flutter:文件系统目录、文件读写
参考
参考:老孟 文件存储和网络请求
数据存储
Dart的 IO 库包含了文件读写的相关类,它属于 Dart 语法标准的一部分,所以通过 Dart IO 库,无论是 Dart VM 下的脚本还是 Flutter,都是通过 Dart IO 库来操作文件的。但是不同的平台对应的文件系统是不同的,比如文件路径,因此通常使用Google 官方维护的插件 path_provider。
安装
在项目的 pubspec.yaml 文件中添加依赖
dependencies:
path_provider: ^2.0.11
安装
flutter pub get
常用方法
getTemporaryDirectory
临时目录,适用于下载的缓存文件,此目录随时可以清除,此目录为应用程序私有目录,其他应用程序无法访问此目录。
getApplicationSupportDirectory
获取应用程序的支持目录。这个函数返回一个Future对象,表示应用程序的支持目录。
getLibraryDirectory
返回应用程序的库目录。这个目录通常用于存储应用程序的共享库或插件。
getApplicationDocumentsDirectory
应用程序的文档目录。文档目录是应用程序可以使用的持久性存储空间,通常用于存储用户生成的文件或其他数据。
getExternalStorageDirectory
应用程序可以访问顶级存储的目录的路径。由于此功能仅在Android上可用,因此应在发出此函数调用之前确定当前操作系统。
getExternalCacheDirectories
存储特定于应用程序的外部缓存数据的目录的路径。
getDownloadsDirectory
存储下载文件的目录的路径,这通常仅与台式机操作系统有关。 在Android和iOS上,此函数将引发[UnsupportedError]异常。
方法使用场景
下面从 Android 和 iOS 平台的角度介绍其文件路径,最后给出路径使用的建议以及使用过程中需要注意的事项。
安卓文件存储
Android 文件存储分为内部存储和外部存储。
内部存储:
- 其他应用无法访问这些数据
- 当应用卸载的时候,这些数据也会被删除,避免垃圾文件
- 不需要申请额外权限
- 存储的空间有限,此目录数据随时可能被系统清除,也可以通过 设置 中的 清除数据 可以清除此目录数据。
内部存储目录结构:
- cache 目录:对应 getTemporaryDirectory 方法,用于缓存文件,此目录随时可能被系统清除。
- files 目录:对应 getApplicationSupportDirectory 方法。
- code_cache:此目录存储 Flutter 相关代码和资源
- shared_prefs:SharePreferences(轻量级的本地存储) 的默认路径
- app_flutter:对应 getApplicationDocumentsDirectory方法。
- app_flutter/dbName:使用 sqlite(轻量级的关系型数据库,用于本地存储和管理应用程序的数据) 的默认路径,sqlite 也可以指定位置。
外部存储
- 当应用卸载的时候,这些数据也会被删除,避免垃圾文件
- 不需要申请额外权限
- 空间大且不会被系统清除,通过 设置 中的 清除数据 可以清除此目录数据。
- 用户可以直接对文件进行删除、导入操作。
外部存储目录结构
- cache:缓存目录,对应 getExternalCacheDirectories 方法。
- files:对应 getExternalStorageDirectories 方法。
苹果文件存储
iOS 文件存储相比 Android 要简单的多,因为 iOS 对用户隐私保护非常严格,每个 iOS 应用程序都有一个单独的文件系统,而且只能在对应的文件系统中进行操作,此区域被称为沙盒。
每个应用沙盒含有3个文件夹:Documents, Library 和 tmp:
- Documents:应用程序数据文件写入到这个目录下。这个目录用于存储用户数据。保存应用程序的重要数据文件和用户数据文件等。对应 getApplicationDocumentsDirectory 方法。
- Library:对应 getLibraryDirectory 方法
- tmp:存放临时文件,不会被备份,而且这个文件下的数据有可能随时被清除的可能,按照官方说法每三天清理一次缓存数据。
总结
- SharePreferences 和 sqlite 数据建议存放在内部存储,插件已经帮我们完成了,无需手动处理。
- 严格保密的数据,比如用户数据,建议存放在内部存储,对应 getApplicationSupportDirectory 方法。
- 其余所有的数据建议存放
Android/data/包名/,对应 getExternalCacheDirectories 和 getExternalStorageDirectories 方法。
基本使用
flutter官方示例
文件读写
文件夹
创建文件夹
ElevatedButton(onPressed: () async{
// 获取应用程序目录
Directory appDocumentDriectory = await getApplicationDocumentsDirectory();
// 路径,Platform.pathSeparator 平台下的路径分隔符
String path = '${appDocumentDriectory.path}${Platform.pathSeparator}myAppName';
// 读取对应路径下的文件夹
var dir = Directory(path);
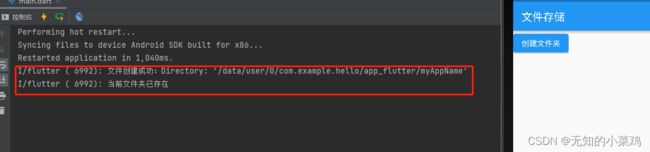
if(dir.existsSync()){
print("当前文件夹已存在");
}else{
// 创建文件,可选参数recursive:true表示可以创建嵌套文件夹,false表示只能创建最后一级文件夹(上一级文件不存在会报错),默认false
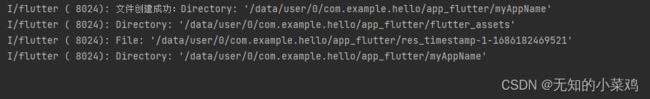
var result = await dir.create(recursive: true);
print("文件创建成功:${result}");
}
}, child: const Text("创建文件夹"));
遍历文件夹
ElevatedButton(onPressed: () async{
// 获取应用程序目录
Directory appDocumentDirectory = await getApplicationDocumentsDirectory();
String path = '${appDocumentDirectory.path}${Platform.pathSeparator}';
// 文件列表,可选参数recursive,默认值为false,只遍历当前目录;设置为true时会遍历当前目录及子目录
Stream<FileSystemEntity> fileList = Directory(path).list();
await for(FileSystemEntity fileSystemEntity in fileList){
print(fileSystemEntity);
}
}, child: const Text("遍历文件"))
await for(FileSystemEntity fileSystemEntity in fileList){
print('$fileSystemEntity');
FileSystemEntityType type = FileSystemEntity.typeSync(fileSystemEntity.path);
}
文件的类型:
- file:文件
- directory:文件夹
- link:链接文件,比如:HTML文件、PDF文件、图片文件、音频文件、文本文件、JSON文件
- notFound:未知
文件夹重命名
_dirRename() async{
Directory documentsDirectory = await getApplicationDocumentsDirectory();
String path = '${documentsDirectory.path}${Platform.pathSeparator}dirName';
var dir = Directory(path);
var newName= await dir.rename('${dir.parent.absolute.path}${Platform.pathSeparator}newName');
}
删除文件夹
ElevatedButton(onPressed: () async{
// 获取应用程序文件目录
Directory appDocumentDirectory = await getApplicationDocumentsDirectory();
String path ='${appDocumentDirectory.path}${Platform.pathSeparator}myAppName';
try{
// 可选参数recursive,默认false,只删除文件夹,如果文件夹下有内容则无法删除并抛出异常;true删除文件夹及文件夹下所有内容
var dir = await Directory(path).delete();
print('文件夹$path删除成功');
}catch(err){
print('文件夹$path删除失败:$err');
}
}, child: const Text("删除文件夹"))
文件
创建文件
ElevatedButton(onPressed: () async{
// 获取应用程序目录
Directory appDocumentDirectory = await getApplicationDocumentsDirectory();
// 路径
String path = '${appDocumentDirectory.path}${Platform.pathSeparator}myAppName${Platform.pathSeparator}test.txt';
File file = File(path);
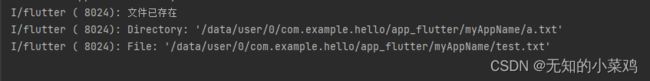
if(file.existsSync()){
print("文件已存在");
}else{
// 文件创建也存在recursive属性
var file = await File(path).create();
print("文件创建成功:$file");
}
}, child: const Text("创建文件"))
写入字符串,覆盖写入
ElevatedButton(onPressed: () async{
// 获取应用程序目录
Directory appDocumentDirectory = await getApplicationDocumentsDirectory();
// 路径
String path = '${appDocumentDirectory.path}${Platform.pathSeparator}myAppName${Platform.pathSeparator}test.txt';
File file = File(path);
if(file.existsSync()){
var res = await file.writeAsString("写入数据");
print("写入成功:$res");
}else{
print("文件不存在");
}
}, child: const Text("写入数据")),
file.writeAsBytes(Utf8Encoder().convert("bytes 格式"));
追加写入
file.openWrite(mode: FileMode.append).write('追加写入');
读取数据
读取字符串
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: () async {
// 应用程序目录
Directory appDocumentDirectory =
await getApplicationDocumentsDirectory();
// 路径
String path =
'${appDocumentDirectory.path}${Platform.pathSeparator}myAppName${Platform.pathSeparator}test.txt';
File file = File(path);
if (file.existsSync()) {
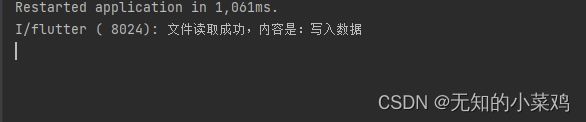
var res = await file.readAsString(encoding: utf8);
print("文件读取成功,内容是:$res");
} else {
print("文件不存在");
}
},
child: const Text("文件读取"))
List<String> lines = await file.readAsLines();
lines.forEach((element) {
print('$element');
});
读取 bytes 并转换为String
Utf8Decoder().convert(await file.readAsBytes());
删除
file.delete();
读取 assets 文件
读取项目中文件,项目中使用的文件一般都放在lib/assets下

如果需要访问,需要在pubspec.yaml 文件中添加配置,例如:
assets:
- assets/json/
读取
_loadAsset(BuildContext context) async{
var jsonStr = await DefaultAssetBundle.of(context)
.loadString('assets/json/data.json');
var list = json.decode(jsonStr);
list.forEach((element) {
print('$element');
});
}