分布式补充技术 01.AOP技术
01.AOP技术是对于面向对象编程(OOP)的补充。是按照OCP原则进行的编写,(ocp是修改模块权限不行,扩充可以)
02.写一个例子:
创建一个新的java项目,在main主启动类中,写如下代码。
package com.company;
interface mainService{
void send();
}
class DefaultServiceImpl implements mainService
{
@Override
public void send() {
System.out.println("hello");
}
}
public class main {
public static void main(String[] args){
DefaultServiceImpl defaultService=new DefaultServiceImpl();
defaultService.send();
}
}
一个接口,一个接口实现类,一个main主方法。
03.如果要实现显示接口实现类中的send方法运行的时间,一般的就在实现类中的send方法前后添加system.currenttimeMills
@Override
public void send() {
System.out.println("start:"+System.currentTimeMillis());
System.out.println("hello");
System.out.println("end:"+System.currentTimeMillis());
}
04.如果在项目的发布后,或者以后接口实现类以后代码多,如何去修改项目呢?实现显示运行时间呢?
方法一:继续写一个子类去继承接口实现类。
class DefaultServiceImpl implements mainService
{
@Override
public void send() {
// System.out.println("start:"+System.currentTimeMillis());
System.out.println("hello");
// System.out.println("end:"+System.currentTimeMillis());
}
}
class logDefaultImpl extends DefaultServiceImpl
{
@Override
public void send() {
System.out.println("start:"+System.currentTimeMillis());
System.out.println("hello");
System.out.println("end:"+System.currentTimeMillis());
}
}
package com.company;
interface mainService{
void send();
}
class DefaultServiceImpl implements mainService
{
@Override
public void send() {
// System.out.println("start:"+System.currentTimeMillis());
System.out.println("hello");
// System.out.println("end:"+System.currentTimeMillis());
}
}
class logDefaultImpl extends DefaultServiceImpl
{
@Override
public void send() {
System.out.println("start:"+System.currentTimeMillis());
System.out.println("hello");
System.out.println("end:"+System.currentTimeMillis());
}
}
public class main {
public static void main(String[] args){
mainService logDefaultImpl=new logDefaultImpl();
logDefaultImpl.send();
}
}
方法二:如果接口实现类被final修饰的话,不能用子类来继承,可以写一个集合来实现运行时间的功能
final class DefaultServiceImpl implements mainService
{
@Override
public void send() {
System.out.println("hello");
}
}
创建一个新的类,也同样实现接口mainService:
在这个类中声明一个接口的变量:
class logDefaultImpl implements mainService
{
private mainService mainservice;
public logDefaultImpl(mainService mainservice){
this.mainservice=mainservice;
}
@Override
public void send() {
System.out.println("start:"+System.currentTimeMillis());
mainservice.send();
System.out.println("end:"+System.currentTimeMillis());
}
}
在main主方法中:
public class main {
public static void main(String[] args){
mainService DefaultServiceImpl=new DefaultServiceImpl();
DefaultServiceImpl.send();
mainService log=new logDefaultImpl(new DefaultServiceImpl());
log.send();
}
}
通过构造函数,将final修饰的接口实现类传入到新的类中,结合方法,来实现显示运行时间的功能。
05.AOP技术的底层实现。
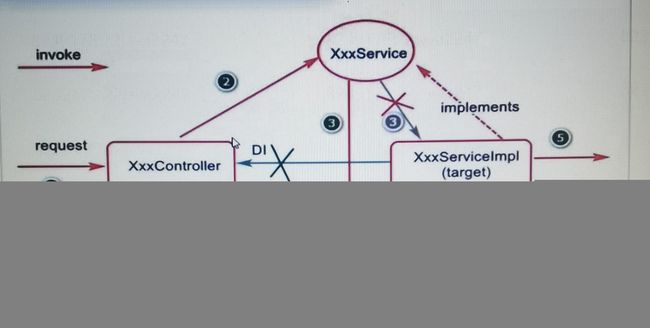
AOP对象是通过代理对象来实现的,代理对象有两种,一种是通过JDK来实现的,一种是通过CGlib来实现的。

jdk的代理就好像是使用一个新的类去继承接口,再来包含目标接口实现类
cglib是写一个子类去继承目标接口实现类。
06.AOP的术语
1切面:就是写了相关扩展功能的类
2.通知:就是切面中的相关方法
3.连接点:就是需要扩展的方法
4.切入点:就是连接点所在的类,有的时候也可能是一整个包。

07.在springboot中去实现AOP技术
先在maven项目中导入相关的依赖。

<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aopartifactId>
dependency>
在去写切面类,这里需要用注解@Aspect标识这个类是切面类,用@Component来将类交给spring容器进行管理。还需要使用到log4j来进行日志管理@Slf4j。
package com.cy.common;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Slf4j//日志
@Aspect//标识切面类
@Component//交给spring容器管理
public class sysLogAspect {
@Pointcut("bean(sysUserServiceImpl)")
//@Pointcut标识连接点(多个切入点的集合)
public void logPointCut(){}
@Around("logPointCut()")//这个是环绕通知,属性是切入点
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
//还是计算运行时间
//并且执行方法
Long startTime=System.currentTimeMillis();
Object object= joinPoint.proceed();//调用本切面的其他方法或者其他切面的通知和目标
Long endTime=System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("总时长是:",endTime-startTime);
return object;
}
}
@Pointcut标识连接点(多个切入点的集合),这里用来写的是连接点bean标识spring容器中的类,括号中的是类名,一般是接口的实现类impl。
这个切面的意义在于sysUserServiceImpl这个接口实现类的每一个方法都扩展了功能,记录运行时间。
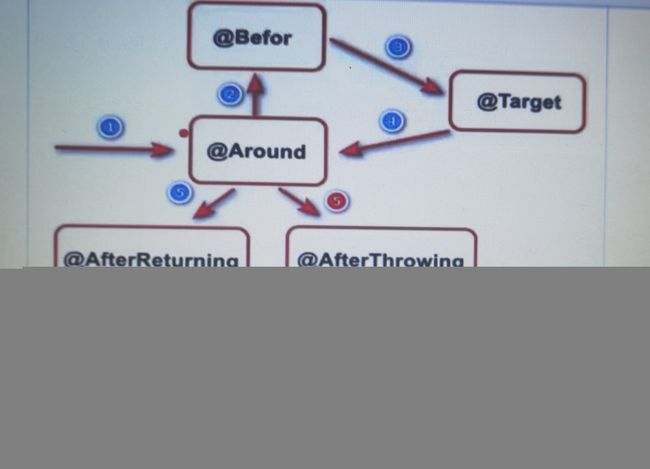
07.在springboot项目导入AOP依赖后,项目实现路径发送了改变。
springboot版本2.x后,默认AOP代理是Cglib
运行:
package com.cy.common;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Slf4j
@Aspect
@Component
public class sysTimeAspect {
@Pointcut("bean(sysUserServiceImpl)")
public void doTime(){}
@Around("doTime()")
public Object aroud(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
Long startTime=System.currentTimeMillis();
Object object= joinPoint.proceed();
Long endTime=System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("总时长是:",endTime-startTime);
System.out.println("通知around");
return object;
}
//前置
@Before("doTime()")
public void before() {
System.out.println("通知before");
}
//后置
@After("doTime()")
public void after() {
System.out.println("通知before");
}
//正常
@AfterReturning("doTime()")
public void AfterReturn() {
System.out.println("通知AfterReturning");
}
//异常
@AfterThrowing("doTime()")
public void AfterThrow() {
System.out.println("通知AfterThrowing");
}
}
使用通知@AfterThrowing,在切面中去写一个异常通知,就是目标接口类方法运行时候有异常,切面类处理。
@Slf4j
@Aspect
@Component
public class sysExceptionAspect {
@AfterThrowing(pointcut = "bean(sysUserServiceImpl)",throwing = "e")//pointcut是连接点,throwing是抛出的异常
public void doHandlerException(JoinPoint jp//这个是切入点,Throwable e){
MethodSignature ms= (MethodSignature)jp.getSignature();
log.error("{},exception msg is {}",ms.getName(),e.getMessage());
}
}
如果想要所有的接口实现类的运行方法报错时候有这个切面的类的AfterThrowing来处理异常,可以在bean中去写bean(*ServiceImpl)