Java学习路线(26)——XML与设计模式
一、XML
(一)XML的概念: XML是可扩展标记语言(Extensible Markup Language),一种数据表示形式,可以描述非常复杂的数据结构,常用于传输和存储数据。
(二)XML的特点
- XML的数据是纯文本形式的,默认采用UTF-8编码
- 可嵌套
(三)XML使用场景: XML内容经常当做消息进行网络传输,或作为配置文件用于存储系统信息。
(四)XML语法
1、文件格式: 【xxx_xxx.xml】
2、文档声明(必须在第一行):
3、标签规则
- 标签是由一对闭合标签(如
)组成,其中根标签有且只有一个。 - 特殊标签如单闭合标签,则必须有结束标记(如
) - 标签可定义属性,属性和标签名用空格隔开,属性值必须用引号进行赋值。(如
) - 注释: 采用 【】的格式
- 正文中的尖括号可能会与标签发生冲突,所以需要用特殊字符代替尖括号,特殊字符格式:【&xxxx;】
| 特殊字符 | 被代替字符 |
|---|---|
| < | < |
| > | > |
| & | & |
| &apos | ’ |
| " | " |
- XML数据区CDATA: 【
(1)XML示例
<student>
<name>病态王子name>
<sex>男sex>
<hobby>傲娇hobby>
<info>
<age>25age>
<addr>中国addr>
info>
<sql>
select id from user where age > 20;
sql>
student>
(2)XML浏览器解析结果
病态王子
男
傲娇
25
中国
select id from user where age > 20;
(五)文档约束
**1、概念:**文档约束是用来限定xml文件中的标签以及属性的写法。
2、分类:
(1)DTD
DTD约束文档xxx.dtd
<!ELEMENT 暑假(书+)>
<!ELEMENT 书(书名,作者,售价)>
<!ELEMENT 书名(#PCDATA)>
<!ELEMENT 作者(#PCDATA)>
<!ELEMENT 售价(#PCDATA)>
编写xml导入DTD文档
DTD约束的优缺点
- 优点: 可以约束XML文件的编写
- 缺点: 不能约束具体数据类型
(2)schema
概念: schema是一种强约束XML,本身也受到其他约束文件的要求
使用步骤
- 1、编写schema约束文档,文档名为 【xxx.xsd】
- 2、XML导入schema约束文档
text.xsd
<schema xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
targetNamespace="http://www.itcast.cn"
elementFormDefault="qualified" >
<element name="书架">
<complexType>
<sequence maxOccurs="unbounded">
<element name="书">
<complexType>
<sequence>
<element name="书名" type="string"/>
<element name="作者" type="string"/>
<element name="售价" type="double"/>
sequence>
complexType>
element>
sequence>
complexType>
element>
schema>
XML引入schema约束
<书架 xmlns="http://www.itcast.cn"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.itcast.cn text.xsd">
<书>
<书名>《红楼梦》书名>
<作者>曹雪芹作者>
<售价>20.0售价>
书>
书架>
二、XML解析
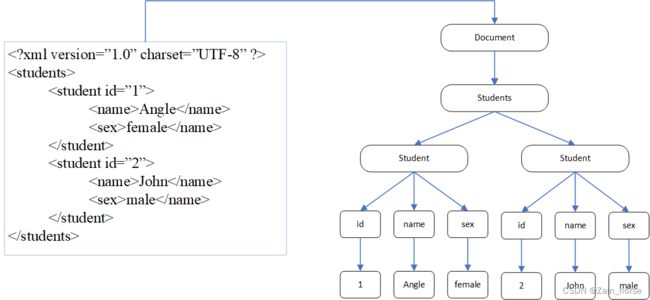
(一)概念: XML解析是使用程序读取XML中的数据。
(二)解析方式:
1、SAX解析
2、DOM解析
(1)DOM解析文档对象流程
- 读取文档进入内存,根节点为Document对象
- XML根节点为第 2 层节点
- 元素标签为第 3 层节点Element对象
- 属性标签为第 4 层节点Attibute对象
- 文本内容为第 5 层节点Text对象
(三)常见解析工具
| 工具 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| JAXP | SUN公司提供的一套XML解析API |
| JDOM | JDOM基于树形结构,利用纯JAVA技术对XML文档实现解析、生成、序列化以及其他多种操作 |
| dom4j | JDOM puls,用来读写XML文件 。具有性能好、功能强和易使用的特点。 |
| jsoup | 功能强大DOM方式的XML解析开发包,针对HTML解析更加方便 |
(四)使用Dom4j解析XML
1、使用流程
- 下载jar包:dom4j-2.1.1.jar
- 导入jar包
- 使用jar包
2、Dom4j解析
(1)获取Document对象
| 构造器/方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| SAXReader() | 创建Dom4j的解析器 |
| Document read(String url) | 加载XML成为Document对象 |
(2)获取根元素对象
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Element getRootElement() | 获取根元素对象 |
(3)Element元素对象API
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| List |
获取当前元素下所有子元素 |
| List |
获取当前元素下指定名字的所有子元素 |
| Element element(String name) | 获取当前元素下指定名字的第一个子元素 |
| String getName() | 获取元素名称 |
| String attributeValue(String name) | 根据属性名获取属性值 |
| String elementText(子元素名) | 获取指定名称的子元素文本 |
| String elementTextTrim(子元素名) | 获取指定名称的子元素文本并去除前后空格 |
| String getText() | 获取文本 |
| String attributeValue(属性名) | 获取属性值 |
@Test
public void parseData() throws DocumentException {
//1、创建解析器
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
//2、XML加载
// Document document = reader.read("D:\\JavaBase\\JavaSEpro\\src\\text.xml");
//默认在src寻找对应文件名称的文件进行加载
Document document = reader.read(Dom4JParseDemo.class.getResourceAsStream("/text.xml"));
//3、获取根元素
Element root = document.getRootElement();
System.out.println("根元素:"+root.getName());
//4、子元素(一级)
List<Element> elements = root.elements();
System.out.println("===============一级子元素==============");
for (Element e :elements) {
System.out.println(e.getName());
}
//5、获取指定元素以及元素值
System.out.println("===============指定子元素==============");
System.out.println(root.elementText("name"));
System.out.println(root.elementTextTrim("hobby"));
//6、根据元素获取属性值
Attribute idAttr = root.attribute("id");
System.out.println(idAttr.getName() + " = " +idAttr.getValue());
}
/*打印输出*/
根元素:student
===============一级子元素==============
name
sex
hobby
info
sql
===============指定子元素==============
病态王子
傲娇
id = 1
3、文件解析案例
(1)需求: 按照所给的XML文件,将文件数据按指定样式输出
(2)实现:
素材data.xml
<contactList>
<contact id="1">
<name>潘金莲name>
<gender>女gender>
<email>[email protected]email>
contact>
<contact id="2">
<name>武松name>
<gender>男gender>
<email>[email protected]email>
contact>
<contact id="3">
<name>武大郎name>
<gender>男gender>
<email>[email protected]email>
contact>
contactList>
实现代码
@Test
public void parseDemo() throws DocumentException {
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
Document document = reader.read(Dom4JParseDemo.class.getResourceAsStream("/data.xml"));
Element root = document.getRootElement();
String rootName = root.getName();
List<Element> memberNode = root.elements();
for (Element e :memberNode) {
System.out.println(e.getName() + "{id=" + e.attribute("id").getValue() + ", name=" + e.elementTextTrim("gender") + ", email=" + e.elementTextTrim("email") + "}");
}
}
打印输出
contact{id=1, name=女, [email protected]}
contact{id=2, name=男, [email protected]}
contact{id=3, name=男, [email protected]}
二、XML文件检索
(一)使用工具:Xpath
(二)Xpath使用
1、导入jar包: dom4j和jaxen
2、通过dom4j获取Document
3、利用XPath完成解析操作
(三)相关API
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Node selectSingleNode(“表达式”) | 获取符合表达式的唯一元素 |
| List |
获取符合表达式的所有元素 |
(四)三种搜索方式
1、绝对路径搜索
public class XPathDemo {
@Test
public void parse1() throws DocumentException {
//1、解析器
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
//2、Document对象
Document document = reader.read(XPathDemo.class.getResourceAsStream("/data.xml"));
//3、XPath路径搜索
//绝对路径搜索
List<Node> nodes = document.selectNodes("/contactList/contact/name");
for (Node node:nodes) {
Element element = (Element) node;
System.out.println(element.getTextTrim());
}
}
}
/*打印输出*/
潘金莲
武松
武大郎
2、相对路径搜索
public class XPathDemo {
@Test
public void parse1() throws DocumentException {
//1、解析器
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
//2、Document对象
Document document = reader.read(XPathDemo.class.getResourceAsStream("/data.xml"));
//3、XPath路径搜索
//相对路径搜索
List<Node> nodes = document.getRootElement().selectNodes("./contact/name");
for (Node node:nodes) {
Element element = (Element) node;
System.out.println(element.getTextTrim());
}
}
}
/*打印输出*/
潘金莲
武松
武大郎
3、全文搜索
public class XPathDemo {
@Test
public void parse1() throws DocumentException {
//1、解析器
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
//2、Document对象
Document document = reader.read(XPathDemo.class.getResourceAsStream("/data.xml"));
//3、Xpath全文检索(只要符合该路径就会匹配)
//注意:// --> 代表全文搜索, / --> 代表当前路径,两者可以混合使用
//例如 //contect/name 代表全文搜索所有contect的一级元素为name的属性值。
List<Node> nodes = document.selectNodes("//name");
for (Node node:nodes) {
Element element = (Element) node;
System.out.println(element.getTextTrim());
}
}
}
/*打印输出*/
潘金莲
武松
武大郎
4、属性查找
public class XPathDemo {
@Test
public void parse1() throws DocumentException {
//1、解析器
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
//2、Document对象
Document document = reader.read(XPathDemo.class.getResourceAsStream("/data.xml"));
//3、XPath路径搜索
System.out.println("===========方式1===========");
//所有id属性
List<Node> nodes = document.selectNodes("//@id");
for (Node node:nodes) {
Attribute element = (Attribute) node;
System.out.println(element.getValue());
}
System.out.println("===========方式2===========");
//name标签中中包含id属性的元素
List<Node> nodes1 = document.selectNodes("//contact[@id]");
for (Node node:nodes1) {
Element element = (Element) node;
System.out.println(element.getName());
}
System.out.println("===========方式3===========");
//name标签中中包含id属性值为1的元素
List<Node> nodes2 = document.selectNodes("//contact[@id=1]");
for (Node node:nodes2) {
Element element = (Element) node;
System.out.println(element.getName());
}
}
}
/*打印输出*/
===========方式1===========
1
2
3
===========方式2===========
contact
contact
contact
===========方式3===========
contact
三、设计模式
(一)工厂模式
1、概念: 一种由内部创建对象的模式,对外提供获取对象的方法。
2、作用:
- 工厂方法可以封装对象的创建细节,例如对象初始化
- 可以实现类与类之间的解耦操作(核心思想)——就是不让类直接关联起来。
3、实现:
public class FactoryDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Computer c1 = FactoryPattern.getComputer("mac");
Computer c2 = FactoryPattern.getComputer("huawei");
c1.run();
c2.run();
}
}
class Computer{
protected String name;
protected double price;
public Computer(){}
public Computer(String name, double price) {
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
}
public void run(){
System.out.println(this.name + "正在启动。。。");
};
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Computer{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
'}';
}
}
class Mac extends Computer{
public Mac() {
}
public Mac(String mac, double price) {
this.name = mac;
this.price = price;
}
}
class HuaWei extends Computer{
public HuaWei() {
}
public HuaWei(String name, double price) {
super(name, price);
}
}
class FactoryPattern{
public static Computer getComputer(String info){
switch (info){
case "mac":
return new Mac("Mac",9999);
case "huawei":
return new HuaWei("HuaWei",5999);
default:
return null;
}
}
}
/*打印输出*/
Mac正在启动。。。
HuaWei正在启动。。。
(二)装饰模式
1、概念: 创建一个新类,包装原始类,增强原始类的功能。
2、作用:
- 不改变原类的基础上,动态扩展类的方法。——实际上是一个带有原始类的工具类。
- 可以实现类与类之间的解耦操作(核心思想)——就是不让类直接关联起来。
3、实现:
public class DecaratorDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream();
System.out.println(inputStream.read());
byte[] bytes = new byte[100];
System.out.println(inputStream.read(bytes));
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bytes));
}
}
abstract class InputStream{
public abstract int read();
public abstract int read(byte[] buffer);
}
class FileInputStream extends InputStream{
@Override
public int read() {
System.out.println("读取了一个字节a");
return 97;
}
@Override
public int read(byte[] buffer) {
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
buffer[i] = (byte) (97 + i);
}
System.out.println("读取了一个字节数组");
return 26;
}
}
/*打印输出*/
读取了一个字节a
97
读取了一个字节数组
26
[97, 98, 99, 100, 101, 102, 103, 104, 105, 106, 107, 108, 109, 110, 111, 112, 113, 114, 115, 116, 117, 118, 119, 120, 121, 122, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]