【SpringCloud-1】注册中心-Eureka
springcloud微服务,相对于dubbo这种SOA架构,提供了一站式的全套解决方案,什么意思呢?就是说springcloud不需要依赖其他组件,自己提供了全套的 常规项目需要使用的技术和解决问题的方案。 比如dubbo需要依赖zk作为注册中心,springcloud有自己的注册中心,对于其他如链路追踪啊,服务降级啊……各种它都有,所以称为springcloud全家桶。 理论上来说,普通项目只需要使用springcloud就足够了。
那是不是意味着,SpringCloud就完美了呢? 它和dubbo相比选谁? 其实,存在即合理,都不错!
- 微服务,就是短小精干的服务,适合小项目,快速开发,上线,部署。功能简单,项目之间可以互不影响。 比如,通常做一些上层业务系统。
- 另外,微服务之间的调用是http,性能自然是没有dubbo的rpc好。 如果说量级不是很大,也没啥问题,否则还是建议rpc。
- 实际上呢,通常都会两者结合。 上层业务系统用springcloud,下层中台系统用dubbo。因为中台系统通常都比较庞大,调用量也高,需要提供稳定的能力。
下面先不说dubbo,来看看springcloud吧。
先搭建项目的架构:
如上,整个springcloud中会学习很多模块,所以先搭建一个父项目,在父pom中引入基本依赖:
4.0.0
com.lagou.edu
lagou-parent
1.0-SNAPSHOT
lagou-service-common
lagou-service-autodeliver-8090
lagou-service-autodeliver-8091
lagou-service-resume-8080
lagou-service-resume-8081
lagou-cloud-eureka-server-8761
lagou-cloud-eureka-server-8762
lagou-cloud-hystrix-dashboard-9000
lagou-cloud-hystrix-turbine-9001
lagou-service-autodeliver-8096
lagou-cloud-configserver-9006
lagou-cloud-stream-producer-9090
lagou-cloud-stream-consumer-9091
lagou-cloud-stream-consumer-9092
pom
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-parent
2.1.6.RELEASE
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-dependencies
Greenwich.RELEASE
pom
import
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-logging
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
org.projectlombok
lombok
1.18.4
provided
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-actuator
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-devtools
true
com.sun.xml.bind
jaxb-core
2.2.11
javax.xml.bind
jaxb-api
com.sun.xml.bind
jaxb-impl
2.2.11
org.glassfish.jaxb
jaxb-runtime
2.2.10-b140310.1920
javax.activation
activation
1.1.1
org.apache.maven.plugins
maven-compiler-plugin
1.8
1.8
utf-8
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-maven-plugin
一:Eureka搭建:
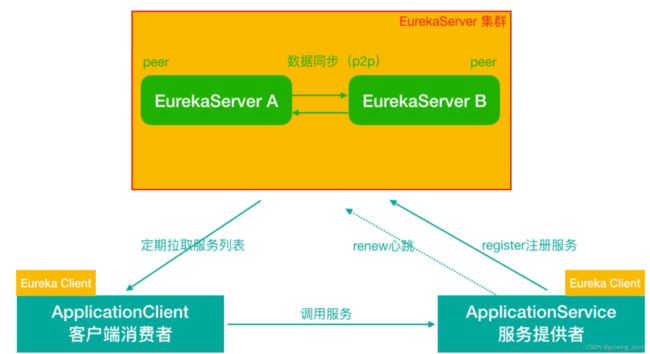
作为注册中心,主要是两部分:Server端和Client端
Server端:
Server1的配置:
lagou-parent
com.lagou.edu
1.0-SNAPSHOT
4.0.0
lagou-cloud-eureka-server-8761
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-server
#eureka server服务端口
server:
port: 8761
spring:
application:
name: lagou-cloud-eureka-server # 应用名称,应用名称会在Eureka中作为服务名称
# eureka 客户端配置(和Server交互),Eureka Server 其实也是一个Client
eureka:
instance:
hostname: LagouCloudEurekaServerA # 当前eureka实例的主机名
client:
service-url:
# 配置客户端所交互的Eureka Server的地址(Eureka Server集群中每一个Server其实相对于其它Server来说都是Client)
# 集群模式下,defaultZone应该指向其它Eureka Server,如果有更多其它Server实例,逗号拼接即可(这里只是本机测试,最好还是写ip地址)
defaultZone: http://LagouCloudEurekaServerB:8762/eureka
register-with-eureka: true # 集群模式下可以改成true,将自己注册到Eureka Server中
fetch-registry: true # 集群模式下可以改成true,自己作为客户端,要从Eureka Server获取服务信息,默认为true
dashboard:
enabled: trueServer2的配置:
#eureka server服务端口
server:
port: 8762
spring:
application:
name: lagou-cloud-eureka-server # 应用名称,应用名称会在Eureka中作为服务名称
# eureka 客户端配置(和Server交互),Eureka Server 其实也是一个Client
eureka:
instance:
hostname: LagouCloudEurekaServerB # 当前eureka实例的主机名
client:
service-url: # 配置客户端所交互的Eureka Server的地址
defaultZone: http://LagouCloudEurekaServerA:8761/eureka
register-with-eureka: true
fetch-registry: true启动类:
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.server.EnableEurekaServer;
@SpringBootApplication
// 声明当前项目为Eureka服务
@EnableEurekaServer
public class LagouEurekaServerApp8761 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(LagouEurekaServerApp8761.class,args);
}
}Client端:
有了注册中心之后,剩下的就是把业务服务作为client端,注册到Eureka。 业务服务中分为服务提供者和服务消费者。
先在父工程中的pom引入一个公共依赖:
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-commons
服务提供者:
lagou-parent
com.lagou.edu
1.0-SNAPSHOT
4.0.0
lagou-service-resume-8080
com.lagou.edu
lagou-service-common
1.0-SNAPSHOT
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client
配置文件yml:
server:
port: 8080
spring:
application:
name: lagou-service-resume
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/lagou?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8
username: root
password: 123456
jpa:
database: MySQL
show-sql: true
hibernate:
naming:
physical-strategy: org.hibernate.boot.model.naming.PhysicalNamingStrategyStandardImpl #避免将驼峰命名转换为下划线命名
cloud:
# config客户端配置,和ConfigServer通信,并告知ConfigServer希望获取的配置信息在哪个文件中
config:
name: lagou-service-resume #配置文件名称
profile: dev #后缀名称
label: master #分支名称
uri: http://localhost:9006 #ConfigServer配置中心地址
rabbitmq:
host: 127.0.0.1
port: 5672
username: guest
password: guest
#注册到Eureka服务中心
eureka:
client:
service-url:
# 注册到集群,就把多个Eurekaserver地址使用逗号连接起来即可;注册到单实例(非集群模式),那就写一个就ok
defaultZone: http://LagouCloudEurekaServerA:8761/eureka,http://LagouCloudEurekaServerB:8762/eureka
instance:
prefer-ip-address: true #服务实例中显示ip,而不是显示主机名(兼容老的eureka版本)
# 实例名称: 192.168.1.103:lagou-service-resume:8080,我们可以自定义它
instance-id: ${spring.cloud.client.ip-address}:${spring.application.name}:${server.port}:@project.version@
# 自定义Eureka元数据
metadata-map:
cluster: cl1
region: rn1
management:
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
include: "*"启动类:
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.domain.EntityScan;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.EnableDiscoveryClient;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.support.PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer;
@SpringBootApplication
@EntityScan("com.lagou.edu.pojo")
//@EnableEurekaClient // 开启Eureka Client(Eureka独有)
@EnableDiscoveryClient // 开启注册中心客户端 (通用型注解,比如注册到Eureka、Nacos等)
// 说明:从SpringCloud的Edgware版本开始,不加注解也ok,但是建议大家加上
public class LagouResumeApplication8080 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(LagouResumeApplication8080.class,args);
}
}服务提供者配置好了,其实服务消费者也是一样的。 因为都是作为Eureka的client端。 那么,消费者如何调用提供者?
二:Eureka细节:
原数据:
1、标准元数据:主机名、IP地址、端⼝号等信息,这些信息都会被发布在服务注册表中,⽤于服务之间的调⽤。
2、⾃定义元数据: 可以使⽤ eureka.instance.metadata-map 配置,符合 KEY/VALUE 的存储格式。这 些元数据可以在远程客户端中访问。 类似于
eureka客户端:
不管是服务提供者或者是消费者,都称为Eureka客户端
服务每隔30秒会向注册中⼼续约(⼼跳)⼀次,如果没有续约,租约在90秒后到期,然后服务会被失效。每隔30秒的续约操作我们称之为⼼跳检测。往往不需要我们调整这两个配置
另外,(消费者)服务启动时会拉取服务列表缓存到本地,然后 每隔 30 秒服务会从注册中⼼中拉取一次,这个时间可以通过配置修改。
eureka服务端:
服务下线
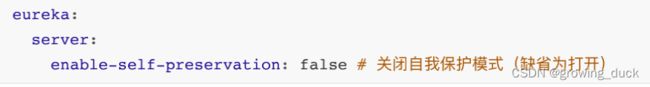
1 )当服务正常关闭操作时,会发送服务下线的 REST 请求给 EurekaServer 。2 )服务中⼼接受到请求后,将该服务置为下线状态失效剔除
三:源码解析-启动过程
1、eureka启动过程:
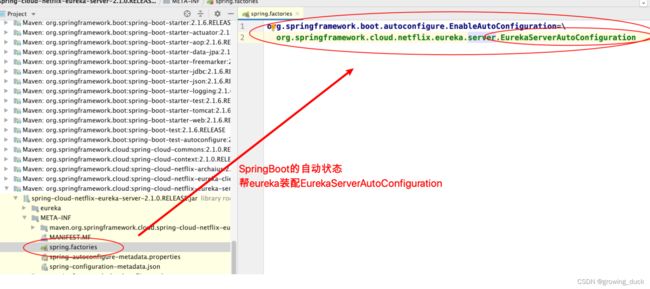
⼊⼝:SpringCloud充分利⽤了SpringBoot的⾃动装配的特点 。观察eureka-server的jar包,发现在META-INF下⾯有配置⽂件spring.factories:
springboot 应⽤启动时会加载 EurekaServerAutoConfifiguration ⾃动配置类
基于上面三个点,来具体看看:
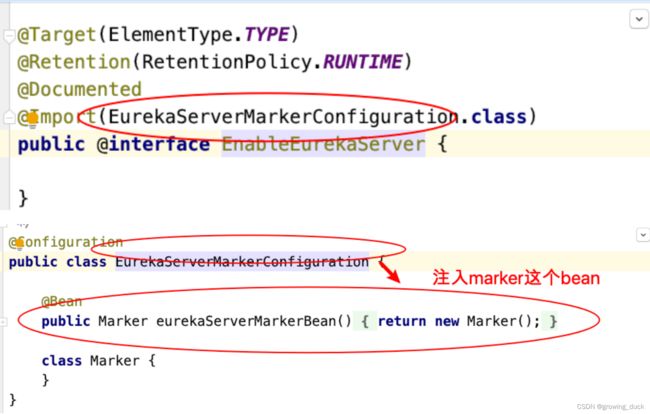
1、需要有⼀个 marker bean ,才能装配 Eureka Server ,那么这个 marker其实是由@EnableEurekaServer 注解决定的,如下:所以只有添加了@EnableEurekaServer注解,才会有后续的动作,这是成为⼀个EurekaServer的前提。
2、查看EurekaServerAutoConfiguration,此类是核心配置类,装配了一些bean。 这些bean的作用如下:
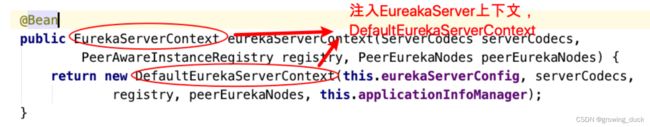
第二个对等节点注册器,简单理解就是把每个server实例,注册为server集群中的节点。 他需要依赖第三个bean PeerEurekaNodes来封装,更新节点信息。 细看PeerEurekaNodes:
它有个start方法,里面构建了线程池,在线程任务执行run方法时,就会执行更新的方法。
那线程任务何时执行呢?回到核心配置类中,还装配了一个bean,叫做DefaultEurekaServerContext。
在装配过程中,当DefaultEurekaServerContext在实例化后,会调用自己的初始化方法,当中,就调用了PeerEurekaNodes的start方法:
最后,在主配置类中还有两个bean可以看一下:
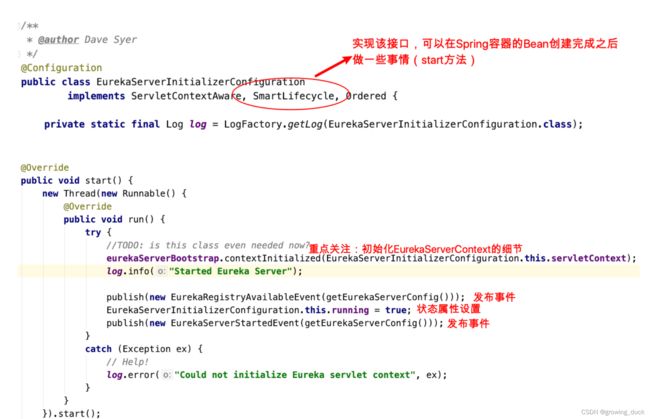
3、关注EurekaServerInitializerConfiguration。 此类是核心配置类中引入的另一个配置类:
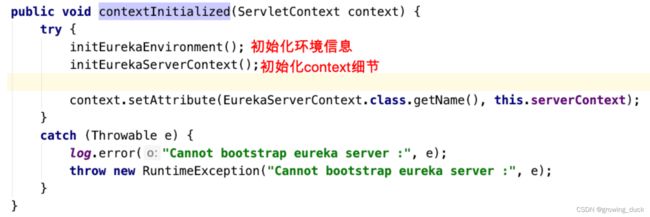
进⼊EurekaServerBootstrap#contextInitialized接着进入context细节:
其实主要就是同步其他节点信息,并将自己对外提供服务(同时开启定时任务,每60s执行一次失效剔除)。