Springboot之Jasypt配置文件加密/解密【源码分析】
Springboot Jasypt源码分析
- 一、Springboot Jasypt源码猜想
- 二、Springboot Jasypt源码分析
-
- 2.1 JasyptSpringBootAutoConfiguration
- 2.2 EnableEncryptablePropertiesConfiguration
- 2.3 EnableEncryptablePropertiesBeanFactoryPostProcessor
- 2.4 EncryptablePropertySourceConverter.convertPropertySources(MutablePropertySources propSources)
- 2.5 EncryptablePropertySourceConverter.makeEncryptable(PropertySource
propertySource) - 2.6 EncryptablePropertySourceConverter.convertPropertySource(PropertySource
propertySource) - 2.7 CachingDelegateEncryptablePropertySource.getProperty(String name)
- 2.8 EncryptablePropertySource.getProperty
- 2.9 DefaultPropertyResolver.resolvePropertyValue
文章系列
【一、Springboot之Jasypt配置文件加密/解密】
【二、Springboot之Jasypt配置文件加密/解密【源码分析】】
一、Springboot Jasypt源码猜想
Jasypt 是一个 java 库,可以使开发者不需要太多操作来给 Java 项目添加基本加密功能,而且不需要知道加密原理。Jasypt 为开发人员提供了一种简单易用加密功能,包括:密码认证、字符串加密等。
那么Jasypt在 Springboot 项目中是如何运行的呢???
在 Springboot 中,所以配置文件都是通过 Environment 来管理的,项目启动时,会先初始化 Environment 对象,然后通过 Springboot 自动装配机制,将 Environment 对象封装为 PropertySource,并添加到 MutablePropertySources 中,最后再进行属性注入的时候,通过调用 PropertySource 的 getProperty(String key) 方法,获取并注入属性值。有关 SpringBoot配置文件解析过程详细解析,可查看 《https://blog.csdn.net/qq_33375499/article/details/122651673》。
由此可以猜想,Springboot 在启动过程中,将所以配置文件添加到 MutablePropertySources 对象中,Jasypt 通过将 MutablePropertySources 对象中的所有 PropertySource 进行循环遍历,然后对 PropertySource 进行代理 / 包装,使得在调用 getProperty(String key) 方法时候,能够进行解密处理。最后通过 MutablePropertySources 提供的 replace(String name, PropertySource propertySource) 方法,替换其中的 PropertySource 为 Jasypt的代理类 / 包装类。
二、Springboot Jasypt源码分析
Jasypt 整合 Springboot 过程中,借用了 Springboot 自动装配原理,由此可见,入口在 jasypt-spring-boot-starter jar包中,如下图:
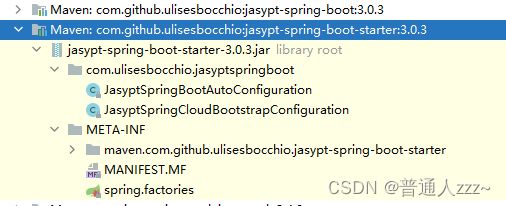
其中 spring.factories 内容为:
// springboot 自动装配机制
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=com.ulisesbocchio.jasyptspringboot.JasyptSpringBootAutoConfiguration
// Spring Cloud 配置启动加载项
org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.BootstrapConfiguration=com.ulisesbocchio.jasyptspringboot.JasyptSpringCloudBootstrapConfiguration
2.1 JasyptSpringBootAutoConfiguration
JasyptSpringBootAutoConfiguration 类中添加了 @Import 注解(关于 @Import 注解详解,可以参考《 SpringBoot 核心原理》),既将 EnableEncryptablePropertiesConfiguration 导入进 Spring IoC容器中。
@Configuration
@Import({EnableEncryptablePropertiesConfiguration.class})
public class JasyptSpringBootAutoConfiguration {
public JasyptSpringBootAutoConfiguration() {
}
}
2.2 EnableEncryptablePropertiesConfiguration
@Configuration
@Import({EncryptablePropertyResolverConfiguration.class, CachingConfiguration.class})
@Slf4j
public class EnableEncryptablePropertiesConfiguration {
@Bean
public static EnableEncryptablePropertiesBeanFactoryPostProcessor enableEncryptablePropertySourcesPostProcessor(final ConfigurableEnvironment environment, EncryptablePropertySourceConverter converter) {
return new EnableEncryptablePropertiesBeanFactoryPostProcessor(environment, converter);
}
}
EnableEncryptablePropertiesConfiguration 也添加了 @Import ,但其中导入的 EncryptablePropertyResolverConfiguration、CachingConfiguration 本身并没有特别的。
EncryptablePropertyResolverConfiguration 类主要将 Jasypt 一些核心Bean导入进 Spring IoC 容器中,如:EncryptablePropertySourceConverter(可加密属性源转换器)、EnvCopy(环境copy对象)、JasyptEncryptorConfigurationProperties(Jasypt 加密器配置属性对象)等等,不过需要值得注意的是,在 EncryptablePropertyResolverConfiguration 中,注入了一个 StringEncryptor 类型的 Bean,该 Bean 用于获取自定义解密器类。
@Bean(name = ENCRYPTOR_BEAN_NAME)
public StringEncryptor stringEncryptor(final EnvCopy envCopy, final BeanFactory bf) {
/**
* 获取 自定义加密器 Bean 名称
* ENCRYPTOR_BEAN_PLACEHOLDER = String.format("${%s:jasyptStringEncryptor}", jasypt.encryptor.bean)
*/
final String customEncryptorBeanName = envCopy.get().resolveRequiredPlaceholders(ENCRYPTOR_BEAN_PLACEHOLDER);
// 是否自定义
final boolean isCustom = envCopy.get().containsProperty(ENCRYPTOR_BEAN_PROPERTY);
return new DefaultLazyEncryptor(envCopy.get(), customEncryptorBeanName, isCustom, bf);
}
EnableEncryptablePropertiesConfiguration 在 Jasypt的加解密核心流程中,主要注入了 EnableEncryptablePropertiesBeanFactoryPostProcessor Bean对象。
2.3 EnableEncryptablePropertiesBeanFactoryPostProcessor
该类实现了 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 接口,Spring IoC容器在注入该 Bean 进行初始化后,会执行其中的 postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) 方法。
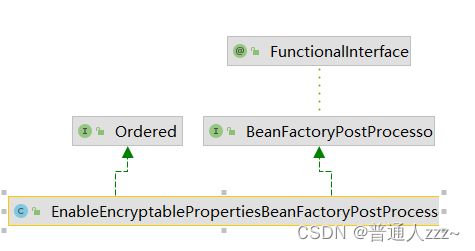
public class EnableEncryptablePropertiesBeanFactoryPostProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor, Ordered {
private static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(EnableEncryptablePropertiesBeanFactoryPostProcessor.class);
private final ConfigurableEnvironment environment;
private final EncryptablePropertySourceConverter converter;
public EnableEncryptablePropertiesBeanFactoryPostProcessor(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, EncryptablePropertySourceConverter converter) {
this.environment = environment;
this.converter = converter;
}
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
LOG.info("Post-processing PropertySource instances");
// 获取 environment 中所有的 MutablePropertySources
MutablePropertySources propSources = environment.getPropertySources();
// 通过 converter 将其中所有的PropertySource进行转换包装:用于在调用 propertySource.getProperty(String name) 时,进行解密
converter.convertPropertySources(propSources);
}
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE - 100;
}
}
EnableEncryptablePropertiesBeanFactoryPostProcessor 主要左右是,启用可加密属性,将environment 中所有的 MutablePropertySources的PropertySource进行转换包装,使得Spring框架在调用 propertySource.getProperty(String name) 时,执行解密方法,进而注入明文到对应的实体类中。
2.4 EncryptablePropertySourceConverter.convertPropertySources(MutablePropertySources propSources)
public class EncryptablePropertySourceConverter {
/**
* 转换
*/
public void convertPropertySources(MutablePropertySources propSources) {
StreamSupport.stream(propSources.spliterator(), false)
// 过滤获取非EncryptablePropertySource的PropertySources
.filter(ps -> !(ps instanceof EncryptablePropertySource))
// 将所有的非EncryptablePropertySource的PropertySource转换成EncryptablePropertySource
.map(this::makeEncryptable)
.collect(toList())
// 调用 MutablePropertySources.replace()方法
// 将转换之后的EncryptablePropertySource替换到MutablePropertySources中
.forEach(ps -> propSources.replace(ps.getName(), ps));
}
}
EncryptablePropertySourceConverter.convertPropertySources(MutablePropertySources propSources) 方法主要核心逻辑是将 Spring 环境变量中的 PropertySource 对象,转换为 Jasypt 中的 EncryptablePropertySource 对象,使得 Spring 在调用 propertySource.getProperty() 方法时,能够通过代理模式或包装器模式执行 EncryptablePropertySource 中的解密方法,从而完成配置文件的解密过程。
2.5 EncryptablePropertySourceConverter.makeEncryptable(PropertySource propertySource)
public class EncryptablePropertySourceConverter {
/**
* 转换PropertySource对象
*/
public <T> PropertySource<T> makeEncryptable(PropertySource<T> propertySource) {
// 如果已经失 EncryptablePropertySource 对象,或 存在skipPropertySourceClasses(跳过属性源类)中,直接返回
if (propertySource instanceof EncryptablePropertySource || skipPropertySourceClasses.stream().anyMatch(skipClass -> skipClass.equals(propertySource.getClass()))) {
log.info("Skipping PropertySource {} [{}", propertySource.getName(), propertySource.getClass());
return propertySource;
}
// 转换PropertySource对象
PropertySource<T> encryptablePropertySource = convertPropertySource(propertySource);
log.info("Converting PropertySource {} [{}] to {}", propertySource.getName(), propertySource.getClass().getName(),
AopUtils.isAopProxy(encryptablePropertySource) ? "AOP Proxy" : encryptablePropertySource.getClass().getSimpleName());
return encryptablePropertySource;
}
}
2.6 EncryptablePropertySourceConverter.convertPropertySource(PropertySource propertySource)
public class EncryptablePropertySourceConverter {
private <T> PropertySource<T> convertPropertySource(PropertySource<T> propertySource) {
// 判断采用什么模式:InterceptionMode.PROXY--->代理、InterceptionMode.WRAPPER--->包装
return interceptionMode == InterceptionMode.PROXY
? proxyPropertySource(propertySource) : instantiatePropertySource(propertySource);
}
/**
* 代理
*/
private <T> PropertySource<T> proxyPropertySource(PropertySource<T> propertySource) {
//Silly Chris Beams for making CommandLinePropertySource getProperty and containsProperty methods final. Those methods
//can't be proxied with CGLib because of it. So fallback to wrapper for Command Line Arguments only.
// 判断是否能被代理,如果不能,走包装器代码逻辑
if (CommandLinePropertySource.class.isAssignableFrom(propertySource.getClass())
// Other PropertySource classes like org.springframework.boot.env.OriginTrackedMapPropertySource
// are final classes as well
|| Modifier.isFinal(propertySource.getClass().getModifiers())) {
return instantiatePropertySource(propertySource);
}
// 创建代理对象
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory();
proxyFactory.setTargetClass(propertySource.getClass());
proxyFactory.setProxyTargetClass(true);
proxyFactory.addInterface(EncryptablePropertySource.class);
proxyFactory.setTarget(propertySource);
// EncryptablePropertySourceMethodInterceptor类实现了Interceptor接口,代理模式,直接走其中的 invoke 方法逻辑
proxyFactory.addAdvice(new EncryptablePropertySourceMethodInterceptor<>(propertySource, propertyResolver, propertyFilter));
return (PropertySource<T>) proxyFactory.getProxy();
}
/**
* 初始化 PropertySource 对象,采用代理模式或者包装器模式
*/
private <T> PropertySource<T> instantiatePropertySource(PropertySource<T> propertySource) {
PropertySource<T> encryptablePropertySource;
// 无论如何都需要代理
if (needsProxyAnyway(propertySource)) {
encryptablePropertySource = proxyPropertySource(propertySource);
} else if (propertySource instanceof SystemEnvironmentPropertySource) { // 包装器
encryptablePropertySource = (PropertySource<T>) new EncryptableSystemEnvironmentPropertySourceWrapper((SystemEnvironmentPropertySource) propertySource, propertyResolver, propertyFilter);
} else if (propertySource instanceof MapPropertySource) { // 包装器
encryptablePropertySource = (PropertySource<T>) new EncryptableMapPropertySourceWrapper((MapPropertySource) propertySource, propertyResolver, propertyFilter);
} else if (propertySource instanceof EnumerablePropertySource) { // 包装器
encryptablePropertySource = new EncryptableEnumerablePropertySourceWrapper<>((EnumerablePropertySource) propertySource, propertyResolver, propertyFilter);
} else { // 包装器
encryptablePropertySource = new EncryptablePropertySourceWrapper<>(propertySource, propertyResolver, propertyFilter);
}
return encryptablePropertySource;
}
}
最后,通过代码分析,你会发行,不管采用代理模式,还是包装器模式,最终调用的都是 CachingDelegateEncryptablePropertySource 中的 getProperty(String name) 方法。
2.7 CachingDelegateEncryptablePropertySource.getProperty(String name)
首先,先看看 CachingDelegateEncryptablePropertySource 的类结构图,如下,继承了 org.springframework.core.env.PropertySource 类,重写了其中的 Object getProperty(String name) 方法。

public class CachingDelegateEncryptablePropertySource<T> extends PropertySource<T> implements EncryptablePropertySource<T> {
@Override
public Object getProperty(String name) {
// Can be called recursively, so, we cannot use computeIfAbsent.
// 是否存在缓存
if (cache.containsKey(name)) {
return cache.get(name);
}
synchronized (this) {
// 双重校验
if (!cache.containsKey(name)) {
/**
* 调用 EncryptablePropertySource 的 getProperty 方法
* resolver:密码解释器
* filter:过滤器
* delegate:PropertySource 对象,用于获取密文
* name:配置文件key值
*/
Object resolved = getProperty(resolver, filter, delegate, name);
// 不为空,缓存
if (resolved != null) {
cache.put(name, resolved);
}
}
return cache.get(name);
}
}
}
2.8 EncryptablePropertySource.getProperty
通过代码分析,在 Springboot 与 Jasypt 整合中,最终调用的是 EncryptablePropertySource.getProperty 方法,该方法通过其中的 EncryptablePropertyResolver resolver 参数,将密文进行解析。
public interface EncryptablePropertySource<T> {
PropertySource<T> getDelegate();
Object getProperty(String name);
void refresh();
/**
* getProperty 方法
* resolver:密码解释器
* filter:过滤器
* delegate:PropertySource 对象,用于获取密文
* name:配置文件key值
*/
default Object getProperty(EncryptablePropertyResolver resolver, EncryptablePropertyFilter filter, PropertySource<T> source, String name) {
// 获取配置文件中的值
Object value = source.getProperty(name);
if (filter.shouldInclude(source, name) && value instanceof String) {
String stringValue = String.valueOf(value);
// 解密
return resolver.resolvePropertyValue(stringValue);
}
return value;
}
}
2.9 DefaultPropertyResolver.resolvePropertyValue
希望来了,终极类!!!!!
经过上面的 Springboot Jasypt源码分析 可知,最终调用的是 EncryptablePropertyResolver.resolvePropertyValue(String value) 方法,该方法将需要解密的字符串进行解密返回,代码如下:
public class DefaultPropertyResolver implements EncryptablePropertyResolver {
@Override
public String resolvePropertyValue(String value) {
return Optional.ofNullable(value)
// 处理占位符
.map(environment::resolvePlaceholders)
// 判断是否已加密:是否以默认prefix = "ENC(", suffix = ")"前缀开头,后缀结尾
// 这也是配置文件中为什么需要 ENC() 包裹密文的原因
.filter(detector::isEncrypted)
.map(resolvedValue -> {
try {
// 去除前缀、后缀,默认prefix = "ENC(", suffix = ")"
String unwrappedProperty = detector.unwrapEncryptedValue(resolvedValue.trim());
// 处理占位符
String resolvedProperty = environment.resolvePlaceholders(unwrappedProperty);
// 解密
return encryptor.decrypt(resolvedProperty);
} catch (EncryptionOperationNotPossibleException e) {
throw new DecryptionException("Unable to decrypt: " + value + ". Decryption of Properties failed, make sure encryption/decryption " +
"passwords match", e);
}
})
// 如果没有加密,直接返回value值
.orElse(value);
}
}
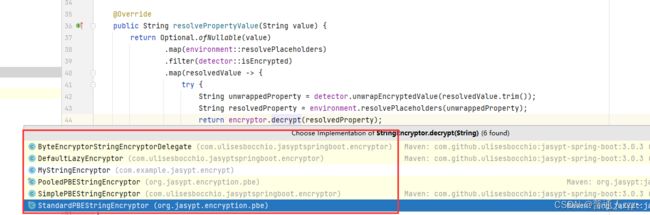
在 Jasypt 中,StringEncryptor 接口存在四种默认实现,分别是:
- ByteEncryptorStringEncryptorDelegate:字节加解密器,最终通过 Base64 加解密
- SimplePBEStringEncryptor:字符串加解密器,最终通过 Base64 加解密
- StandardPBEStringEncryptor:允许用户指定用于加密的算法(和提供者)、要使用的密码、散列迭代次数以及用于获取加密密钥的盐生成器。
- PooledPBEStringEncryptor:线程池 StandardPBEStringEncryptor 加解密器