Spring Cloud Alibaba - Sentinel源码分析
目录
一、Sentinel核心源码分析
1、Sentinel核心概念
1.1、Node之间的关系
2、Sentinel源码入口
2.1、SlotChain解析
2.2、NodeSelectorSlot解析
2.3、ClusterBuilderSlot解析
一、Sentinel核心源码分析
Sentinel是分布式系统的防御系统。以流量为切入点,通过动态设置的流量控制、服务熔断等手段达到 保护系统的目的,通过服务降级增强服务被拒后用户的体验。
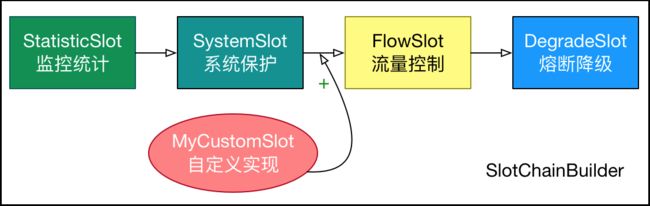
在 Sentinel 里面,所有的资源都对应一个资源名称以及一个 Entry。Entry 可以通过对主流框架的适配自动创建,也可以通过注解的方式或调用SphU API 显式创建;每一个 Entry 创建的时候,同时也会创建一系列功能插槽(slot chain)。这些插槽有不同的职责,例如:
- NodeSelectorSlot 负责收集资源的路径,并将这些资源的调用路径,以树状结构存储起来,用于根据调用路径来限流降级;
- ClusterBuilderSlot 则用于存储资源的统计信息以及调用者信息,例如该资源的 RT, QPS, thread count 等等,这些信息将用作为多维度限流,降级的依据;
- StatisticSlot 则用于记录、统计不同纬度的 runtime 指标监控信息;
- FlowSlot 则用于根据预设的限流规则以及前面 slot 统计的状态,来进行流量控制;
- AuthoritySlot 则根据配置的黑白名单和调用来源信息,来做黑白名单控制;
- DegradeSlot 则通过统计信息以及预设的规则,来做熔断降级;
- SystemSlot 则通过系统的状态,例如 load1 等,来控制总的入口流量;
重要的概念:
- slot chain:插槽
- Node:根节点
- Context:对资源操作时的上下文环境,每个资源操作(`针对Resource进行的entry/exit`)必须属于一个Context,如果程序中未指定Context,会创建name为"sentinel_default_context"的默认Context。一个Context生命周期内可能有多个资源操作,Context生命周期内的最后一个资源exit时会清理该Context,这也预示这真个Context生命周期的结束。
- Entry:表示一次资源操作,内部会保存当前调用信息。在一个Context生命周期中多次资源操作,也就是对应多个Entry,这些Entry形成parent/child结构保存在Entry实例中
总体的框架
Sentinel 将 ProcessorSlot 作为 SPI 接口进行扩展(1.7.2 版本以前 SlotChainBuilder 作为 SPI),使得 Slot Chain 具备了扩展的能力。您可以自行加入自定义的 slot 并编排 slot 间的顺序,从而可以给 Sentinel 添加自定义的功能。
Sentinel源码下载
Sentinel源码地址
1、Sentinel核心概念
Sentinel作为ali开源的一款轻量级流控框架,主要以流量为切入点,从流量控制、熔断降级、系统负载保护等多个维度来帮助用户保护服务的稳定性。相比于Hystrix,Sentinel的设计更加简单,在 Sentinel中资源定义和规则配置是分离的,也就是说用户可以先通过Sentinel API给对应的业务逻辑定义资源(埋点),然后在需要的时候再配置规则,通过这种组合方式,极大的增加了Sentinel流控的灵活性。
引入Sentinel带来的性能损耗非常小。只有在业务单机量级超过25W QPS的时候才会有一些显著的影响(5% - 10% 左右),单机QPS不太大的时候损耗几乎可以忽略不计。
Sentinel提供两种埋点方式:
- try-catch 方式(通过 SphU.entry(...)),用户在 catch 块中执行异常处理
- if-else 方式(通过 SphO.entry(...)),当返回 false 时执行异常处理
官方案例:
NodeSelectorSlot
这个 slot 主要负责收集资源的路径,并将这些资源的调用路径,以树状结构存储起来,用于根据调用路径来限流降级。
ContextUtil.enter("entrance1", "appA");
Entry nodeA = SphU.entry("nodeA");
if (nodeA != null) {
nodeA.exit();
}
ContextUtil.exit();改写Demo
一个资源
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.context.ContextUtil;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.BlockException;
public class ContextBySingleResourceDemo {
public void ContextUtil(){
//创建一个来自appA访问的Context
//Context的名称为entrance1
ContextUtil.enter("entrance1", "appA");
// Entry就是一个资源操作对象
Entry nodeA = null;
try {
//获取资源resource的entry
nodeA = SphU.entry("resource1");//后续会展开这个位置
// 如果代码走到这个位置,说明当前资源的请求通过了流控,可以继续进行相关业务处理
} catch (BlockException e) {
// 如果没有通过走到了这里,就表示请求被限流,这里进行降级操作
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if (nodeA != null) {
nodeA.exit();
}
}
//释放Context
ContextUtil.exit();
}
}多个资源
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.context.ContextUtil;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.BlockException;
public class ContextByMultiResourceDemo {
public void ContextUtil(){
//创建一个来自appA访问的Context
//Context的名称为entrance1
ContextUtil.enter("entrance1", "appA");
// Entry就是一个资源操作对象
Entry nodeA = null;
Entry nodeB = null;
try {
//获取资源resource1的entry
nodeA = SphU.entry("resource1");
// 如果代码走到这个位置,说明当前资源的请求通过了流控,可以继续进行相关业务处理
//获取资源resource2的entry
nodeB = SphU.entry("resource2");
// 如果代码走到这个位置,说明当前资源的请求通过了流控,可以继续进行相关业务处理
} catch (BlockException e) {
// 如果没有通过走到了这里,就表示请求被限流,这里进行降级操作
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if (nodeA != null) {
nodeA.exit();
}
if (nodeB != null) {
nodeB.exit();
}
}
//释放Context
ContextUtil.exit();
}
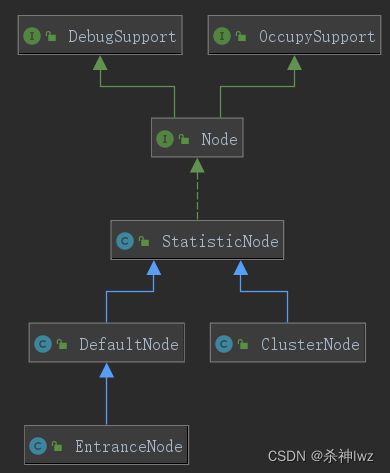
}1.1、Node之间的关系
- Node:接口,Sentinel 里面的各种种类的统计节点
- StatisticNode:统计节点,是Node的实现类,用于完成数据统计
- EntranceNode:DefaultNode的子类,入口节点,一个Context会有一个入口节点,用于统计当前Context的总体流量数据,统计维度为Context
- DefaultNode:默认节点,用于统计一个resource在当前Context中的流量数据,DefaultNode持有指定的Context和指定的Resource的统计数据,意味着DefaultNode是以Context和Resource为维度的统计节点
- ClusterNode:ClusterNode保存的是同一个Resource的相关的统计信息,是以Resource为维度的,不区分Context,这个是和DefaultNode的区别
Node之间的关系
Node 接口定义了一个 Node 类所需要提供的各项指标数据统计的相关功能,为外部屏蔽滑动窗口的存在。提供记录请求被拒绝、请求被放行、请求处理异常、请求处理成功的方法,以及获取当前时间窗口统计的请求总数、平均耗时等方法。
2、Sentinel源码入口
在微服务的使用Sentinel实际工作场景中,我们只需要引入对应依赖:spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-sentinel,就会进行自动装配,所以我们之间看META-INF/spring.factories,然后我们这里从SentinelAutoConfiguration开始看起。
利用@SentinelResource注解作为切点,然后在通过AOP环绕通知,来进行增强,在执行原方法前,来执行对应操作,当然这里我们可以看出,一旦出现了限流或者限流就会走BlockException。
@EnableConfigurationProperties({SentinelProperties.class})
public class SentinelAutoConfiguration {
...
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public SentinelResourceAspect sentinelResourceAspect() {
return new SentinelResourceAspect();
}
...
//----------------------------
@Aspect//切面
public class SentinelResourceAspect extends AbstractSentinelAspectSupport {
public SentinelResourceAspect() {
}
//指定切入点为SentinelResource注解
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.annotation.SentinelResource)")
public void sentinelResourceAnnotationPointcut() {
}
// 环绕通知
@Around("sentinelResourceAnnotationPointcut()")
public Object invokeResourceWithSentinel(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
Method originMethod = resolveMethod(pjp);
SentinelResource annotation = originMethod.getAnnotation(SentinelResource.class);
if (annotation == null) {
// Should not go through here.
throw new IllegalStateException("Wrong state for SentinelResource annotation");
}
String resourceName = getResourceName(annotation.value(), originMethod);
EntryType entryType = annotation.entryType();
int resourceType = annotation.resourceType();
Entry entry = null;
try {
// 创建资源操作对象
entry = SphU.entry(resourceName, resourceType, entryType, pjp.getArgs());
// 调用原方法
return pjp.proceed();
} catch (BlockException ex) {
return handleBlockException(pjp, annotation, ex);
} catch (Throwable ex) {
Class[] exceptionsToIgnore = annotation.exceptionsToIgnore();
// The ignore list will be checked first.
if (exceptionsToIgnore.length > 0 && exceptionBelongsTo(ex, exceptionsToIgnore)) {
throw ex;
}
if (exceptionBelongsTo(ex, annotation.exceptionsToTrace())) {
traceException(ex);
return handleFallback(pjp, annotation, ex);
}
// No fallback function can handle the exception, so throw it out.
throw ex;
} finally {
if (entry != null) {
entry.exit(1, pjp.getArgs());
}
}
}在创建资源操作对象的时候我们需要先创建Context,但是明显这里没有显示创建,但是实际上我们如果看Context概念的话,就会知道,如果程序中未指定Context,会创建name为"sentinel_default_context"的默认Context,然后我们继续往下跟踪。
public class SphU {
...
public static Entry entry(String name, int resourceType, EntryType type, Object[] args) throws BlockException {
//限流方法
return Env.sph.entryWithType(name, resourceType, type, 1, args);
}进入到entry方法中,这里的entryWithType方法就是我们要看的真正的限流的方法,具体的实现方法在com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.CtSph.entryWithType
public class CtSph implements Sph {
...
public Entry entryWithType(String name, int resourceType, EntryType entryType, int count, Object[] args) throws BlockException {
return this.entryWithType(name, resourceType, entryType, count, false, args);
}
public Entry entryWithType(String name, int resourceType, EntryType entryType, int count, boolean prioritized, Object[] args) throws BlockException {
// 这里将资源的名称和信息封装称为资源对象
StringResourceWrapper resource = new StringResourceWrapper(name, entryType, resourceType);
// 返回一个Entry资源操作对象
// prioritized属性表示优先级,默认值为false,表示当前请求不按照优先级执行,直接执行
return this.entryWithPriority(resource, count, prioritized, args);
}
private Entry entryWithPriority(ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args) throws BlockException {
// 从当前线程中获取Context
// 一个请求会占用一个线程,并且绑定一个Context
Context context = ContextUtil.getContext();
// 一个请求对应一个Context
// 如果当前类型为NullContext,表示此时请求已经超出了阈值,无需检测规则
if (context instanceof NullContext) {
return new CtEntry(resourceWrapper, (ProcessorSlot)null, context);
} else {
// 此时如果获取Context为空,就创建默认的sentinel_default_context,并且会放入到当前线程中
if (context == null) {
context = CtSph.InternalContextUtil.internalEnter("sentinel_default_context");
}
// 判断全局开关,如果是关闭状态,直接返回无需检测规则
if (!Constants.ON) {
return new CtEntry(resourceWrapper, (ProcessorSlot)null, context);
} else {
/**
* 这里是整个架构的核心所在,这里是在构建一个处理链,这个处理链是一个单向链表结构,类似于Filter一样,构建这个链条的
* 原因是对业务进行解耦,像限流资源保护有很多,比如限流、降级、热点参数、系统降级等等,如果都写在一起就耦合很严重,我们知道oop的
* 思想就是让每个类确定各自的职责,不要让他做不相干的事情,所以这里将业务进行全面解耦,然后在解耦的同时又通过链式编程将它们串起来
*/
ProcessorSlotInternalContextUtil.internalEnter(Constants.CONTEXT_DEFAULT_NAME);
private final static class InternalContextUtil extends ContextUtil {
static Context internalEnter(String name) {
// 从这里继续跟踪
return trueEnter(name, "");
}
static Context internalEnter(String name, String origin) {
return trueEnter(name, origin);
}
}首先这里要明确一下,一个Context的组成实际上需要name(名称)和origin(来源),所以方法上传入这两个参数
protected static Context trueEnter(String name, String origin) {
// 从当前线程中获取当前context名称
Context context = contextHolder.get();
// 如果当前context为空
if (context == null) {
// 从缓存中获取,当前缓存中key值为:Context名称,value值为:EntranceNode
// (因为后续创建的是EntranceNode),需要它的原因是因为构建Context需要EntranceNode
Map localCacheNameMap = contextNameNodeMap;
// 在缓存中获取EntranceNode
DefaultNode node = localCacheNameMap.get(name);
if (node == null) {
// 当前缓存的size>Context的最大数量,返回NULL_Context类型
if (localCacheNameMap.size() > Constants.MAX_CONTEXT_NAME_SIZE) {
setNullContext();
return NULL_CONTEXT;
} else {
LOCK.lock();
try {
node = contextNameNodeMap.get(name);
// 这里两次判断是采用了双重检测锁的机制:为了防止并发创建
if (node == null) {
if (contextNameNodeMap.size() > Constants.MAX_CONTEXT_NAME_SIZE) {
setNullContext();
return NULL_CONTEXT;
} else {
// node赋值为EntranceNode
node = new EntranceNode(new StringResourceWrapper(name, EntryType.IN), null);
// Add entrance node.
// 将新建的EntranceNode添加到ROOT中
Constants.ROOT.addChild(node);
// 将新建的EntranceNode添加到缓存中
Map newMap = new HashMap<>(contextNameNodeMap.size() + 1);
newMap.putAll(contextNameNodeMap);
newMap.put(name, node);
contextNameNodeMap = newMap;
}
}
} finally {
LOCK.unlock();
}
}
}
// 将name和node封装成Context
context = new Context(node, name);
// 设定来源
context.setOrigin(origin);
// 将context写入到当前线程中
contextHolder.set(context);
}
// 返回Context
return context;
} CtSph中,位置的chain.entry方法
//CtSph中entryWithPriority()
try {
// 针对资源操作
chain.entry(context, resourceWrapper, (Object)null, count, prioritized, args);
} catch (BlockException var9) {
e.exit(count, args);
throw var9;
} catch (Throwable var10) {
RecordLog.info("Sentinel unexpected exception", var10);
}官方定义:Sentinel 将 ProcessorSlot作为 SPI 接口进行扩展(1.7.2 版本以前 SlotChainBuilder作为 SPI),使得 Slot Chain 具备了扩展的能力。您可以自行加入自定义的 slot 并编排 slot 间的顺序,从而可以给 Sentinel 添加自定义的功能。
2.1、SlotChain解析
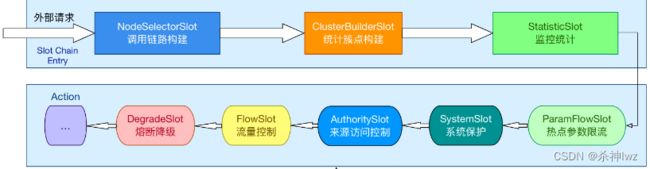
lookProcessChain()用于构建一个责任链。Sentinel的处理核心都在这个责任链中,链中每一个节点是一个Slot实例,这个链通过BlockException异常来告知调用入口最终的执行情况
//CtSph中entryWithPriority()
// 获取chain链
ProcessorSlot这个位置我们要具体分析SlotChainProvider这个类型,它的主要作用就是通过已解析的槽链构建器,创建槽链的提供者
从这里我们可以看出SlotChainBuilder及ProcessorSlot 使用Java SPI技术实现可配置化,即在/META-INF/services/接口全限命名 的文件中配置实现类,然后由ServiceLoader实现加载
public final class SlotChainProvider {
...
public static ProcessorSlotChain newSlotChain() {
if (slotChainBuilder != null) {
return slotChainBuilder.build();
}
// 读取配置文件在/META-INF/services/接口全限定命名的文件中配置实现类.
// Resolve the slot chain builder SPI.
slotChainBuilder = SpiLoader.of(SlotChainBuilder.class).loadFirstInstanceOrDefault();
if (slotChainBuilder == null) {
// Should not go through here.
RecordLog.warn("[SlotChainProvider] Wrong state when resolving slot chain builder, using default");
//使用默认的DefaultSlotChainBuilder来构建ProcessorSlotChain
slotChainBuilder = new DefaultSlotChainBuilder();
} else {
RecordLog.info("[SlotChainProvider] Global slot chain builder resolved: {}",
slotChainBuilder.getClass().getCanonicalName());
}
//使用DefaultSlotChainBuilder构建
return slotChainBuilder.build();
}
private SlotChainProvider() {}
}
其实现在使用的是使用DefaultSlotChainBuilder.build()来创建的
在这个其中,做了几件事:
1. 创建DefaultProcessorSlotChain
2. 读取/META-INF/services/中的配置文件
3. 强制转型为AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot(所有插槽的抽象父类)
@Spi(isDefault = true)
public class DefaultSlotChainBuilder implements SlotChainBuilder {
@Override
public ProcessorSlotChain build() {
// 创建DefaultProcessorSlotChain
ProcessorSlotChain chain = new DefaultProcessorSlotChain();
// 读取配置文件在/META-INF/services/接口全限定命名的文件
List sortedSlotList = SpiLoader.of(ProcessorSlot.class).loadInstanceListSorted();
for (ProcessorSlot slot : sortedSlotList) {
if (!(slot instanceof AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot)) {
RecordLog.warn("The ProcessorSlot(" + slot.getClass().getCanonicalName() + ") is not an instance of AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot, can't be added into ProcessorSlotChain");
continue;
}
chain.addLast((AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot) slot);
}
return chain;
}
} 具体读取内容如下:
# Sentinel default ProcessorSlots
com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.nodeselector.NodeSelectorSlot
com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.clusterbuilder.ClusterBuilderSlot
com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.logger.LogSlot
com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.statistic.StatisticSlot
com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.authority.AuthoritySlot
com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.system.SystemSlot
com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow.FlowSlot
com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.degrade.DegradeSlot
com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.degrade.DefaultCircuitBreakerSlot这些就是Sentinel提供的默认功能插槽
分析到这里我们就可以回到CtSph中,查看entry方法这个时候我们就知道了实际上调用entry方法的是DefaultProcessorSlotChain
//CtSph中entryWithPriority()
try {
// 针对资源操作
chain.entry(context, resourceWrapper, (Object)null, count, prioritized, args);
} catch (BlockException var9) {
e.exit(count, args);
throw var9;
} catch (Throwable var10) {
RecordLog.info("Sentinel unexpected exception", var10);
}那我们向下跟踪
public class DefaultProcessorSlotChain extends ProcessorSlotChain {
...
@Override
public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, Object t, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args)
throws Throwable {
// 转到下一个节点
first.transformEntry(context, resourceWrapper, t, count, prioritized, args);
}这个位置是转入到下一个节点,那么下一个节点明显就是NodeSelectorSlot
2.2、NodeSelectorSlot解析
public abstract class AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot implements ProcessorSlot {
...
void transformEntry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, Object o, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args)
throws Throwable {
T t = (T)o;
entry(context, resourceWrapper, t, count, prioritized, args);
}
//-->NodeSelectorSlot
@Spi(isSingleton = false, order = Constants.ORDER_NODE_SELECTOR_SLOT)
public class NodeSelectorSlot extends AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot {
private volatile Map map = new HashMap(10);
@Override
public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, Object obj, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args)
throws Throwable {
// 从缓存中获取,创建DefaultNode
DefaultNode node = map.get(context.getName());
// 双重判断,如果判断为空
if (node == null) {
synchronized (this) {
node = map.get(context.getName());
if (node == null) {
// 创建一个DefaultNode并且放入到缓存中
node = new DefaultNode(resourceWrapper, null);
HashMap cacheMap = new HashMap(map.size());
cacheMap.putAll(map);
cacheMap.put(context.getName(), node);
map = cacheMap;
// Build invocation tree
// 将新建的Node添加到调用树中
((DefaultNode) context.getLastNode()).addChild(node);
}
}
}
context.setCurNode(node);
// 触发下一个节点
fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, prioritized, args);
}
@Override
public void exit(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, int count, Object... args) {
fireExit(context, resourceWrapper, count, args);
}
} NodeSelectorSlot具体内容官网有给出解释:
这个 slot 主要负责收集资源的路径,并将这些资源的调用路径,以树状结构存储起来,用于根据调用路径来限流降级。
DefaultNode用于统计一个resource在当前Context中的流量数据,所以再结合NodeSelectorSlot,最终得出结论:处理不同的Context name,同一个Resource name的情况
2.3、ClusterBuilderSlot解析
官方定义:ClusterBuilderSlot:则用于存储资源的统计信息以及调用者信息,例如该资源的 RT, QPS, thread count 等等,这些信息将用作为多维度限流,降级的依据;
//NodeSelectorSlot.entry()
// 触发下一个节点
fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, prioritized, args);再触发下一个节点以后,调用的是父级AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot.fireEntry()方法,然后next调用transformEntry
//AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot
@Override
public void fireEntry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, Object obj, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args)
throws Throwable {
if (next != null) {
next.transformEntry(context, resourceWrapper, obj, count, prioritized, args);
}
}
//next就代表循环到下一个节点所以这里调用entry的就是ClusterBuilderSlot
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
void transformEntry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, Object o, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args)
throws Throwable {
T t = (T)o;
entry(context, resourceWrapper, t, count, prioritized, args);
}ClusterBuilderSlot
//ClusterBuilderSlot.entry
@Override
public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, DefaultNode node, int count,
boolean prioritized, Object... args)
throws Throwable {
if (clusterNode == null) {
synchronized (lock) {
if (clusterNode == null) {
// Create the cluster node.
clusterNode = new ClusterNode(resourceWrapper.getName(), resourceWrapper.getResourceType());
// key为资源 value为ClusterNode
HashMap newMap = new HashMap<>(Math.max(clusterNodeMap.size(), 16));
newMap.putAll(clusterNodeMap);
newMap.put(node.getId(), clusterNode);
clusterNodeMap = newMap;
}
}
}
// 添加节点
node.setClusterNode(clusterNode);
/*
* if context origin is set, we should get or create a new {@link Node} of
* the specific origin.
*/
// 确认资源的来源
if (!"".equals(context.getOrigin())) {
Node originNode = node.getClusterNode().getOrCreateOriginNode(context.getOrigin());
context.getCurEntry().setOriginNode(originNode);
}
fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, prioritized, args);
} 总结:
ClusterNode作用就是与DefaultNode进行关联,即不同的DefaultNode都关联了一个ClusterNode,这样我们在不同上下文中都可以拿到当前资源一个总的流量统计情况。
干我们这行,啥时候懈怠,就意味着长进的停止,长进的停止就意味着被淘汰,只能往前冲,直到凤凰涅槃的一天!