PostgreSQL数据库分区裁剪——enable_partition_pruning
在PostgreSQL 10版本之前,PostgreSQL数据库实际上是没有单独的创建分区表的DDL语句,都是通过表继承的原理来创建分区表,这样使得在PostgreSQL中使用分区表不是很方便,到PostgreSQL 10之后,PostgreSQL扩展了创建表的DDL语句,可以用这个DDL语句来创建分区表,原先使用继承的方式还是可以创建分区表,但这两种分区表是不能混用的。于是PostgreSQL 10增加的分区表叫声明式分区(Declarative Partitioning),原先使用表继承的方式仍然可以实现分区表的功能。而使用继承的方式实现的分区表的分区裁剪是靠设置参数“constraint_exclusion=partition”来实现的,而如果使用了声明式分区表,则需要使用参数“enable_partition_pruning”来控制是否使用分区裁剪功能(Enables plan-time and run-time partition pruning. Allows the query planner and executor to compare partition bounds to conditions in the query to determine which partitions must be scanned)。PostgreSQL支持静态条件分区裁剪,Greenplum通过ORCA 优化器实现了动态分区裁剪。参考关于PostgreSQL的分区表的历史及分区裁剪参数enable_partition_pruning与constraint_exclusion的区别文档对分区裁剪进行学习。
创建声明式分区表
创建声明式分区表SQL如下所示CREATE TABLE ptab01 (id int not null, tm timestamptz not null) PARTITION BY RANGE (tm);。首先我们看一下其抽象查询语法树AST,RawStmt结构体是单个语句的raw解析树的存储结构(container for any one statement’s raw parse tree)。CreateStmt结构体定义在src/include/nodes/parsenodes.h文件中,relation代表需要创建的关系表,tableElts代表列定义,partspec代表PARTITION BY子句。
/* Optional partition key specification */
OptPartitionSpec: PartitionSpec { $$ = $1; } | /*EMPTY*/ { $$ = NULL; }
PartitionSpec: PARTITION BY ColId '(' part_params ')'
{
PartitionSpec *n = makeNode(PartitionSpec);
n->strategy = $3; n->partParams = $5; n->location = @1; $$ = n;
}

该SQL使用的时part_elem的规则一,分区键是列名。从其他规则来看,可以partition by函数表达式或表达式,而不仅仅是列名。
part_params: part_elem { $$ = list_make1($1); } | part_params ',' part_elem { $$ = lappend($1, $3); }
part_elem: ColId opt_collate opt_class
{ PartitionElem *n = makeNode(PartitionElem);
n->name = $1; n->collation = $2; n->opclass = $3;
n->expr = NULL; n->location = @1; $$ = n; }
| func_expr_windowless opt_collate opt_class
{ PartitionElem *n = makeNode(PartitionElem);
n->expr = $1; n->collation = $2; n->opclass = $3;
n->name = NULL; n->location = @1; $$ = n;
}
| '(' a_expr ')' opt_collate opt_class
{ PartitionElem *n = makeNode(PartitionElem);
n->name = NULL; n->location = @1; $$ = n;
n->expr = $2; n->collation = $4; n->opclass = $5;
}
parse_analyze函数进入查询语句分析transformStmt流程,对于该SQL直接是走右下角的default的流程(result = makeNode(Query); result->commandType = CMD_UTILITY; result->utilityStmt = (Node *) parseTree; break;)。
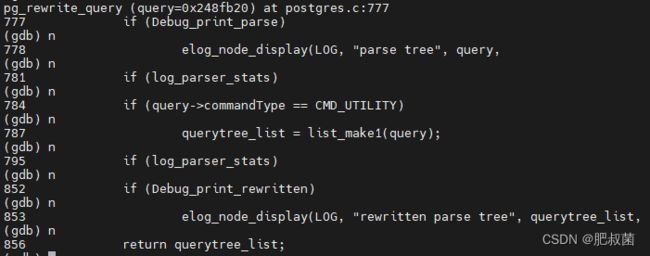
进入pg_rewrite_query函数流程,如下是elog_node_display(LOG, "parse tree", ...)语句打印的查询语句分析transformStmt流程之后的解析树。utilityStmt就是上述流程的抽象查询语法树AST RawStmt结构体。commandType为5代表的是CMD_UTILITY。

该SQL不需要经过QueryWrite查询重写过程,将其作为querytree_list的元素,调用elog_node_display(LOG, "rewritten parse tree", querytree_list...)函数输出重写的解析树。

进入执行器,从执行流程可以看出其执行策略是PORTAL_MULTI_QUERY,走default分支的ProcessUtilitySlow函数。首先调用transformCreateStmt进行语法分析(transform阶段下放到这里了),将语法树转为CreateStmt、TableLikeClause、UTILITY_SUBCOMMAND PlannedStmt(由于建表语句中会有serial,check等额外的特性,这些需要额外的PlannedStmt来处理,因此会增加PlannedStmt)。
PortalStart PORTAL_MULTI_QUERY Need do nothing now
PortalRun
| -- PortalRunMulti
| -- PortalRunUtility (pstmt->utilityStmt {type = T_CreateStmt, relation = 0x248e830, tableElts = 0x248eba8, inhRelations = 0x0, partbound = 0x0, partspec = 0x248efb0, ofTypename = 0x0, constraints = 0x0, options = 0x0, oncommit = ONCOMMIT_NOOP, tablespacename = 0x0, accessMethod = 0x0, if_not_exists = false})
| -- ProcessUtility
| -- standard_ProcessUtility
| -- ProcessUtilitySlow
| case T_CreateStmt: case T_CreateForeignTableStmt:
| -- List *stmts = transformCreateStmt <-- transform阶段下放到这里了
| -- while (stmts != NIL)
| -- Node *stmt = (Node *) linitial(stmts); stmts = list_delete_first(stmts);
| -- if (IsA(stmt, CreateStmt))
| -- else if (IsA(stmt, TableLikeClause))
| -- else ProcessUtility(wrapper, queryString, false, PROCESS_UTILITY_SUBCOMMAND, params, NULL, None_Receiver, NULL);
建表走如下流程:
CreateStmt *cstmt = (CreateStmt *) stmt;
Datum toast_options; static char *validnsps[] = HEAP_RELOPT_NAMESPACES;
/* Create the table itself */
address = DefineRelation(cstmt, RELKIND_RELATION, InvalidOid, NULL, queryString);
/* parse and validate reloptions for the toast table */
toast_options = transformRelOptions((Datum) 0, cstmt->options, "toast", validnsps, true, false);
(void) heap_reloptions(RELKIND_TOASTVALUE, toast_options, true);
NewRelationCreateToastTable(address.objectId,toast_options);
分区裁剪
postgres=# explain select * from ptab01 where tm='2020-01-07'::timestamptz;
QUERY PLAN
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Seq Scan on ptab01_202001 (cost=0.00..80.80 rows=1 width=12)
Filter: (tm = '2020-01-07 00:00:00-08'::timestamp with time zone)
(2 rows)
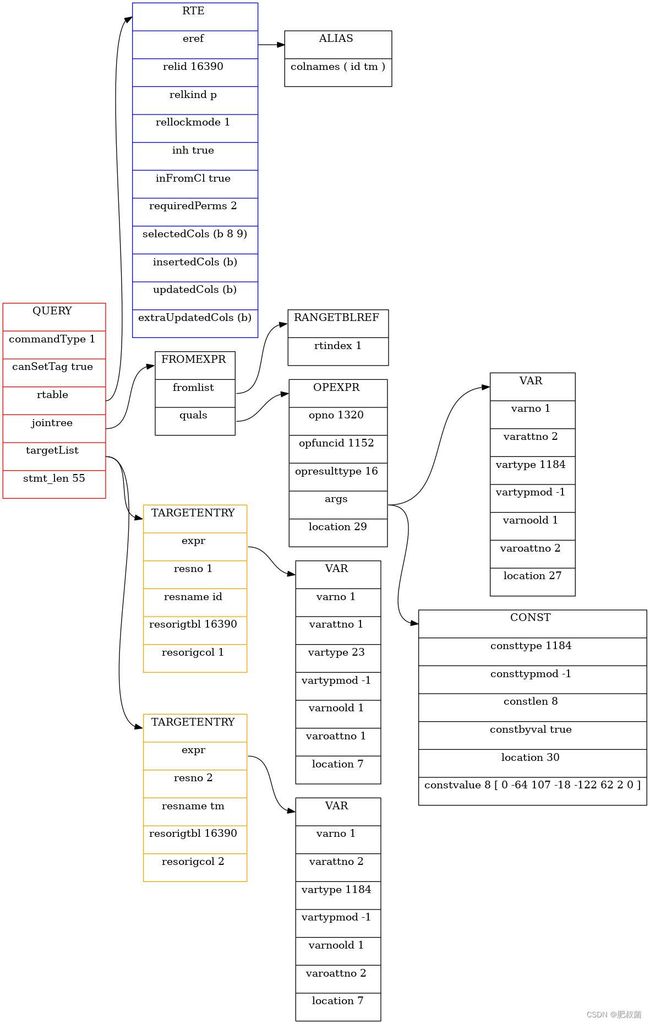
从上面可以看出,声明式分区表只扫描了包括指定时间实际的分区ptab01_202001,没有扫描其他时间段的分区。首先我们看一下其抽象查询语法树AST,RawStmt结构体是单个语句的raw解析树的存储结构(container for any one statement’s raw parse tree),也就是elog_node_display(LOG, "raw tree", parseTree, ...)打印出来的解析器输出。Select型查询语句SelectStmt定义在src/include/nodes/parsenodes.h中,如下其包含目标列域targetList、from子句fromClause、where条件whereClause。where条件whereClause结构体执行A_Expr结构体(有如下成员NodeTag type、A_Expr_Kind kind、List *name、Node *lexper、Node *rexpr、int location),其中name指明了这是等号条件,左边的等式是ColumnRef,右边是被强制转换的常量’2020-01-07’;targetLost执行RESTARTGET节点,其包含的是COLUMNREF,这里其代表A_START也就是“*”(所有列)[ 从下图可以看出ColumnRef能代表两种类型的节点,一是单列,而是所有列 ]。

从调用堆栈可以看出transformOptionalSelectInto函数并没有执行有效代码,只是调用了transformStmt,进行后续针对不同类型的Stmt分类处理。走transformSelectStmt函数处理T_SelectStmt节点。
transformOptionalSelectInto (pstate=0x1de9848, parseTree=0x1dc4c80)
if (IsA(parseTree, SelectStmt))
SelectStmt *stmt = (SelectStmt *) parseTree;
while (stmt && stmt->op != SETOP_NONE) --> stmt->op == SETOP_NONE
if (stmt->intoClause)
return transformStmt(pstate, parseTree);
transformStmt (pstate=0x1de9848, parseTree=0x1dc4c80) at analyze.c:277
switch (nodeTag(parseTree))
case T_SelectStmt:
SelectStmt *n = (SelectStmt *) parseTree;
if (n->valuesLists)
else if (n->op == SETOP_NONE) <-- 走这个分支
result = transformSelectStmt(pstate, n);
return result;
transformSelectStmt (pstate=0x1de9848, stmt=0x1dc4c80) at analyze.c:1200
Query *qry = makeNode(Query);
qry->commandType = CMD_SELECT;
transformFromClause(pstate, stmt->fromClause);
首先对From子句进行转换,transformFromClauseItem函数将会对fromClause列表元素RANGEVAR结构体进行转换,图中的RANGEVAR不是CTE reference/tuplestore reference,所以只能是plain relation reference,调用transformTableEntry函数。

下一步会走到transformStmt函数中的T_SelectStmt分支,op为SETOP_NONE,因此会执行transformSelectStmt函数。由于没有with、into、window等子句,直接处理From子句(仅有RangeVar节点),执行transformFromClause子句。
enable_partition_pruning GUC参数出现在query_planner的prune_append_rel_partitions和创建执行计划的create_append_plan、create_merge_append_plan。和constraint exclusion不同的是,enable_partition_pruning GUC参数额外出现在了根据最优路径创建执行计划的流程中。
prune_append_rel_partitions函数处理关系表的baserestrictinfo(rel->baserestrictinfo为SQL关联到relation上的SQL谓词表达式列表),利用在查询优化阶段可以evaluated的quals表达式去确定分区的最小集合,并返回包含匹配分区indexes(该index用于rel’s part_rels array数组的寻址)的Bitmapset(静态分区裁剪)。执行流程如下:
Bitmapset *prune_append_rel_partitions(RelOptInfo *rel){
List *clauses = rel->baserestrictinfo;
List *pruning_steps; GeneratePruningStepsContext gcontext;
if (rel->nparts == 0) return NULL; /* If there are no partitions, return the empty set */
if (!enable_partition_pruning || clauses == NIL) return bms_add_range(NULL, 0, rel->nparts - 1); /* If pruning is disabled or if there are no clauses to prune with, return all partitions. */
/* Process clauses to extract pruning steps that are usable at plan time. If the clauses are found to be contradictory, we can return the empty set. */
gen_partprune_steps(rel, clauses, PARTTARGET_PLANNER,&gcontext);
if (gcontext.contradictory) return NULL;
pruning_steps = gcontext.steps;
if (pruning_steps == NIL) return bms_add_range(NULL, 0, rel->nparts - 1); /* If there's nothing usable, return all partitions */
/* Set up PartitionPruneContext */
PartitionPruneContext context;
context.strategy = rel->part_scheme->strategy; context.partnatts = rel->part_scheme->partnatts;
context.nparts = rel->nparts; context.boundinfo = rel->boundinfo;
context.partcollation = rel->part_scheme->partcollation; context.partsupfunc = rel->part_scheme->partsupfunc;
context.stepcmpfuncs = (FmgrInfo *) palloc0(sizeof(FmgrInfo) *context.partnatts *list_length(pruning_steps));
context.ppccontext = CurrentMemoryContext;
/* These are not valid when being called from the planner */
context.planstate = NULL; context.exprcontext = NULL; context.exprstates = NULL;
return get_matching_partitions(&context, pruning_steps); /* Actual pruning happens here. */
}
执行堆栈:
query_planner --> add_other_rels_to_query --> expand_inherited_rtentry --> expand_partitioned_rtentry --> prune_append_rel_partitions
expand_inherited_rtentry --> expand_appendrel_subquery --> expand_inherited_rtentry --> expand_partitioned_rtentry --> prune_append_rel_partitions

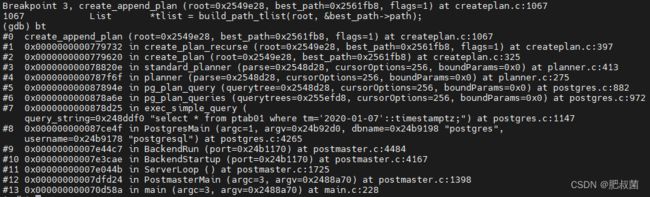
create_append_plan和create_merge_append_plan函数在创建执行计划阶段进行分区裁剪,关于enable_partition_pruning为true分支,这两种情况执行都很相似,都是为执行期间进行分区裁剪收集信息(动态分区裁剪),并创建PartitionPruneInfo结构体存放该信息。
static Plan *create_append_plan(PlannerInfo *root, AppendPath *best_path, int flags){
...
/* If any quals exist, they may be useful to perform further partition pruning during execution. Gather information needed by the executor to do partition pruning. */
if (enable_partition_pruning){
List *prunequal = extract_actual_clauses(rel->baserestrictinfo, false);
if (best_path->path.param_info){
List *prmquals = best_path->path.param_info->ppi_clauses;
prmquals = extract_actual_clauses(prmquals, false); prmquals = (List *) replace_nestloop_params(root,(Node *) prmquals);
prunequal = list_concat(prunequal, prmquals);
}
if (prunequal != NIL)
partpruneinfo = make_partition_pruneinfo(root, rel, best_path->subpaths, prunequal);
}
plan->appendplans = subplans; plan->nasyncplans = nasyncplans; plan->first_partial_plan = best_path->first_partial_path; // or node->mergeplans = subplans;
plan->part_prune_info = partpruneinfo;
}
执行堆栈:
create_plan_recurse --> case T_Append: create_append_plan
create_merge_append_plan
create_plan_recurse --> case T_MergeAppend: create_merge_append_plan
src/backend/optimizer/plan/setrefs.c/set_append_references中会对part_prune_info中的rtindex进行修正,其调用者set_plan_references函数在create_plan创建执行计划之后。
static Plan *set_append_references(PlannerInfo *root, Append *aplan, int rtoffset)
if (aplan->part_prune_info){
foreach(l, aplan->part_prune_info->prune_infos){
List *prune_infos = lfirst(l); ListCell *l2;
foreach(l2, prune_infos){
PartitionedRelPruneInfo *pinfo = lfirst(l2);
pinfo->rtindex += rtoffset;
}
}
}
standard_planner --> set_plan_references --> set_plan_refs --> set_append_references --> set_plan_refs --> set_append_references
--> set_customscan_references --> set_plan_refs --> set_append_references
--> set_subqueryscan_references --> set_plan_references
在src/backend/executor/nodeAppend.c文件中Append节点初始化ExecInitAppend流程中包含了动态分区裁剪初始化的流程(同样MergeAppend节点初始化ExecInitMergeAppend也包含相同流程),如下所示:
AppendState *ExecInitAppend(Append *node, EState *estate, int eflags){
/* If run-time partition pruning is enabled, then set that up now */
if (node->part_prune_info != NULL){
/* Set up pruning data structure. This also initializes the set of subplans to initialize (validsubplans) by taking into account the result of performing initial pruning if any. */
PartitionPruneState *prunestate = ExecInitPartitionPruning(&appendstate->ps, list_length(node->appendplans), node->part_prune_info, &validsubplans);
appendstate->as_prune_state = prunestate;
nplans = bms_num_members(validsubplans);
/* When no run-time pruning is required and there's at least one subplan, we can fill as_valid_subplans immediately, preventing later calls to ExecFindMatchingSubPlans. */
if (!prunestate->do_exec_prune && nplans > 0)
appendstate->as_valid_subplans = bms_add_range(NULL, 0, nplans - 1);
}else{
nplans = list_length(node->appendplans);
/* When run-time partition pruning is not enabled we can just mark all subplans as valid; they must also all be initialized. */
appendstate->as_valid_subplans = validsubplans = bms_add_range(NULL, 0, nplans - 1);
appendstate->as_prune_state = NULL;
}
create table ptab01_202001 partition of ptab01 for values from ('2020-01-01') to ('2020-02-01');
create table ptab01_202002 partition of ptab01 for values from ('2020-02-01') to ('2020-03-01');
create table ptab01_202003 partition of ptab01 for values from ('2020-03-01') to ('2020-04-01');
create table ptab01_202004 partition of ptab01 for values from ('2020-04-01') to ('2020-05-01');
create table ptab01_202005 partition of ptab01 for values from ('2020-05-01') to ('2020-06-01');
insert into ptab01 select extract(epoch from seq), seq from generate_series('2020-01-01'::timestamptz, '2020-05-31 23:59:59'::timestamptz, interval '10 seconds') as seq;