【String字符串之前篇】
目录
- 1.什么是字符串
- 2.常用字符串的写法
- 3.String字符串的底层原理
- 3.字符串的比较
-
- 3.1双等号和equals
- 3.2 compareTo(String s) 方法
- 3.3compareToIgnoreCase方法
- 4.String查找方法
- 5.字符串的转换
-
- 5.1字符串与数字转换
- 5.2 大小写转换
- 5.3 字符串与数组的转换
1.什么是字符串
对于"Holl world “(双引号)印出来的这一串字符叫做字符串。而 ‘A’ (单引号)仅仅是字符
甚至于(” ") 双引号里面没有什么字符就叫做空字符串。
2.常用字符串的写法
我们常用的字符串构造方法有三种
分别是:
使用常量构造
使用new String构造
使用字符串构造
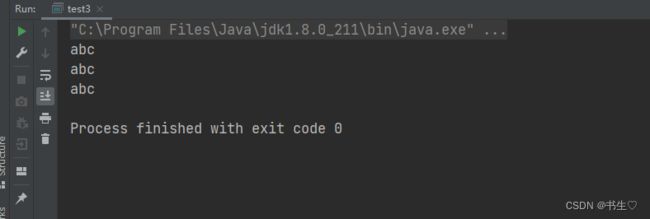
public class test3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//第一种,使用常量构造
String str="abc";
//第二种,使用new String构造
String str1=new String("abc");
//第三种使用字符串构造
char[] ch={'a','b','c'};
String str2=new String(ch);
System.out.println(str);
System.out.println(str1);
System.out.println(str2);
}
}
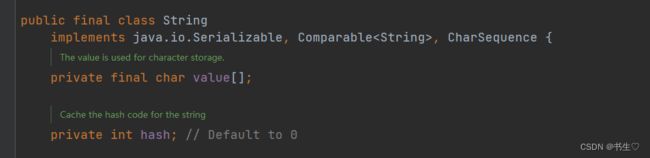
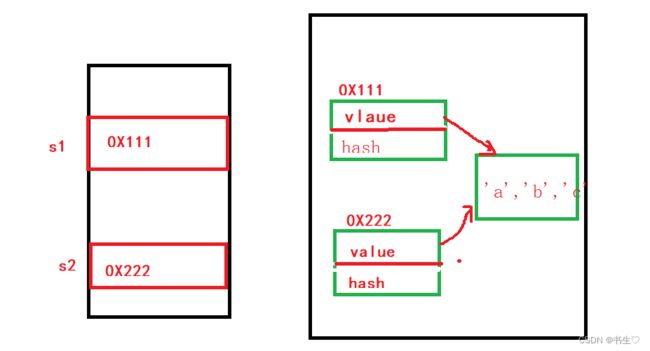
3.String字符串的底层原理
我们查看String的底层代码得知,字符串分为两部分,一个是value数组,一个是哈希值
并且value数组还是以private修饰的。
3.字符串的比较
3.1双等号和equals
说起比较,我们一般会想到 “==”,但是在我们引用变量(字符串)中,也会使用equals来进行比较。
对于基本变量来说,我们使用“双等号”就可以判断是否相等
对于引用变量来说,我们使用“双等号”判断是去比较两个引用变量引用的是否为同一个对象,使用equals才是判断两个字符串是否相等。
equals按照字典序比较
public class Test4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a=10;
int b=20;
int c=10;
System.out.println(a==b);
System.out.println(a==c);
System.out.println("===============");
String str1="abc";
String str2=new String("abc");
String str3="def";
System.out.println(str1==str2);
System.out.println(str1.equals(str2));
System.out.println(str1==str3);
}
}
3.2 compareTo(String s) 方法
方法: 按照字典序进行比较
与equals不同的是,equals返回的是boolean类型,而compareTo返回的是int类型。
具体比较方式:
- 先按照字典次序大小比较,如果出现不等的字符,直接返回这两个字符的大小差值
- 如果前k个字符相等(k为两个字符长度最小值),返回值两个字符串长度差值
public class Test4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1="abc";
String str2="abcdef";
String str3="abc";
System.out.println(str1.compareTo(str3));
System.out.println(str1.compareTo(str2));
System.out.println(str2.compareTo(str3));
}
}
3.3compareToIgnoreCase方法
方法:与compareTo方式相同,但是忽略大小写比较
public class Test4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = new String("abc");
String s2 = new String("ac");
String s3 = new String("ABc");
String s4 = new String("abcdef");
System.out.println(s1.compareToIgnoreCase(s2)); // 不同输出字符差值-1
System.out.println(s1.compareToIgnoreCase(s3)); // 相同输出 0
System.out.println(s1.compareToIgnoreCase(s4)); // 前k个字符完全相同,输出长度差值 -3
}
}
4.String查找方法
字符串查找也是字符串中非常常见的操作,String类提供的常用查找的方法:
char charAt(int index)
//返回index位置上字符,如果index为负数或者越界,抛出IndexOutOfBoundsException异常
int indexOf(int ch) //返回ch第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1
int indexOf(int ch, intfromIndex)//从fromIndex位置开始找ch第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1
int indexOf(String str) //返回str第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1
int indexOf(String str, intfromIndex)//从fromIndex位置开始找str第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1
int lastIndexOf(int ch) //从后往前找,返回ch第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1
int lastIndexOf(int ch, intfromIndex)//从fromIndex位置开始找,从后往前找ch第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1
int lastIndexOf(String str) //从后往前找,返回str第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1
int lastIndexOf(String str, intfromIndex)//从fromIndex位置开始找,从后往前找str第一次出现的位置,没有返
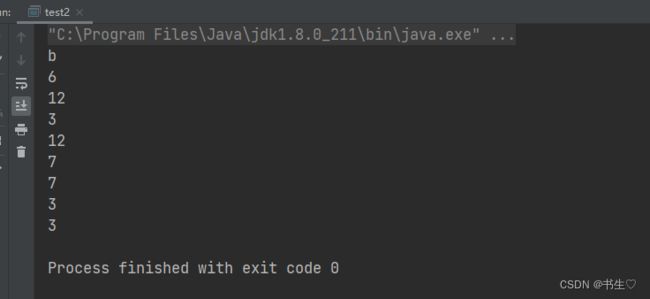
public class test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "aaabbbccddeeff";
System.out.println(str.charAt(3));
System.out.println(str.indexOf('c'));
System.out.println(str.indexOf('f', 10));
System.out.println(str.indexOf("bbb"));
System.out.println(str.indexOf("ff", 10));
System.out.println(str.lastIndexOf('c'));
System.out.println(str.lastIndexOf('c', 10));
System.out.println(str.lastIndexOf("bbb"));
System.out.println(str.lastIndexOf("bbb", 10));
}
}
5.字符串的转换
5.1字符串与数字转换
将数字,布尔类型,对象等转换为字符串的话需要借助String中的.valueOf方法
然而如果想将字符串变为数字的话,就需要借助包装类的parseInt/parseDouble等方法。
class Student
{
public String name;
public int age;
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
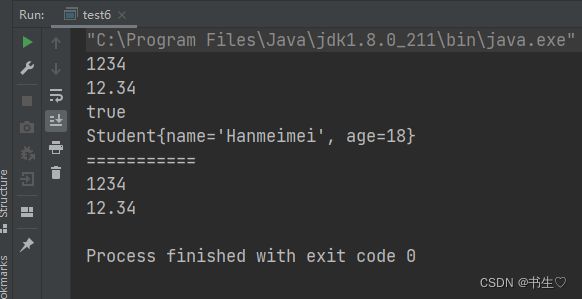
public class test6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = String.valueOf(1234);
String s2 = String.valueOf(12.34);
String s3 = String.valueOf(true);
String s4 = String.valueOf(new Student("Hanmeimei", 18));
System.out.println(s1);
System.out.println(s2);
System.out.println(s3);
System.out.println(s4);
System.out.println("===========");
int data1 = Integer.parseInt("1234");
double data2 = Double.parseDouble("12.34");
System.out.println(data1);
System.out.println(data2);
}
}
5.2 大小写转换
这里我们就需要两个方法
toUpperCase()//转大写
toLowerCase()//转小写
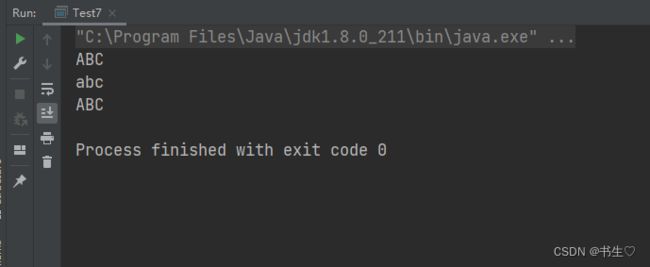
public class Test7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1="abc";
String str2="ABC";
String str3="Abc";
System.out.println(str1.toUpperCase());
System.out.println(str2.toLowerCase());
System.out.println(str3.toUpperCase());
}
}
5.3 字符串与数组的转换
当我们想要将字符串变为数组的时候,我们就需要通过字符串去调用toCharArray()变为字符数组
而当我们将数组变为字符串的时候,我们直接new String就可以了。
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "hello";
// 字符串转数组
char[] ch = s.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < ch.length; i++) {
System.out.print(ch[i]);
}
System.out.println();
// 数组转字符串
String s2 = new String(ch);
System.out.println(s2);
}