pandas join表的拼接操作
文章目录
- Relational Connection
-
- `merge`
- Index Connection
- Directional Connection
-
- `concat`
- `append` and `assign`
- Operation similar to connection
-
- `compare`
- `combine`
Relational Connection
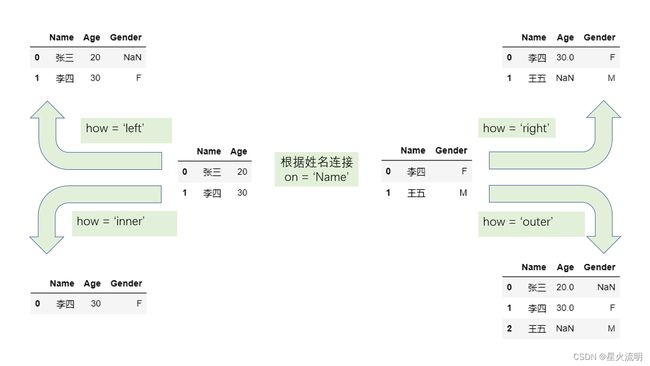
merge
df1.merge(df2, on, how)
df.merge(dsf2, left_on, right_on, how)
df1.merge(df2, on, how, suffixes)
on is a column or a list, the base columns of merging.
Similarly, left_on for left table, right_on for right table.
how is a str in [‘left’, ‘right’, ‘inner’, ‘outer’], default ‘inner’
suffixes is a list with two suffixes,
used to distinguish columns with same name in different tables.
Specially,
merge can check out the correspondence in two tables
with a parameter validate
df1.merge(df2, on, how, validate)
validate is a str in [‘1:1’, ‘1:m’, ‘m:1’, ‘m:m’].
Index Connection
df1.join(df2, how, lsuffix, rsuffix)
Directional Connection
concat
pd.concat(dfs, axis, join, keys)
dfs is a list of dataframe joined.
axis is the direction, default 0.
join is a str in [‘left’, ‘right’, ‘inner’, ‘outer’], default ‘outer’.
keys is a list of tips to mark the origin of data.
append and assign
append adds a series to table as a new row.
assign adds a series to table as a new column.
df.append(s, ignore_index)
df.assign(col_name=s)
s is a series to be added.
ignore_index is a bool value.
If true, use a automatic index; if false, use s.name as index.
col_name is the name of new column.
Operation similar to connection
compare
df1.compare(df2)
df1.compare(df2, keep_shape=True)
It compares two tables, and outputs a dataframe of difference.
keep_shape means that keep the old shape, default False.
combine
df1.combine(df2, func)
df1.combine(df2, func, overwrite=False)
func,
inputs two column with same name in two tables,
outputs a new column.
overtwrite=False can preserve columns
in the called table
that do not appear in the passed in parameter table,
without setting missing values.