如何让你的allure报告测试步骤更清晰,更具吸引力?
引言
在软件测试中,清晰的测试步骤对于团队的协作和问题跟踪至关重要,Allure报告是一种强大的工具,能够将测试结果以直观和易于理解的方式呈现给您的团队和客户。
想要让Allure报告更具吸引力和可读性吗?那就不要错过我的精彩建议和技巧,让测试步骤在报告中更加清晰、有序,并为产品质量和用户体验增添亮点!
一、allure step测试用例步骤说明
allure step编写测试用例有两种方式
1、with allure.step()用在测试用例中
公共方法代码:
# common_fucntion.py
import allure
import pytest
from common.tools.log_util import Logger
runlog=Logger().get_log
'''
流程性的用例,添加测试步骤,让用例更清晰
用例步骤:1.登陆, 2.浏览商品 3.添加购物车 4.生成订单 5.支付成功
'''
def login(username, password):
'''登陆'''
# print("前置操作:先登陆")
allure.attach("username:{},password:{}".format(username,password),"前置操作:先登陆")
def open_goods():
'''浏览商品'''
# print("浏览商品")
allure.attach("这是浏览商品操作")
def add_shopping_cart(goods_id="10086"):
'''添加购物车'''
print("添加购物车")
# runlog.info("这是runlog.info打印出的信息")
# runlog.error("这是runlog.error打印出的信息")
def buy_goods():
'''生成订单'''
print("buy")
def pay_goods():
'''支付'''
print("pay")
用例代码:
import allure
import sys
from projects.demo_project.interface import common_function
@allure.story(u'with allure.step()')
def test_case003(self):
"""测试用例三
流程性的用例,添加测试步骤,让报告更清晰
用例步骤:1.登录 2.浏览商品 3:添加购物车 4.生成订单 5.支付成功
"""
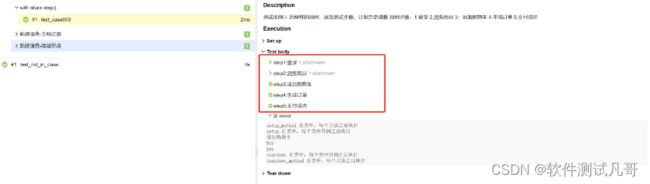
with allure.step("step1:登录"):
common_function.login("zhangsan", "12345")
with allure.step("step2:浏览商品"):
common_function.open_goods()
with allure.step("step3:添加购物车"):
common_function.add_shopping_cart()
with allure.step("step4:生成订单"):
common_function.buy_goods()
with allure.step("step5:支付成功"):
common_function.pay_goods()
测试报告:
2、@allure.step()用装饰器的方式修饰在测试步骤的函数上面
公共方法代码:
# common_fucntion.py
import allure
import pytest
'''
流程性的用例,添加测试步骤,让用例更清晰
用例步骤:1.登陆, 2.浏览商品 3.添加购物车 4.生成订单 5.支付成功
'''
@allure.step("step:登录")
def login(username, password):
'''登陆'''
print("前置操作:先登陆")
@allure.step("step:浏览商品")
def open_goods():
'''浏览商品'''
print("浏览商品")
@allure.step("step:添加购物车")
def add_shopping_cart(goods_id="10086"):
'''添加购物车'''
print("添加购物车")
@allure.step("step:生成订单")
def buy_goods():
'''生成订单'''
print("buy")
@allure.step#("step:支付")
def pay_goods():
'''支付'''
print("pay")
测试用例代码:
from projects.demo_project.interface import common_function_allure_step
@allure.story(u'@allure.step()')
def test_case004(self):
"""测试用例三
流程性的用例,添加测试步骤,让报告更清晰
用例步骤:1.登录 2.浏览商品 3:添加购物车 4.生成订单 5.支付成功
"""
common_function_allure_step.login("zhangsan", "12345")
common_function_allure_step.open_goods()
common_function_allure_step.add_shopping_cart()
common_function_allure_step.buy_goods()
common_function_allure_step.pay_goods()
报告效果图:
allure.step这两种用法,要结合实际编写测试用例中的场景,看哪种方式更适合,也可以结合着使用。
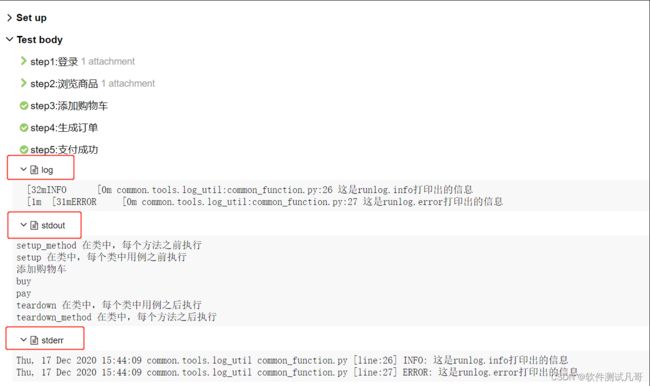
但allure.step也并不是完美的,当报告中想在步骤中显示参数、预期结果,实际结果,或者截图,文件等内容时,用print或logging来输出。看一下下面截图效果
print的信息显示在了stdout中,logging.info信息显示在log中,当有logging.error时,又出现了stderr。显然很乱,也没有在对应的测试步骤中显示。为了解决这个问题,研究了allure.attach()这个方法,可以解决。
二、allure.attach():补充说明测试结果
用法1: allure.attach(body, name, attachment_type, extension)
参数说明:
body:要显示的内容或附件
name:附件名字
attachment_type:附件类型
extension:附件扩展名
attachment_type提供的附件类型:
样例:
实现
def login(username, password):
'''登陆'''
# print("前置操作:先登陆")
allure.attach("username:{},password:{}".format(username,password),"前置操作:先登陆")
def open_goods():
'''浏览商品'''
# print("浏览商品")
allure.attach("这是内容:浏览商品操作","这是标题")
用法二:allure.attach.file(source, name, attachment_type, extension)
source:文件路径,相当于传一个文件
其他参数和上面一致
注:allure.attach() 和 allure.attach.file() 的区别:
allure.attach()表示自己写一个文件,allure.attach.file()从外部传一个文件
最后感谢每一个认真阅读我文章的人,看着粉丝一路的上涨和关注,礼尚往来总是要有的,虽然不是什么很值钱的东西,如果你用得到的话可以直接拿走:
些资料,对于【软件测试】的朋友来说应该是最全面最完整的备战仓库,这个仓库也陪伴上万个测试工程师们走过最艰难的路程,希望也能帮助到你!
在我的QQ技术交流群里(技术交流和资源共享,广告勿扰)