Spring Cloud - Eureka原理、注册、搭建、应用(全过程详解)
目录
一、Eureka 注册原理
1.1、为什么要使用 Eureka
1.2、Eureka 的工作流程及原理
1.3、eureka 的作用
二、具体实现
2.1、搭建注册中心
2.2、服务注册和部署
2.2.1、user-service 服务注册
2.2.2、服务部署
2.2.3、order-service 服务注册
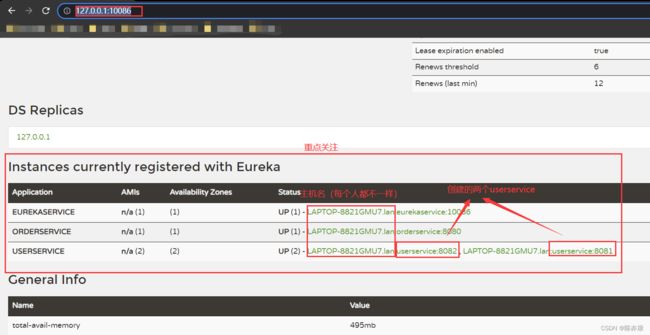
2.2.4、验证服务
2.3、服务发现
2.3.1、在order-service完成服务拉取
三、小结
一、Eureka 注册原理
1.1、为什么要使用 Eureka
上一章我们讲到,利用 RestTemplate 发送 http 请求时,将 url 写成了 "http://localhost:8081/user/" + order.getUserId() ,这无疑将 url 写死了,当有多台主机操控不同微服务时,难道还使用 localhost 访问自己主机的 ip 吗?这只是其中一个背景,总的来讲,有以下三种原因:
- 服务消费者该如何获取服务提供者的地址信息?
- 如果有多个服务提供者,消费者该如何选择?
- 消费者如何得知服务提供者的健康状态?
1.2、Eureka 的工作流程及原理
ps:案例是上一章所讲的 “根据订单id查询订单的同时,把订单所属的用户信息一起返回” 。
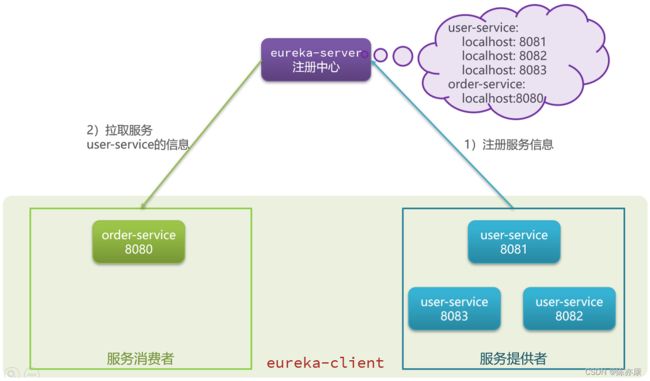
1)首先存在下图中三个角色,其中 order-service(服务消费者 - 订单服务)、user-service(服务提供者 - 用户服务)统称为 eureka-client,也就是 eureka 的客户端。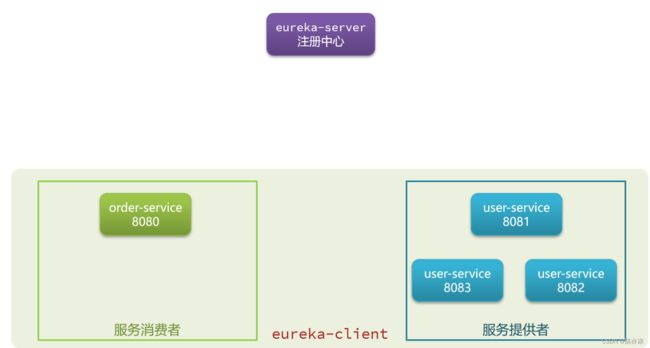
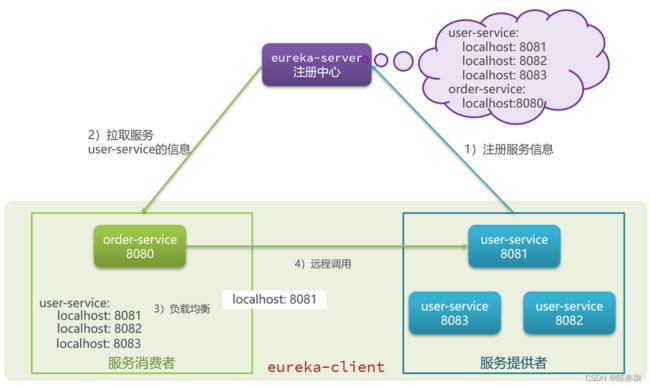
2)接着,eureka-service 会分别去获取并注册服务提供者和服务消费者的 ip 地址和端口号,同时,order-service 也会通过 注册中心拉取 user-service 的信息(ip 和 端口号)如下图
3)order-service 远程调用 user-service,首先会通过负载均衡,通过负载均衡算法(例如轮询)找到合适的 user-service ,如下图
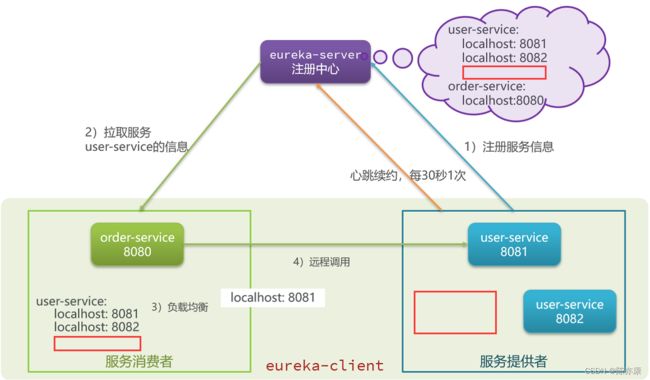
4)之后,服务提供者中集群的每一个 service 都需要向注册中心每 30 秒发送一个心跳请求,这个请求不携带业务逻辑,只是用来表明自己还存在,没有挂掉~ 一旦超过一定时间,注册中心没有收到心跳包,注册中心就会认为这个服务下线(删除这个服务注册),同时 order-service 也就拉取不到这个服务的 IP 和端口号了~ 如下图
1.3、eureka 的作用
消费者该如何获取服务提供者具体信息?
- 服务提供者启动时向eureka注册自己的信息
- eureka保存这些信息
- 消费者根据服务名称向eureka拉取提供者信息
如果有多个服务提供者,消费者该如何选择?
- 服务消费者利用负载均衡算法,从服务列表中挑选一个
消费者如何感知服务提供者健康状态?
- 服务提供者会每隔30秒向EurekaServer发送心跳请求,报告健康状态
- eureka会更新记录服务列表信息,心跳不正常会被剔除
- 消费者就可以拉取到最新的信息
二、具体实现
2.1、搭建注册中心
搭建 Eureka服务步骤如下:
1)创建项目,引入spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-server的依赖
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-server
2)编写启动类,添加@EnableEurekaServer注解
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.server.EnableEurekaServer;
@EnableEurekaServer //自动装配的开关
@SpringBootApplication
public class EurekaApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(EurekaApplication.class, args);
}
}
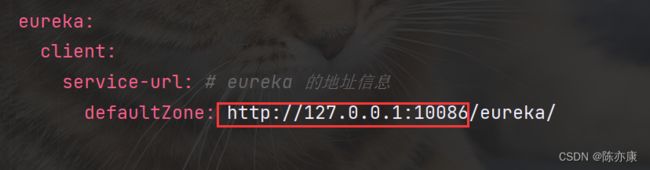
3)添加application.yml文件,编写下面的配置
server:
port: 10086 # 服务端口
spring:
application:
name: eurekaservice # 服务名称
eureka:
client:
service-url: # eureka 的地址信息
defaultZone: http://127.0.0.1:10086/eureka/
2.2、服务注册和部署
2.2.1、user-service 服务注册
按照刚刚所讲的案例,我们只需要将 user-service 服务注册到 EurekaServer 即可,步骤如下:
1)在user-service项目引入spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client的依赖
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client
2)在application.yml文件原配置的基础下,添加下面的配置(若重复,需要删掉 spring)
spring:
application:
name: userservice # 服务名称
eureka:
client:
service-url: # eureka 的地址信息
defaultZone: http://127.0.0.1:10086/eureka/
2.2.2、服务部署
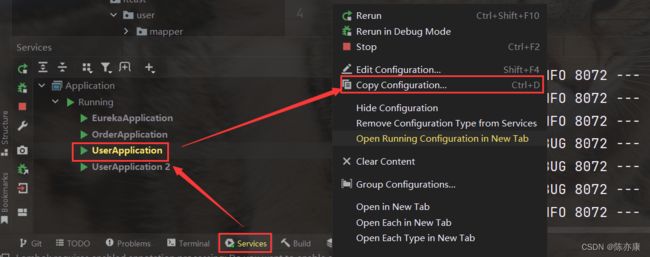
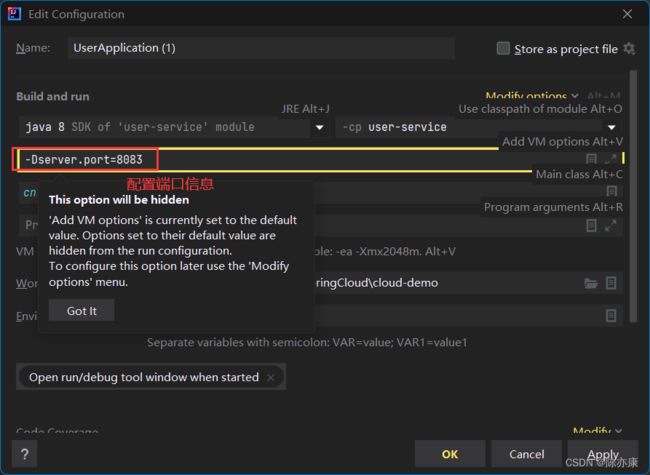
我们可以将user-service多次启动, 模拟多实例部署,但为了避免端口冲突,需要修改端口设置:
最后启动服务即可~
2.2.3、order-service 服务注册
order-service虽然是消费者,但与user-service一样都是eureka的client端,同样可以实现服务注册(和注册 user-service 唯一不同的是要对 spring.application.name 重新命名):
1)在order-service项目引入spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client的依赖
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client
2)在application.yml文件原配置的基础下,添加下面的配置(若重复,需要删掉 spring)
spring:
application:
name: orderservice
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://127.0.0.1:10086/eureka/2.2.4、验证服务
在浏览器中输入 application.yml 中配置的 eureka 路径即可,如下图:
2.3、服务发现
2.3.1、在order-service完成服务拉取
服务拉取是基于服务名称获取服务列表,然后在对服务列表做负载均衡
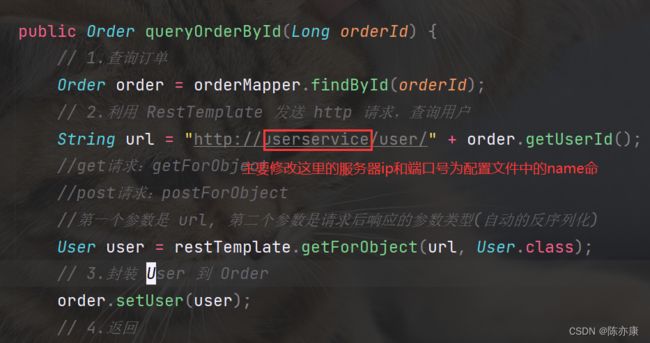
1)修改OrderService的代码,修改访问的url路径,用服务名代替ip、端口:
import cn.itcast.order.mapper.OrderMapper;
import cn.itcast.order.pojo.Order;
import cn.itcast.order.pojo.User;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
@Service
public class OrderService {
@Autowired
private OrderMapper orderMapper;
@Autowired
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
public Order queryOrderById(Long orderId) {
// 1.查询订单
Order order = orderMapper.findById(orderId);
// 2.利用 RestTemplate 发送 http 请求,查询用户
String url = "http://userservice/user/" + order.getUserId();
//get请求:getForObject
//post请求:postForObject
//第一个参数是 url, 第二个参数是请求后响应的参数类型(自动的反序列化)
User user = restTemplate.getForObject(url, User.class);
// 3.封装 User 到 Order
order.setUser(user);
// 4.返回
return order;
}
}
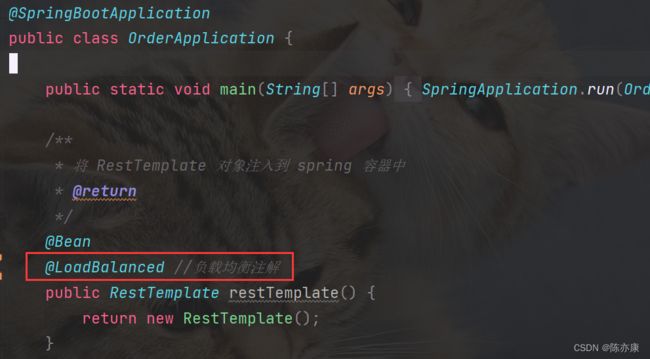
2)在order-service项目的启动类OrderApplication中的RestTemplate添加负载均衡注解:
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.LoadBalanced;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
//@MapperScan 注解的作用相当于在指定包下的所有 mapper 接口上都加上了 @mapper 注解
@MapperScan("cn.itcast.order.mapper")
@SpringBootApplication
public class OrderApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(OrderApplication.class, args);
}
/**
* 将 RestTemplate 对象注入到 spring 容器中
* @return
*/
@Bean
@LoadBalanced //负载均衡注解
public RestTemplate restTemplate() {
return new RestTemplate();
}
}
最后重启你的所有服务,通过 order-service 向 user-service 发送两个的 http请求,就可以在日志中看到负载均衡的效果啦(记得提前清除两个 user-service 的日志信息,防止干扰)~
三、小结
你学费了吗?