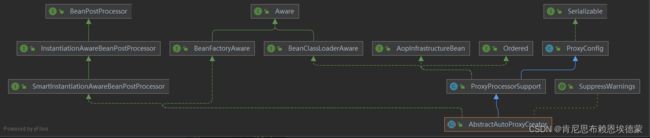
spring.aop 随笔1 主流程
0. 当一个闹钟不响的时候,太痛了。
真人改编的故事,给整破防了.
不完全的参考链接吧(这次写的时候,没太参照某篇文章,绝大多数是对源码的理解吧)
代理模式的入门概述
Spring AOP中optimize
spring boot aop 中的proxyTargetClass
既然是随笔的话,那我要写的稍微奔放一点了…
1. Spring Aop配置结构
Spring AOP 的演进过程
1. 1 借鉴上文中原始的xml配置结构:
<bean class="ProxyFactoryBean">
<property name="interceptorNames">
<list>
<value>advice1value>
<value>advice2value>
list>
property>
bean>
-
ProxyFactoryBean:用于生成代理bean的工厂
-
Advisor:给代理bean绑定用于增强的advice
NameMatchMethodPointcutAdvisor 根据aspect expression 进行绑定
RegexpMethodPointcutAdvisor 根据正则 -
AutoProxyCreator(自动代理)
spring提供了一个默认的、替代ProxyFactoryBean创建出代理bean的AutoProxyCreator:
BeanNameAutoProxyCreator:配置减少至 -> 增强类(前面那仨)+被代理的Bean
DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator:仅仅只需指定被代理的bean(默认使用ioc中所有的advisor去拦截)
通过对比可知:“自动”即帮我们自动生成了相应的ProxyFactory
1.2 @AspectJ配置方式
-
使用 @Aspect 注解的 bean 都会被 Spring 当做用来实现 AOP 的配置类(必须是一个spring bean)
-
@Pointcut 就是用来匹配 Spring 容器中的所有 bean 的方法的
配置 pointcut 就是配置我们需要拦截哪些方法,方法保留签名即可,无需实现 -
作用同Advisor的注解:
@Before
@AfterReturning
@AfterThrowing
@After
会拦截正常返回和异常的情况
@Around
Spring 提供了非常简单的获取入参的方法,使用 org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint 作为 Advice 的第一个参数即可
1.3 schema-based 配置
咋说呢,优点即可观性好
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="businessService" expression="execution(* com.javadoop.springaoplearning.service.*.*(..))"/>
<aop:pointcut id="businessService2" expression="com.javadoop.SystemArchitecture.businessService()"/>
aop:config>
<aop:config>
<aop:aspect ref="logArgsAspect">
<aop:pointcut id="internalPointcut"
expression="com.javadoop.SystemArchitecture.businessService()" />
aop:aspect>
aop:config>
2. spring aop 源码
Spring AOP 源码解析
近来,有种钻源码的冲动;
考虑到spring的源码特点:支路旁系众多,这里就不搞那么多花里胡哨的了
通过IDE的debug以及UML功能我们可以发现DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator 到头来是一个 BeanPostProcessor;
于是,我们从 getBean的过程 中着手分析创建代理的时机…这得从spring ioc说起了
只要跟随 step into 即可
2.1 从 ioc 到 AopProxy构建
protected Object initializeBean(String beanName, Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
return null;
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
// 如果实现了的话,回调 BeanNameAware、BeanClassLoaderAware 或 BeanFactoryAware 的实现,该Bean可以借此获取上下文的相关属性
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
}
Object wrappedBean = bean;
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
// step into...
// 先看看是不是在这里???
// 回调 beanPostProcessor 的before钩子
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
try {
// 执行 bean属性 init-method 方法
invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
(mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null),
beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex);
}
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
// 回调 beanPostProcessor 的after钩子
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
return wrappedBean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
// step out ...
// 有点尴尬,并不是那么回事
return bean;
}
// org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#initializeBean(java.lang.String, java.lang.Object, org.springframework.beans.factory.support.RootBeanDefinition)
protected Object initializeBean(String beanName, Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
return null;
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
// 如果实现了的话,回调 BeanNameAware、BeanClassLoaderAware 或 BeanFactoryAware 的实现,该Bean可以借此获取上下文的相关属性
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
}
Object wrappedBean = bean;
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
// 回调 beanPostProcessor 的before钩子
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
try {
// 执行 bean属性 init-method 方法
invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
(mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null),
beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex);
}
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
// step into ...
// 那这下子估计没跑了
// 回调 beanPostProcessor 的after钩子
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
return wrappedBean;
}
// org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.AbstractAutoProxyCreator#postProcessAfterInitialization
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(@Nullable Object bean, String beanName) {
if (bean != null) {
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName);
// 代理bean提前暴露其引用(remove返回的bean并不是当前bean)
if (this.earlyProxyReferences.remove(cacheKey) != bean) {
// step into ...
// 这个方法返回的bean大抵便是代理后的bean
return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
}
}
return bean;
}
// org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.AbstractAutoProxyCreator#wrapIfNecessary
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {
// 我需要的方法是创建出代理bean的方法,这一坨判断与我无关
if (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) && this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) {
return bean;
}
if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this.advisedBeans.get(cacheKey))) {
return bean;
}
if (isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) || shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
// 看着官方注释,估计没跑了
// 返回了 advice advisor interceptor 的集合
// Create proxy if we have advice.
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null);
if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE);
// step into ...
Object proxy = createProxy(
bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors,
// spring aop 框架中 对被代理的接口的默认实现类(被代理bean的一个包装类而已)
// This is the default implementation of the TargetSource interface, as used by the Spring AOP framework
new SingletonTargetSource(bean));
this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());
return proxy;
}
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
// org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.AbstractAutoProxyCreator#createProxy
protected Object createProxy(Class<?> beanClass, @Nullable String beanName,
@Nullable Object[] specificInterceptors, TargetSource targetSource) {
if (this.beanFactory instanceof ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) {
AutoProxyUtils.exposeTargetClass((ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) this.beanFactory, beanName, beanClass);
}
// 回滚spring aop最远古的配置方式,就需要配置ProxyFactoryBean
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory();
proxyFactory.copyFrom(this);
if (!proxyFactory.isProxyTargetClass()) {
if (shouldProxyTargetClass(beanClass, beanName)) {
proxyFactory.setProxyTargetClass(true);
}
else {
// step into ...
// 进入窥一窥,有点好奇
evaluateProxyInterfaces(beanClass, proxyFactory);
}
}
// 如果 specificInterceptors 中有 advice 和 interceptor,它们也会被包装成 advisor
Advisor[] advisors = buildAdvisors(beanName, specificInterceptors);
proxyFactory.addAdvisors(advisors);
proxyFactory.setTargetSource(targetSource);
customizeProxyFactory(proxyFactory);
proxyFactory.setFrozen(this.freezeProxy);
if (advisorsPreFiltered()) {
proxyFactory.setPreFiltered(true);
}
return proxyFactory.getProxy(getProxyClassLoader());
}
// org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.AbstractAutoProxyCreator#createProxy
protected void evaluateProxyInterfaces(Class<?> beanClass, ProxyFactory proxyFactory) {
// 获取这个类实现的所有接口
Class<?>[] targetInterfaces = ClassUtils.getAllInterfacesForClass(beanClass, getProxyClassLoader());
boolean hasReasonableProxyInterface = false;
for (Class<?> ifc : targetInterfaces) {
if (!isConfigurationCallbackInterface(ifc) && !isInternalLanguageInterface(ifc) &&
ifc.getMethods().length > 0) {
hasReasonableProxyInterface = true;
break;
}
}
// 将其实现的接口都列入到代理工厂bean中
if (hasReasonableProxyInterface) {
// Must allow for introductions; can't just set interfaces to the target's interfaces only.
for (Class<?> ifc : targetInterfaces) {
proxyFactory.addInterface(ifc);
}
}
else {
// 如果没有实现接口 -> 生成代理的bean就以这个类作为代理的目标类
proxyFactory.setProxyTargetClass(true);
}
}
// org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.AbstractAutoProxyCreator#createProxy
protected Object createProxy(Class<?> beanClass, @Nullable String beanName,
@Nullable Object[] specificInterceptors, TargetSource targetSource) {
if (this.beanFactory instanceof ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) {
AutoProxyUtils.exposeTargetClass((ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) this.beanFactory, beanName, beanClass);
}
// 回滚spring aop最远古的配置方式,就需要配置ProxyFactoryBean
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory();
proxyFactory.copyFrom(this);
if (!proxyFactory.isProxyTargetClass()) {
if (shouldProxyTargetClass(beanClass, beanName)) {
proxyFactory.setProxyTargetClass(true);
}
else {
// 找到代理bean需要涉及到的目标接口
evaluateProxyInterfaces(beanClass, proxyFactory);
}
}
// 如果 specificInterceptors 中有 advice 和 interceptor,它们也会被包装成 advisor
Advisor[] advisors = buildAdvisors(beanName, specificInterceptors);
proxyFactory.addAdvisors(advisors);
proxyFactory.setTargetSource(targetSource);
customizeProxyFactory(proxyFactory);
proxyFactory.setFrozen(this.freezeProxy);
if (advisorsPreFiltered()) {
proxyFactory.setPreFiltered(true);
}
// step into ...
return proxyFactory.getProxy(getProxyClassLoader());
}
// org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactory#getProxy(java.lang.ClassLoader)
public Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
return
// step into ...
createAopProxy()
.getProxy(classLoader);
}
// org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyCreatorSupport#createAopProxy
protected final synchronized AopProxy createAopProxy() {
if (!this.active) {
activate();
}
return
// 这里没有啥逻辑,就直接返回 AopProxyFactory 的引用
getAopProxyFactory()
// step into ...
.createAopProxy(this);
}
// org.springframework.aop.framework.DefaultAopProxyFactory#createAopProxy
// 先在这停留吧,接下来应该按两种代理模式兵分两路浏览源码了 ....
@Override
public AopProxy createAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException {
/* 翻译一下,如果需要代理的bean:
* 代理优化策略 (isOptimize默认false) ||
* 强制使用类代理策略(proxy-target-class默认true) ||
* 被代理的类是否有实现的接口
*/
if (config.isOptimize() || config.isProxyTargetClass() || hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(config)) {
Class<?> targetClass = config.getTargetClass();
if (targetClass == null) {
throw new AopConfigException("TargetSource cannot determine target class: " +
"Either an interface or a target is required for proxy creation.");
}
// 被代理的bean是 接口实现类 || 代理类
if (targetClass.isInterface() || Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass)) {
// JDK 代理方式
return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);
}
// ceglib 代理方式
return new ObjenesisCglibAopProxy(config);
}
else {
return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);
}
}
2.2 spring自带拦截器ExposeInvocationInterceptor
ExposeInvocationInterceptor
简单地说,就是为了在拦截器链过程中传递被代理方法 MethodInvocation 的调用
2.2.1 ExposeInvocationInterceptor保存MethodInvocation到线程本地
// org.springframework.aop.interceptor.ExposeInvocationInterceptor#invoke
// 拦截器链index:0的ExposeInvocationInterceptor
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
// step into ...
// 先看一下这个spring.MethodInvocation(并不是java反射包sum.reflect下的)
MethodInvocation oldInvocation = invocation.get();
invocation.set(mi);
try {
return mi.proceed();
}
finally {
invocation.set(oldInvocation);
}
}
// MethodInvocation作用:给拦截器提供被调的方法
// MethodInvocation是一个连接点,可以被方法拦截器拦截。
/**
* Description of an invocation to a method, given to an interceptor
* upon method-call.
*
* A method invocation is a joinpoint and can be intercepted by a
* method interceptor.
*
* @author Rod Johnson
* @see MethodInterceptor
*/
public interface MethodInvocation extends Invocation {
// 获取被调用的方法。
// 此方法是Joinpoint.getStaticPart()方法的友好实现(结果相同)
/**
* Get the method being called.
* This method is a friendly implementation of the
* {@link Joinpoint#getStaticPart()} method (same result).
* @return the method being called
*/
Method getMethod();
}
// org.springframework.aop.interceptor.ExposeInvocationInterceptor#invoke
private static final ThreadLocal<MethodInvocation> invocation = new NamedThreadLocal<>("Current AOP method invocation");
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
MethodInvocation oldInvocation = invocation.get();
invocation.set(mi);
try {
return mi.proceed();
}
finally {
// 将 MethodInvocation 被调方法存入 threadlocal
invocation.set(oldInvocation);
}
}
2.2.2 ExposeInvocationInterceptor从threadLocal获取MethodInvocation
// org.springframework.aop.aspectj.AspectJAroundAdvice#invoke
// 例如:我们在拦截器链index:1的AroundAdvice
// public class AspectJAroundAdvice extends AbstractAspectJAdvice ...
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
if (!(mi instanceof ProxyMethodInvocation)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("MethodInvocation is not a Spring ProxyMethodInvocation: " + mi);
}
ProxyMethodInvocation pmi = (ProxyMethodInvocation) mi;
ProceedingJoinPoint pjp = lazyGetProceedingJoinPoint(pmi);
// step into ...
JoinPointMatch jpm = getJoinPointMatch(pmi);
return invokeAdviceMethod(pjp, jpm, null, null);
}
// 该重载方式,需要methodInvocation被调方法作为入参
// Note: We can't use JoinPointMatch.getClass().getName() as the key, since
// Spring AOP does all the matching at a join point, and then all the invocations.
// Under this scenario, if we just use JoinPointMatch as the key, then
// 'last man wins' which is not what we want at all.
// Using the expression is guaranteed to be safe, since 2 identical expressions
// are guaranteed to bind in exactly the same way.
@Nullable
protected JoinPointMatch getJoinPointMatch(ProxyMethodInvocation pmi) {
String expression = this.pointcut.getExpression();
return (expression != null ? (JoinPointMatch) pmi.getUserAttribute(expression) : null);
}
// 如果没有MethodInvocation入参的情况下,ExposeInvocationInterceptor就发挥作用了
// org.springframework.aop.aspectj.AbstractAspectJAdvice#getJoinPointMatch()
/**
* Get the current join point match at the join point we are being dispatched on.
*/
@Nullable
protected JoinPointMatch getJoinPointMatch() {
// step into ...
MethodInvocation mi = ExposeInvocationInterceptor.currentInvocation();
if (!(mi instanceof ProxyMethodInvocation)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("MethodInvocation is not a Spring ProxyMethodInvocation: " + mi);
}
return getJoinPointMatch((ProxyMethodInvocation) mi);
}
org.springframework.aop.aspectj.AbstractAspectJAdvice#getJoinPointMatch---------------------------
// org.springframework.aop.interceptor.ExposeInvocationInterceptor#currentInvocation
// 这里的this.invocation即前面提及的threadlocal
/**
* Return the AOP Alliance MethodInvocation object associated with the current invocation.
* @return the invocation object associated with the current invocation
* @throws IllegalStateException if there is no AOP invocation in progress,
* or if the ExposeInvocationInterceptor was not added to this interceptor chain
*/
public static MethodInvocation currentInvocation() throws IllegalStateException {
// 前面做了set,这里直接get
MethodInvocation mi = invocation.get();
if (mi == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"No MethodInvocation found: Check that an AOP invocation is in progress and that the " +
"ExposeInvocationInterceptor is upfront in the interceptor chain. Specifically, note that " +
"advices with order HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE will execute before ExposeInvocationInterceptor! " +
"In addition, ExposeInvocationInterceptor and ExposeInvocationInterceptor.currentInvocation() " +
"must be invoked from the same thread.");
}
return mi;
}
2.3 ReflectiveMethodInvocation.proceed
JDK、CgLib代理模式,除了AopProxy初始化过程十分近似以外,当两者以各自方式完成代理类的字节码生成之后并defindClass之后,
两者在演进拦截器链以及调用代理方法的过程也由Spring-aop紧紧的耦合在一起
提示:spring-aop包下的MethodInvocation接口完成了对方法调用行为的一个抽象表示,一开始看名字我也以为是sun.misc或者java.lang.reflect包下的
使用@Around、@Before生成的AdvisedInterceptor对@Pointcut方法进行增强的测试案例中,可以看到调用栈输出的信息中有这么一个"循环调用":
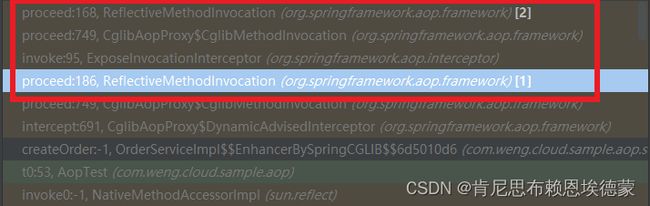
当增强顺序为:@Around(@Before -> ProxyMethod)时,@Before的增强方法对应的MethodInvocation由@Around内部来调用(ProceedingJointPoint.proceed())
JDK代理中拦截链演进的过程:
// org.springframework.aop.framework.ReflectiveMethodInvocation#proceed
@Override
@Nullable
public Object proceed() throws Throwable {
// We start with an index of -1 and increment early.
if (this.currentInterceptorIndex == this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1) {
return invokeJoinpoint();
}
// 每个递归都会使得 拦截器 当前索引累加1
Object interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice =
this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.get(++this.currentInterceptorIndex);
if (interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice instanceof InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) {
// Evaluate dynamic method matcher here: static part will already have
// been evaluated and found to match.
InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher dm =
(InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice;
Class<?> targetClass = (this.targetClass != null ? this.targetClass : this.method.getDeclaringClass());
if (dm.methodMatcher.matches(this.method, targetClass, this.arguments)) {
// invoke是真正是执行拦截的效果(增强),但是
// 具体实现基于advice的类型 Around、Before ...
return dm.interceptor.invoke(this);
}
else {
// 递归方式来演进到下一个拦截器
// 该advice不匹配
// Dynamic matching failed.
// Skip this interceptor and invoke the next in the chain.
return proceed();
}
}
else {
// step into ...
// 通过这个尾递归调用执行拦截器方法
// It's an interceptor, so we just invoke it: The pointcut will have
// been evaluated statically before this object was constructed.
return ((MethodInterceptor) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice).invoke(this);
}
}
// org.springframework.aop.interceptor.ExposeInvocationInterceptor#invoke
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
MethodInvocation oldInvocation = invocation.get();
invocation.set(mi);
try {
// step into ...
// 这里快进到下一个拦截器(我们自定义的拦截器)
return mi.proceed();
}
finally {
invocation.set(oldInvocation);
}
}
// 这里是我测试的时候使用@Around增强的调用方法(从这类的名字基本上就知道了)
// org.springframework.aop.aspectj.AspectJAroundAdvice#invoke
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
if (!(mi instanceof ProxyMethodInvocation)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("MethodInvocation is not a Spring ProxyMethodInvocation: " + mi);
}
ProxyMethodInvocation pmi = (ProxyMethodInvocation) mi;
ProceedingJoinPoint pjp = lazyGetProceedingJoinPoint(pmi);
JoinPointMatch jpm = getJoinPointMatch(pmi);
// step into ...
// 前面组装参数(@Around的advice方法的参数,例如JoinPoint这些),这里就是调用我们写的advice方法体了
return invokeAdviceMethod(pjp, jpm, null, null);
}
// 这里其实就是Advice通过传入的参数找到连接点,执行调用的过程
// org.springframework.aop.aspectj.AbstractAspectJAdvice#invokeAdviceMethod(org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint, org.aspectj.weaver.tools.JoinPointMatch, java.lang.Object, java.lang.Throwable)
// As above, but in this case we are given the join point.
protected Object invokeAdviceMethod(JoinPoint jp, @Nullable JoinPointMatch jpMatch,
@Nullable Object returnValue, @Nullable Throwable t) throws Throwable {
// step into ...
return invokeAdviceMethodWithGivenArgs(argBinding(jp, jpMatch, returnValue, t));
}
// 还是在Advice类里面,这次是真正的调用我们写的@Around的方法体了
// org.springframework.aop.aspectj.AbstractAspectJAdvice#invokeAdviceMethodWithGivenArgs
protected Object invokeAdviceMethodWithGivenArgs(Object[] args) throws Throwable {
Object[] actualArgs = args;
if (this.aspectJAdviceMethod.getParameterCount() == 0) {
actualArgs = null;
}
try {
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(this.aspectJAdviceMethod);
// step into ...
// 这里我们擦亮眼睛,注意以下这个 this.aspectJAdviceMethod 的类型
// protected transient java.lang.reflect.Method aspectJAdviceMethod
// TODO AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection
return this.aspectJAdviceMethod.invoke(this.aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectInstance(), actualArgs);
}
catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
throw new AopInvocationException("Mismatch on arguments to advice method [" +
this.aspectJAdviceMethod + "]; pointcut expression [" +
this.pointcut.getPointcutExpression() + "]", ex);
}
catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
throw ex.getTargetException();
}
}
// java.lang.reflect.Method#invoke
@CallerSensitive
public Object invoke(Object obj, Object... args)
throws IllegalAccessException, IllegalArgumentException,
InvocationTargetException
{
if (!override) {
if (!Reflection.quickCheckMemberAccess(clazz, modifiers)) {
Class<?> caller = Reflection.getCallerClass();
checkAccess(caller, clazz, obj, modifiers);
}
}
MethodAccessor ma = methodAccessor; // read volatile
if (ma == null) {
// step into ...
// 终于看到jdk包下的api了
// 这里创建MethodAccessor
ma = acquireMethodAccessor();
}
return ma.invoke(obj, args);
}
// java.lang.reflect.Method#invoke
@CallerSensitive
public Object invoke(Object obj, Object... args)
throws IllegalAccessException, IllegalArgumentException,
InvocationTargetException
{
if (!override) {
if (!Reflection.quickCheckMemberAccess(clazz, modifiers)) {
Class<?> caller = Reflection.getCallerClass();
checkAccess(caller, clazz, obj, modifiers);
}
}
MethodAccessor ma = methodAccessor; // read volatile
if (ma == null) {
ma = acquireMethodAccessor();
}
// step into ...
return ma.invoke(obj, args);
}
// sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl#invoke
public Object invoke(Object var1, Object[] var2) throws IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException {
return this.delegate.invoke(var1, var2);
}
// sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl#invoke
public Object invoke(Object var1, Object[] var2) throws IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException {
// 这个"flation"很有说法 -> 跟使用NativeMethodAccessorImpl直接执行&DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl代理执行有关
// Native版本一开始启动快,但是随着运行时间变长,速度变慢
// Java版本一开始加载慢,但是随着运行时间变长,速度变快
// 正是因为两种存在这些问题,所以第一次加载时使用的是NativeMethodAccessorImpl,而当反射调用次数超过15次之后,则使用MethodAccessorGenerator生成的MethodAccessorImpl对象去实现反射。
if (++this.numInvocations > ReflectionFactory.inflationThreshold() && !ReflectUtil.isVMAnonymousClass(this.method.getDeclaringClass())) {
MethodAccessorImpl var3 = (MethodAccessorImpl)(new MethodAccessorGenerator()).generateMethod(this.method.getDeclaringClass(), this.method.getName(), this.method.getParameterTypes(), this.method.getReturnType(), this.method.getExceptionTypes(), this.method.getModifiers());
this.parent.setDelegate(var3);
}
// step into ...
return invoke0(this.method, var1, var2);
}
// 报错信息里边是不是经常在栈顶(最深的方法)看到invoke0这个方法?
// 这个是由本地方法支撑实现的,非java实现,Java反射到这就没了
private static native Object invoke0(Method var0, Object var1, Object[] var2);
// 回到java调用栈之后的第一个方法即我们自定义的advice方法体 ...
CgLib代理中的拦截链演进:
// org.springframework.aop.framework.ReflectiveMethodInvocation#proceed
@Override
@Nullable
public Object proceed() throws Throwable {
// We start with an index of -1 and increment early.
if (this.currentInterceptorIndex == this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1) {
return invokeJoinpoint();
}
Object interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice =
this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.get(++this.currentInterceptorIndex);
if (interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice instanceof InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) {
// Evaluate dynamic method matcher here: static part will already have
// been evaluated and found to match.
InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher dm =
(InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice;
Class<?> targetClass = (this.targetClass != null ? this.targetClass : this.method.getDeclaringClass());
if (dm.methodMatcher.matches(this.method, targetClass, this.arguments)) {
return dm.interceptor.invoke(this);
}
else {
// 该advice不匹配
// Dynamic matching failed.
// Skip this interceptor and invoke the next in the chain.
return proceed();
}
}
else {
// step into ...
// 先调用拦截链index:0的ExposeInvocationInterceptor
// 通过这个尾递归调用执行拦截器方法
// It's an interceptor, so we just invoke it: The pointcut will have
// been evaluated statically before this object was constructed.
return ((MethodInterceptor) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice).invoke(this);
}
}
// org.springframework.aop.interceptor.ExposeInvocationInterceptor#invoke
private static final ThreadLocal<MethodInvocation> invocation =
new NamedThreadLocal<>("Current AOP method invocation");
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
MethodInvocation oldInvocation = invocation.get();
// 将代理方法调用器存入线程本地变量
invocation.set(mi);
try {
// step into ...
// 执行这个调用
return mi.proceed();
}
finally {
invocation.set(oldInvocation);
}
}
// org.springframework.aop.framework.CglibAopProxy.CglibMethodInvocation
/**
* Implementation of AOP Alliance MethodInvocation used by this AOP proxy.
*/
private static class CglibMethodInvocation extends ReflectiveMethodInvocation {
@Nullable
private final MethodProxy methodProxy;
public CglibMethodInvocation(Object proxy, @Nullable Object target, Method method,
Object[] arguments, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass,
List<Object> interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers, MethodProxy methodProxy) {
super(proxy, target, method, arguments, targetClass, interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers);
// Only use method proxy for public methods not derived from java.lang.Object
this.methodProxy = (Modifier.isPublic(method.getModifiers()) &&
method.getDeclaringClass() != Object.class && !AopUtils.isEqualsMethod(method) &&
!AopUtils.isHashCodeMethod(method) && !AopUtils.isToStringMethod(method) ?
methodProxy : null);
}
@Override
@Nullable
public Object proceed() throws Throwable {
try {
// step into ...
return super.proceed();
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Exception ex) {
if (ReflectionUtils.declaresException(getMethod(), ex.getClass())) {
throw ex;
}
else {
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(ex);
}
}
}
/**
* Gives a marginal performance improvement versus using reflection to
* invoke the target when invoking public methods.
*/
@Override
protected Object invokeJoinpoint() throws Throwable {
if (this.methodProxy != null) {
return this.methodProxy.invoke(this.target, this.arguments);
}
else {
return super.invokeJoinpoint();
}
}
}
// org.springframework.aop.framework.ReflectiveMethodInvocation#proceed
// 这里的调用链及其演进过程跟jdk方式是共用一个process方法的
// 都是由index:0的ExposeInvocationInterceptor.invoke发起的
// 于是乎,我就当偷个懒吧...
@Override
@Nullable
public Object proceed() throws Throwable {
// We start with an index of -1 and increment early.
if (this.currentInterceptorIndex == this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1) {
return invokeJoinpoint();
}
Object interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice =
this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.get(++this.currentInterceptorIndex);
if (interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice instanceof InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) {
// Evaluate dynamic method matcher here: static part will already have
// been evaluated and found to match.
InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher dm =
(InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice;
Class<?> targetClass = (this.targetClass != null ? this.targetClass : this.method.getDeclaringClass());
if (dm.methodMatcher.matches(this.method, targetClass, this.arguments)) {
return dm.interceptor.invoke(this);
}
else {
// Dynamic matching failed.
// Skip this interceptor and invoke the next in the chain.
return proceed();
}
}
else {
// It's an interceptor, so we just invoke it: The pointcut will have
// been evaluated statically before this object was constructed.
return ((MethodInterceptor) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice).invoke(this);
}
}
3. spring-aop 基类
我们从第二小节着手相关的基类
3.1 代理类创建过程中的基类
3.1.1 ProxyConfig:代理配置类
维护了各种配置(可以多个该对象用于维护全局、局部的代理配置)
package org.springframework.aop.framework;
public class ProxyConfig implements Serializable {
private boolean proxyTargetClass = false;
private boolean optimize = false;
boolean opaque = false;
boolean exposeProxy = false;
private boolean frozen = false;
}
3.1.2 ProxyProcessorSupport:在ProxyConfig的基础上中扩展接入ioc的能力
继承自ProxyConfig,内部可以维护代理配置
实现BeanClassLoaderAware,在初始化的时候将自动注入classloader
package org.springframework.aop.framework;
public class ProxyProcessorSupport extends ProxyConfig implements Ordered, BeanClassLoaderAware, AopInfrastructureBean {
private int order = Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE;
@Nullable
private ClassLoader proxyClassLoader = ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader();
private boolean classLoaderConfigured = false;
}
3.1.3 AdvisedSupport:在ProxyConfig的基础上扩展拦截链的维护能力
其实内部还有很多对advisors的一系列集合API
package org.springframework.aop.framework;
public class AdvisedSupport extends ProxyConfig implements Advised {
/** The AdvisorChainFactory to use. */
AdvisorChainFactory advisorChainFactory = new DefaultAdvisorChainFactory();
/** Cache with Method as key and advisor chain List as value. */
private transient Map<MethodCacheKey, List<Object>> methodCache;
private List<Class<?>> interfaces = new ArrayList<>();
private List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList<>();
private Advisor[] advisorArray = new Advisor[0];
}
3.1.4 ProxyCreatorSupport:在AdvisedSupport的基础上扩展代理对象的创建能力
需要注意:该能力不需要依赖ioc,只要手动注入的配置到位,即可创建代理对象的包装类型(AopProxy)
package org.springframework.aop.framework;
public class ProxyCreatorSupport extends AdvisedSupport {
// AopProxy的工厂类(见3.1.7)
private AopProxyFactory aopProxyFactory;
// 调用内部的AopProxyFactory的AopProxy创建方法
protected final synchronized AopProxy createAopProxy() {...}
}
3.1.5 ProxyFactory:继承ProxyCreatorSupport并调用AopProxy的代理类获取方法
其实就做一件事:链式的调用AopProxy创建、代理类获取
package org.springframework.aop.framework;
public class ProxyFactory extends ProxyCreatorSupport {
// 调用ProxyCreatorSupport的AopProxy创建方法,并调用返回的AopProxy的代理类获取方法
public Object getProxy() {...}
}
3.1.6 AbstractAutoProxyCreator:将ProxyProcessorSupport与ProxyFactory结合
可以猜到这样结合带来的结果:
- ProxyFactory 提供了 代理类获取 的能力
- ProxyProcessorSupport 提供了接入ioc容器来获取相关配置并自动注入到ProxyFactory,这使得代理过程变得"自动"起来
package org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy;
public abstract class AbstractAutoProxyCreator extends ProxyProcessorSupport
implements SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor, BeanFactoryAware {
// 创建ProxyFactory并注入Advisors,并调用其getProxy方法返回代理类
protected Object createProxy(Class<?> beanClass, @Nullable String beanName,
@Nullable Object[] specificInterceptors, TargetSource targetSource) {
...
// 这里发生ProxyFactory的new、set的调用
...
}
}
3.1.7 AopProxyFactory:返回 Aop 代理类的工厂
package org.springframework.aop.framework;
public interface AopProxyFactory {
// 创建出一个AopProxy
AopProxy createAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException;
}
/*-------------------常见实现类------------------------*/
package org.springframework.aop.framework;
public class DefaultAopProxyFactory implements AopProxyFactory, Serializable {
// new Jdk、cglib的AopProxy的实现类并返回
public AopProxy createAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException {...}
}
3.1.8 AopProxy:代理类创建、缓存、返回的统一接口
- 由JDK、cglib各自实现
- 这底层不再是spring-aop的封装了,而是各自包下的组件类
package org.springframework.aop.framework;
public interface AopProxy {
Object getProxy();
Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader);
}
/* --------------- Jdk ------------- */
package org.springframework.aop.framework;
final class JdkDynamicAopProxy implements AopProxy, InvocationHandler, Serializable {
/** Config used to configure this proxy. */
private final AdvisedSupport advised;
public Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
...
Class<?>[] proxiedInterfaces = AopProxyUtils.completeProxiedInterfaces(this.advised, true);
...
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader, proxiedInterfaces, this);
}
}
/* -------------------cglib------------------------ /
package org.springframework.aop.framework;
class CglibAopProxy implements AopProxy, Serializable {
/** The configuration used to configure this proxy. */
protected final AdvisedSupport advised;
public Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
...
// Configure CGLIB Enhancer...
Enhancer enhancer = createEnhancer();
enhancer.setInterfaces(AopProxyUtils.completeProxiedInterfaces(this.advised));
// Generate the proxy class and create a proxy instance.
return createProxyClassAndInstance(enhancer, callbacks);
}
}
3.2 代理类的增强过程
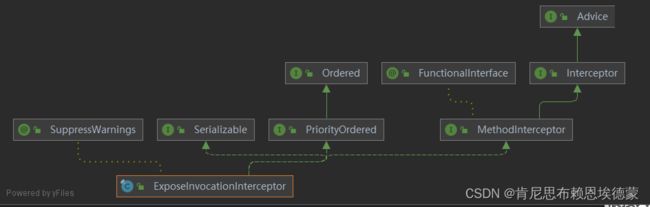
主要由两部分组成:被增强的方法 + 执行增强的拦截器(即用于增强方法的方法)
3.2.1 MethodInvocation:被增强的方法
// 这个很眼熟吧,也俗称AOP模型中的"连接点"
public interface Joinpoint {
// 调用被增强的方法
Object proceed() throws Throwable;
}
// 也是经常可以用到的方法,取得被增强方法的一些参数,常用于增强逻辑里做一些文章
public interface Invocation extends Joinpoint {
Object[] getArguments();
}
public interface MethodInvocation extends Invocation {
// 这个太熟悉,不说了:java.lang.reflect.Method
Method getMethod();
}
public interface ProxyMethodInvocation extends MethodInvocation {
// 返回代理类
Object getProxy();
}
3.3.2 MethodInterceptor:用于增强的拦截器
public interface Advice {}
// 所以源码里面会将interceptor、advice放在一个数组里面,其实两者同源
public interface Interceptor extends Advice {}
@FunctionalInterface
public interface MethodInterceptor extends Interceptor {
// 注意这里与MethodInvocation的耦合
Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable;
}
下面展示一部分常见的拦截器源码:
3.3.2.1 ExposeInvocationInterceptor
public final class ExposeInvocationInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor, PriorityOrdered, Serializable {
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
// 不解释了,前面已经有过说法了
MethodInvocation oldInvocation = invocation.get();
invocation.set(mi);
try {
// 调用被增强方法(如果存在其他的增强拦截器,这里会嵌套调用其他增强拦截器链)
return mi.proceed();
}
finally {
invocation.set(oldInvocation);
}
}
}
3.3.2.2 AspectJAroundAdvice
-
@Around 对应的Advice(增强拦截器)
-
顺带一提:很多@AspectJ的注解都是基于spring.aop的AbstractAspectJAdvice支持的
public class AspectJAroundAdvice extends AbstractAspectJAdvice implements MethodInterceptor, Serializable {
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
if (!(mi instanceof ProxyMethodInvocation)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("MethodInvocation is not a Spring ProxyMethodInvocation: " + mi);
}
ProxyMethodInvocation pmi = (ProxyMethodInvocation) mi;
ProceedingJoinPoint pjp = lazyGetProceedingJoinPoint(pmi);
JoinPointMatch jpm = getJoinPointMatch(pmi);
return invokeAdviceMethod(pjp, jpm, null, null);
}
}
3.3.2.3 CglibAopProxy.DynamicAdvisedInterceptor
-
为什么这个不算是MethodInterceptor,源码不是 private static class DynamicAdvisedInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor ???
-
为什么没有@Override invoke(),而是@Override interceptor() ???
org.springframework.cglib.proxy.MethodInterceptor,懂了吧
3.3.3 spring-aop开始组合两者
-
注意:这里还是spring-aop的代码——这里可以算是JDK、cglib最后的交集了
-
通过浏览代码可以发现是递归执行的,但是通过debug,我们知道每次递归的this不是一个对象了
这是因为切面的增强是嵌套调用的
// 前面都是一坨接口的单继承
// 这里开始是组合了
public class ReflectiveMethodInvocation implements ProxyMethodInvocation, Cloneable {
@Override
@Nullable
public Object proceed() throws Throwable {
// We start with an index of -1 and increment early.
if (this.currentInterceptorIndex == this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1) {
return invokeJoinpoint();
}
Object interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice =
this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.get(++this.currentInterceptorIndex);
if (interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice instanceof InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) {
// Evaluate dynamic method matcher here: static part will already have
// been evaluated and found to match.
InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher dm =
(InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice;
Class<?> targetClass = (this.targetClass != null ? this.targetClass : this.method.getDeclaringClass());
if (dm.methodMatcher.matches(this.method, targetClass, this.arguments)) {
return dm.interceptor.invoke(this);
}
else {
// Dynamic matching failed.
// Skip this interceptor and invoke the next in the chain.
return proceed();
}
}
else {
// 我来翻译一下:MethodInterceptor.invoke(MethodInvocation)
// It's an interceptor, so we just invoke it: The pointcut will have
// been evaluated statically before this object was constructed.
return ((MethodInterceptor) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice).invoke(this);
}
}
}