练习:三子棋(python 列表list“全局变量”特性、插值字符串格式化、set 元素不重复特性)
Python 官网:https://www.python.org/
这里,才 python 前沿。可惜是英文原版。所以,我要练习英文阅读。
- 好文力荐
- My CSDN主页、My HOT博
- My Python 学习个人备忘录
- 老齐教室
自学并不是什么神秘的东西,一个人一辈子自学的时间总是比在学校学习的时间长,没有老师的时候总是比有老师的时候多。
—— 华罗庚
练习:三子棋
目录
1、游戏说明及技巧
2、规则和说明打印
3、当前棋局状况刻划
4、玩家落子位置确认
5、当前棋局判胜
6、历史棋局回放
7、简单→困难模式
8、对“玩家落最后一子”的优化——自动
9、简单模式
10、困难模式
11、本笔记完整代码
念头滋生:我读到大佬的文章三子棋,用 C 写的,学到了逻辑,偷过来 python 一把。
游戏说明
三子棋,是黑白棋的一种。三子棋是一种民间传统游戏,又叫九宫棋、圈圈叉叉、一条龙、井字棋等。将正方形对角线连起来,相对两边依次摆上三个双方棋子,只要将自己的三个棋子走成一条线,对方就算输了。但是,有很多时候会出现和棋的情况。
游戏规则
如果两个人都掌握了技巧,那么一般来说就是平棋。一般来说,第二步下在棋盘中心最有利(因为先手不能够下在棋盘中心),下在角上次之,下在边上再次之。最大的好处就是,随便找个地方就可以玩这个简单而有趣的游戏了。
游戏菜单
游戏菜单制作,这里就不再赘述。如果有兴趣,请点击 蓝色超链接文字参阅我前面的学习笔记 聊天消息敏感词屏蔽系统(字符串替换 str.replace(str1, *) )、Python 个性计算器(可不断加挂功能模块实现个性化),查看其中对菜单制作的讲述。“三子棋”菜单就是 从我前面写的菜单修改而来。
说明和规则打印
代码
def myprint(title, s):
'''文本打印'''
print(f"{cut_line()}\n\n{color(1,'f_green')}{title:=^37}\n{'(三子棋)':^38}{color(0)}")
k = True
sign = list(',.;:-/:,()()。!?;、“”……')
for i in s:
if k is True:
print(f"\n\n{' '*4}{i}", end='')
k = 3
else:
print(i, end='')
if i not in sign:
k += 1
if k > 16 and i not in sign:
print(f"\n")
k = 1
print(f"\n\n{cut_line()}")
wait()
当前对弈棋局状况刻划
由于三子棋棋盘简单,总共只有九格。所以决定用插值字符串格式化的形式来刻划棋盘,显示棋局状况。(本来打算用 ASCII 制表符来刻划棋盘,但总是对不齐数据。没办法,只好用英文 ‘|±’ 这三个符号来操作了,虽然不那么好看,但对于同样是英文字母的棋子 ‘ox’ 。用了插值字符串格式化字符串,进行了上下左右在41的宽度
居中显示,也 好看那么一点点。)
代码
def chessboard_show(chess_signs):
''' 当前棋局状况列印 '''
s = chess_signs # 变量取别名,简化写代码。
blank = f"{'':>15}"
gui_head()
print(f"\n{blank} {s[0]} | {s[1]} | {s[2]} \
\n{blank}{'-'*3}+{'-'*3}+{'-'*3}\
\n{blank} {s[3]} | {s[4]} | {s[5]} \
\n{blank}{'-'*3}+{'-'*3}+{'-'*3}\
\n{blank} {s[6]} | {s[7]} | {s[8]} ")
gui_tail()
玩家落子位置确认
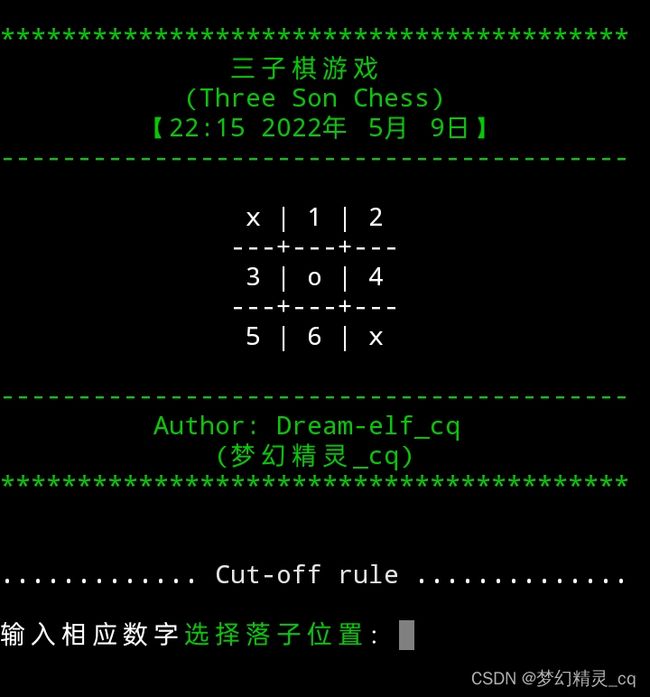
思路:从棋局状况存放列表 chess_signs 中,解析可以落子的位置列表 blank_chess 。将可落子的位置按1开始编码并存入落子位置状况棋局列表 tem_chess 。调用当前棋局状况列显函数打印可以落子位置,供玩家选择。玩家选择落子位置后,确认玩家落子位置,写入棋局状况存放列表 chess_signs 相应位置。
代码
def ischessman():
''' 确认玩家落子位置 '''
blank_chess = [k for k,i in enumerate(chess_signs) if i == ' ']
tem_chess = chess_signs[:] # 拷贝棋局布子状况。
for m,i in enumerate(blank_chess):
for k in tem_chess: # 将可落子的位置按1开始编码并存入落子位置状况棋局列表。
if k == ' ':
tem_chess[i] = m+1
chessboard_show(tem_chess) # 调用当前棋局状况列显可以落子位置。
while True:
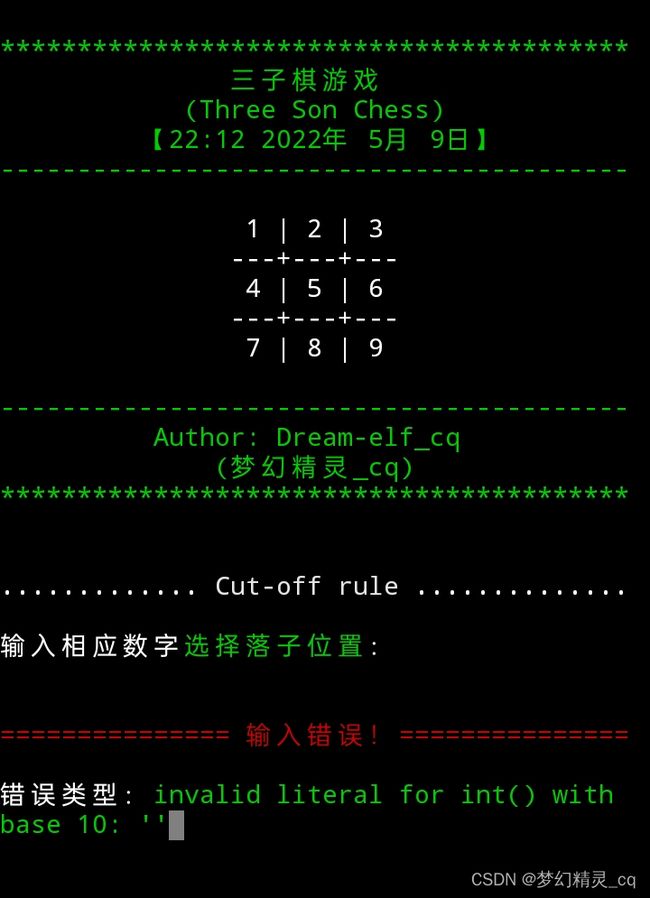
try: # 选择项错误捕获。
isman = int(input(f"{cut_line()}输入相应数字{color(1,'f_green')}选择落子位置{color(0)}:"))
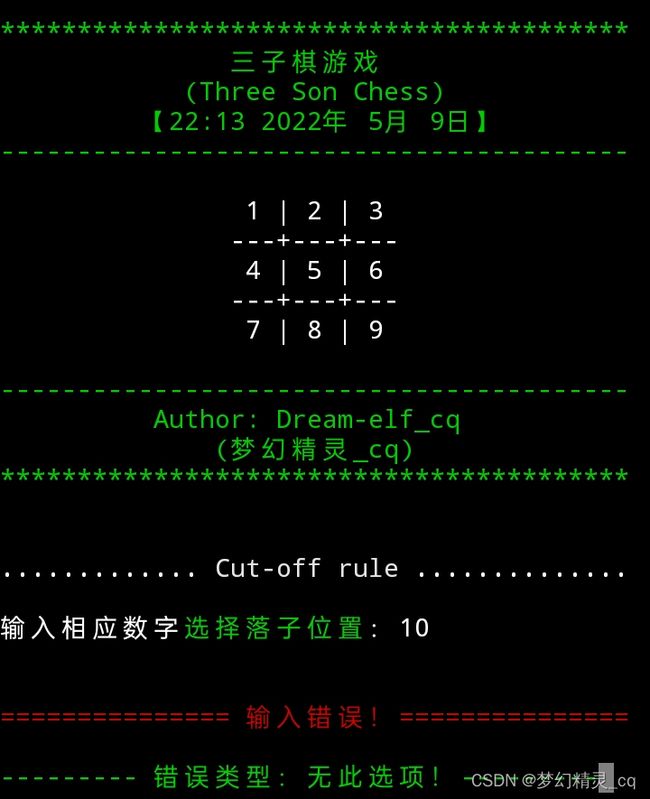
if isman not in range(1, len(blank_chess)+1): # 合法选择序号范围设定。
error_show()
input(f"\n{color(1,'f_green')}{' 错误类型:无此选项!':-^29}{color(0)}")
clear() # 清屏
chessboard_show(tem_chess) # 调用当前棋局状况列显可以落子位置。
continue # 继续选择落子位置。
break
except Exception as error:
error_show()
input(f"\n错误类型:{color(1,'f_green')}{error}{color(0)}")
clear() # 清屏
chessboard_show(tem_chess) # 调用当前棋局状况列显可以落子位置。
continue # 继续选择落子位置。
chess_signs[tem_chess.index(isman)] = you # 写入玩家落子位置。
选择落子位置超限提示代码
error_show()
input(f"\n{color(1,'f_green')}{' 错误类型:无此选项!':-^29}{color(0)}")
clear() # 清屏
chessboard_show(tem_chess) # 调用当前棋局状况列显可以落子位置。
continue # 继续选择落子位置。
int(input()) 捕获异常提示代码
error_show()
input(f"\n错误类型:{color(1,'f_green')}{error}{color(0)}")
clear() # 清屏
chessboard_show(tem_chess) # 调用当前棋局状况列显可以落子位置。
continue # 继续选择落子位置。
“用户输入,都是不可靠的”,曾记得那位大佬说过,我深以为然。对弈棋局落子位置选择输入,我作了超出范围报错和 int(input()) 异常捕获,增加了我程序的稳定性,不因报错而终止运行。注意:一定要报错提示后,清屏后重新调用“当前棋局状况刻划函数”显示可以选择的落子位置,才可以让用户体验更佳。
chessboard_show(tem_chess) # 调用当前棋局状况列显可以落子位置。
当前棋局状况判定胜者
不满足于 CSDN 上的“三子棋”博文的“一致” C 算法。 我用 list 存储当前对弈棋局落子位置状况,今天成功使用 set 特性判断胜利者。(算法完成了 python 代码实现)
获胜组合列表:三横三竖两对角线,三子连珠。用 python 集合存放每组获胜组合,据其特性,一旦出现“三子连珠”,存放获胜组合的集合将只有一个元素。缘于此,只需每次行棋后,判当前棋局状况中的“三子连珠”,如有则输出胜者。无则继续直到无处落子,输出“平局”提示。
代码
def isvictor():
''' 判胜:三子连珠。 '''
tem = chess_signs # 对弈棋局状况存放列表别名。
win_list = [{tem[0], tem[1], tem[2]},
{tem[3], tem[4], tem[5]},
{tem[6], tem[7], tem[8]},
{tem[0], tem[3], tem[6]},
{tem[1], tem[4], tem[7]},
{tem[2], tem[5], tem[8]},
{tem[0], tem[4], tem[8]},
{tem[2], tem[4], tem[6]}
] # 获胜组合列表:三横三竖两对角线,三子连珠。用 python 集合存放获胜组合,据其特性,一旦出现“三子连珠”,存放获胜组合的集合将只有一个元素。缘于此,只需每次行棋后,判当前棋局状况中的“三子连珠”,如有则输出胜者。无则继续直到无处落子,输出“平局”提示。
for i in win_list: # 遍历判胜。
if len(i) is 1:
if list(i)[0] == 'o': # 集合不可以用下标引用,要先用 list 转化。
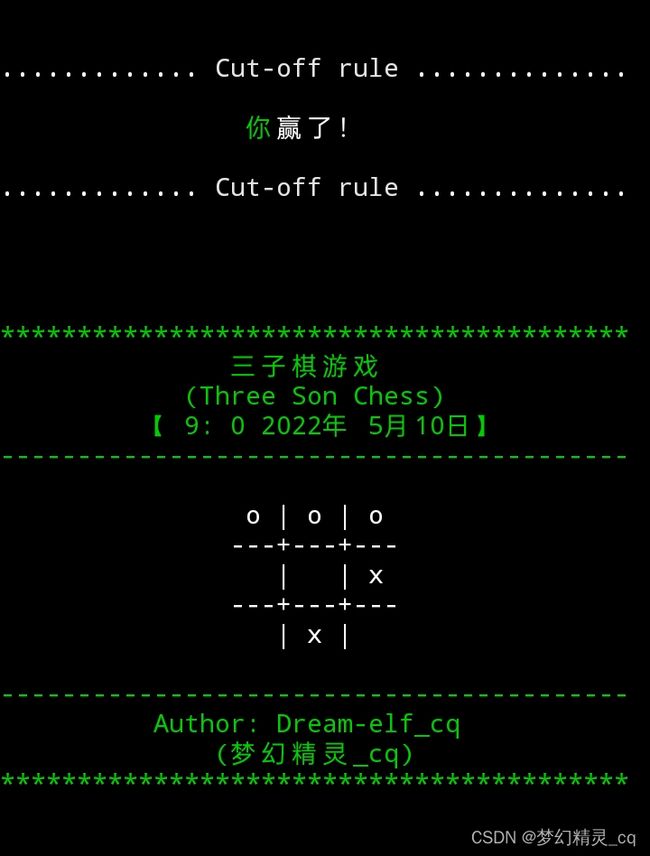
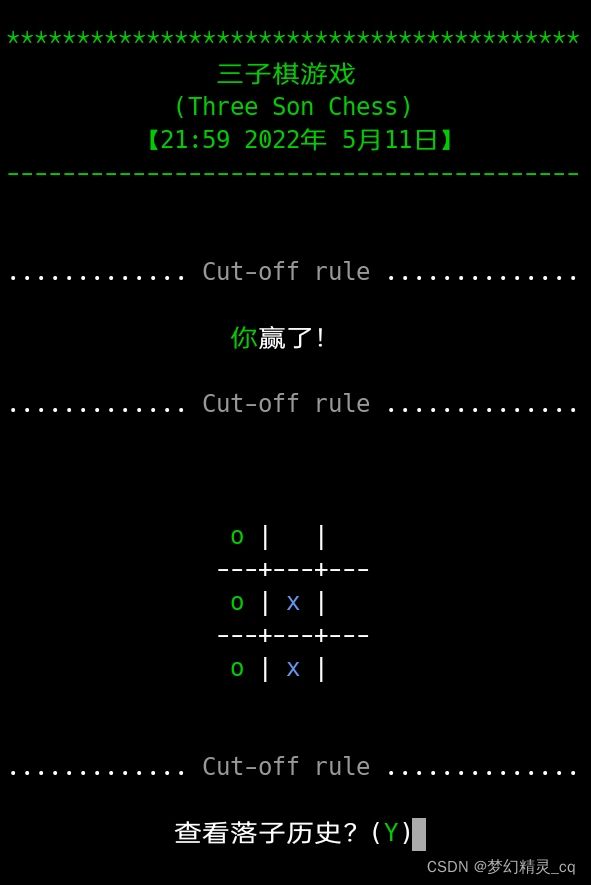
print(f"{cut_line()}{' ':>16}{color('你', 'f_green')}赢了!{cut_line()}")
chessboard_show(tem) # 显示当前棋局状况。
wait() # 暂停。
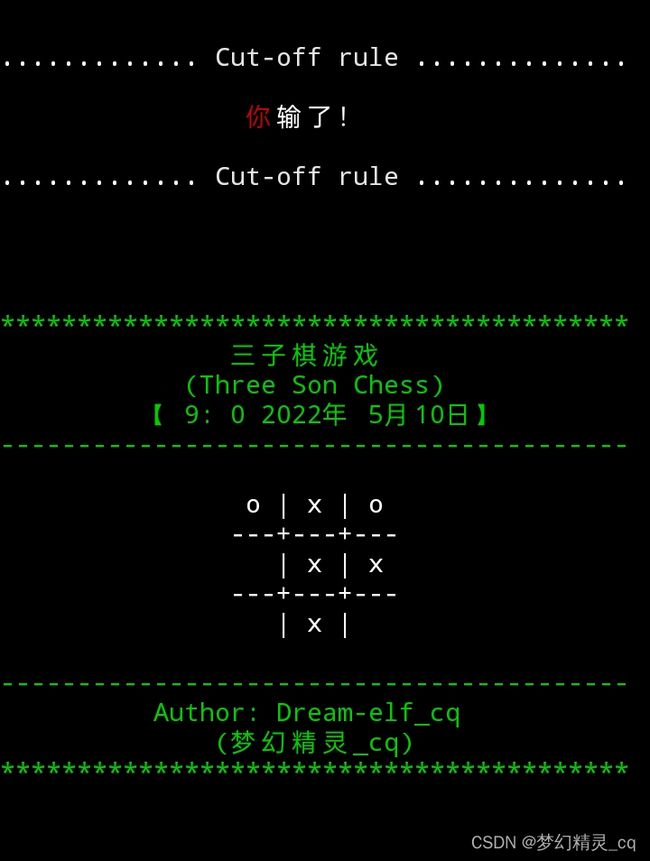
elif list(i)[0] == 'x':
print(f"{cut_line()}{' ':>16}{color('你', 'f_red')}输了!{cut_line()}")
chessboard_show(tem) # 显示当前棋局状况。
wait() # 暂停。
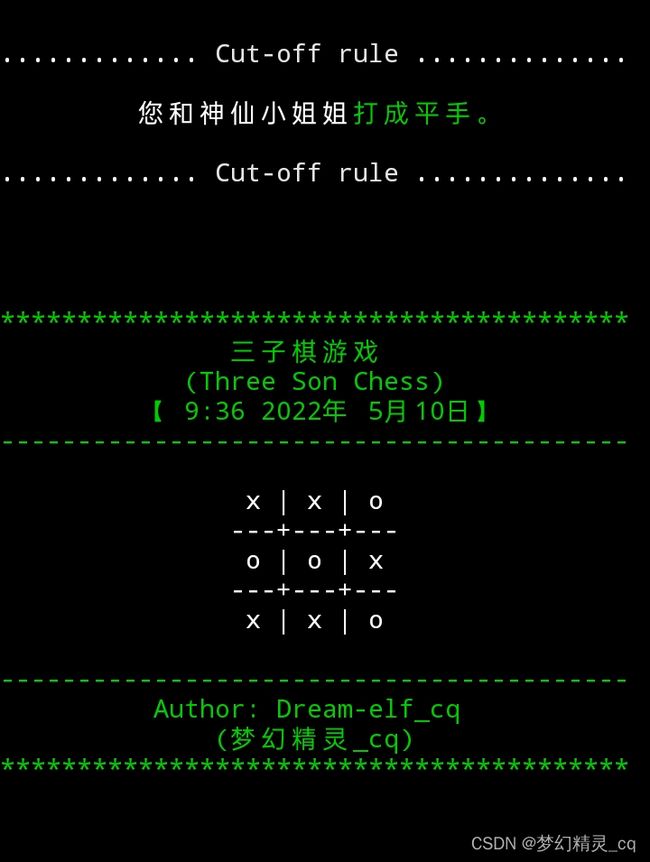
if ' ' not in tem:
print(f"{cut_line()}{' ':>9}您和神仙小姐姐{color('打成平手。', 'f_green')}{cut_line()}")
chessboard_show(tem) # 显示当前棋局状况。
wait() # 暂停。
无处落子,未出胜者,判平局。
if ' ' not in tem: # 无处落子,未出胜者,判平局。
print(f"{cut_line()}{' ':>9}您和神仙小姐姐{color('打成平手。', 'f_green')}{cut_line()}")
chessboard_show(tem) # 显示当前棋局状况。
wait() # 暂停。
简单模式
简单游戏模式,设计流程是:随机模块 choice 方法确定先手(‘o’ or ‘x’),人 ( ischessman() )/机( choice方法随机落子)依次落子,每次落子后都“判胜” ( isvictor() ),如有胜出则结束对弈,无处落子未出胜者,判平局。
调试程序时,随手也修正了些显示效果,视觉稍好一些。(前面已贴出的代码片,就保留原有的样子,修正后的代码,参阅全部做好好后贴出的完整代码。)
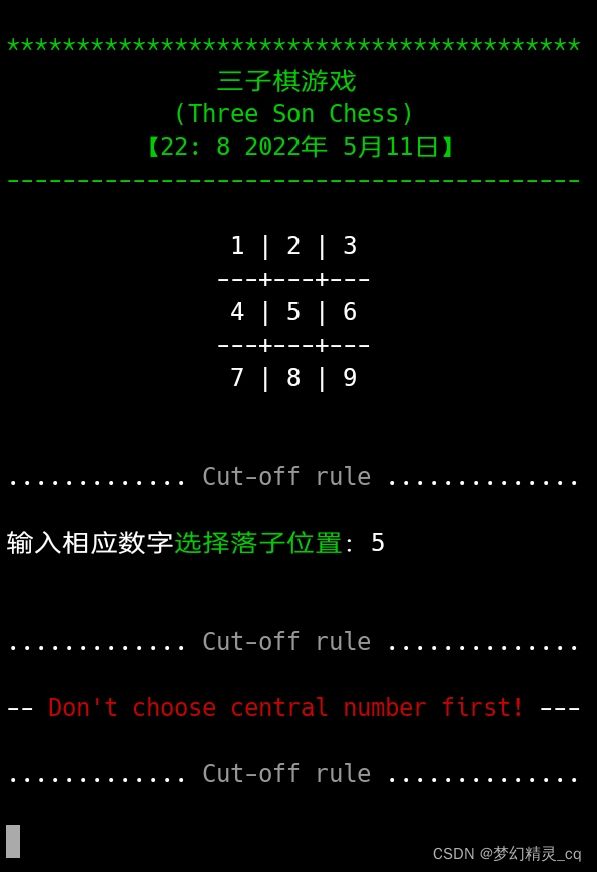
游戏规则中有最要的一条:第一个走棋的人,不可以在正中间落子。
先手落子中心报错代码
if tem_chess.index(isman) == 4 and len(set(chess_signs)) == 1: # 开局先手落子中心,报错。
tip = " Don't choose central number first! "
input(f"{cut_line()}{color(tip, 'f_red'):-^50}{cut_line()}")
continue
代码
def easy_chess():
''' 简单游戏模式 '''
from random import choice # 加载随机数模块的随机选择方法。
start_data() # 棋局状况存放“清零”。
first = choice(('o','x')) # 随机确定先手。
win = False
clear() # 清屏。
while not win:
if first == 'o':
blank_chess, tem_chess = isblank_places() # 获取可以落子位置。
ischessman() # 调用函数实施玩家落子。
history_chess.append(chess_signs.copy()) # 保存历史棋局状况。
win = isvictor() # 判定胜利者。
first = 'x' # 玩家落子后更替“先手”。
else:
blank_chess, tem_chess = isblank_places() # 获取可以落子位置。
isman = choice(range(1, len(blank_chess)+1))
chess_signs[tem_chess.index(isman)] = computer # 写入机器落子位置。
history_chess.append(chess_signs.copy()) # 保存历史棋局状况。
win = isvictor() # 判定胜利者。
first = 'o' # 玩家落子后更替“先手”。
历史棋局回放
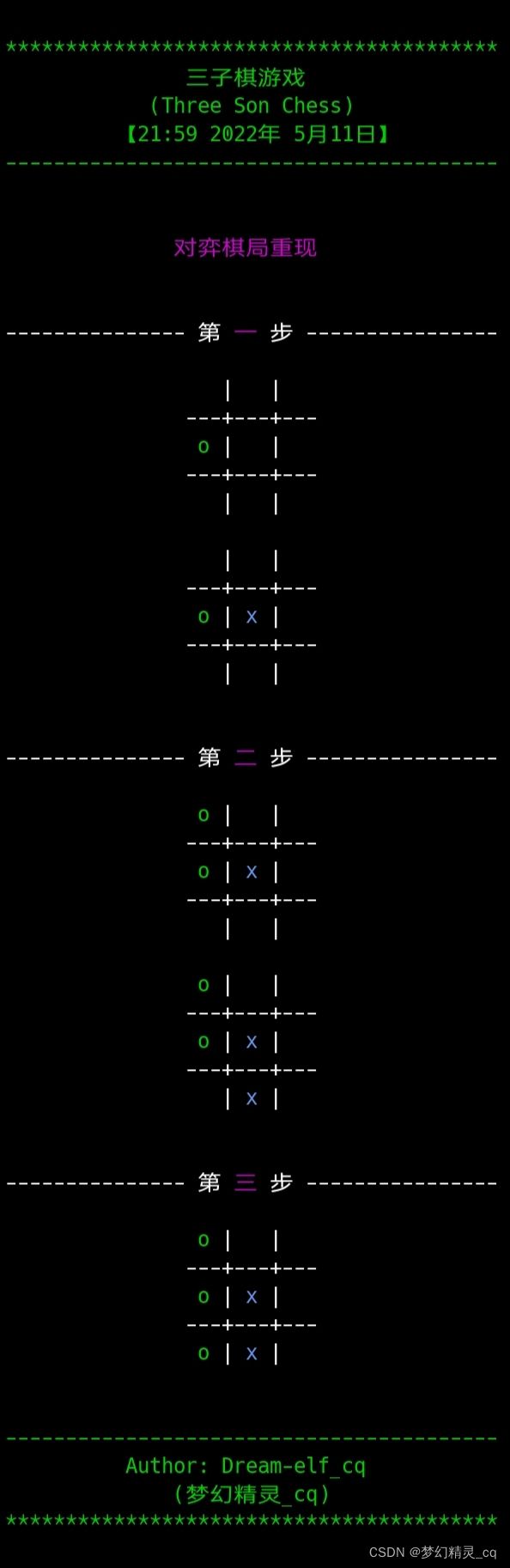
我想要实现棋局回放,把每次双走棋的棋盘“快照”,依次保存在一个列表中,如果在棋局结束后选择查看,遍历 history_chess 列表,调用棋局“刻印”函数 chessboard_show() 依次还原每次对弈即可。
代码
def history_show():
''' 历史棋局再现 '''
flag = input(f"{cut_line()}{'':>12}查看落子历史?({color('Y','f_green')})")
m, chinese_nums = 0, list('一二三四五')
if flag in list('Yy'):
clear() # 清屏。
gui_head() # 界面头。
print(f"\n\n{color(' 对弈棋局重现 ', 'f_purple'):^44}")
for k,i in enumerate(history_chess):
if k%2 == 0: # 打印落子次数。
print(f"\n\n{'':->15} 第 {color(chinese_nums[m], 'f_purple')} 步 {'':->16}")
m += 1
chessboard_show(i)
gui_tail() # 界面尾。
wait()
简单→困难模式
简单模式单单机器随机落子,也太简单了些,几无可玩性。没有一点点挑战性,次次赢(不“老眼昏花”的话)。所以在做好困难模式机器算法后,机器每次落子,我给简单模式加入了88%的机率调用机器“最优算法”落子。
简单模式中设置概率调用困难模式的机器最优算法落子,让仅仅随机空位落子的简单模式也能有些许聪明(0~100可以设置,0即简单模式,100就是困难模式——赢不了机器,最多平局。)
简单模式中的调用机器最优算法代码
n = 88 # 机器最优算法落子机率。机器落子仅用随机模块太简单无趣,在代码中设此参数,控制简单程度。
flag = probability(n) # 机率调用机器最优算法落子。
if flag:
hard_isman() # 机器最优算法落子。
else:
blank_chess, tem_chess = isblank_places() # 获取可以落子位置。
isman = choice(range(1, len(blank_chess)+1))
chess_signs[tem_chess.index(isman)] = computer # 写入机器落子位置。
概率选择最优算法函数代码
def probability(n):
''' 参数 n 为 True 的百分比机率 '''
from random import choice, shuffle # 加载随机数模块的选择和打散方法。
prob = [1]*n + [0]*(100-n) # 根据参数生成机率选择列表。
for i in range(3):
shuffle(prob) # 打散(洗牌)三次。
return choice(prob) # 返回机率随机数
困难模式
代码
def hard_chess():
''' 困难游戏模式 '''
from random import choice # 加载随机数模块的随机选择方法。
start_data() # 棋局状况存放“清零”。
first = choice(('o','x')) # 随机确定先手。
win = False
while not win:
if first == 'o':
blank_chess, tem_chess = isblank_places() # 获取可以落子位置。
ischessman() # 调用函数实施玩家落子。
history_chess.append(chess_signs.copy()) # 保存历史棋局状况。
win = isvictor() # 判定胜利者。
first = 'x' # 玩家落子后更替“先手”。
else:
blank_chess, tem_chess = isblank_places() # 获取可以落子位置。
hard_isman() # 机器算法落子。 history_chess.append(chess_signs.copy()) # 保存历史棋局状况。
history_chess.append(chess_signs.copy())
win = isvictor() # 判定胜利者。
first = 'o' # 玩家落子后更替“先手”。
代码运行效果
“困难模式”,赢不过机器的哦。我无法可想,用了最笨的穷举法,代码臃肿乏味,这里就不贴了。如果感觉兴趣,请跳转完整代码查看。只是,在游戏中还是感觉不到臃肿,好像机器也“灵动聪慧”咯。
对玩家落最后一子的优化——自动
棋盘只有最后一个空位的时候,还要手动去摆弄,感觉就是不爽。弄了段代码,让存储棋局状况的列表 chess_signs 仅有一个 ’ ’ 时,用 index 方法寻其位置,直接赋值 = you 落子空位。
代码
tem = chess_signs # 棋局状况存放列表别名。
if tem.count(' ') == 1: # 棋盘仅有最后一个空位。
tem[tem.index(' ')] = you # 落子最后一个空位。
return # 落子最后一个空位后,返回上层调用。
这样子,才感觉一口气顺畅了——有想法的感觉——真好!
完整 Python 代码(完整代码为最后完成调试后的最终代码,前面贴出的代码是调试出功能就上传的,可能后来已作优化。完整代码中的对应部分,可能比前面贴出的“高级”哦。这是个人记笔记定CSDN博文的习惯所致,敬请谅解。)
我的解题思路,已融入代码注释,博文中就不再赘述。
(如果从语句注释不能清楚作用,请评论区留言指教和探讨。)
#!/sur/bin/nve python
# coding: utf-8
'''
Game: 三子棋
filename: three_son_chess.py
author: 梦幻精灵_cq
date: 2022-05-08 start, 2022-5-14 Hard mode is finished.
'''
from mypythontools import cut_line, clear, color, wait # mypythontools,自码功能模块。
# Game Data
'''
三行三列的三子棋九宫棋盘。
1、存储棋局状况列表初始样子。
chess_signs =
[' ', ' ', ' ',
' ', ' ', ' ',
' ', ' ', ' ']
2、棋盘刻划样子
| |
---+---+---
x | o |
---+---+---
x | |
3、对弈双方棋子
you, computer = f"{color(1, 'f_green')}o{color(0)}", f"{color(1, 'f_blue')}x{color(0)}" # player 棋子字符:玩家'o',computer'x',为了打印好看,加入了色彩输出控制字符。
4、用列表 history_chess 复刻保存每次落子(双方)情景,以期重现对弈情境。
5、游戏主执行代码块:three_son_chess()
'''
title = '三子棋游戏'
readme = '三子棋,是黑白棋的一种。三子棋是一种民间传统游戏,又叫九宫棋(棋盘九格)、圈圈叉叉(三子棋一般对弈双方一方棋子是圈,则另一方则是叉)、一条龙(胜出规则:三子直线珠连)、井字棋(九格棋盘如“井”字)等。棋盘是将一个将正方形均分九个方格,对弈双方依次在棋盘上九个格子中落子,只要将自己的三个棋子走成一条线(“三子连珠”:三行、三列和两条对角线),对方就算输了。但是,有很多时候会出现和棋的情况。'
rules = '如果两个人都掌握了技巧,那么一般来说就是平棋。一般来说,第二步下在棋盘中心最有利(因为先手不能够下在棋盘中心),下在角上次之,下在边上再次之。最大的好处就是,随便找个地方就可以玩这个简单而有趣的游戏了。'
you, computer = f"{color(1, 'f_green')}o{color(0)}", f"{color(1, 'f_blue')}x{color(0)}" # player 棋子字符:玩家'o',computer'x',为了打印好看,加入了色彩输出控制字符。
history_chess = [] # 历史棋局状况存放列表。
chess_signs = [' ']*9 # 棋局状况初值,开局后写入对弈状况。(考虑到三子棋只有九个棋盘落子位置,决定采用方便快捷的 list 来存放博弈双方的落子位置状况。)
def three_son_chess(): # game main
'''主执行代码块'''
while True: # 菜单列印和确认死循环,不主动退出就一直执行循环。
menu_show() # 屏幕打印菜单。
is_menu() # 菜单选择。
# game munutools ---==== 菜单功能函数 ====---
def localtime_show():
''' 当前时间格式化字符获取 '''
from time import localtime
t = localtime() # 获取当前时间数组。
return f"{t[3]:2d}:{t[4]:2d} {t[0]}年{t[1]:2d}月{t[2]:2d}日" # 为了齐整,我设置了当前时间格式化字符串中,时、分、月、日分别用两个英文字符位。
def error_show():
''' 红色打印错误提示 '''
print(f"\n\n{color(1, 'f_red')}{' 输入错误!':=^36}{color(0)}")
def gui_head():
''' 界面头 '''
print(f"\n\n{color(1, 'f_green')}{'':*^41}\n{title:^36}\n{'(Three Son Chess)':^41}\n{'【':>10}{localtime_show()}】\n{'':-^41}{color(0)}")
def gui_tail():
''' 界面尾 '''
print(f"\n\n{color(1, 'f_green')}{'':-^41}\n{'Author: Dream-elf_cq':^41}\n{'(梦幻精灵_cq)':^37}\n{'':*^41}{color(0)}")
def menu_show():
''' 菜单打印模块 '''
menus = ('简单模式', '困难模式', '游戏说明', '游戏规则', '退出') # 这次不象以前练习,设计为动态菜单列表。如需添加菜单项,只需把菜单项字符串放在列表相应位置就好。(注意:增加菜单后,记得到“菜单确认”模块修改 range() 合法菜单选择范围,不然无法选中新增菜单序号。并增添相应的 elif 选项。)
clear() # 清屏。
gui_head() # 界面头调用。
for k,i in enumerate(menus): # 遍历枚举函数 enumerate() ,方便列印菜单序号。
if i != '退出': # 其她菜单打印。
print(f"\n{k+1:>16}. {i}")
else: # 退出菜单打印。
exit_s = f" {0}. {i} "
print(f"\n{'':>13}{exit_s:=^13}")
gui_tail() # 界面尾调用。
def is_menu():
''' 菜单确认 '''
while True:
try: # 菜单选择错误捕获。
menu = int(input(f"\n\n{'菜单选择:':>12}"))
if menu not in range(5): # 合法菜单选择序号范围设定。
error_show()
input(f"\n{color(1,'f_green')}{' 错误类型:没有此项菜单!':-^29}{color(0)}")
break
except Exception as error:
error_show()
input(f"\n错误类型:{color(1,'f_green')}{error}{color(0)}")
# 菜单项增加后,就得增加一个 elif 。
if menu == 0: # 0. 退出
clear()
print(f"{cut_line()}{color(' 欢迎下次使用“三子棋”游戏 ', 'f_purple'):=^39}{cut_line()}")
exit()
elif menu == 1: # 1. 简单模式
while True:
if not easy_chess():
break
elif menu == 2: # 2. 困难模式
while True:
start_data() # 初始游戏数据。
if not hard_chess():
break
elif menu == 3: # 3. 游戏说明
myprint('游戏说明', readme)
elif menu == 4: # 4. 游戏规则
myprint('游戏规则', rules)
# game tools ---==== 下面是,游戏功能模块函数 ====---
def start_data():
''' 初始游戏数据:
Python 列表特性,会保存历史数据。
在已有执行游戏过程,进行下一局游戏,得
将上次游戏数据在列表中“清零”。 '''
history_chess.clear() # 历史棋局状况存放列表“清零”。
#for i in range(9): # 用英文空格' '填充九个落子位置的初始字符,开局后写入对弈状况。注意:由于 python 中列表的存储特性,不可以用 = 赋值的方式“清零”列表。(我“清零”无果,最后只好采用 ' ' 逐个赋值替换九个落子位置的字符。)
# chess_signs[i] = ' '
chess_signs.clear() # 棋局状况存放列表“清零”。
chess_signs.extend([' ']*9) # 英文空格填充九个棋子位置。(“clear”+“extend”感觉也和 “for”+“=”优雅)
def myprint(title, s):
''' 标题、文本打印 '''
clear() # 清屏。
gui_head() # 界面头。
print(f"\n\n{color(1,'f_purple')}{title:^37}{color(0)}")
k = True # 换行计数器。
sign = list(',.;:-/:,()()。!?;、“”……')
for i in s:
if k is True:
print(f"\n\n{' '*4}{i}", end='')
k = 3
else:
print(i, end='')
if i not in sign:
k += 1
if k > 16 and i not in sign:
print(f"\n")
k = 1
print()
gui_tail() # 界面尾。
wait() # 暂停。
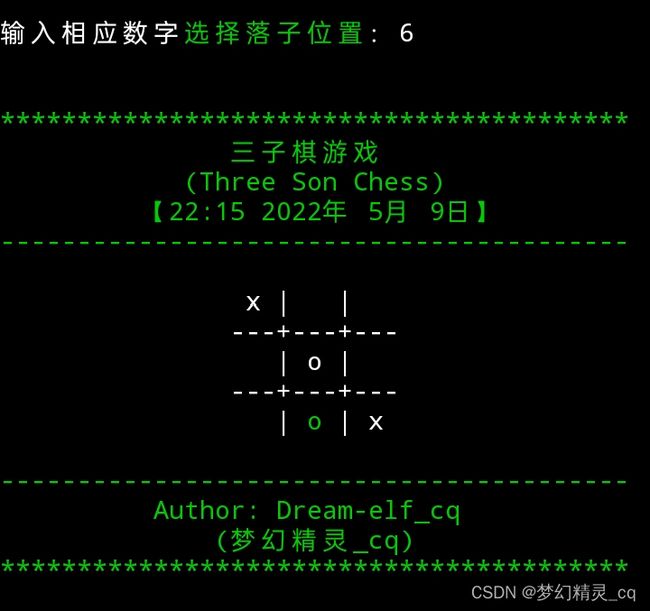
def chessboard_show(chess_signs):
''' 棋盘列印棋局状况 '''
s = chess_signs
blank = f"{'':>15}"
print(f"\n{blank} {s[0]} | {s[1]} | {s[2]} \
\n{blank}{'-'*3}+{'-'*3}+{'-'*3}\
\n{blank} {s[3]} | {s[4]} | {s[5]} \
\n{blank}{'-'*3}+{'-'*3}+{'-'*3}\
\n{blank} {s[6]} | {s[7]} | {s[8]} ") # 由于三子棋棋盘简单,总共只有九格。所以决定用插值字符串格式化的形式来刻划棋盘,显示棋局状况。
def isblank_places():
''' 落子位置获取(棋盘空位) '''
blank_chess = [k for k,i in enumerate(chess_signs) if i == ' '] # 解析可以落子的位置列表。
tem_chess = chess_signs[:] # 拷贝棋局布子状况。
for m,i in enumerate(blank_chess):
for k in tem_chess: # 将可落子的位置按1开始编码并存入落子位置状况棋局列表。
if k == ' ':
tem_chess[i] = m+1
return blank_chess, tem_chess # 返回空位棋盘状况和以 1 始序的落子选择棋局刻划数据。
def ischessman():
''' 确认玩家落子位置,写入棋局列表 '''
blank_chess, tem_chess = isblank_places() # 获取可以落子位置
while True:
tem = chess_signs # 棋局状况存放列表别名。
if tem.count(' ') == 1: # 仅有最后一个空位。
tem[tem.index(' ')] = you # 落子最后一个空位。
return # 落子最后一个空位后,返回上层调用。
try: # 选择项错误捕获。
clear() # 清屏。
gui_head() # 界面头。
chessboard_show(tem_chess) # 显示当前棋局可以落子位置,按序号选择落子位置。
isman = int(input(f"{cut_line()}输入相应数字{color(1,'f_green')}选择落子位置{color(0)}:"))
if isman not in range(1, len(blank_chess)+1): # 合法选择序号范围设定。
error_show()
input(f"\n{color(1,'f_green')}{' 错误类型:无此选项!':-^29}{color(0)}")
continue # 继续选择落子位置。
if tem_chess.index(isman) == 4 and len(set(chess_signs)) == 1: # 开局先手落子中心,报错。
tip = " Don't choose central number first! "
input(f"{cut_line()}{color(tip, 'f_red'):-^50}{cut_line()}")
continue
break
except Exception as error:
error_show()
input(f"\n错误类型:{color(1,'f_green')}{error}{color(0)}")
continue # 继续选择落子位置。
chess_signs[tem_chess.index(isman)] = you # 写入玩家落子位置。
def isvictor():
''' 判胜:三子连珠。'''
tem = chess_signs # 对弈棋局状况存放列表别名。
win_list = [{tem[0], tem[1], tem[2]},
{tem[3], tem[4], tem[5]},
{tem[6], tem[7], tem[8]},
{tem[0], tem[3], tem[6]},
{tem[1], tem[4], tem[7]},
{tem[2], tem[5], tem[8]},
{tem[0], tem[4], tem[8]},
{tem[2], tem[4], tem[6]}
] # 穷举获胜组合列表:三横三竖两对角线,三子连珠。用 python 集合存放每组获胜组合,据其特性,一旦出现“三子连珠”,存放获胜组合的集合将只有一个元素。缘于此,只需每次行棋后,判当前棋局状况中的“三子连珠”,如有则输出胜者。无则继续直到无处落子,输出“平局”提示。
for i in win_list: # 遍历判胜。
if len(i) == 1: # 三子连珠,打印获胜信息。
if list(i)[0] == you: # 集合不可以用下标引用,要先用 list 转化。
gui_head() # 界面头。
print(f"{cut_line()}{color(1, 'f_black', 'b_yellow')}{' 真厉害!':-^37}{color(0)}\n\n{' ':>16}{color('你', 'f_green')}赢了!{cut_line()}")
chessboard_show(tem) # 显示当前棋局状况。
history_show() # 列显棋局落子历史。
return True
elif list(i)[0] == computer:
gui_head() # 界面头。
print(f"{cut_line()}{color(1, 'f_black', 'b_red')}{' 可惜啊!':-^37}{color(0)}\n\n{' ':>16}{color('你', 'f_red')}输了!{cut_line()}")
chessboard_show(tem) # 显示当前棋局状况。
history_show() # 列显棋局落子历史。
return True
if ' ' not in tem: # 无处落子,未出胜者,判平局。
gui_head() # 界面头。
print(f"{cut_line()}{color(1,'f_black', 'b_green')}{' 不错哩。':-^37}{color(0)}\n\n{' ':>10}您和神仙小姐姐{color('打成平手。', 'f_green')}{cut_line()}")
chessboard_show(tem) # 显示当前棋局状况。
history_show() # 列显棋局落子历史。
return True
def easy_chess():
''' 简单游戏模式 '''
from random import choice # 加载随机数模块的随机选择方法。
start_data() # 棋局状况存放“清零”。
history_chess.append('简单模式') # 记录游戏模式。
first = choice(('o','x')) # 随机确定先手。
win = False
clear() # 清屏。
while not win:
if first == 'o':
blank_chess, tem_chess = isblank_places() # 获取可以落子位置。
ischessman() # 调用函数实施玩家落子。
history_chess.append(chess_signs.copy()) # 保存历史棋局状况。
win = isvictor() # 判定胜利者。
first = 'x' # 玩家落子后更替“先手”。
else:
n = 88 # 机器最优算法落子机率。机器落子仅用随机模块太简单无趣,在代码中设此参数,控制简单程度。
flag = probability(n) # 机率调用机器最优算法落子。
if flag:
hard_isman() # 机器最优算法落子。
else:
blank_chess, tem_chess = isblank_places() # 获取可以落子位置。
isman = choice(range(1, len(blank_chess)+1))
chess_signs[tem_chess.index(isman)] = computer # 写入机器落子位置。
history_chess.append(chess_signs.copy()) # 保存历史棋局状况。
win = isvictor() # 判定胜利者。
first = 'o' # 玩家落子后更替“先手”。
def probability(n):
''' 参数 n 为 True 的百分比机率 '''
from random import choice, shuffle # 加载随机数模块的选择和打散方法。
prob = [1]*n + [0]*(100-n) # 根据参数生成机率选择列表。
for i in range(3):
shuffle(prob) # 打散(洗牌)三次。
return choice(prob) # 返回机率随机数
def history_show():
''' 历史棋局再现 '''
flag = input(f"{cut_line()}{'':>12}查看落子历史?({color('Y','f_green')})")
m, chinese_nums = 0, list('一二三四五')
if flag in list('Yy'):
clear() # 清屏。
gui_head() # 界面头。
s = f" “{color(history_chess[0], 'f_purple')}”对弈棋局重现 "
print(f"\n\n{s:^40}")
for k,i in enumerate(history_chess[1:]): # 剔除第一位的游戏模式字符。
if k%2 == 0: # 打印落子次数。
print(f"\n\n{'':->15} 第 {color(chinese_nums[m], 'f_purple')} 步 {'':->16}")
m += 1
chessboard_show(i)
gui_tail() # 界面尾。
wait()
def hard_chess():
''' 困难游戏模式 '''
from random import choice # 加载随机数模块的随机选择方法。
start_data() # 棋局状况存放“清零”。
history_chess.append('困难模式') # 记录游戏模式。
first = choice(('o','x')) # 随机确定先手。
win = False
while not win:
if first == 'o':
blank_chess, tem_chess = isblank_places() # 获取可以落子位置。
ischessman() # 调用函数实施玩家落子。
history_chess.append(chess_signs.copy()) # 保存历史棋局状况。
win = isvictor() # 判定胜利者。
first = 'x' # 玩家落子后更替“先手”。
else:
blank_chess, tem_chess = isblank_places() # 获取可以落子位置。
hard_isman() # 机器算法落子。 history_chess.append(chess_signs.copy()) # 保存历史棋局状况。
history_chess.append(chess_signs.copy())
win = isvictor() # 判定胜利者。
first = 'o' # 玩家落子后更替“先手”。
def hard_isman():
''' 困难游戏模式机器算法 '''
from random import choice # 加载随机数模块的随机选择方法。
tem = chess_signs # 存储棋局状况列表别名,方便简短代码语句。
# 拦截对手:两端落子 }===>
# 扫描第一行
if tem[0] == you and tem[1] == you: # 第一行前两位对方有子,
if tem[2] == ' ':
tem[2] = computer # 机器落子第一行右。
return # 成功落子后返回。
elif tem[1] == you and tem[2] == you: # 第一行后两位有对手子,
if tem[0] == ' ':
tem[0] = computer # 机器落子第一行前。
return # 成功落子后返回。
# 扫描第二行
if tem[3] == you and tem[4] == you: # 第二行前两位对方有子,
if tem[5] == ' ':
tem[5] = computer # 机器落子第二行右。
return # 成功落子后返回。
elif tem[4] == you and tem[5] == you: # 第一行后两位有子,
if tem[3] == ' ':
tem[3] = computer # 机器落子第一行前。
return # 成功落子后返回。
# 扫描第三行
if tem[6] == you and tem[7] == you: # 第三行前两位有子,
if tem[8] == ' ':
tem[8] = computer # 机器落子第三行右。
return # 成功落子后返回。
elif tem[7] == you and tem[8] == you: # 第一行后两位有子,
if tem[6] == ' ':
tem[6] = computer # 机器落子第三行右。
return # 成功落子后返回。
# 扫描第一列
if tem[0] == you and tem[6] == you: # 第一列前两位有子,
if tem[6] == ' ':
tem[6] = computer # 机器落子第一列下。
return # 成功落子后返回。
elif tem[6] == you and tem[3] == you: # 第一列下两位有子,
if tem[0] == ' ':
tem[0] = computer # 机器落子第一列上。
return # 成功落子后返回。
# 扫描第二列
if tem[1] == you and tem[4] == you: # 第二列前两位有子,
if tem[7] == ' ':
tem[7] = computer # 机器落子第二列下。
return # 成功落子后返回。
elif tem[4] == you and tem[1] == you: # 第二列下两位有子,
if tem[1] == ' ':
tem[1] = computer # 机器落子第二列上。
return # 成功落子后返回。
# 扫描第三列
if tem[2] == you and tem[5] == you: # 第三列前两位有子,
if tem[8] == ' ':
tem[8] = computer # 机器落子第三列下。
return # 成功落子后返回。
elif tem[5] == you and tem[8] == you: # 第三列下两位有子,
if tem[2] == ' ':
tem[2] = computer # 机器落子第三列上。
return # 成功落子后返回。
# 扫描左上右下对角
if tem[0] == you and tem[4] == you: # 左上右下对角线前两位有子,
if tem[8] == ' ':
tem[8] = computer # 机器落子右下角。
return # 成功落子后返回。
elif tem[8] == you and tem[4] == you: # 左上右下对角后两位有子,
if tem[0] == ' ':
tem[0] = computer # 机器落子左上角。
return # 成功落子后返回。
# 扫描左下右上对角
if tem[6] == you and tem[4] == you: # 左下右上对角线前两位有子,
if tem[2] == ' ':
tem[2] = computer # 机器落子右上角。
return # 成功落子后返回。
elif tem[2] == you and tem[4] == you: # 左下右上对角后两位有子,
if tem[6] == ' ':
tem[6] = computer # 机器落子左下角。
return # 成功落子后返回。
# 拦截对手:中间落子 }===>
if tem[0] == you and tem[2] == you: # 第一行两端对方有子,
if tem[1] == ' ':
tem[1] = computer # 机器落子第一行中。
return # 成功落子后返回。
if tem[3] == you and tem[5] == you: # 第二行两端对方有子,
if tem[4] == ' ':
tem[4] = computer # 机器落子中心。
return # 成功落子后返回。
if tem[6] == you and tem[8] == you: # 第三行两端对方有子,
if tem[7] == ' ':
tem[7] = computer # 机器落子第三行中。
return # 成功落子后返回。
if tem[0] == you and tem[6] == you: # 第一列上下对方有子,
if tem[3] == ' ':
tem[3] = computer # 机器落子第一列中。
return # 成功落子后返回。
if tem[1] == you and tem[7] == you: # 第二列上下对方有子,
if tem[4] == ' ':
tem[4] = computer # 机器落子中心。
return # 成功落子后返回。
if tem[2] == you and tem[8] == you: # 第三列上下对方有子,
if tem[5] == ' ':
tem[5] = computer # 机器落子第三列中。
return # 成功落子后返回。
# 扫描对角线
if tem[0] == you and tem[8] == you: # 左上右下对角上下对方有子,
if tem[4] == ' ':
tem[4] = computer # 机器落子中心。
return # 成功落子后返回。
if tem[2] == you and tem[7] == you: # 左下右上对角上下对方有子,
if tem[4] == ' ':
tem[4] = computer # 机器落子中心。
return # 成功落子后返回。
# 机器算法最优落子
# 在可以落子位置中最佳落子:中心最佳(首选),四角次之,边中间最差。算法依此序优先选择落子位置。
if list(set(tem))[0] == ' ' and len(set(tem)) == 1: # 先手。
tem[choice((0, 2, 6, 8))] = computer # 任意落子四角。
return # 成功落子后返回。
if tem[4] == ' ' and len(set(tem)) == 2: # 对方先手,机器落子中心。
tem[4] = computer
return # 成功落子后返回。
if tem[4] == ' ': # 中心空,
tem[4] = computer # 机器落子中心。
return # 成功落子后返回。
if tem[0] == computer: # 左上角有子,
if tem[1] == ' ' and tem[2] == ' ': # 第一行后两位皆空。
tem[1] = computer # 机器落子第一行中。
return # 成功落子后返回。
elif tem[3] == ' ' and tem[6] == ' ': # 第一列后两位皆空,
tem[3] = computer # 机器落子第一列中。
return # 成功落子后返回。
if tem[2] == computer: # 右上角有子,
if tem[1] == ' ' and tem[0] == ' ': # 第一行前两位皆空。
tem[1] = computer # 机器落子第一行中。
return # 成功落子后返回。
elif tem[5] == ' ' and tem[8] == ' ': # 第三列后两位皆空,
tem[5] = computer # 机器落子第三列中。
return # 成功落子后返回。
if tem[6] == computer: # 左下角有子,
if tem[3] == ' ' and tem[0] == ' ': # 第一列前两位皆空。
tem[3] = computer # 机器落子第一列中。
return # 成功落子后返回。
elif tem[7] == ' ' and tem[8] == ' ': # 第三行后两位皆空,
tem[7] = computer # 机器落子第三行中。
return # 成功落子后返回。
if tem[8] == computer: # 右下角有子,
if tem[7] == ' ' and tem[6] == ' ': # 第三行前两位皆空。
tem[7] = computer # 机器落子第三行中。
return # 成功落子后返回。
elif tem[5] == ' ' and tem[2] == ' ': # 第三行后两位皆空,
tem[5] = computer # 机器落子第三列中。
return # 成功落子后返回。
if tem[4] == computer:
for i in (0, 2, 6, 8): # 遍历四角位置。
if tem[i] == ' ': # 四角为空,
tem[i] = computer # 机器落子。
return # 成功落子后返回上层调用。
# 扫描第一行
if tem[0] == computer and tem[1] == computer: # 第一行前两位有子,
if tem[2] == ' ':
tem[2] = computer # 机器落子第一行右。
return # 成功落子后返回。
elif tem[1] == computer and tem[2] == computer: # 第一行后两位有子,
if tem[0] == ' ':
tem[0] = computer # 机器落子第一行前。
return # 成功落子后返回。
# 扫描第二行
if tem[3] == computer and tem[4] == computer: # 第二行前两位有子,
if tem[5] == ' ':
tem[5] = computer # 机器落子第二行右。
return # 成功落子后返回。
elif tem[4] == computer and tem[5] == computer: # 第一行后两位有子,
if tem[3] == ' ':
tem[3] = computer # 机器落子第一行前。
return # 成功落子后返回。
# 扫描第三行
if tem[6] == computer and tem[7] == computer: # 第三行前两位有子,
if tem[8] == ' ':
tem[8] = computer # 机器落子第三行右。
return # 成功落子后返回。
elif tem[7] == computer and tem[8] == computer: # 第一行后两位有子,
if tem[6] == ' ':
tem[6] = computer # 机器落子第三行右。
return # 成功落子后返回。
# 扫描第一列
if tem[0] == computer and tem[6] == computer: # 第一列前两位有子,
if tem[6] == ' ':
tem[6] = computer # 机器落子第一列下。
return # 成功落子后返回。
elif tem[6] == computer and tem[3] == computer: # 第一列下两位有子,
if tem[0] == ' ':
tem[0] = computer # 机器落子第一列上。
return # 成功落子后返回。
# 扫描第二列
if tem[1] == computer and tem[4] == computer: # 第二列前两位有子,
if tem[7] == ' ':
tem[7] = computer # 机器落子第二列下。
return # 成功落子后返回。
elif tem[4] == computer and tem[1] == computer: # 第二列下两位有子,
if tem[1] == ' ':
tem[1] = computer # 机器落子第二列上。
return # 成功落子后返回。
# 扫描第三列
if tem[2] == computer and tem[5] == computer: # 第三列前两位有子,
if tem[8] == ' ':
tem[8] = computer # 机器落子第三列下。
return # 成功落子后返回。
elif tem[5] == computer and tem[8] == computer: # 第三列下两位有子,
if tem[2] == ' ':
tem[2] = computer # 机器落子第三列上。
return # 成功落子后返回。
# 扫描左上右下对角
if tem[0] == computer and tem[4] == computer: # 左上右下对角线前两位有子,
if tem[8] == ' ':
tem[8] = computer # 机器落子右下角。
return # 成功落子后返回。
elif tem[8] == computer and tem[4] == computer: # 左上右下对角后两位有子,
if tem[0] == ' ':
tem[0] = computer # 机器落子左上角。
return # 成功落子后返回。
# 扫描左下右上对角
if tem[6] == computer and tem[4] == computer: # 左下右上对角线前两位有子,
if tem[2] == ' ':
tem[2] = computer # 机器落子右上角。
return # 成功落子后返回。
elif tem[2] == computer and tem[4] == computer: # 左下右上对角后两位有子,
if tem[6] == ' ':
tem[6] = computer # 机器落子左下角。
return # 成功落子后返回。
if tem.count(' ') == 1: # 仅有最后一个空位。
tem[tem.index(' ')] = computer # 机器落子最后一个空位。
# ---==== Codes The end ====---
if __name__ == '__main__': # 直接运行本 *.py 文件,执行后面的代码。
three_son_chess() # 召唤游戏主模块。
参考文章:
- 大佬 C《三子棋》
-
上一篇: 聊天消息敏感词屏蔽系统(字符串替换 str.replace(str1, *))
下一篇:
我的HOT博:
- New:Python班里有人和我同生日难吗?(概率probability、蒙特卡洛随机模拟法)(1878阅读)
- Python字符串居中显示(1068阅读)
- 练习:求偶数和、阈值分割和求差( list 对象的两个基础小题)(1559阅读)
- 用 pandas 解一道小题(1918阅读)
- 可迭代对象和四个函数(1045阅读)
- “快乐数”判断(1207阅读)
- 罗马数字转换器(构造元素取模)(1897阅读)
- 罗马数字(转换器|罗生成器)(2630阅读)
- Hot:让QQ群昵称色变的代码(19143阅读)
- Hot:斐波那契数列(递归| for )(3473阅读)
- 柱状图中最大矩形(1626阅读)
- 排序数组元素的重复起止(1216阅读)
- 电话拨号键盘字母组合(1290阅读)
- 密码强度检测器(1751阅读)
- 求列表平衡点(1787阅读)
- Hot: 字符串统计(3716阅读)
- Hot:尼姆游戏(聪明版首发)(3356阅读)尼姆游戏(优化版)(909阅读)
推荐条件 点阅破千
回首页

精品文章:
- 好文力荐:《python 完全自学教程》齐伟书稿免费连载
- OPP三大特性:封装中的property
- 通过内置对象理解python'
- 正则表达式
- python中“*”的作用
- Python 完全自学手册
- 海象运算符
- Python中的 `!=`与`is not`不同
- 学习编程的正确方法
来源:老齐教室
回首页
Python 入门指南【Python 3.6.3】
好文力荐:
-
全栈领域优质创作者——寒佬(还是国内某高校学生)好文:《非技术文—关于英语和如何正确的提问》,“英语”和“会提问”是学习的两大利器。
-
【8大编程语言的适用领域】先别着急选语言学编程,先看它们能干嘛
-
靠谱程序员的好习惯
CSDN实用技巧博文:
- 8个好用到爆的Python实用技巧
- python忽略警告