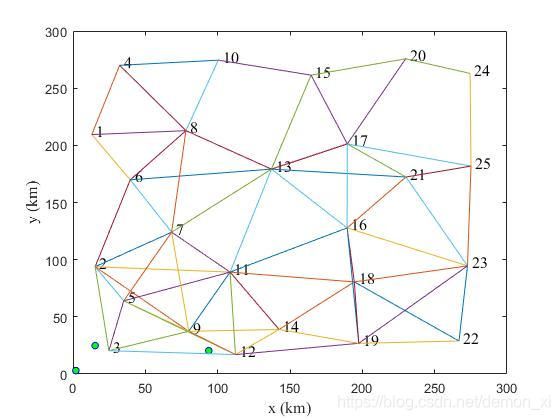
MATLAB-K最短路径算法(KSP,K-shortest pathes)
MATLAB-K最短路径算法(KSP,K-shortest pathes)
MATLAB代码封装成函数,直接使用。
参考:
k最短路径算法之Yen’s Algorithm
基于网络流量的SDN最短路径转发应用
算法背景
K 最短路径问题是最短路径问题的扩展和变形。1959 年,霍夫曼(Hoffman) 和帕夫雷(Pavley)在论文中第一次提出k 最短路径问题。 k 最短路径问题通常包括两类:有限制的k 最短路问题和无限制的K 最短路问题。 前者要求最短路径集合不含有回路,而后者对所求得的最短路径集合无限制。
算法简介
Yen’s算法是Yen 在1971 年提出的以其名字命名 的Yen 算法。Yen’s算法采用了递推法中的偏离路径算法思想,适用于非负权边的有向无环图结构。
算法思想
算法可分为两部分,算出第1条最短路径P(1),然后在此基础上依次依次算出其他的K-1条最短路径。在求P(i+1) 时,将P(i)上除了终止节点外的所有节点都视为偏离节点,并计算每个偏离节点到终止节点的最短路径,再与之前的P(i)上起始节点到偏离节点的路径拼接,构成候选路径,进而求得最短偏离路径。
##算法实例
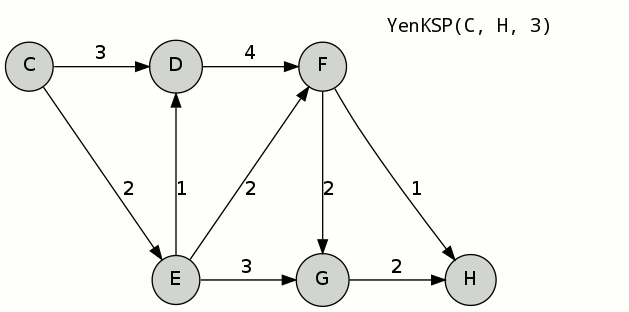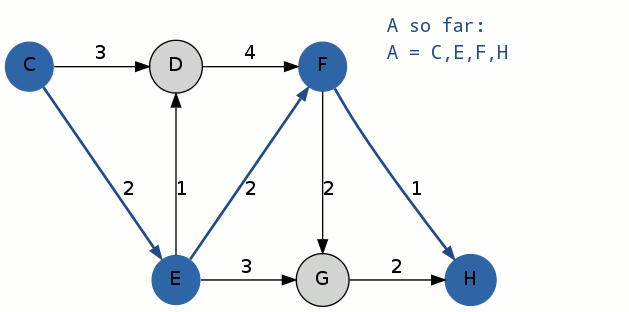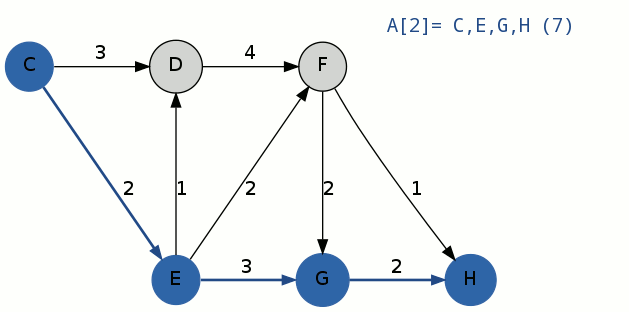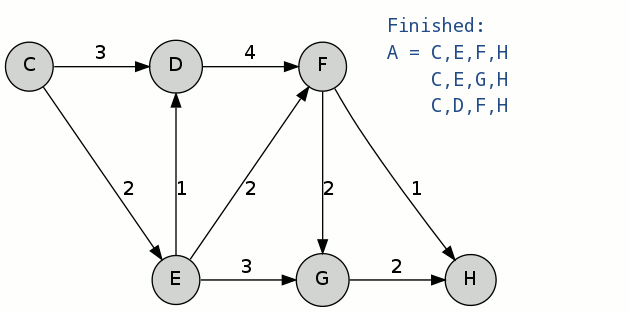
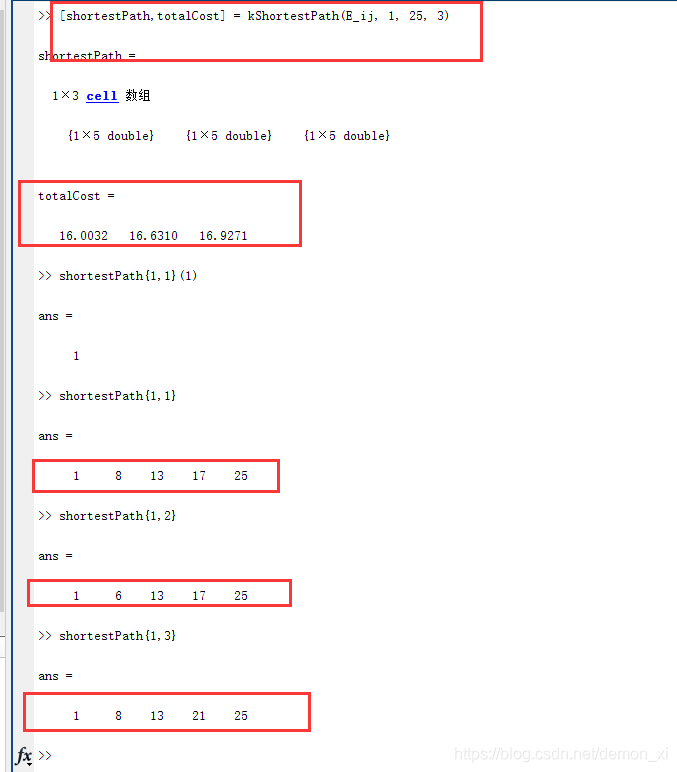
根据个人的理解,我归纳出了以下步骤:
调用K条最短路径算法,源C,目的H,K为3。B为偏离路径集合。
1.通过Dijkstra算法计算得到最短路径A^1:C-E-F-H,其中,花费为5,A[1] = C-E-F-H;
2.将A[1]作为迭代路径,进行第一次迭代:
(1)以部分迭代路径(即A[1])C路径中,C点为起点,将C-E路径之间的权值设为无穷大,进行一次Dijkstra,得到路径A^2-1:C-D-F-H,花费为8,将A^2-1路径加入B;
(2)以部分迭代路径(即A[1])C-E路径中,E为起点,将E-F路径之间的权值设为无穷大,进行一次Dijkstra,得到路径A^2-2:C-E-G-H,花费为7,将A^2-2路径加入B;
(3)以部分迭代路径(即A[1])C-E-F路径中,F为起点,将F-H路径之间的权值设为无穷大,进行一次Dijkstra,得到路径A^2-3:C-E-F-G-H,花费为8,将A^2-3路径加入B;
迭代完成,B集合中有三条路径:C-D-F-H,C-E-G-H,C-E-F-G-H;选出花费最小的偏离路径C-E-G-H,A[2] = C-E-G-H,移出B集合。
3.将A[2]作为迭代路径,进行第二次迭代:
(1)以部分迭代路径(即A[2])C路径中,C点为起点,将C-E路径之间的权值设为无穷大,进行一次Dijkstra,得到路径A^3-1:C-D-F-H,但B集合已存在该路径,故不存在偏移路径;
(2)以部分迭代路径(即A[2])C-E路径中,E点为起点,将E-G、E-F路径之间的权值设为无穷大 (注意,这里设置两条路径的权值原因是这两条路径分别存在于A[1]和A[2]中),进行一次Dijkstra,得到路径A^3-2:C-E-D-F-H,花费为8,将A^3-2加入B;
(3)以部分迭代路径(即A[2])C-E-G路径中,G点为起点,将C-H路径之间的权值设为无穷大,不存在偏移路径。
迭代完成,B集合中有三条路径:C-D-F-H,C-E-F-G-H,C-E-D-F-H;由于三条路径花费均为8,则根据最小节点数进行判断,选出偏离路径C-D-F-H,A[3] = C-D-F-H。
此时,选出了三条最短路径,分别是:
A[1] = C-E-F-H
A[2] = C-E-G-H
A[3] = C-D-F-H
matlab代码:
函数已封装成模块,可直接使用。
% 文件名:kShortestPath.m
% 时间:2020年10月16日
% 作者:乐观的阿锡
% 功能:K最短路径算法
function [shortestPaths, totalCosts] = kShortestPath(netCostMatrix, source, destination, k_paths)
if source > size(netCostMatrix,1) || destination > size(netCostMatrix,1)
warning('The source or destination node are not part of netCostMatrix');
shortestPaths=cell(1,k_paths); %定义最短路径为元胞数组
totalCosts=zeros(1,k_paths);
else
%---------------------INITIALIZATION---------------------
k=1;
[path cost] = dijkstra(netCostMatrix, source, destination);
%P is a cell array that holds all the paths found so far:
if isempty(path)
shortestPaths=cell(1,k_paths);
totalCosts=zeros(1,k_paths);
else
path_number = 1;
P{path_number,1} = path; P{path_number,2} = cost;
current_P = path_number;
%X is a cell array of a subset of P (used by Yen's algorithm below):
size_X=1;
X{size_X} = {path_number; path; cost};
%S path_number x 1
S(path_number) = path(1); %deviation vertex is the first node initially 偏离顶点是最初的第一个顶点
% K = 1 is the shortest path returned by dijkstra():
shortestPaths{k} = path ;
totalCosts(k) = cost;
%--------------------------------------------------------
while (k < k_paths && size_X ~= 0 )
%remove P from X
for i=1:length(X)
if X{i}{1} == current_P
size_X = size_X - 1;
X(i) = [];%delete cell
break;
end
end
%---------------------------------------
P_ = P{current_P,1}; %P_ is current P, just to make is easier for the notations
%Find w in (P_,w) in set S, w was the dev vertex(偏离顶点) used to found P_
w = S(current_P);
for i = 1: length(P_)
if w == P_(i)
w_index_in_path = i;
end
end
for index_dev_vertex= w_index_in_path: length(P_) - 1 %index_dev_vertex is index in P_ of deviation vertex
temp_netCostMatrix = netCostMatrix;
%------
%Remove vertices in P before index_dev_vertex and there incident edges
for i = 1: index_dev_vertex-1
v = P_(i);
temp_netCostMatrix(v,:)=inf;
temp_netCostMatrix(:,v)=inf;
end
%------
%remove incident edge of v if v is in shortestPaths (K) U P_ with similar sub_path to P_....
SP_sameSubPath=[];
index =1;
SP_sameSubPath{index}=P_;
for i = 1: length(shortestPaths)
if length(shortestPaths{i}) >= index_dev_vertex
if P_(1:index_dev_vertex) == shortestPaths{i}(1:index_dev_vertex)
index = index+1;
SP_sameSubPath{index}=shortestPaths{i};
end
end
end
v_ = P_(index_dev_vertex);
for j = 1: length(SP_sameSubPath)
next = SP_sameSubPath{j}(index_dev_vertex+1);
temp_netCostMatrix(v_,next)=inf;
end
%------
%get the cost of the sub path before deviation vertex v
sub_P = P_(1:index_dev_vertex);
cost_sub_P=0;
for i = 1: length(sub_P)-1
cost_sub_P = cost_sub_P + netCostMatrix(sub_P(i),sub_P(i+1));
end
%call dijkstra between deviation vertex to destination node
[dev_p c] = dijkstra(temp_netCostMatrix, P_(index_dev_vertex), destination);
if ~isempty(dev_p)
path_number = path_number + 1;
P{path_number,1} = [sub_P(1:end-1) dev_p] ; %concatenate sub path- to -vertex -to- destination
P{path_number,2} = cost_sub_P + c ;
S(path_number) = P_(index_dev_vertex);
size_X = size_X + 1;
X{size_X} = {path_number; P{path_number,1} ;P{path_number,2} };
else
%warning('k=%d, isempty(p)==true!\n',k);
end
end
%---------------------------------------
%Step necessary otherwise if k is bigger than number of possible paths
%the last results will get repeated !
if size_X > 0
shortestXCost= X{1}{3}; %cost of path
shortestX= X{1}{1}; %ref number of path
for i = 2 : size_X
if X{i}{3} < shortestXCost
shortestX= X{i}{1};
shortestXCost= X{i}{3};
end
end
current_P = shortestX;
%******
k = k+1;
shortestPaths{k} = P{current_P,1};
totalCosts(k) = P{current_P,2};
%******
else
%k = k+1;
end
end
end
end
算法演示
算法步骤
作为Dijkstra 最短路径算法的扩展,K 最短路径算法可以在给定有向图中确定K条候选路径且每条路径可提供从源节点到目的节点的最小权重和。为了实现K最短路径算法,应用Dijkstra算法和路径偏离的思想,更具体地说,首先通过Dijkstra算法找出源节点和目的节点之间的最短路径,再依次移除最短路径上的每条链路,重新计算源节点和目的节点之间的最短路径,重复该过程,直到找到K条路径。
基于K最短路径算法的路由选择过程的步骤可总结如下:
(1) 表征考虑的网络图为一个权重图,设置K=1;
(2) 在图 中应用Dijkstra算法获得单用户流的从源交换机到目的交换机的一条候选最短路径;
(3) 依次移除最短路径上的每条链路,应用Dijkstra算法重新计算到的最短路径;
(4) 根据获得的候选路径,选择提供最小 的一条路径;
(5) 重复步骤(3)和步骤(4),直到 k=K;
(6) 获得的K条路径集合置为且第K条路径对应的路由。