Linux 虚拟文件系统 VFS 源码剖析
转自:Linux 虚拟文件系统 VFS 源码剖析 -- 以 ext4 为例(Part1) - 知乎
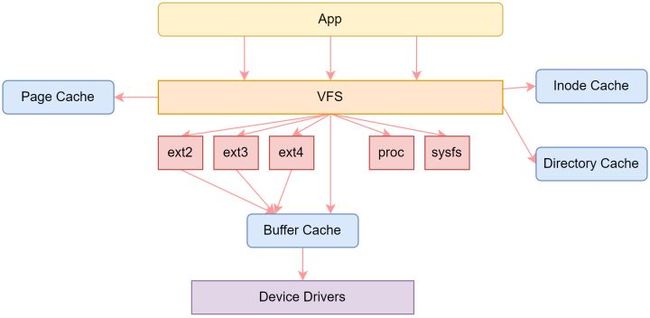
虚拟文件系统(Virtual File System, VFS)是 Linux 内核的一个组件,用于处理与文件和文件系统相关的所有系统调用。VFS 是内核提供文件系统接口给用户态应用程序通用接口层,同时也提供了抽象化操作接口,以便底层各种文件系统实现。
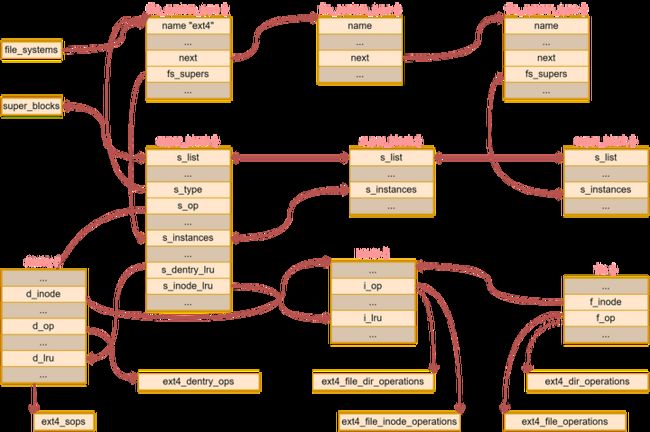
1、VFS 数据结构
VFS 涉及到的数据结构比较复杂,比较重要的是下面 5 个:
- file_system_type
- super_block
- dentry
- inode
- file
file_system_type 表示一种文件系统,比如 ext2、ext4 等。
而 super_block 代表具体某个已经挂载的文件系统,标识一个文件系统实例。每个物理的磁盘、硬盘都有一个文件控制块 FCB,super_block 相当于 FCB 的内存映像。
dentry 表示目录,VFS 将目录也当作文件,也有一个 inode,不过 dentry 的操作函数和普通文件操作函数不同。
inode 包含了内核在操作文件或目录时需要的全部信息。对于 UNIX 风格的文件系统,这些信息可以根据需要从磁盘索引结点直接读入或者写会磁盘。磁盘上的一个索引结点代表一个文件,内核中一个 inode 代表打开的一个文件。
file 是从进程角度表示一个打开的文件。
2、file_system_type
Linux 使用 file_system_type 表示一种文件系统,比如 ext2、ext4、exfat 等等。文件系统可以有多个实例,每个实例都使用 super_block 表征。
/// include/linux/fs.h
2230 struct file_system_type {
2231 const char *name;
2232 int fs_flags;
2233 #define FS_REQUIRES_DEV 1
2234 #define FS_BINARY_MOUNTDATA 2
2235 #define FS_HAS_SUBTYPE 4
2236 #define FS_USERNS_MOUNT 8 /* Can be mounted by userns root */
2237 #define FS_DISALLOW_NOTIFY_PERM 16 /* Disable fanotify permission events */
2238 #define FS_THP_SUPPORT 8192 /* Remove once all fs converted */
2239 #define FS_RENAME_DOES_D_MOVE 32768 /* FS will handle d_move() during rename() internally. */
2240 int (*init_fs_context)(struct fs_context *);
2241 const struct fs_parameter_spec *parameters;
2242 struct dentry *(*mount) (struct file_system_type *, int,
2243 const char *, void *);
2244 void (*kill_sb) (struct super_block *);
2245 struct module *owner;
2246 struct file_system_type * next;
2247 struct hlist_head fs_supers;
2248
2249 struct lock_class_key s_lock_key;
2250 struct lock_class_key s_umount_key;
2251 struct lock_class_key s_vfs_rename_key;
2252 struct lock_class_key s_writers_key[SB_FREEZE_LEVELS];
2253
2254 struct lock_class_key i_lock_key;
2255 struct lock_class_key i_mutex_key;
2256 struct lock_class_key i_mutex_dir_key;
2257 };- name 表示文件系统名字,比如 ext2、ext4;
- fs_flags 是一些 FS_ 标志位;
- init_fs_context/parameters 和 fs_context 有关系;
- mount 函数指针指向挂载文件系统实例的函数;
- kill_sb ==========
- next 指针用于将文件系统链接成链表;
- fs_supers 是链表头,用于链接文件系统的所有实例;
2.1、register_filesystem()/unregister_filesystem()
在挂载某个文件系统实例前,Linux 必须支持该文件系统。换句话说,需要将该文件系统注册到 Linux。向 Linux 注册文件系统是通过 register_filesystem() 函数。
Linux 使用链表管理注册的文件系统,所有的文件系统都被链接到一个链表上。Linux 中的文件系统链表没有头节点,全局变量 file_systems 指向该链表的第一个元素。
/// fs/filesystem.c
34 static struct file_system_type *file_systems;
35 static DEFINE_RWLOCK(file_systems_lock);Linux 不允许同一个文件系统重复注册。find_filesystem() 函数可以查找时候已经注册某个文件系统。find_filesystem() 函数返回的是指针的指针,如果存在,*p 指向该文件系统,否则 *p 为 NULL。find_filesystem() 函数的处理手法值得我们学习:如何将查找和插入结合,在查找失败时,可以利用查找结果直接插入元素。
/// fs/filesystem.c
49 static struct file_system_type **find_filesystem(const char *name, unsigned len)
50 {
51 struct file_system_type **p;
52 for (p = &file_systems; *p; p = &(*p)->next)
53 if (strncmp((*p)->name, name, len) == 0 &&
54 !(*p)->name[len])
55 break;
56 return p;
57 }register_filesystem() 函数将一个文件系统注册到全局链表 file_systems 上,如果已经存在,则返回 -EBUSY,表示注册失败。其主要逻辑时调用 find_filesystem() 函数查找链表中是否已经存在待注册文件系统,不存在时才将待注册文件系统添加到链表中。
/// fs/filesystem.c
72 int register_filesystem(struct file_system_type * fs)
73 {
74 int res = 0;
75 struct file_system_type ** p;
76
77 if (fs->parameters &&
78 !fs_validate_description(fs->name, fs->parameters))
79 return -EINVAL;
80
81 BUG_ON(strchr(fs->name, '.'));
82 if (fs->next)
83 return -EBUSY;
84 write_lock(&file_systems_lock);
85 p = find_filesystem(fs->name, strlen(fs->name));
86 if (*p)
87 res = -EBUSY;
88 else
89 *p = fs;
90 write_unlock(&file_systems_lock);
91 return res;
92 }unregister_filesystem() 函数是从全局链表 file_systems 中删除某个文件系统。
/// fs/filesystem.c
108 int unregister_filesystem(struct file_system_type * fs)
109 {
110 struct file_system_type ** tmp;
111
112 write_lock(&file_systems_lock);
113 tmp = &file_systems;
114 while (*tmp) {
115 if (fs == *tmp) {
116 *tmp = fs->next;
117 fs->next = NULL;
118 write_unlock(&file_systems_lock);
119 synchronize_rcu();
120 return 0;
121 }
122 tmp = &(*tmp)->next;
123 }
124 write_unlock(&file_systems_lock);
125
126 return -EINVAL;
127 }2.2、get_fs_type()
get_fs_type() 函数根据名字 name 查找是否注册了某个文件系统,如果注册了就返回指向对应 file_system_type 的指针。
/// fs/filesystem.c
254 static struct file_system_type *__get_fs_type(const char *name, int len)
255 {
256 struct file_system_type *fs;
257
258 read_lock(&file_systems_lock);
259 fs = *(find_filesystem(name, len));
260 if (fs && !try_module_get(fs->owner))
261 fs = NULL;
262 read_unlock(&file_systems_lock);
263 return fs;
264 }
265
266 struct file_system_type *get_fs_type(const char *name)
267 {
268 struct file_system_type *fs;
269 const char *dot = strchr(name, '.');
270 int len = dot ? dot - name : strlen(name);
271
272 fs = __get_fs_type(name, len);
273 if (!fs && (request_module("fs-%.*s", len, name) == 0)) {
274 fs = __get_fs_type(name, len);
275 if (!fs)
276 pr_warn_once("request_module fs-%.*s succeeded, but still no fs?\n",
277 len, name);
278 }
279
280 if (dot && fs && !(fs->fs_flags & FS_HAS_SUBTYPE)) {
281 put_filesystem(fs);
282 fs = NULL;
283 }
284 return fs;
285 }2.3、ext4_fs_type
ext4 在 module 初始化时调用 register_filesystem() 函数将 ext4_fs_type 注册到 Linux 系统中。ext4_fs_type 定义如下。mount 和 kill_sb 函数指针分别指向 ext4_mount() 和 kill_block_super() 两个函数。
/// fs/ext4/super.c
6681 static struct file_system_type ext4_fs_type = {
6682 .owner = THIS_MODULE,
6683 .name = "ext4",
6684 .mount = ext4_mount,
6685 .kill_sb = kill_block_super,
6686 .fs_flags = FS_REQUIRES_DEV,
6687 };ext4_mount() 函数直接调用 mount_bdev() 函数。
/// fs/ext4/super.c
6619 static struct dentry *ext4_mount(struct file_system_type *fs_type, int flags,
6620 const char *dev_name, void *data)
6621 {
6622 return mount_bdev(fs_type, flags, dev_name, data, ext4_fill_super);
6623 }mount_bdev() 和 kill_block_super() 两个函数都不是 ext4 专有函数,都是通用函数。
3、super_block
super_block 代表一个具体某个已经挂载的文件系统,标识一个文件系统实例的信息,比如:
- 依附的物理硬件
- 索引结点 inode 和数据块 block 的位置
- block 的大小(字节)
- 文件系统类型
- 最长文件名
- 最大文件大小
- 根目录的 inode 位置
- 支持的操作
3.1、super_operations
super_operations 中定义了超级块支持的操作,是一组函数指针,指向比如 inode 分配、销毁与释放,以及将 inode 数据写回磁盘等函数。
/// include/linux/fs.h
1935 struct super_operations {
1936 struct inode *(*alloc_inode)(struct super_block *sb);
1937 void (*destroy_inode)(struct inode *);
1938 void (*free_inode)(struct inode *);
1939
1940 void (*dirty_inode) (struct inode *, int flags);
1941 int (*write_inode) (struct inode *, struct writeback_control *wbc);
1942 int (*drop_inode) (struct inode *);
1943 void (*evict_inode) (struct inode *);
1944 void (*put_super) (struct super_block *);
1945 int (*sync_fs)(struct super_block *sb, int wait);
1946 int (*freeze_super) (struct super_block *);
1947 int (*freeze_fs) (struct super_block *);
1948 int (*thaw_super) (struct super_block *);
1949 int (*unfreeze_fs) (struct super_block *);
1950 int (*statfs) (struct dentry *, struct kstatfs *);
1951 int (*remount_fs) (struct super_block *, int *, char *);
1952 void (*umount_begin) (struct super_block *);
1953
1954 int (*show_options)(struct seq_file *, struct dentry *);
1955 int (*show_devname)(struct seq_file *, struct dentry *);
1956 int (*show_path)(struct seq_file *, struct dentry *);
1957 int (*show_stats)(struct seq_file *, struct dentry *);
1958 #ifdef CONFIG_QUOTA
1959 ssize_t (*quota_read)(struct super_block *, int, char *, size_t, loff_t);
1960 ssize_t (*quota_write)(struct super_block *, int, const char *, size_t, loff_t);
1961 struct dquot **(*get_dquots)(struct inode *);
1962 #endif
1963 int (*bdev_try_to_free_page)(struct super_block*, struct page*, gfp_t);
1964 long (*nr_cached_objects)(struct super_block *,
1965 struct shrink_control *);
1966 long (*free_cached_objects)(struct super_block *,
1967 struct shrink_control *);
1968 };3.2、super_block
/// include/linux/fs.h
1416 struct super_block {
1417 struct list_head s_list; /* Keep this first */
1418 dev_t s_dev; /* search index; _not_ kdev_t */
1419 unsigned char s_blocksize_bits;
1420 unsigned long s_blocksize; /* 块大小 */
1421 loff_t s_maxbytes; /* Max file size */
1422 struct file_system_type *s_type;
1423 const struct super_operations *s_op;
1424 const struct dquot_operations *dq_op;
1425 const struct quotactl_ops *s_qcop;
1426 const struct export_operations *s_export_op;
1427 unsigned long s_flags;
1428 unsigned long s_iflags; /* internal SB_I_* flags */
1429 unsigned long s_magic;
1430 struct dentry *s_root; /* 挂载点 */
1431 struct rw_semaphore s_umount;
1432 int s_count; /* 引用计数 */
1433 atomic_t s_active;
1434 #ifdef CONFIG_SECURITY
1435 void *s_security;
1436 #endif
1437 const struct xattr_handler **s_xattr;
1438 #ifdef CONFIG_FS_ENCRYPTION
1439 const struct fscrypt_operations *s_cop;
1440 struct key *s_master_keys; /* master crypto keys in use */
1441 #endif
1442 #ifdef CONFIG_FS_VERITY
1443 const struct fsverity_operations *s_vop;
1444 #endif
1445 #ifdef CONFIG_UNICODE
1446 struct unicode_map *s_encoding;
1447 __u16 s_encoding_flags;
1448 #endif
1449 struct hlist_bl_head s_roots; /* alternate root dentries for NFS */
1450 struct list_head s_mounts; /* list of mounts; _not_ for fs use */
1451 struct block_device *s_bdev;
1452 struct backing_dev_info *s_bdi;
1453 struct mtd_info *s_mtd;
1454 struct hlist_node s_instances;
1455 unsigned int s_quota_types; /* Bitmask of supported quota types */
1456 struct quota_info s_dquot; /* Diskquota specific options */
1457
1458 struct sb_writers s_writers;
1459
1460 /*
1461 * Keep s_fs_info, s_time_gran, s_fsnotify_mask, and
1462 * s_fsnotify_marks together for cache efficiency. They are frequently
1463 * accessed and rarely modified.
1464 */
1465 void *s_fs_info; /* Filesystem private info */
1466
1467 /* Granularity of c/m/atime in ns (cannot be worse than a second) */
1468 u32 s_time_gran;
1469 /* Time limits for c/m/atime in seconds */
1470 time64_t s_time_min;
1471 time64_t s_time_max;
1472 #ifdef CONFIG_FSNOTIFY
1473 __u32 s_fsnotify_mask;
1474 struct fsnotify_mark_connector __rcu *s_fsnotify_marks;
1475 #endif
1476
1477 char s_id[32]; /* Informational name */
1478 uuid_t s_uuid; /* UUID */
1479
1480 unsigned int s_max_links;
1481 fmode_t s_mode;
1482
1483 /*
1484 * The next field is for VFS *only*. No filesystems have any business
1485 * even looking at it. You had been warned.
1486 */
1487 struct mutex s_vfs_rename_mutex; /* Kludge */
1488
1489 /*
1490 * Filesystem subtype. If non-empty the filesystem type field
1491 * in /proc/mounts will be "type.subtype"
1492 */
1493 const char *s_subtype;
1494
1495 const struct dentry_operations *s_d_op; /* default d_op for dentries */
1496
1497 /*
1498 * Saved pool identifier for cleancache (-1 means none)
1499 */
1500 int cleancache_poolid;
1501
1502 struct shrinker s_shrink; /* per-sb shrinker handle */
1503
1504 /* Number of inodes with nlink == 0 but still referenced */
1505 atomic_long_t s_remove_count;
1506
1507 /* Pending fsnotify inode refs */
1508 atomic_long_t s_fsnotify_inode_refs;
1509
1510 /* Being remounted read-only */
1511 int s_readonly_remount;
1512
1513 /* per-sb errseq_t for reporting writeback errors via syncfs */
1514 errseq_t s_wb_err;
1515
1516 /* AIO completions deferred from interrupt context */
1517 struct workqueue_struct *s_dio_done_wq;
1518 struct hlist_head s_pins;
1519
1520 /*
1521 * Owning user namespace and default context in which to
1522 * interpret filesystem uids, gids, quotas, device nodes,
1523 * xattrs and security labels.
1524 */
1525 struct user_namespace *s_user_ns;
1526
1527 /*
1528 * The list_lru structure is essentially just a pointer to a table
1529 * of per-node lru lists, each of which has its own spinlock.
1530 * There is no need to put them into separate cachelines.
1531 */
1532 struct list_lru s_dentry_lru;
1533 struct list_lru s_inode_lru;
1534 struct rcu_head rcu;
1535 struct work_struct destroy_work;
1536
1537 struct mutex s_sync_lock; /* sync serialisation lock */
1538
1539 /*
1540 * Indicates how deep in a filesystem stack this SB is
1541 */
1542 int s_stack_depth;
1543
1544 /* s_inode_list_lock protects s_inodes */
1545 spinlock_t s_inode_list_lock ____cacheline_aligned_in_smp;
1546 struct list_head s_inodes; /* all inodes */
1547
1548 spinlock_t s_inode_wblist_lock;
1549 struct list_head s_inodes_wb; /* writeback inodes */
1550 } __randomize_layout;Linux 中挂载的 super_block 除了链接到对应的 file_system_type::fs_supers 链表上,还将其链接到全局链表 super_blocks 中。
/// fs/super.c
45 static LIST_HEAD(super_blocks);
46 static DEFINE_SPINLOCK(sb_lock);3.4、ext4_sops
/// fs/ext4/super.c
1664 static const struct super_operations ext4_sops = {
1665 .alloc_inode = ext4_alloc_inode,
1666 .free_inode = ext4_free_in_core_inode,
1667 .destroy_inode = ext4_destroy_inode,
1668 .write_inode = ext4_write_inode,
1669 .dirty_inode = ext4_dirty_inode,
1670 .drop_inode = ext4_drop_inode,
1671 .evict_inode = ext4_evict_inode,
1672 .put_super = ext4_put_super,
1673 .sync_fs = ext4_sync_fs,
1674 .freeze_fs = ext4_freeze,
1675 .unfreeze_fs = ext4_unfreeze,
1676 .statfs = ext4_statfs,
1677 .remount_fs = ext4_remount,
1678 .show_options = ext4_show_options,
1679 #ifdef CONFIG_QUOTA
1680 .quota_read = ext4_quota_read,
1681 .quota_write = ext4_quota_write,
1682 .get_dquots = ext4_get_dquots,
1683 #endif
1684 .bdev_try_to_free_page = bdev_try_to_free_page,
1685 };4、inode
索引结点 inode 包含了内核在操作文件或目录时(目录也被当作文件看待)需要的全部信息。对于 UNIX 风格的文件系统,这些信息可以根据需要从磁盘索引结点直接读入或者写会磁盘。磁盘上的一个索引结点代表一个文件,内核中一个 inode 代表打开的一个文件。
- 文件类型
- 文件大小
- 访问权限
- 访问或修改时间
- 文件位置(指向磁盘数据块)
4.1、inode_operations
/// include/linux/fs.h
1864 struct inode_operations {
1865 struct dentry * (*lookup) (struct inode *,struct dentry *, unsigned int);
1866 const char * (*get_link) (struct dentry *, struct inode *, struct delayed_call *);
1867 int (*permission) (struct inode *, int);
1868 struct posix_acl * (*get_acl)(struct inode *, int);
1869
1870 int (*readlink) (struct dentry *, char __user *,int);
1871
1872 int (*create) (struct inode *,struct dentry *, umode_t, bool);
1873 int (*link) (struct dentry *,struct inode *,struct dentry *);
1874 int (*unlink) (struct inode *,struct dentry *);
1875 int (*symlink) (struct inode *,struct dentry *,const char *);
1876 int (*mkdir) (struct inode *,struct dentry *,umode_t);
1877 int (*rmdir) (struct inode *,struct dentry *);
1878 int (*mknod) (struct inode *,struct dentry *,umode_t,dev_t);
1879 int (*rename) (struct inode *, struct dentry *,
1880 struct inode *, struct dentry *, unsigned int);
1881 int (*setattr) (struct dentry *, struct iattr *);
1882 int (*getattr) (const struct path *, struct kstat *, u32, unsigned int);
1883 ssize_t (*listxattr) (struct dentry *, char *, size_t);
1884 int (*fiemap)(struct inode *, struct fiemap_extent_info *, u64 start,
1885 u64 len);
1886 int (*update_time)(struct inode *, struct timespec64 *, int);
1887 int (*atomic_open)(struct inode *, struct dentry *,
1888 struct file *, unsigned open_flag,
1889 umode_t create_mode);
1890 int (*tmpfile) (struct inode *, struct dentry *, umode_t);
1891 int (*set_acl)(struct inode *, struct posix_acl *, int);
1892 } ____cacheline_aligned;4.2、inode
文件和目录都有一个 inode,但是 i_op 指向的 inode_operations 实现却是不同。
605 /*
606 * Keep mostly read-only and often accessed (especially for
607 * the RCU path lookup and 'stat' data) fields at the beginning
608 * of the 'struct inode'
609 */
610 struct inode {
611 umode_t i_mode;
612 unsigned short i_opflags;
613 kuid_t i_uid;
614 kgid_t i_gid;
615 unsigned int i_flags;
616
617 #ifdef CONFIG_FS_POSIX_ACL
618 struct posix_acl *i_acl;
619 struct posix_acl *i_default_acl;
620 #endif
621
622 const struct inode_operations *i_op;
623 struct super_block *i_sb;
624 struct address_space *i_mapping;
625
626 #ifdef CONFIG_SECURITY
627 void *i_security;
628 #endif
629
630 /* Stat data, not accessed from path walking */
631 unsigned long i_ino;
632 /*
633 * Filesystems may only read i_nlink directly. They shall use the
634 * following functions for modification:
635 *
636 * (set|clear|inc|drop)_nlink
637 * inode_(inc|dec)_link_count
638 */
639 union {
640 const unsigned int i_nlink;
641 unsigned int __i_nlink;
642 };
643 dev_t i_rdev;
644 loff_t i_size;
645 struct timespec64 i_atime;
646 struct timespec64 i_mtime;
647 struct timespec64 i_ctime;
648 spinlock_t i_lock; /* i_blocks, i_bytes, maybe i_size */
649 unsigned short i_bytes;
650 u8 i_blkbits;
651 u8 i_write_hint;
652 blkcnt_t i_blocks;
653
654 #ifdef __NEED_I_SIZE_ORDERED
655 seqcount_t i_size_seqcount;
656 #endif
657
658 /* Misc */
659 unsigned long i_state;
660 struct rw_semaphore i_rwsem;
661
662 unsigned long dirtied_when; /* jiffies of first dirtying */
663 unsigned long dirtied_time_when;
664
665 struct hlist_node i_hash;
666 struct list_head i_io_list; /* backing dev IO list */
667 #ifdef CONFIG_CGROUP_WRITEBACK
668 struct bdi_writeback *i_wb; /* the associated cgroup wb */
669
670 /* foreign inode detection, see wbc_detach_inode() */
671 int i_wb_frn_winner;
672 u16 i_wb_frn_avg_time;
673 u16 i_wb_frn_history;
674 #endif
675 struct list_head i_lru; /* inode LRU list */
676 struct list_head i_sb_list;
677 struct list_head i_wb_list; /* backing dev writeback list */
678 union {
679 struct hlist_head i_dentry;
680 struct rcu_head i_rcu;
681 };
682 atomic64_t i_version;
683 atomic64_t i_sequence; /* see futex */
684 atomic_t i_count;
685 atomic_t i_dio_count;
686 atomic_t i_writecount;
687 #if defined(CONFIG_IMA) || defined(CONFIG_FILE_LOCKING)
688 atomic_t i_readcount; /* struct files open RO */
689 #endif
690 union {
691 const struct file_operations *i_fop; /* former ->i_op->default_file_ops */
692 void (*free_inode)(struct inode *);
693 };
694 struct file_lock_context *i_flctx;
695 struct address_space i_data;
696 struct list_head i_devices;
697 union {
698 struct pipe_inode_info *i_pipe;
699 struct block_device *i_bdev;
700 struct cdev *i_cdev;
701 char *i_link;
702 unsigned i_dir_seq;
703 };
704
705 __u32 i_generation;
706
707 #ifdef CONFIG_FSNOTIFY
708 __u32 i_fsnotify_mask; /* all events this inode cares about */
709 struct fsnotify_mark_connector __rcu *i_fsnotify_marks;
710 #endif
711
712 #ifdef CONFIG_FS_ENCRYPTION
713 struct fscrypt_info *i_crypt_info;
714 #endif
715
716 #ifdef CONFIG_FS_VERITY
717 struct fsverity_info *i_verity_info;
718 #endif
719
720 void *i_private; /* fs or device private pointer */
721 } __randomize_layout;4.3、ext4_file_inode_operations
/// fs/ext4/file.c
930 const struct inode_operations ext4_file_inode_operations = {
931 .setattr = ext4_setattr,
932 .getattr = ext4_file_getattr,
933 .listxattr = ext4_listxattr,
934 .get_acl = ext4_get_acl,
935 .set_acl = ext4_set_acl,
936 .fiemap = ext4_fiemap,
937 };4.4、ext4_dir_inode_operations
/// fs/ext4/namei.c
4194 /*
4195 * directories can handle most operations...
4196 */
4197 const struct inode_operations ext4_dir_inode_operations = {
4198 .create = ext4_create,
4199 .lookup = ext4_lookup,
4200 .link = ext4_link,
4201 .unlink = ext4_unlink,
4202 .symlink = ext4_symlink,
4203 .mkdir = ext4_mkdir,
4204 .rmdir = ext4_rmdir,
4205 .mknod = ext4_mknod,
4206 .tmpfile = ext4_tmpfile,
4207 .rename = ext4_rename2,
4208 .setattr = ext4_setattr,
4209 .getattr = ext4_getattr,
4210 .listxattr = ext4_listxattr,
4211 .get_acl = ext4_get_acl,
4212 .set_acl = ext4_set_acl,
4213 .fiemap = ext4_fiemap,
4214 };4.5、ext4_special_inode_operations
/// fs/ext4/namei.c
4216 const struct inode_operations ext4_special_inode_operations = {
4217 .setattr = ext4_setattr,
4218 .getattr = ext4_getattr,
4219 .listxattr = ext4_listxattr,
4220 .get_acl = ext4_get_acl,
4221 .set_acl = ext4_set_acl,
4222 };5、dentry
dentry 表示一个目录,Linux 系统将目录也当作一个文件,文件内容是文件名或者目录名。
5.1、dentry_operations
/// include/linux/dcache.h
135 struct dentry_operations {
136 int (*d_revalidate)(struct dentry *, unsigned int);
137 int (*d_weak_revalidate)(struct dentry *, unsigned int);
138 int (*d_hash)(const struct dentry *, struct qstr *);
139 int (*d_compare)(const struct dentry *,
140 unsigned int, const char *, const struct qstr *);
141 int (*d_delete)(const struct dentry *);
142 int (*d_init)(struct dentry *);
143 void (*d_release)(struct dentry *);
144 void (*d_prune)(struct dentry *);
145 void (*d_iput)(struct dentry *, struct inode *);
146 char *(*d_dname)(struct dentry *, char *, int);
147 struct vfsmount *(*d_automount)(struct path *);
148 int (*d_manage)(const struct path *, bool);
149 struct dentry *(*d_real)(struct dentry *, const struct inode *);
150 } ____cacheline_aligned;5.2、dentry
/// include/linux/dcache.h
89 struct dentry {
90 /* RCU lookup touched fields */
91 unsigned int d_flags; /* protected by d_lock */
92 seqcount_spinlock_t d_seq; /* per dentry seqlock */
93 struct hlist_bl_node d_hash; /* lookup hash list */
94 struct dentry *d_parent; /* parent directory */
95 struct qstr d_name;
96 struct inode *d_inode; /* Where the name belongs to - NULL is
97 * negative */
98 unsigned char d_iname[DNAME_INLINE_LEN]; /* small names */
99
100 /* Ref lookup also touches following */
101 struct lockref d_lockref; /* per-dentry lock and refcount */
102 const struct dentry_operations *d_op;
103 struct super_block *d_sb; /* The root of the dentry tree */
104 unsigned long d_time; /* used by d_revalidate */
105 void *d_fsdata; /* fs-specific data */
106
107 union {
108 struct list_head d_lru; /* LRU list */
109 wait_queue_head_t *d_wait; /* in-lookup ones only */
110 };
111 struct list_head d_child; /* child of parent list */
112 struct list_head d_subdirs; /* our children */
113 /*
114 * d_alias and d_rcu can share memory
115 */
116 union {
117 struct hlist_node d_alias; /* inode alias list */
118 struct hlist_bl_node d_in_lookup_hash; /* only for in-lookup ones */
119 struct rcu_head d_rcu;
120 } d_u;
121 } __randomize_layout;5.3、ext4_dentry_ops
/// fs/ext4/dir.c
671 #ifdef CONFIG_UNICODE
672 const struct dentry_operations ext4_dentry_ops = {
673 .d_hash = generic_ci_d_hash,
674 .d_compare = generic_ci_d_compare,
675 };
676 #endif6、file
从进程的角度,标识打开的文件。主要维持如下信息
- 文件读写的标记的位置
- 打开文件的权限
- 指向 inode 的指针
6.1、file_operations
/// include/linux/fs.h
1822 struct file_operations {
1823 struct module *owner;
1824 loff_t (*llseek) (struct file *, loff_t, int);
1825 ssize_t (*read) (struct file *, char __user *, size_t, loff_t *);
1826 ssize_t (*write) (struct file *, const char __user *, size_t, loff_t *);
1827 ssize_t (*read_iter) (struct kiocb *, struct iov_iter *);
1828 ssize_t (*write_iter) (struct kiocb *, struct iov_iter *);
1829 int (*iopoll)(struct kiocb *kiocb, bool spin);
1830 int (*iterate) (struct file *, struct dir_context *);
1831 int (*iterate_shared) (struct file *, struct dir_context *);
1832 __poll_t (*poll) (struct file *, struct poll_table_struct *);
1833 long (*unlocked_ioctl) (struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long);
1834 long (*compat_ioctl) (struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long);
1835 int (*mmap) (struct file *, struct vm_area_struct *);
1836 unsigned long mmap_supported_flags;
1837 int (*open) (struct inode *, struct file *);
1838 int (*flush) (struct file *, fl_owner_t id);
1839 int (*release) (struct inode *, struct file *);
1840 int (*fsync) (struct file *, loff_t, loff_t, int datasync);
1841 int (*fasync) (int, struct file *, int);
1842 int (*lock) (struct file *, int, struct file_lock *);
1843 ssize_t (*sendpage) (struct file *, struct page *, int, size_t, loff_t *, int);
1844 unsigned long (*get_unmapped_area)(struct file *, unsigned long, unsigned long, unsigned long, unsigned long);
1845 int (*check_flags)(int);
1846 int (*flock) (struct file *, int, struct file_lock *);
1847 ssize_t (*splice_write)(struct pipe_inode_info *, struct file *, loff_t *, size_t, unsigned int);
1848 ssize_t (*splice_read)(struct file *, loff_t *, struct pipe_inode_info *, size_t, unsigned int);
1849 int (*setlease)(struct file *, long, struct file_lock **, void **);
1850 long (*fallocate)(struct file *file, int mode, loff_t offset,
1851 loff_t len);
1852 void (*show_fdinfo)(struct seq_file *m, struct file *f);
1853 #ifndef CONFIG_MMU
1854 unsigned (*mmap_capabilities)(struct file *);
1855 #endif
1856 ssize_t (*copy_file_range)(struct file *, loff_t, struct file *,
1857 loff_t, size_t, unsigned int);
1858 loff_t (*remap_file_range)(struct file *file_in, loff_t pos_in,
1859 struct file *file_out, loff_t pos_out,
1860 loff_t len, unsigned int remap_flags);
1861 int (*fadvise)(struct file *, loff_t, loff_t, int);
1862 } __randomize_layout;5.2、file
/// include/linux/fs.h
916 struct file {
917 union {
918 struct llist_node fu_llist;
919 struct rcu_head fu_rcuhead;
920 } f_u;
921 struct path f_path;
922 struct inode *f_inode; /* cached value */
923 const struct file_operations *f_op;
924
925 /*
926 * Protects f_ep_links, f_flags.
927 * Must not be taken from IRQ context.
928 */
929 spinlock_t f_lock;
930 enum rw_hint f_write_hint;
931 atomic_long_t f_count;
932 unsigned int f_flags;
933 fmode_t f_mode;
934 struct mutex f_pos_lock;
935 loff_t f_pos;
936 struct fown_struct f_owner;
937 const struct cred *f_cred;
938 struct file_ra_state f_ra;
939
940 u64 f_version;
941 #ifdef CONFIG_SECURITY
942 void *f_security;
943 #endif
944 /* needed for tty driver, and maybe others */
945 void *private_data;
946
947 #ifdef CONFIG_EPOLL
948 /* Used by fs/eventpoll.c to link all the hooks to this file */
949 struct list_head f_ep_links;
950 struct list_head f_tfile_llink;
951 #endif /* #ifdef CONFIG_EPOLL */
952 struct address_space *f_mapping;
953 errseq_t f_wb_err;
954 errseq_t f_sb_err; /* for syncfs */
955 } __randomize_layout
956 __attribute__((aligned(4))); /* lest something weird decides that 2 is OK */6.3、ext4_file_operations
/// fs/ext4/file.c
910 const struct file_operations ext4_file_operations = {
911 .llseek = ext4_llseek,
912 .read_iter = ext4_file_read_iter,
913 .write_iter = ext4_file_write_iter,
914 .iopoll = iomap_dio_iopoll,
915 .unlocked_ioctl = ext4_ioctl,
916 #ifdef CONFIG_COMPAT
917 .compat_ioctl = ext4_compat_ioctl,
918 #endif
919 .mmap = ext4_file_mmap,
920 .mmap_supported_flags = MAP_SYNC,
921 .open = ext4_file_open,
922 .release = ext4_release_file,
923 .fsync = ext4_sync_file,
924 .get_unmapped_area = thp_get_unmapped_area,
925 .splice_read = generic_file_splice_read,
926 .splice_write = iter_file_splice_write,
927 .fallocate = ext4_fallocate,
928 };6.4、ext4_dir_operations
目录的文件操作
/// fs/ext4/dir.c
658 const struct file_operations ext4_dir_operations = {
659 .llseek = ext4_dir_llseek,
660 .read = generic_read_dir,
661 .iterate_shared = ext4_readdir,
662 .unlocked_ioctl = ext4_ioctl,
663 #ifdef CONFIG_COMPAT
664 .compat_ioctl = ext4_compat_ioctl,
665 #endif
666 .fsync = ext4_sync_file,
667 .open = ext4_dir_open,
668 .release = ext4_release_dir,
669 };
670
671 #ifdef CONFIG_UNICODE
672 const struct dentry_operations ext4_dentry_ops = {
673 .d_hash = generic_ci_d_hash,
674 .d_compare = generic_ci_d_compare,
675 };
676 #endif7、fs_context
fs_context 是 file_system_type 和 super_block 之间的桥梁,创建和配置 super_block 都离不开 fs_context,主要在 mount 调用时使用。
7.1、fs_context_operations
/// include/linux/fs_context.h
115 struct fs_context_operations {
116 void (*free)(struct fs_context *fc);
117 int (*dup)(struct fs_context *fc, struct fs_context *src_fc);
118 int (*parse_param)(struct fs_context *fc, struct fs_parameter *param);
119 int (*parse_monolithic)(struct fs_context *fc, void *data);
120 int (*get_tree)(struct fs_context *fc);
121 int (*reconfigure)(struct fs_context *fc);
122 };7.2、fs_context
/// include/linux/fs_context.h
90 struct fs_context {
91 const struct fs_context_operations *ops;
92 struct mutex uapi_mutex; /* Userspace access mutex */
93 struct file_system_type *fs_type;
94 void *fs_private; /* The filesystem's context */
95 void *sget_key;
96 struct dentry *root; /* The root and superblock */
97 struct user_namespace *user_ns; /* The user namespace for this mount */
98 struct net *net_ns; /* The network namespace for this mount */
99 const struct cred *cred; /* The mounter's credentials */
100 struct p_log log; /* Logging buffer */
101 const char *source; /* The source name (eg. dev path) */
102 void *security; /* Linux S&M options */
103 void *s_fs_info; /* Proposed s_fs_info */
104 unsigned int sb_flags; /* Proposed superblock flags (SB_*) */
105 unsigned int sb_flags_mask; /* Superblock flags that were changed */
106 unsigned int s_iflags; /* OR'd with sb->s_iflags */
107 unsigned int lsm_flags; /* Information flags from the fs to the LSM */
108 enum fs_context_purpose purpose:8;
109 enum fs_context_phase phase:8; /* The phase the context is in */
110 bool need_free:1; /* Need to call ops->free() */
111 bool global:1; /* Goes into &init_user_ns */
112 bool oldapi:1; /* Coming from mount(2) */
113 };8、ext4_mount
在 ext4_fs_type 这节介绍时,ext4_mount 直接调用 mount_bdev 函数。
8.1、mount_bdev() 函数定义如下。
- 调用 blkdev_get_by_path() 函数打开一个 block 设备
- 调用 sget() 查找或许新建一个 super_block
/// fs/super.c
1365 struct dentry *mount_bdev(struct file_system_type *fs_type,
1366 int flags, const char *dev_name, void *data,
1367 int (*fill_super)(struct super_block *, void *, int))
1368 {
1369 struct block_device *bdev;
1370 struct super_block *s;
1371 fmode_t mode = FMODE_READ | FMODE_EXCL;
1372 int error = 0;
1373
1374 if (!(flags & SB_RDONLY))
1375 mode |= FMODE_WRITE;
1376
1377 bdev = blkdev_get_by_path(dev_name, mode, fs_type);
1378 if (IS_ERR(bdev))
1379 return ERR_CAST(bdev);
1380
1381 /*
1382 * once the super is inserted into the list by sget, s_umount
1383 * will protect the lockfs code from trying to start a snapshot
1384 * while we are mounting
1385 */
1386 mutex_lock(&bdev->bd_fsfreeze_mutex);
1387 if (bdev->bd_fsfreeze_count > 0) {
1388 mutex_unlock(&bdev->bd_fsfreeze_mutex);
1389 error = -EBUSY;
1390 goto error_bdev;
1391 }
1392 s = sget(fs_type, test_bdev_super, set_bdev_super, flags | SB_NOSEC,
1393 bdev);
1394 mutex_unlock(&bdev->bd_fsfreeze_mutex);
1395 if (IS_ERR(s))
1396 goto error_s;
1397
1398 if (s->s_root) {
1399 if ((flags ^ s->s_flags) & SB_RDONLY) {
1400 deactivate_locked_super(s);
1401 error = -EBUSY;
1402 goto error_bdev;
1403 }
1404
1405 /*
1406 * s_umount nests inside bd_mutex during
1407 * __invalidate_device(). blkdev_put() acquires
1408 * bd_mutex and can't be called under s_umount. Drop
1409 * s_umount temporarily. This is safe as we're
1410 * holding an active reference.
1411 */
1412 up_write(&s->s_umount);
1413 blkdev_put(bdev, mode);
1414 down_write(&s->s_umount);
1415 } else {
1416 s->s_mode = mode;
1417 snprintf(s->s_id, sizeof(s->s_id), "%pg", bdev);
1418 sb_set_blocksize(s, block_size(bdev));
1419 error = fill_super(s, data, flags & SB_SILENT ? 1 : 0);
1420 if (error) {
1421 deactivate_locked_super(s);
1422 goto error;
1423 }
1424
1425 s->s_flags |= SB_ACTIVE;
1426 bdev->bd_super = s;
1427 }
1428
1429 return dget(s->s_root);
1430
1431 error_s:
1432 error = PTR_ERR(s);
1433 error_bdev:
1434 blkdev_put(bdev, mode);
1435 error:
1436 return ERR_PTR(error);
1437 }传入 sget() 函数的set_bdev_super 和 test_bdev_super 是两个函数指针,其定义如下:
/// fs/super.c
1253 static int set_bdev_super(struct super_block *s, void *data)
1254 {
1255 s->s_bdev = data;
1256 s->s_dev = s->s_bdev->bd_dev;
1257 s->s_bdi = bdi_get(s->s_bdev->bd_bdi);
1258
1259 if (blk_queue_stable_writes(s->s_bdev->bd_disk->queue))
1260 s->s_iflags |= SB_I_STABLE_WRITES;
1261 return 0;
1262 }
1360 static int test_bdev_super(struct super_block *s, void *data)
1361 {
1362 return (void *)s->s_bdev == data;
1363 }8.2、sget()
sget() 函数用于查找或许新建一个 super_block 结构。首先在 file_system_type::fs_supers 链表上查找一个未使用的 super_block 结构,同时也会释放不用的 super_block。如果没有找到,就调用 alloc_super() 函数重新申请一个 super_block 结构。
/// fs/super.c
568 /**
569 * sget - find or create a superblock
570 * @type: filesystem type superblock should belong to
571 * @test: comparison callback
572 * @set: setup callback
573 * @flags: mount flags
574 * @data: argument to each of them
575 */
576 struct super_block *sget(struct file_system_type *type,
577 int (*test)(struct super_block *,void *),
578 int (*set)(struct super_block *,void *),
579 int flags,
580 void *data)
581 {
582 struct user_namespace *user_ns = current_user_ns();
583 struct super_block *s = NULL;
584 struct super_block *old;
585 int err;
586
587 /* We don't yet pass the user namespace of the parent
588 * mount through to here so always use &init_user_ns
589 * until that changes.
590 */
591 if (flags & SB_SUBMOUNT)
592 user_ns = &init_user_ns;
593
594 retry:
595 spin_lock(&sb_lock);
596 if (test) {
597 hlist_for_each_entry(old, &type->fs_supers, s_instances) {
598 if (!test(old, data))
599 continue;
600 if (user_ns != old->s_user_ns) {
601 spin_unlock(&sb_lock);
602 destroy_unused_super(s);
603 return ERR_PTR(-EBUSY);
604 }
605 if (!grab_super(old))
606 goto retry;
607 destroy_unused_super(s);
608 return old;
609 }
610 }
611 if (!s) {
612 spin_unlock(&sb_lock);
613 s = alloc_super(type, (flags & ~SB_SUBMOUNT), user_ns);
614 if (!s)
615 return ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM);
616 goto retry;
617 }
618
619 err = set(s, data);
620 if (err) {
621 spin_unlock(&sb_lock);
622 destroy_unused_super(s);
623 return ERR_PTR(err);
624 }
625 s->s_type = type;
626 strlcpy(s->s_id, type->name, sizeof(s->s_id));
627 list_add_tail(&s->s_list, &super_blocks);
628 hlist_add_head(&s->s_instances, &type->fs_supers);
629 spin_unlock(&sb_lock);
630 get_filesystem(type);
631 register_shrinker_prepared(&s->s_shrink);
632 return s;
633 }8.3、alloc_super()
/// fs/ext4/super.c
191 /**
192 * alloc_super - create new superblock
193 * @type: filesystem type superblock should belong to
194 * @flags: the mount flags
195 * @user_ns: User namespace for the super_block
196 *
197 * Allocates and initializes a new &struct super_block. alloc_super()
198 * returns a pointer new superblock or %NULL if allocation had failed.
199 */
200 static struct super_block *alloc_super(struct file_system_type *type, int flags,
201 struct user_namespace *user_ns)
202 {
203 struct super_block *s = kzalloc(sizeof(struct super_block), GFP_USER);
204 static const struct super_operations default_op;
205 int i;
206
207 if (!s)
208 return NULL;
209
210 INIT_LIST_HEAD(&s->s_mounts);
211 s->s_user_ns = get_user_ns(user_ns);
212 init_rwsem(&s->s_umount);
213 lockdep_set_class(&s->s_umount, &type->s_umount_key);
214 /*
215 * sget() can have s_umount recursion.
216 *
217 * When it cannot find a suitable sb, it allocates a new
218 * one (this one), and tries again to find a suitable old
219 * one.
220 *
221 * In case that succeeds, it will acquire the s_umount
222 * lock of the old one. Since these are clearly distrinct
223 * locks, and this object isn't exposed yet, there's no
224 * risk of deadlocks.
225 *
226 * Annotate this by putting this lock in a different
227 * subclass.
228 */
229 down_write_nested(&s->s_umount, SINGLE_DEPTH_NESTING);
230
231 if (security_sb_alloc(s))
232 goto fail;
233
234 for (i = 0; i < SB_FREEZE_LEVELS; i++) {
235 if (__percpu_init_rwsem(&s->s_writers.rw_sem[i],
236 sb_writers_name[i],
237 &type->s_writers_key[i]))
238 goto fail;
239 }
240 init_waitqueue_head(&s->s_writers.wait_unfrozen);
241 s->s_bdi = &noop_backing_dev_info;
242 s->s_flags = flags;
243 if (s->s_user_ns != &init_user_ns)
244 s->s_iflags |= SB_I_NODEV;
245 INIT_HLIST_NODE(&s->s_instances);
246 INIT_HLIST_BL_HEAD(&s->s_roots);
247 mutex_init(&s->s_sync_lock);
248 INIT_LIST_HEAD(&s->s_inodes);
249 spin_lock_init(&s->s_inode_list_lock);
250 INIT_LIST_HEAD(&s->s_inodes_wb);
251 spin_lock_init(&s->s_inode_wblist_lock);
252
253 s->s_count = 1;
254 atomic_set(&s->s_active, 1);
255 mutex_init(&s->s_vfs_rename_mutex);
256 lockdep_set_class(&s->s_vfs_rename_mutex, &type->s_vfs_rename_key);
257 init_rwsem(&s->s_dquot.dqio_sem);
258 s->s_maxbytes = MAX_NON_LFS;
259 s->s_op = &default_op;
260 s->s_time_gran = 1000000000;
261 s->s_time_min = TIME64_MIN;
262 s->s_time_max = TIME64_MAX;
263 s->cleancache_poolid = CLEANCACHE_NO_POOL;
264
265 s->s_shrink.seeks = DEFAULT_SEEKS;
266 s->s_shrink.scan_objects = super_cache_scan;
267 s->s_shrink.count_objects = super_cache_count;
268 s->s_shrink.batch = 1024;
269 s->s_shrink.flags = SHRINKER_NUMA_AWARE | SHRINKER_MEMCG_AWARE;
270 if (prealloc_shrinker(&s->s_shrink))
271 goto fail;
272 if (list_lru_init_memcg(&s->s_dentry_lru, &s->s_shrink))
273 goto fail;
274 if (list_lru_init_memcg(&s->s_inode_lru, &s->s_shrink))
275 goto fail;
276 return s;
277
278 fail:
279 destroy_unused_super(s);
280 return NULL;
281 }9、ext4_create
当创建一个文件时,会进入 ext4_create() 函数
9.1、ext4_create()
创建一个新的文件,就会分配一个 inode,ext4_create() 函数的核心是创建一个 inode。
/// fs/ext4/namei.c
2626 /*
2627 * By the time this is called, we already have created
2628 * the directory cache entry for the new file, but it
2629 * is so far negative - it has no inode.
2630 *
2631 * If the create succeeds, we fill in the inode information
2632 * with d_instantiate().
2633 */
2634 static int ext4_create(struct inode *dir, struct dentry *dentry, umode_t mode,
2635 bool excl)
2636 {
2637 handle_t *handle;
2638 struct inode *inode;
2639 int err, credits, retries = 0;
2640
2641 err = dquot_initialize(dir);
2642 if (err)
2643 return err;
2644
2645 credits = (EXT4_DATA_TRANS_BLOCKS(dir->i_sb) +
2646 EXT4_INDEX_EXTRA_TRANS_BLOCKS + 3);
2647 retry:
2648 inode = ext4_new_inode_start_handle(dir, mode, &dentry->d_name, 0,
2649 NULL, EXT4_HT_DIR, credits);
2650 handle = ext4_journal_current_handle();
2651 err = PTR_ERR(inode);
2652 if (!IS_ERR(inode)) {
2653 inode->i_op = &ext4_file_inode_operations;
2654 inode->i_fop = &ext4_file_operations;
2655 ext4_set_aops(inode);
2656 err = ext4_add_nondir(handle, dentry, &inode);
2657 if (!err)
2658 ext4_fc_track_create(handle, dentry);
2659 }
2660 if (handle)
2661 ext4_journal_stop(handle);
2662 if (!IS_ERR_OR_NULL(inode))
2663 iput(inode);
2664 if (err == -ENOSPC && ext4_should_retry_alloc(dir->i_sb, &retries))
2665 goto retry;
2666 return err;
2667 }ext4_new_inode_start_handle() 定义如下
/// fs/ext4/ext4.h
2737 #define ext4_new_inode_start_handle(dir, mode, qstr, goal, owner, \
2738 type, nblocks) \
2739 __ext4_new_inode(NULL, (dir), (mode), (qstr), (goal), (owner), \
2740 0, (type), __LINE__, (nblocks))__ext4_new_inode() 定义如下
/// fs/ext4/ialloc.c
913 /*
914 * There are two policies for allocating an inode. If the new inode is
915 * a directory, then a forward search is made for a block group with both
916 * free space and a low directory-to-inode ratio; if that fails, then of
917 * the groups with above-average free space, that group with the fewest
918 * directories already is chosen.
919 *
920 * For other inodes, search forward from the parent directory's block
921 * group to find a free inode.
922 */
923 struct inode *__ext4_new_inode(handle_t *handle, struct inode *dir,
924 umode_t mode, const struct qstr *qstr,
925 __u32 goal, uid_t *owner, __u32 i_flags,
926 int handle_type, unsigned int line_no,
927 int nblocks)
928 {
929 struct super_block *sb;
930 struct buffer_head *inode_bitmap_bh = NULL;
931 struct buffer_head *group_desc_bh;
932 ext4_group_t ngroups, group = 0;
933 unsigned long ino = 0;
934 struct inode *inode;
935 struct ext4_group_desc *gdp = NULL;
936 struct ext4_inode_info *ei;
937 struct ext4_sb_info *sbi;
938 int ret2, err;
939 struct inode *ret;
940 ext4_group_t i;
941 ext4_group_t flex_group;
942 struct ext4_group_info *grp = NULL;
943 bool encrypt = false;
944
945 /* Cannot create files in a deleted directory */
946 if (!dir || !dir->i_nlink)
947 return ERR_PTR(-EPERM);
948
949 sb = dir->i_sb;
950 sbi = EXT4_SB(sb);
951
952 if (unlikely(ext4_forced_shutdown(sbi)))
953 return ERR_PTR(-EIO);
954
955 ngroups = ext4_get_groups_count(sb);
956 trace_ext4_request_inode(dir, mode);
957 inode = new_inode(sb);
958 if (!inode)
959 return ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM);
960 ei = EXT4_I(inode);
// ...9.2、alloc_inode()
new_inode() ==> new_inode_pseudo() ==> alloc_inode()
/// fs/inode.c
228 static struct inode *alloc_inode(struct super_block *sb)
229 {
230 const struct super_operations *ops = sb->s_op;
231 struct inode *inode;
232
233 if (ops->alloc_inode)
234 inode = ops->alloc_inode(sb);
235 else
236 inode = kmem_cache_alloc(inode_cachep, GFP_KERNEL);
237
238 if (!inode)
239 return NULL;
240
241 if (unlikely(inode_init_always(sb, inode))) {
242 if (ops->destroy_inode) {
243 ops->destroy_inode(inode);
244 if (!ops->free_inode)
245 return NULL;
246 }
247 inode->free_inode = ops->free_inode;
248 i_callback(&inode->i_rcu);
249 return NULL;
250 }
251
252 return inode;
253 }
918 /**
919 * new_inode_pseudo - obtain an inode
920 * @sb: superblock
921 *
922 * Allocates a new inode for given superblock.
923 * Inode wont be chained in superblock s_inodes list
924 * This means :
925 * - fs can't be unmount
926 * - quotas, fsnotify, writeback can't work
927 */
928 struct inode *new_inode_pseudo(struct super_block *sb)
929 {
930 struct inode *inode = alloc_inode(sb);
931
932 if (inode) {
933 spin_lock(&inode->i_lock);
934 inode->i_state = 0;
935 spin_unlock(&inode->i_lock);
936 INIT_LIST_HEAD(&inode->i_sb_list);
937 }
938 return inode;
939 }
940
941 /**
942 * new_inode - obtain an inode
943 * @sb: superblock
944 *
945 * Allocates a new inode for given superblock. The default gfp_mask
946 * for allocations related to inode->i_mapping is GFP_HIGHUSER_MOVABLE.
947 * If HIGHMEM pages are unsuitable or it is known that pages allocated
948 * for the page cache are not reclaimable or migratable,
949 * mapping_set_gfp_mask() must be called with suitable flags on the
950 * newly created inode's mapping
951 *
952 */
953 struct inode *new_inode(struct super_block *sb)
954 {
955 struct inode *inode;
956
957 spin_lock_prefetch(&sb->s_inode_list_lock);
958
959 inode = new_inode_pseudo(sb);
960 if (inode)
961 inode_sb_list_add(inode);
962 return inode;
963 }