掘金/华为云/阿里云等平台优质作者。技术范围:SpringBoot、Vue、SSM、HLMT、Jsp、PHP、Nodejs、Python、爬虫、数据可视化、小程序、大数据、机器学习等设计与开发。主要内容:免费功能设计
- 集成学习(Ensemble Learning)基础知识1
代码骑士
#机器学习集成学习机器学习人工智能
文章目录一、集成学习1、基本概念2、回顾:误差的偏差-方差分解3、为什么集成学习有效?4、基学习器:“好而不同”5、集成学习的两个基本问题(1)如何训练出具有差异性的多个基学习器?(2)如何将多个基学习器的预测结果集成为最终的强学习器预测结果?二、自助法(Bagging)1、Bagging2、BootstrapBootstrap采样的数学性质3、Bagging:集成学习的两个基本问题(1)如何训练
- RabbitMQ中如何确保你的消息只被消费一次
昔我往昔
MQrabbitmqruby分布式
在SpringBoot项目中,确保RabbitMQ消息只被消费一次是一个常见且重要的问题。为了确保消息在RabbitMQ中只被消费一次,我们通常依赖于消息确认机制(acknowledgment),以及幂等性设计。以下是一些常见的做法来实现这一目标。1.使用消息确认机制(Ack)RabbitMQ提供了消息确认机制,允许消费者在成功处理消息后通知RabbitMQ服务器。这可以确保在消息消费完成前,不会
- Python个人学习笔记(17):模块(sys、pickle&json)
NEET_LH
樵夫老师Python零基础课程个人学习笔记python学习笔记
五、sys模块sys.exit():退出while1:print(123)sys.exit(0)#程序退出,0是正常退出,1是非正常退出,记录在日志中sys.version:得到当前解释器的运行环境sys.platform:运行平台,win32=windows代码:print(sys.version)print(sys.platform)结果:3.13.0(tags/v3.13.0:60403a5
- python学习笔记之异常(内置标准异常总结)
Molly_DD
Python学习笔记python软件测试
python异常处理机制异常处理是python的一种高级工具,当异常发生时,程序会停止当前的所有工作,跳转到异常处理部分去执行。异常既可以是程序错误引发的,也可以由代码主动触发。异常处理基本结构try:可能引发异常的代码except异常类型名称:异常处理代码else:没有发生异常时执行的代码异常报错:try:classtest:defgetdata(self):returnself.datay=t
- 物联网 - JetLinks与ThingsBoard技术选型对比
天机️灵韵
物联网开源项目物联网
JetLinks与ThingsBoard作为两款主流的开源物联网平台,在技术架构、功能特性及适用场景上存在显著差异。以下从技术选型的关键维度进行深度对比分析:JetLinks与ThingsBoard物联网平台的深度技术对比及选型建议,综合多个维度分析两者的核心差异与适用场景:一、技术架构与性能技术栈JetLinks:基于Java8、SpringBoot2.x、WebFlux、Netty等,采用响应
- 不要再走弯路了2025最全的黑客入门学习路线在这
渗透代老师
学习网络安全web安全网络python
基于入门网络安全/黑客打造的:黑客&网络安全入门&进阶学习资源包在大多数的思维里总觉得[学习]得先收集资料、学习编程、学习计算机基础,这样不是不可以,但是这样学效率太低了!你要知道网络安全是一门技术,任何技术的学习一定是以实践为主的。也就是说很多的理论知识其实是可以在实践中去验证拓展的,这样学习比起你啃原理、啃书本要好理解很多。所以想要学习网络安全选对正确的学习方法很重要,这可以帮你少走很多弯路。
- 202年充电计划——自学手册 网络安全(黑客技术)
网安康sir
web安全安全网络pythonlinux
基于入门网络安全/黑客打造的:黑客&网络安全入门&进阶学习资源包前言什么是网络安全网络安全可以基于攻击和防御视角来分类,我们经常听到的“红队”、“渗透测试”等就是研究攻击技术,而“蓝队”、“安全运营”、“安全运维”则研究防御技术。如何成为一名黑客很多朋友在学习安全方面都会半路转行,因为不知如何去学,在这里,我将这个整份答案分为黑客(网络安全)入门必备、黑客(网络安全)职业指南、黑客(网络安全)学习
- 自学网络安全(黑客技术)2025年 —90天学习计划
网安CILLE
web安全学习安全网络网络安全
基于入门网络安全/黑客打造的:黑客&网络安全入门&进阶学习资源包前言什么是网络安全网络安全可以基于攻击和防御视角来分类,我们经常听到的“红队”、“渗透测试”等就是研究攻击技术,而“蓝队”、“安全运营”、“安全运维”则研究防御技术。如何成为一名黑客很多朋友在学习安全方面都会半路转行,因为不知如何去学,在这里,我将这个整份答案分为黑客(网络安全)入门必备、黑客(网络安全)职业指南、黑客(网络安全)学习
- C++学习note8(结构体)
技术小白Byteman
c++学习开发语言算法visualstudio
一,结构体用法结构体为用户自定义的数据类型,放在主函数前,其定义方法如下:structStudent{stringname;intage;intgrade;};代码示例:#includeusingnamespacestd;#includestructStudent{/此处Student也可为student(不硬性要求大小写)stringname;intage;intgrade;}s3;/在此顺便创
- C++学习note7(指针)
技术小白Byteman
c++学习开发语言windowsvisualstudio算法数据结构
一,指针的定义指针用于记录变量的地址。代码示例:#includeusingnamespacestd;intmain(){inta=0;int*p;(int*为一体)p=&a;p为a的地址coutusingnamespacestd;intmain(){int*p=NULL;*p=100;定义空指针后不可对其进行访问,故程序出错coutusingnamespacestd;intmain(){int*p
- 学习使用 Git 和 GitHub 开发项目的教程推荐
vortex5
学习gitgithub
Git和GitHub是现代软件开发中不可或缺的工具,无论你是个人开发者还是团队成员,掌握它们都能极大提升效率。本文精选了一系列优质教程资源,涵盖从基本Git命令到进阶多人协作的内容。这些教程既有文字形式,也有视频或交互式资源,适合不同学习风格的人。一、为何要学习Git和GitHub?Git是一个分布式版本控制系统,让你追踪代码变更、回滚错误并与他人协作;GitHub则将其扩展为一个云端平台,支持代
- 使用Java实现Oracle表结构转换为PostgreSQL的示例方案(AI)
秉承初心
AI创造javaoraclepostgresql
核心代码importjava.sql.*;importjava.util.ArrayList;importjava.util.HashMap;importjava.util.List;importjava.util.Map;publicclassOracleToPGConverter{//类型映射表privatestaticfinalMapTYPE_MAPPING=newHashMapcolumn
- Java并发编程之ReentrantReadWriteLock
Johnny Lnex
Java并发编程java开发语言jvm
基本使用方法创建锁对象首先,通过newReentrantReadWriteLock()创建一个锁实例。获取读锁和写锁使用readLock()方法获得读锁对象,使用writeLock()方法获得写锁对象。使用锁保护共享资源在需要保护的代码块前后分别调用lock()和unlock()方法,确保对共享资源的访问安全。示例代码:importjava.util.concurrent.locks.Reentr
- 物理服务器与云服务器的区别是什么
苹果企业签名分发
服务器运维
首先,我需要确定用户的基本背景。可能是一个刚开始学习服务器知识的学生,或者是一个企业里负责IT基础设施的人员,想要了解如何选择服务器类型。不管怎样,用户需要的是两者的核心区别,可能还涉及成本、性能、管理等方面的考虑。物理服务器和云服务器,这两个概念在硬件、部署方式、资源管理上都有不同。首先,物理服务器是实实在在的硬件设备,企业自己购买和维护,而云服务器是基于虚拟化技术的资源,由云服务商提供,用户按
- java中如何根据已有word文件快速生成目录和页码?
bug菌¹
全栈Bug调优(实战版)javawordpython生成目录生成页码文件操作
本文收录于《全栈Bug调优(实战版)》专栏,主要记录项目实战过程中所遇到的Bug或因后果及提供真实有效的解决方案,希望能够助你一臂之力,帮你早日登顶实现财富自由;同时,欢迎大家关注&&收藏&&订阅!持续更新中,up!up!up!!全文目录:问题描述解决方案优化基于Docx4j的TOC生成性能问题及日志警告解决方案**1.性能优化****1.1避免使用FOP渲染获取页码****1.2使用更高效的文档
- java 离线语音_Java通过JNA&麦克风调离线语音唤醒
不吃芹菜的鸭梨君
java离线语音
packagecom.day.iFlyInterface.commonUtil.dll.ivw;importjava.io.File;importjava.io.FileInputStream;importjava.io.FileNotFoundException;importjava.io.IOException;importjava.util.Arrays;importjavax.sound.
- springBoot中myBatisPlus的使用
无足鸟丶
springboot后端java
MyBatis-Plus是一个MyBatis的增强工具,在SpringBoot项目里使用它能极大提升开发效率。下面为你详细介绍在SpringBoot中使用MyBatis-Plus的步骤以及示例代码。1.创建SpringBoot项目你可以借助SpringInitializr(https://start.spring.io/)来创建一个新的SpringBoot项目,添加以下依赖:SpringWebSp
- springBoot中不添加依赖 , 手动生成一个token ,并校验token (使用简单 , 但是安全会低一点)
无足鸟丶
springboot安全后端
在SpringBoot里,即便不添加额外依赖,也能手动生成和校验Token。下面以简单的基于时间戳和密钥的方式来生成和校验Token为例,介绍具体实现步骤。实现思路生成Token:把用户信息、时间戳等数据组合起来,再用密钥进行哈希处理,生成一个唯一的Token。校验Token:从Token里提取出用户信息和时间戳,重新进行哈希处理,然后与原Token进行对比,同时检查时间戳是否过期。代码实现1.创
- 二分查找排序算法
周凡杨
java二分查找排序算法折半
一:概念 二分查找又称
折半查找(
折半搜索/
二分搜索),优点是比较次数少,查找速度快,平均性能好;其缺点是要求待查表为有序表,且插入删除困难。因此,折半查找方法适用于不经常变动而 查找频繁的有序列表。首先,假设表中元素是按升序排列,将表中间位置记录的关键字与查找关键字比较,如果两者相等,则查找成功;否则利用中间位置记录将表 分成前、后两个子表,如果中间位置记录的关键字大于查找关键字,则进一步
- java中的BigDecimal
bijian1013
javaBigDecimal
在项目开发过程中出现精度丢失问题,查资料用BigDecimal解决,并发现如下这篇BigDecimal的解决问题的思路和方法很值得学习,特转载。
原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/ugg/article/de
- Shell echo命令详解
daizj
echoshell
Shell echo命令
Shell 的 echo 指令与 PHP 的 echo 指令类似,都是用于字符串的输出。命令格式:
echo string
您可以使用echo实现更复杂的输出格式控制。 1.显示普通字符串:
echo "It is a test"
这里的双引号完全可以省略,以下命令与上面实例效果一致:
echo Itis a test 2.显示转义
- Oracle DBA 简单操作
周凡杨
oracle dba sql
--执行次数多的SQL
select sql_text,executions from (
select sql_text,executions from v$sqlarea order by executions desc
) where rownum<81;
&nb
- 画图重绘
朱辉辉33
游戏
我第一次接触重绘是编写五子棋小游戏的时候,因为游戏里的棋盘是用线绘制的,而这些东西并不在系统自带的重绘里,所以在移动窗体时,棋盘并不会重绘出来。所以我们要重写系统的重绘方法。
在重写系统重绘方法时,我们要注意一定要调用父类的重绘方法,即加上super.paint(g),因为如果不调用父类的重绘方式,重写后会把父类的重绘覆盖掉,而父类的重绘方法是绘制画布,这样就导致我们
- 线程之初体验
西蜀石兰
线程
一直觉得多线程是学Java的一个分水岭,懂多线程才算入门。
之前看《编程思想》的多线程章节,看的云里雾里,知道线程类有哪几个方法,却依旧不知道线程到底是什么?书上都写线程是进程的模块,共享线程的资源,可是这跟多线程编程有毛线的关系,呜呜。。。
线程其实也是用户自定义的任务,不要过多的强调线程的属性,而忽略了线程最基本的属性。
你可以在线程类的run()方法中定义自己的任务,就跟正常的Ja
- linux集群互相免登陆配置
林鹤霄
linux
配置ssh免登陆
1、生成秘钥和公钥 ssh-keygen -t rsa
2、提示让你输入,什么都不输,三次回车之后会在~下面的.ssh文件夹中多出两个文件id_rsa 和 id_rsa.pub
其中id_rsa为秘钥,id_rsa.pub为公钥,使用公钥加密的数据只有私钥才能对这些数据解密 c
- mysql : Lock wait timeout exceeded; try restarting transaction
aigo
mysql
原文:http://www.cnblogs.com/freeliver54/archive/2010/09/30/1839042.html
原因是你使用的InnoDB 表类型的时候,
默认参数:innodb_lock_wait_timeout设置锁等待的时间是50s,
因为有的锁等待超过了这个时间,所以抱错.
你可以把这个时间加长,或者优化存储
- Socket编程 基本的聊天实现。
alleni123
socket
public class Server
{
//用来存储所有连接上来的客户
private List<ServerThread> clients;
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Server s = new Server();
s.startServer(9988);
}
publi
- 多线程监听器事件模式(一个简单的例子)
百合不是茶
线程监听模式
多线程的事件监听器模式
监听器时间模式经常与多线程使用,在多线程中如何知道我的线程正在执行那什么内容,可以通过时间监听器模式得到
创建多线程的事件监听器模式 思路:
1, 创建线程并启动,在创建线程的位置设置一个标记
2,创建队
- spring InitializingBean接口
bijian1013
javaspring
spring的事务的TransactionTemplate,其源码如下:
public class TransactionTemplate extends DefaultTransactionDefinition implements TransactionOperations, InitializingBean{
...
}
TransactionTemplate继承了DefaultT
- Oracle中询表的权限被授予给了哪些用户
bijian1013
oracle数据库权限
Oracle查询表将权限赋给了哪些用户的SQL,以备查用。
select t.table_name as "表名",
t.grantee as "被授权的属组",
t.owner as "对象所在的属组"
- 【Struts2五】Struts2 参数传值
bit1129
struts2
Struts2中参数传值的3种情况
1.请求参数绑定到Action的实例字段上
2.Action将值传递到转发的视图上
3.Action将值传递到重定向的视图上
一、请求参数绑定到Action的实例字段上以及Action将值传递到转发的视图上
Struts可以自动将请求URL中的请求参数或者表单提交的参数绑定到Action定义的实例字段上,绑定的规则使用ognl表达式语言
- 【Kafka十四】关于auto.offset.reset[Q/A]
bit1129
kafka
I got serveral questions about auto.offset.reset. This configuration parameter governs how consumer read the message from Kafka when there is no initial offset in ZooKeeper or
- nginx gzip压缩配置
ronin47
nginx gzip 压缩范例
nginx gzip压缩配置 更多
0
nginx
gzip
配置
随着nginx的发展,越来越多的网站使用nginx,因此nginx的优化变得越来越重要,今天我们来看看nginx的gzip压缩到底是怎么压缩的呢?
gzip(GNU-ZIP)是一种压缩技术。经过gzip压缩后页面大小可以变为原来的30%甚至更小,这样,用
- java-13.输入一个单向链表,输出该链表中倒数第 k 个节点
bylijinnan
java
two cursors.
Make the first cursor go K steps first.
/*
* 第 13 题:题目:输入一个单向链表,输出该链表中倒数第 k 个节点
*/
public void displayKthItemsBackWard(ListNode head,int k){
ListNode p1=head,p2=head;
- Spring源码学习-JdbcTemplate queryForObject
bylijinnan
javaspring
JdbcTemplate中有两个可能会混淆的queryForObject方法:
1.
Object queryForObject(String sql, Object[] args, Class requiredType)
2.
Object queryForObject(String sql, Object[] args, RowMapper rowMapper)
第1个方法是只查
- [冰川时代]在冰川时代,我们需要什么样的技术?
comsci
技术
看美国那边的气候情况....我有个感觉...是不是要进入小冰期了?
那么在小冰期里面...我们的户外活动肯定会出现很多问题...在室内呆着的情况会非常多...怎么在室内呆着而不发闷...怎么用最低的电力保证室内的温度.....这都需要技术手段...
&nb
- js 获取浏览器型号
cuityang
js浏览器
根据浏览器获取iphone和apk的下载地址
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" content="text/html"/>
<meta name=
- C# socks5详解 转
dalan_123
socketC#
http://www.cnblogs.com/zhujiechang/archive/2008/10/21/1316308.html 这里主要讲的是用.NET实现基于Socket5下面的代理协议进行客户端的通讯,Socket4的实现是类似的,注意的事,这里不是讲用C#实现一个代理服务器,因为实现一个代理服务器需要实现很多协议,头大,而且现在市面上有很多现成的代理服务器用,性能又好,
- 运维 Centos问题汇总
dcj3sjt126com
云主机
一、sh 脚本不执行的原因
sh脚本不执行的原因 只有2个
1.权限不够
2.sh脚本里路径没写完整。
二、解决You have new mail in /var/spool/mail/root
修改/usr/share/logwatch/default.conf/logwatch.conf配置文件
MailTo =
MailFrom
三、查询连接数
- Yii防注入攻击笔记
dcj3sjt126com
sqlWEB安全yii
网站表单有注入漏洞须对所有用户输入的内容进行个过滤和检查,可以使用正则表达式或者直接输入字符判断,大部分是只允许输入字母和数字的,其它字符度不允许;对于内容复杂表单的内容,应该对html和script的符号进行转义替换:尤其是<,>,',"",&这几个符号 这里有个转义对照表:
http://blog.csdn.net/xinzhu1990/articl
- MongoDB简介[一]
eksliang
mongodbMongoDB简介
MongoDB简介
转载请出自出处:http://eksliang.iteye.com/blog/2173288 1.1易于使用
MongoDB是一个面向文档的数据库,而不是关系型数据库。与关系型数据库相比,面向文档的数据库不再有行的概念,取而代之的是更为灵活的“文档”模型。
另外,不
- zookeeper windows 入门安装和测试
greemranqq
zookeeper安装分布式
一、序言
以下是我对zookeeper 的一些理解: zookeeper 作为一个服务注册信息存储的管理工具,好吧,这样说得很抽象,我们举个“栗子”。
栗子1号:
假设我是一家KTV的老板,我同时拥有5家KTV,我肯定得时刻监视
- Spring之使用事务缘由(2-注解实现)
ihuning
spring
Spring事务注解实现
1. 依赖包:
1.1 spring包:
spring-beans-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar
spring-context-4.0.0.
- iOS App Launch Option
啸笑天
option
iOS 程序启动时总会调用application:didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:,其中第二个参数launchOptions为NSDictionary类型的对象,里面存储有此程序启动的原因。
launchOptions中的可能键值见UIApplication Class Reference的Launch Options Keys节 。
1、若用户直接
- jdk与jre的区别(_)
macroli
javajvmjdk
简单的说JDK是面向开发人员使用的SDK,它提供了Java的开发环境和运行环境。SDK是Software Development Kit 一般指软件开发包,可以包括函数库、编译程序等。
JDK就是Java Development Kit JRE是Java Runtime Enviroment是指Java的运行环境,是面向Java程序的使用者,而不是开发者。 如果安装了JDK,会发同你
- Updates were rejected because the tip of your current branch is behind
qiaolevip
学习永无止境每天进步一点点众观千象git
$ git push joe prod-2295-1
To
[email protected]:joe.le/dr-frontend.git
! [rejected] prod-2295-1 -> prod-2295-1 (non-fast-forward)
error: failed to push some refs to '
[email protected]
- [一起学Hive]之十四-Hive的元数据表结构详解
superlxw1234
hivehive元数据结构
关键字:Hive元数据、Hive元数据表结构
之前在 “[一起学Hive]之一–Hive概述,Hive是什么”中介绍过,Hive自己维护了一套元数据,用户通过HQL查询时候,Hive首先需要结合元数据,将HQL翻译成MapReduce去执行。
本文介绍一下Hive元数据中重要的一些表结构及用途,以Hive0.13为例。
文章最后面,会以一个示例来全面了解一下,
- Spring 3.2.14,4.1.7,4.2.RC2发布
wiselyman
Spring 3
Spring 3.2.14、4.1.7及4.2.RC2于6月30日发布。
其中Spring 3.2.1是一个维护版本(维护周期到2016-12-31截止),后续会继续根据需求和bug发布维护版本。此时,Spring官方强烈建议升级Spring框架至4.1.7 或者将要发布的4.2 。
其中Spring 4.1.7主要包含这些更新内容。