C primer plus编程练习答案(上)
C primer plus编程练习
C primer plus编程练习答案
- C primer plus编程练习
-
- 第一章初识C语言
- 第二章 C语言概述
- 第三章 数据和C
- 第四章 字符串的格式化输入/输出
- 第五章 运算符,表达式和语句
- 第六章 C控制语句:循环
- 第七章 C 控制语句:分之合跳转
- 第八章 字符输入/输出和输入验证
- 第九章 函数
- 第十章 数组和指针
- 第十一章 字符串和字符串函数
第一章初识C语言
- 你刚被MacroMuscle有限公司聘用。该公司准备进入欧洲市场,需要一个把英寸单位转换为厘米单位(1英寸=2.54厘米)的程序。该程序要提示用户输入英寸值。你的任务是定义程序目标和设计程序。
#include第二章 C语言概述
- 编写一个程序,调用一次 printf()函数,把你的姓名打印在一行。再调用一次 printf()函数,把你的姓名分别打印在两行。然后,再调用两次printf()函数,把你的姓名打印在一行。输出应如下所示(当然要把示例的内容换成你的姓名):
#include- .编写一个程序,打印你的姓名和地址。
#include- 编写一个程序把你的年龄转换成天数,并显示这两个值。这里不用考虑闰年的问题。
#include- 编写一个程序,生成以下输出:
For he’s a jolly good fellow!
For he’s a jolly good fellow!
For he’s a jolly good fellow!
Which nobody can deny!
除了 main()函数以外,该程序还要调用两个自定义函数:一个名为jolly(),用于打印前 3 条消息,调用一次打印一条;另一个函数名为deny(),打印最后一条消息。
#include- .编写一个程序,生成以下输出:
Brazil, Russia, India, China
India, China,
Brazil, Russia
除了main()以外,该程序还要调用两个自定义函数:一个名为br(),调用一次打印一次“Brazil, Russia”;另一个名为ic(),调用一次打印一次“India,China”。其他内容在main()函数中完成。
#include- 编写一个程序,创建一个整型变量toes,并将toes设置为10。程序中还要计算toes的两倍和toes的平方。该程序应打印3个值,并分别描述以示区分。
#include- .许多研究表明,微笑益处多多。编写一个程序,生成以下格式的输出:
Smile!Smile!Smile!
Smile!Smile!
Smile!
该程序要定义一个函数,该函数被调用一次打印一次“Smile!”,根据程序的需要使用该函数。
#include- ** 在C语言中,函数可以调用另一个函数。编写一个程序,调用一个名为one_three()的函数。该函数在一行打印单词“one”,再调用第2个函数two(),然后在另一行打印单词“three”。two()函数在一行显示单词“two”。main()函数在调用 one_three()函数前要打印短语“starting now:”,并在调用完毕后显示短语“done!”。因此,该程序的输出应如下所示:**
starting now:
one
two
three
done!
#include第三章 数据和C
- 通过试验(即编写带有此类问题的程序)观察系统如何处理整数上溢、浮点数上溢和浮点数下溢的情况。
#include - 编写一个程序,要求提示输入一个ASCII码值(如,66),然后打印输入的字符。
#include- 编写一个程序,发出一声警报,然后打印下面的文本:
Startled by the sudden sound, Sally shouted,
"By the Great Pumpkin, what was that!"
#include- 编写一个程序,读取一个浮点数,先打印成小数点形式,再打印成指数形式。然后,如果系统支持,再打印成p记数法(即十六进制记数法)。按以下格式输出(实际显示的指数位数因系统而异):
Enter a floating-point value: 64.25
fixed-point notation: 64.250000
exponential notation: 6.425000e+01
p notation: 0x1.01p+6
#include- 一年大约有3.156×107秒。编写一个程序,提示用户输入年龄,然后显示该年龄对应的秒数。
#include- 一个水分子的质量约为3.0×10−23克。1夸脱水大约是950克。编写一个程序,提示用户输入水的夸脱数,并显示水分子的数量。
#include- 1英寸相当于2.54厘米。编写一个程序,提示用户输入身高(/英寸),然后以厘米为单位显示身高。
#include- 在美国的体积测量系统中,1品脱等于2杯,1杯等于8盎司,1盎司等于2大汤勺,1大汤勺等于3茶勺。编写一个程序,提示用户输入杯数,并以品脱、盎司、汤勺、茶勺为单位显示等价容量。思考对于该程序,为何使用浮点类型比整数类型更合适?
#include第四章 字符串的格式化输入/输出
- .编写一个程序,提示用户输入名和姓,然后以“名,姓”的格式打印出
来。
#include- 编写一个程序,提示用户输入名和姓,并执行一下操作:
a.打印名和姓,包括双引号;
b.在宽度为20的字段右端打印名和姓,包括双引号;
c.在宽度为20的字段左端打印名和姓,包括双引号;
d.在比姓名宽度宽3的字段中打印名和姓。
#include- 编写一个程序,读取一个浮点数,首先以小数点记数法打印,然后以指数记数法打印。用下面的格式进行输出(系统不同,指数记数法显示的位数可能不同):
a.输入21.3或2.1e+001;
b.输入+21.290或2.129E+001;
#include- 编写一个程序,提示用户输入身高(单位:英寸)和姓名,然后以下面的格式显示用户刚输入的信息:
Dabney, you are 6.208 feet tall
使用float类型,并用/作为除号。如果你愿意,可以要求用户以厘米为单位输入身高,并以米为单位显示出来。
#include- 编写一个程序,提示用户输入以兆位每秒(Mb/s)为单位的下载速度和以兆字节(MB)为单位的文件大小。程序中应计算文件的下载时间。注意,这里1字节等于8位。使用float类型,并用/作为除号。该程序要以下面的格式打印 3 个变量的值(下载速度、文件大小和下载时间),显示小数点后面两位数字:
At 18.12 megabits per second, a file of 2.20 megabytes
downloads in 0.97 seconds.
#include- 编写一个程序,先提示用户输入名,然后提示用户输入姓。在一行打印用户输入的名和姓,下一行分别打印名和姓的字母数。字母数要与相应名和姓的结尾对齐,如下所示:
Melissa Honeybee
7 8
接下来,再打印相同的信息,但是字母个数与相应名和姓的开头对齐,
如下所示:
Melissa Honeybee
#include - 编写一个程序,将一个double类型的变量设置为1.0/3.0,一个float类型的变量设置为1.0/3.0。分别显示两次计算的结果各3次:一次显示小数点后面6位数字;一次显示小数点后面12位数字;一次显示小数点后面16位数字。程序中要包含float.h头文件,并显示FLT_DIG和DBL_DIG的值。1.0/3.0的值与这些值一致吗?
#include - 编写一个程序,提示用户输入旅行的里程和消耗的汽油量。然后计算并显示消耗每加仑汽油行驶的英里数,显示小数点后面一位数字。接下来,使用1加仑大约3.785升,1英里大约为1.609千米,把单位是英里/加仑的值转换为升/100公里(欧洲通用的燃料消耗表示法),并显示结果,显示小数点后面 1 位数字。注意,美国采用的方案测量消耗单位燃料的行程(值越大越好),而欧洲则采用单位距离消耗的燃料测量方案(值越低越好)。使用#define 创建符号常量或使用 const 限定符创建变量来表示两个转换系数。
#include 第五章 运算符,表达式和语句
编写一个程序,把用分钟表示的时间转换成用小时和分钟表示的时间。使用#define或const创建一个表示60的符号常量或const变量。通过while循环让用户重复输入值,直到用户输入小于或等于0的值才停止循环。
#include- 编写一个程序,提示用户输入一个整数,然后打印从该数到比该数大10的所有整数(例如,用户输入5,则打印5~15的所有整数,包括5和15)。要求打印的各值之间用一个空格、制表符或换行符分开。
#include- 编写一个程序,提示用户输入天数,然后将其转换成周数和天数。例如,用户输入18,则转换成2周4天。以下面的格式显示结果:编写一个程序,提示用户输入天数,然后将其转换成周数和天数。例如,用户输入18,则转换成2周4天。以下面的格式显示结果:
18 days are 2 weeks, 4 days.
通过while循环让用户重复输入天数,当用户输入一个非正值时(如0或-20),循环结束。
#include- 编写一个程序,提示用户输入一个身高(单位:厘米),并分别以厘米和英寸为单位显示该值,允许有小数部分。程序应该能让用户重复输入身高,直到用户输入一个非正值。其输出示例如下:
182.0 cm = 5 feet, 11.7 inches
Enter a height in centimeters (<=0 to quit): 168.7
168.0 cm = 5 feet, 6.4 inches
Enter a height in centimeters (<=0 to quit): 0
bye
#include - 修改程序addemup.c(程序清单5.13),你可以认为addemup.c是计算20天里赚多少钱的程序(假设第1天赚$1、第2天赚$2、第3天赚$3,以此类推)。修改程序,使其可以与用户交互,根据用户输入的数进行计算(即,用读入的一个变量来代替20)。
#include- 修改编程练习5的程序,使其能计算整数的平方和(可以认为第1天赚$1、第2天赚$4、第3天赚$9,以此类推,这看起来很不错)。C没有平方函数,但是可以用n * n来表示n的平方。
#include- 编写一个程序,提示用户输入一个double类型的数,并打印该数的立方值。自己设计一个函数计算并打印立方值。main()函数要把用户输入的值传递给该函数。
#include- .编写一个程序,显示求模运算的结果。把用户输入的第1个整数作为求模运算符的第2个运算对象,该数在运算过程中保持不变。用户后面输入的数是第1个运算对象。当用户输入一个非正值时,程序结束。其输出示例如下:
This program computes moduli.
Enter an integer to serve as the second operand: 256
Now enter the first operand: 438
438 % 256 is 182
Enter next number for first operand (<= 0 to quit): 1234567
1234567 % 256 is 135
Enter next number for first operand (<= 0 to quit): 0
Done
#include编写一个程序,要求用户输入一个华氏温度。程序应读取double类型的值作为温度值,并把该值作为参数传递给一个用户自定义的函数Temperatures()。该函数计算摄氏温度和开氏温度,并以小数点后面两位数字的精度显示3种温度。要使用不同的温标来表示这3个温度值。下面是华氏温度转摄氏温度的公式:
摄氏温度 = 5.0 / 9.0 * (华氏温度 - 32.0)
开氏温标常用于科学研究,0表示绝对零,代表最低的温度。下面是摄氏温度转开氏温度的公式:
开氏温度 = 摄氏温度 + 273.16
Temperatures()函数中用const创建温度转换中使用的变量。在main()函数中使用一个循环让用户重复输入温度,当用户输入 q 或其他非数字时,循环结束。scanf()函数返回读取数据的数量,所以如果读取数字则返回1,如果读取q则不返回1。可以使用==运算符将scanf()的返回值和1作比较,测试两值是否相等。
#include第六章 C控制语句:循环
- 编写一个程序,创建一个包含26个元素的数组,并在其中储存26个小写字母。然后打印数组的所有内容。
#include2.使用嵌套循环,按下面的格式打印字符:
$
$$
$$$
$$$$
$$$$$
#include- 使用嵌套循环,按下面的格式打印字母:
F
FE
FED
FEDC
FEDCB
FEDCBA
注意:如果你的系统不使用ASCII或其他以数字顺序编码的代码,可以把字符数组初始化为字母表中的字母:char lets[27] =“ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ”;402然后用数组下标选择单独的字母,例如lets[0]是‘A’,等等。
#include4.使用嵌套循环,按下面的格式打印字母:
A
BC
DEF
GHIJ
KLMNO
PQRSTU
如果你的系统不使用以数字顺序编码的代码,请参照练习3的方案解决。
#include5.编写一个程序,提示用户输入大写字母。使用嵌套循环以下面金字塔型的格式打印字母:
A
ABA
ABCBA
ABCDCBA
ABCDEDCBA
打印这样的图形,要根据用户输入的字母来决定。例如,上面的图形是在用户输入E后的打印结果。提示:用外层循环处理行,每行使用3个内层循环,分别处理空格、以升序打印字母、以降序打印字母。如果系统不使用ASCII或其他以数字顺序编码的代码,请参照练习3的解决方案。
#include6.编写一个程序打印一个表格,每一行打印一个整数、该数的平方、该数的立方。要求用户输入表格的上下限。使用一个for循环。
#include- 编写一个程序把一个单词读入一个字符数组中,然后倒序打印这个单词。提示:strlen()函数(第4章介绍过)可用于计算数组最后一个字符的下标。
#include- 编写一个程序,要求用户输入两个浮点数,并打印两数之差除以两数乘积的结果。在用户输入非数字之前,程序应循环处理用户输入的每对值。
#include- 修改练习8,使用一个函数返回计算的结果。
#include- 编写一个程序,要求用户输入一个上限整数和一个下限整数,计算从上限到下限范围内所有整数的平方和,并显示计算结果。然后程序继续提示用户输入上限和下限整数,并显示结果,直到用户输入的上限整数小于下限整数为止。程序的运行示例如下:
Enter lower and upper integer limits: 5 9
The sums of the squares from 25 to 81 is 255
Enter next set of limits: 3 25
The sums of the squares from 9 to 625 is 5520
Enter next set of limits: 5 5
Done
#include11.编写一个程序,在数组中读入8个整数,然后按倒序打印这8个整数。
#include12
考虑下面两个无限序列:
1.0 + 1.0/2.0 + 1.0/3.0 + 1.0/4.0 + ...
1.0 - 1.0/2.0 + 1.0/3.0 - 1.0/4.0 + ...
编写一个程序计算这两个无限序列的总和,直到到达某次数。提示:奇数个-1 相乘得-1,偶数个-1相乘得1。让用户交互地输入指定的次数,当用户输入0或负值时结束输入。查看运行100项、1000项、10000项后的总和,是否发现每个序列都收敛于某值?
#include- 编写一个程序,创建一个包含8个元素的int类型数组,分别把数组元素设置为2的前8次幂。使用for循环设置数组元素的值,使用do while循环显示数组元素的值。
#include编写一个程序,创建两个包含8个元素的double类型数组,使用循环提示用户为第一个数组输入8 个值。第二个数组元素的值设置为第一个数组对应元素的累积之和。例如,第二个数组的第 4个元素的值是第一个数组前4个元素之和,第二个数组的第5个元素的值是第一个数组前5个元素之和(用嵌套循环可以完成,但是利用第二个数组的第5个元素是第二个数组的第4个元素与第一个数组的第5个元素之和,只用一个循环就能完成任务,不需要使用嵌套循环)。最后,使用循环显示两个数组的内容,第一个数组显示成一行,第二个数组显示在第一个数组的下一行,而且每个元素都与第一个数组各元素相对应。
#include编写一个程序,读取一行输入,然后把输入的内容倒序打印出来。可以把输入储存在char类型的数组中,假设每行字符不超过255。回忆一下,根据%c转换说明,scanf()函数一次只能从输入中读取一个字符,而且在用户按下Enter键时scanf()函数会生成一个换行字符(\n)。
#include - Daphne以10%的单利息投资了100美元(也就是说,每年投资获利相当于原始投资的10%)。Deirdre以 5%的复合利息投资了 100 美元(也就是说,利息是当前余额的 5%,包含之前的利息)。编写一个程序,计算需要多少年Deirdre的投资额才会超过Daphne,并显示那时两人的投资额。
#include17
Chuckie Lucky赢得了100万美元(税后),他把奖金存入年利率8%的账户。在每年的最后一天, Chuckie取出10万美元。编写一个程序,计算多少年后Chuckie会取完账户的钱?
#include 18
Rabnud博士加入了一个社交圈。起初他有5个朋友。他注意到他的朋友数量以下面的方式增长。第1周少了1个朋友,剩下的朋友数量翻倍第2
周少了2个朋友,剩下的朋友数量翻倍。一般而言,第N周少了N个朋友,剩下的朋友数量翻倍。编写一个程序,计算并显示Rabnud博士每周的朋友数量。该程序一直运行,直到超过邓巴数(Dunbar’s number)。邓巴数是粗略估算一个人在社交圈中有稳定关系的成员的最大值,该值大约是150。
#include 第七章 C 控制语句:分之合跳转
- 编写一个程序读取输入,读到#字符停止,然后报告读取的空格数、换行符数和所有其他字符的数量。
#include- 编写一个程序读取输入,读到#字符停止。程序要打印每个输入的字符以及对应的ASCII码(十进制)。一行打印8个字符。建议:使用字符计数和求模运算符(%)在每8个循环周期时打印一个换行符。
#include - 编写一个程序,读取整数直到用户输入 0。输入结束后,程序应报告用户输入的偶数(不包括 0)个数、这些偶数的平均值、输入的奇数个数及其奇数的平均值。
#include - 使用if else语句编写一个程序读取输入,读到#停止。用感叹号替换句号,用两个感叹号替换原来的感叹号,最后报告进行了多少次替换。
#include - 使用switch重写练习4。
#include- 编写程序读取输入,读到#停止,报告ei出现的次数。
注意:
该程序要记录前一个字符和当前字符。用“Receive your eieio award”这样的输入来测试。
#include - 编写一个程序,提示用户输入一周工作的小时数,然后打印工资总额、税金和净收入。做如下假设:
a.基本工资 = 1000美元/小时
b.加班(超过40小时) = 1.5倍的时间
c.税率: 前300美元为15%
续150美元为20%
余下的为25%
用#define定义符号常量。不用在意是否符合当前的税法。
#include - 修改练习7的假设a,让程序可以给出一个供选择的工资等级菜单。使用switch完成工资等级选择。运行程序后,显示的菜单应该类似这样:
*****************************************************************
Enter the number corresponding to the desired pay rate or action:
1) $8.75/hr 2) $9.33/hr
3) $10.00/hr 4) $11.20/hr
5) quit
*****************************************************************
如果选择 1~4 其中的一个数字,程序应该询问用户工作的小时数。程序要通过循环运行,除非用户输入 5。如果输入 1~5 以外的数字,程序应提醒用户输入正确的选项,然后再重复显示菜单提示用户输入。使用#define创建符号常量表示各工资等级和税率。
#include 编写一个程序,只接受正整数输入,然后显示所有小于或等于该数的素数。
#include - 1988年的美国联邦税收计划是近代最简单的税收方案。它分为4个类别,每个类别有两个等级。
下面是该税收计划的摘要(美元数为应征税的收入):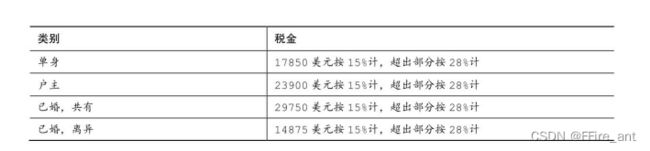
例如,一位工资为20000美元的单身纳税人,应缴纳税费0.15×17850+0.28×(20000−17850)美元。编写一个程序,让用户指定缴纳税金的种类和应纳税收入,然后计算税金。程序应通过循环让用户可以多次输入。
#include - ABC 邮购杂货店出售的洋蓟售价为 2.05 美元/磅,甜菜售价为 1.15美元/磅,胡萝卜售价为 1.09美元/磅。在添加运费之前,100美元的订单有5%的打折优惠。少于或等于5磅的订单收取6.5美元的运费和包装费,5磅~20磅的订单收取14美元的运费和包装费,超过20磅的订单在14美元的基础上每续重1磅增加0.5美元。编写一个程序,在循环中用switch语句实现用户输入不同的字母时有不同的响应,即输入a的响应是让用户输入洋蓟的磅数,b是甜菜的磅数,c是胡萝卜的磅数,q 是退出订购。程序要记录累计的重量。即,如果用户输入 4 磅的甜菜,然后输入 5磅的甜菜,程序应报告9磅的甜菜。然后,该程序要计算货物总价、折扣(如果有的话)、运费和包装费。随后,程序应显示所有的购买信息:物品售价、订购的重量(单位:磅)、订购的蔬菜费用、订单的总费用、折扣(如果有的话)、运费和包装费,以及所有的费用总额。
#include 第八章 字符输入/输出和输入验证
设计一个程序,统计在读到文件结尾之前读取的字符数。
#include**编写一个程序,在遇到 EOF 之前,把输入作为字符流读取。程序要打印每个输入的字符及其相应的ASCII十进制值。注意,在ASCII序列中,空格字符前面的字符都是非打印字符,要特殊处理这些字符。如果非打印字符是换行符或制表符,则分别打印\n或\t。否则,使用控制字符表示法。例如,ASCII的1是Ctrl+A,可显示为^A。注意,A的ASCII值是Ctrl+A的值加上64。其他非打印字符也有类似的关系。除每次遇到换行符打印新的一行之外,每行打印10对值。(注意:不同的操作系统其控制字符可能不同。)
**
#include 编写一个程序,在遇到 EOF 之前,把输入作为字符流读取。该程序要报告输入中的大写字母和小写字母的个数。假设大小写字母数值是连续的。或者使用ctype.h库中合适的分类函数更方便。
#include 编写一个程序,在遇到EOF之前,把输入作为字符流读取。该程序要报告平均每个单词的字母数。不要把空白统计为单词的字母。实际上,标点符号也不应该统计,但是现在暂时不同考虑这么多(如果你比较在意这点,考虑使用ctype.h系列中的ispunct()函数)。
#include - 修改程序清单8.4的猜数字程序,使用更智能的猜测策略。例如,程序最初猜50,询问用户是猜大了、猜小了还是猜对了。如果猜小了,那么下一次猜测的值应是50和100中值,也就是75。如果这次猜大了,那么下一次猜测的值应是50和75的中值,等等。使用二分查找(binary search)策略,如果用户没有欺骗程序,那么程序很快就会猜到正确的答案。
#include 修改程序清单8.8中的get_first()函数,让该函数返回读取的第1个非空白字符,并在一个简单的程序中测试。
#include - 修改第7章的编程练习8,用字符代替数字标记菜单的选项。用q代替5作为结束输入的标记。
#include 编写一个程序,显示一个提供加法、减法、乘法、除法的菜单。获得用户选择的选项后,程序提示用户输入两个数字,然后执行用户刚才选择的操作。该程序只接受菜单提供的选项。程序使用float类型的变量储存用户输入的数字,如果用户输入失败,则允许再次输入。进行除法运算时,如果用户输入0作为第2个数(除数),程序应提示用户重新输入一个新值。该程序的一个运行示例如下:
Enter the operation of your choice:
a. add s. subtract
m. multiply d. divide
q. quit
a
Enter first number: 22 .4
Enter second number: one
one is not an number.
Please enter a number, such as 2.5, -1.78E8, or 3: 1
22.4 + 1 = 23.4
Enter the operation of your choice:
a. add s. subtract
m. multiply d. divide
559q. quit
d
Enter first number: 18.4
Enter second number: 0
Enter a number other than 0: 0.2
18.4 / 0.2 = 92
Enter the operation of your choice:
a. add s. subtract
m. multiply d. divide
q. quit
q
Bye.
#include 第九章 函数
- 设计一个函数min(x, y),返回两个double类型值的较小值。在一个简单的驱动程序中测试该函数。
#include - .设计一个函数chline(ch, i, j),打印指定的字符j行i列。在一个简单的驱动程序中测试该函数。
a.donut()接受一个int类型的参数,打印若干(参数指定数目)个0
b.gear()接受两个int类型的参数,返回int类型的值
c.guess()不接受参数,返回一个int类型的值
d.stuff_it()接受一个double类型的值和double类型变量的地址,把第1个
值储存在指定位置
#include - 编写一个函数,接受3个参数:一个字符和两个整数。字符参数是待打印的字符,第1个整数指定一行中打印字符的次数,第2个整数指定打印指定字符的行数。编写一个调用该函数的程序。
#include - 两数的调和平均数这样计算:先得到两数的倒数,然后计算两个倒数的平均值,最后取计算结果的倒数。编写一个函数,接受两个double类型的参数,返回这两个参数的调和平均数。
#include 编写并测试一个函数larger_of(),该函数把两个double类型变量的值替换为较大的值。例如, larger_of(x, y)会把x和y中较大的值重新赋给两个变量。
#include - 编写并测试一个函数,该函数以3个double变量的地址作为参数,把最小值放入第1个函数,中间值放入第2个变量,最大值放入第3个变量。
#include - 下编写一个函数,从标准输入中读取字符,直到遇到文件结尾。程序要报告每个字符是否是字母。如果是,还要报告该字母在字母表中的数值位置。例如,c和C在字母表中的位置都是3。合并一个函数,以一个字符作为参数,如果该字符是一个字母则返回一个数值位置,否则返回-1。
void salami(num)
{
int num, count;
for (count = 1; count <= num; num++)
printf(" O salami mio!\n");
}
#include - 第6章的程序清单6.20中,power()函数返回一个double类型数的正整数次幂。改进该函数,使其能正确计算负幂。另外,函数要处理0的任何次幂都为0,任何数的0次幂都为1(函数应报告0的0次幂未定义,因此把该值处理为1)。要使用一个循环,并在程序中测试该函数。
#include - 使用递归函数重写编程练习8。
#include - 为了让程序清单9.8中的to_binary()函数更通用,编写一to_base_n()函数接受两个在2~10范围内的参数,然后以第2个参数中指定的进制打印第1个参数的数值。例如,to_base_n(129, 8)显示的结果为201,也就是129的八进制数。在一个完整的程序中测试该函数。
#include 编写并测试Fibonacci()函数,该函数用循环代替递归计算斐波那契数。
#include 第十章 数组和指针
修改程序清单10.7的rain.c程序,用指针进行计算(仍然要声明并初始化数组)。
#include编写一个程序,初始化一个double类型的数组,然后把该数组的内容拷贝至3个其他数组中(在main()中声明这4个数组)。使用带数组表示法的函数进行第1份拷贝。使用带指针表示法和指针递增的函数进行第2份拷贝。把目标数组名、源数组名和待拷贝的元素个数作为前两个函数的参数。第3个函数以目标数组名、源数组名和指向源数组最后一个元素后面的元素的指针。也就是说,给定以下声明,则函数调用如下所示:
double source[5] = {1.1, 2.2, 3.3, 4.4, 5.5};
double target1[5];
double target2[5];
double target3[5];
copy_arr(target1, source, 5);
copy_ptr(target2, source, 5);
copy_ptrs(target3, source, source + 5);
#include 3.编写一个函数,返回储存在int类型数组中的最大值,并在一个简单的程序中测试该函数。
#include编写一个函数,返回储存在double类型数组中最大值的下标,并在一个简单的程序中测试该函数。
#include - 编写一个函数,返回储存在double类型数组中最大值和最小值的差值,并在一个简单的程序中测试该函数。
#include 6.编写一个函数,把double类型数组中的数据倒序排列,并在一个简单的程序中测试该函数。
#include 编写一个程序,初始化一个double类型的二维数组,使用编程练习2中的一个拷贝函数把该数组中的数据拷贝至另一个二维数组中(因为二维数组是数组的数组,所以可以使用处理一维数组的拷贝函数来处理数组中的每个子数组)。
#include 使用编程练习2中的拷贝函数,把一个内含7个元素的数组中第3~第5个元素拷贝至内含3个元素的数组中。该函数本身不需要修改,只需要选择合适的实际参数(实际参数不需要是数组名和数组大小,只需要是数组元素的地址和待处理元素的个数)。
#include 9.编写一个程序,初始化一个double类型的3×5二维数组,使用一个处理变长数组的函数将其拷贝至另一个二维数组中。还要编写一个以变长组为形参的函数以显示两个数组的内容。这两个函数应该能处理任意N×M数组(如果编译器不支持变长数组,就使用传统C函数处理N×5的数组)。
#include - 编写一个函数,把两个数组中相对应的元素相加,然后把结果储存到第 3 个数组中。也就是说,如果数组1中包含的值是2、4、5、8,数组2中包含的值是1、0、4、6,那么该函数把3、4、9、14赋给第3个数组。函数接受3个数组名和一个数组大小。在一个简单的程序中测试该函数。
#include 编写一个程序,声明一个int类型的3×5二维数组,并用合适的值初始化它。该程序打印数组中的值,然后各值翻倍(即是原值的2倍),并显示出各元素的新值。编写一个函数显示数组的内容,再编写一个函数把各元素的值翻倍。这两个函数都以函数名和行数作为参数。
#include - 重写程序清单10.7的rain.c程序,把main()中的主要任务都改成用函数来完成。
#include 编写一个程序,提示用户输入3组数,每组数包含5个double类型的数(假设用户都正确地响应,不会输入非数值数据)。该程序应完成下列任务。
a.把用户输入的数据储存在3×5的数组中
b.计算每组(5个)数据的平均值
c.计算所有数据的平均值
d.找出这15个数据中的最大值
e.打印结果
每个任务都要用单独的函数来完成(使用传统C处理数组的方式)。完成任务b,要编写一个计算并返回一维数组平均值的函数,利用循环调用该函数3次。对于处理其他任务的函数,应该把整个数组作为参数,完成任务c和d的函数应把结果返回主调函数。
14. 以变长数组作为函数形参,完成编程练习13。
#include 第十一章 字符串和字符串函数
1.设计并测试一个函数,从输入中获取下n个字符(包括空白、制表符、换行符),把结果储存在一个数组里,它的地址被传递作为一个参数。
#include- 修改并编程练习1的函数,在n个字符后停止,或在读到第1个空白、制表符或换行符时停止,哪个先遇到哪个停止。不能只使用scanf()。
#include- 设计并测试一个函数,从一行输入中把一个单词读入一个数组中,并丢弃输入行中的其余字符。该函数应该跳过第1个非空白字符前面的所有空白。将一个单词定义为没有空白、制表符或换行符的字符序列。
#include- 设计并测试一个函数,它类似编程练习3的描述,只不过它接受第2个参数指明可读取的最大字符数。
#include- 设计并测试一个函数,搜索第1个函数形参指定的字符串,在其中查找第2个函数形参指定的字符首次出现的位置。如果成功,该函数返指向该字符的指针,如果在字符串中未找到指定字符,则返回空指针(该函数的功能与 strchr()函数相同)。在一个完整的程序中测试该函数,使用一个循环给函数提供输入值。
#include- 编写一个名为is_within()的函数,接受一个字符和一个指向字符串的指针作为两个函数形参。如果指定字符在字符串中,该函数返回一个非零值(即为真)。否则,返回0(即为假)。在一个完整的程序中测试该函数,使用一个循环给函数提供输入值。
#includestrncpy(s1, s2, n)函数把s2中的n个字符拷贝至s1中,截断s2,或者有必要的话在末尾添加空字符。如果s2的长度是n或多于n,目标字符串不能以空字符结尾。该函数返回s1。自己编写一个这样的函数,名为mystrncpy()。在一个完整的程序中测试该函数,使用一个循环给函数提供输入值。
#include- 编写一个名为string_in()的函数,接受两个指向字符串的指针作为参数。如果第2个字符串中包含第1个字符串,该函数将返回第1个字符串开始的地址。例如,string_in(“hats”, “at”)将返回hats中a的地址。否则,该函数返回空指针。在一个完整的程序中测试该函数,使用一个循环给函数提供输入值。
#include - 编写一个函数,把字符串中的内容用其反序字符串代替。在一个完整的程序中测试该函数,使用一个循环给函数提供输入值。
#include 编写一个函数接受一个字符串作为参数,并删除字符串中的空格。在一个程序中测试该函数,使用循环读取输入行,直到用户输入一行空行。该程序应该应用该函数只每个输入的字符串,并显示处理后的字符串。
#include 编写一个函数,读入10个字符串或者读到EOF时停止。该程序为用户提供一个有5个选项的菜单:打印源字符串列表、以ASCII中的顺序打印字符串、按长度递增顺序打印字符串、按字符串中第1个单词的长度打印字符串、退出。菜单可以循环显示,除非用户选择退出选项。当然,该程序要能真正完成菜单中各选项的功能。
#include 编写一个程序,读取输入,直至读到 EOF,报告读入的单词数、大写字母数、小写字母数、标点符号数和数字字符数。使用ctype.h头文件中的函数。
#include 编写一个程序,反序显示命令行参数的单词。例如,命令行参数是see you later,该程序应打印later you see。
#include 编写一个通过命令行运行的程序计算幂。第1个命令行参数是double类型的数,作为幂的底数,第2个参数是整数,作为幂的指数。
#include 使用字符分类函数实现atoi()函数。如果输入的字符串不是纯数字,该函数返回0。
#include - 编写一个程序读取输入,直至读到文件结尾,然后把字符串打印出来。该程序识别和实现下面的命令行参数:
-p 按原样打印
-u 把输入全部转换成大写
-l 把输入全部转换成小写
如果没有命令行参数,则让程序像是使用了-p参数那样运行。
#include 