深度学习HashMap之手撕HashMap
认识哈希表
HashMap其实是数据结构中的哈希表在Java里的实现。
哈希表本质
哈希表也叫散列表,我们先来看看哈希表的定义:
哈希表是根据关键码的值而直接进行访问的数据结构。
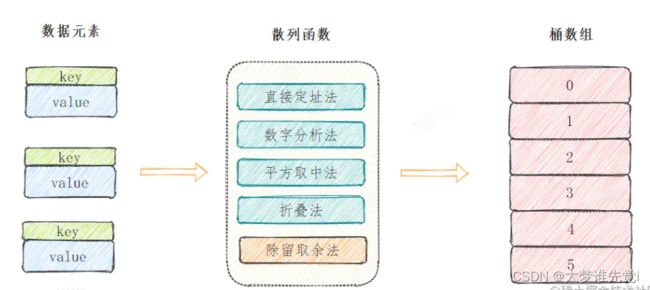
简单说来说,哈希表由两个要素构成:桶数组和散列函数。
桶数组
我们可能知道,有一类基础的数据结构线性表,而线性表又分两种,数组和链表。
哈希表数据结构里,存储元素的数据结构就是数组,数组里的每个单元都可以想象成一个桶(Bucket)。
散列函数
我们需要在元素和桶数组对应位置建立一种映射映射关系,这种映射关系就是散列函数,也可以叫哈希函数。
散列函数构造
散列函数也叫哈希函数,假如我们数据元素的key是整数或者可以转换为一个整数,可以通过这些常见方法来获取映射地址。
- 直接定址法
直接根据key来映射到对应的数组位置,例如1232放到下标1232的位置。
- 数字分析法
取key的某些数字(例如十位和百位)作为映射的位置
- 平方取中法
取key平方的中间几位作为映射的位置
- 折叠法
将key分割成位数相同的几段,然后把它们的叠加和作为映射的位置
- 除留余数法
H(key)=key%p(p<=N),关键字除以一个不大于哈希表长度的正整数p,所得余数为哈希地址,这是应用最广泛的散列函数构造方法。
在Java里,Object类里提供了一个默认的hashCode()方法,它返回的是一个32位int形整数,其实也就是对象在内存里的存储地址。
但是,这个整数肯定是要经过处理的,上面几种方法里直接定址法可以排除,因为我们不可能建那么大的桶数组。
而且我们最后计算出来的散列地址,尽可能要在桶数组长度范围之内,所以我们选择除留取余法。
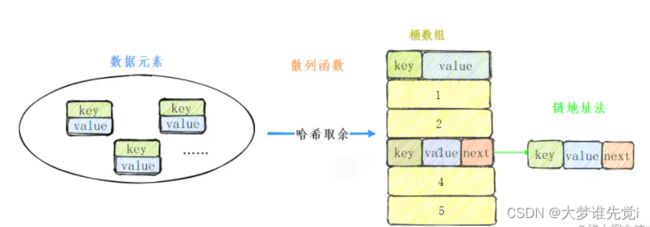
哈希冲突
理想的情况,是每个数据元素经过哈希函数的计算,落在它独属的桶数组的位置。
但是现实通常不如人意,我们的空间是有限的,设计再好的哈希函数也不能完全避免哈希冲突。所谓的哈希冲突,就是不同的key经过哈希函数计算,落到了同一个下标。
既然有了冲突,就得想办法解决冲突,常见的解决哈希冲突的办法有:
链地址法
也叫拉链法,看起来,像在桶数组上再拉一个链表出来,把发生哈希冲突的元素放到一个链表里,查找的时候,从前往后遍历链表,找到对应的key就行了。
开放地址法
开放地址法,简单来说就是给冲突的元素再在桶数组里找到一个空闲的位置。
找到空闲位置的方法有很多种:
- 线行探查法: 从冲突的位置开始,依次判断下一个位置是否空闲,直至找到空闲位置
- 平方探查法: 从冲突的位置x开始,第一次增加12个位置,第二次增加22…,直至找到空闲的位置
- 双散列函数探查法
……
再哈希法
构造多个哈希函数,发生冲突时,更换哈希函数,直至找到空闲位置。
建立公共溢出区
建立公共溢出区,把发生冲突的数据元素存储到公共溢出区。
很明显,接下来我们解决冲突,会使用链地址法。
好了,哈希表的介绍就到这,相信你已经对哈希表的本质有了深刻的理解,接下来,进入coding时间。
HashMap实现
我们实现的简单的HashMap命名为ThirdHashMap,先确定整体的设计:
散列函数:hashCode()+除留余数法
冲突解决:链地址法
内部节点类
我们需要定义一个节点来作为具体数据的载体,它不仅要承载键值对,同样还得作为单链表的节点:
/**
* 节点类
*
* @param
* @param
*/
class Node<K, V> {
//键值对
private K key;
private V value;
//链表,后继
private Node<K, V> next;
public Node(K key, V value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
public Node(K key, V value, Node<K, V> next) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
}
成员变量
主要有四个成员变量,其中桶数组作为装载数据元素的结构:
//默认容量
final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 16;
//负载因子
final float LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
//HashMap的大小
private int size;
//桶数组
Node<K, V>[] buckets;
构造方法
构造方法有两个,无参构造方法,桶数组默认容量,有参指定桶数组容量。
/**
* 无参构造器,设置桶数组默认容量
*/
public ThirdHashMap() {
buckets = new Node[DEFAULT_CAPACITY];
size = 0;
}
/**
* 有参构造器,指定桶数组容量
*
* @param capacity
*/
public ThirdHashMap(int capacity) {
buckets = new Node[capacity];
size = 0;
}
散列函数
散列函数,就是我们前面说的hashCode()和数组长度取余。
/**
* 哈希函数,获取地址
*
* @param key
* @return
*/
private int getIndex(K key, int length) {
//获取hash code
int hashCode = key.hashCode();
//和桶数组长度取余
int index = hashCode % length;
return Math.abs(index);
}
put方法
我用了一个putval方法来完成实际的逻辑,这是因为扩容也会用到这个方法。
大概的逻辑:
- 获取元素插入位置
- 当前位置为空,直接插入
- 位置不为空,发生冲突,遍历链表
- 如果元素key和节点相同,覆盖,否则新建节点插入链表头部
/**
* put方法
*
* @param key
* @param value
* @return
*/
public void put(K key, V value) {
//判断是否需要进行扩容
if (size >= buckets.length * LOAD_FACTOR) resize();
putVal(key, value, buckets);
}
/**
* 将元素存入指定的node数组
*
* @param key
* @param value
* @param table
*/
private void putVal(K key, V value, Node<K, V>[] table) {
//获取位置
int index = getIndex(key, table.length);
Node node = table[index];
//插入的位置为空
if (node == null) {
table[index] = new Node<>(key, value);
size++;
return;
}
//插入位置不为空,说明发生冲突,使用链地址法,遍历链表
while (node != null) {
//如果key相同,就覆盖掉
if ((node.key.hashCode() == key.hashCode())
&& (node.key == key || node.key.equals(key))) {
node.value = value;
return;
}
node = node.next;
}
//当前key不在链表中,插入链表头部
Node newNode = new Node(key, value, table[index]);
table[index] = newNode;
size++;
}
扩容方法
扩容的大概过程:
- 创建两倍容量的新数组
- 将当前桶数组的元素重新散列到新的数组
- 新数组置为map的桶数组
/**
* 扩容
*/
private void resize() {
//创建一个两倍容量的桶数组
Node<K, V>[] newBuckets = new Node[buckets.length * 2];
//将当前元素重新散列到新的桶数组
rehash(newBuckets);
buckets = newBuckets;
}
/**
* 重新散列当前元素
*
* @param newBuckets
*/
private void rehash(Node<K, V>[] newBuckets) {
//map大小重新计算
size = 0;
//将旧的桶数组的元素全部刷到新的桶数组里
for (int i = 0; i < buckets.length; i++) {
//为空,跳过
if (buckets[i] == null) {
continue;
}
Node<K, V> node = buckets[i];
while (node != null) {
//将元素放入新数组
putVal(node.key, node.value, newBuckets);
node = node.next;
}
}
}
get方法
get方法就比较简单,通过散列函数获取地址,这里我省去了有没有成链表的判断,直接查找链表。
/**
* 获取元素
*
* @param key
* @return
*/
public V get(K key) {
//获取key对应的地址
int index = getIndex(key, buckets.length);
if (buckets[index] == null) return null;
Node<K, V> node = buckets[index];
//查找链表
while (node != null) {
if ((node.key.hashCode() == key.hashCode())
&& (node.key == key || node.key.equals(key))) {
return node.value;
}
node = node.next;
}
return null;
}
完整代码:
public class ThirdHashMap<K, V> {
/**
* 节点类
*
* @param
* @param
*/
class Node<K, V> {
//键值对
private K key;
private V value;
//链表,后继
private Node<K, V> next;
public Node(K key, V value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
public Node(K key, V value, Node<K, V> next) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
}
//默认容量
final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 16;
//负载因子
final float LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
//HashMap的大小
private int size;
//桶数组
Node<K, V>[] buckets;
/**
* 无参构造器,设置桶数组默认容量
*/
public ThirdHashMap() {
buckets = new Node[DEFAULT_CAPACITY];
size = 0;
}
/**
* 有参构造器,指定桶数组容量
*
* @param capacity
*/
public ThirdHashMap(int capacity) {
buckets = new Node[capacity];
size = 0;
}
/**
* 哈希函数,获取地址
*
* @param key
* @return
*/
private int getIndex(K key, int length) {
//获取hash code
int hashCode = key.hashCode();
//和桶数组长度取余
int index = hashCode % length;
return Math.abs(index);
}
/**
* put方法
*
* @param key
* @param value
* @return
*/
public void put(K key, V value) {
//判断是否需要进行扩容
if (size >= buckets.length * LOAD_FACTOR) resize();
putVal(key, value, buckets);
}
/**
* 将元素存入指定的node数组
*
* @param key
* @param value
* @param table
*/
private void putVal(K key, V value, Node<K, V>[] table) {
//获取位置
int index = getIndex(key, table.length);
Node node = table[index];
//插入的位置为空
if (node == null) {
table[index] = new Node<>(key, value);
size++;
return;
}
//插入位置不为空,说明发生冲突,使用链地址法,遍历链表
while (node != null) {
//如果key相同,就覆盖掉
if ((node.key.hashCode() == key.hashCode())
&& (node.key == key || node.key.equals(key))) {
node.value = value;
return;
}
node = node.next;
}
//当前key不在链表中,插入链表头部
Node newNode = new Node(key, value, table[index]);
table[index] = newNode;
size++;
}
/**
* 扩容
*/
private void resize() {
//创建一个两倍容量的桶数组
Node<K, V>[] newBuckets = new Node[buckets.length * 2];
//将当前元素重新散列到新的桶数组
rehash(newBuckets);
buckets = newBuckets;
}
/**
* 重新散列当前元素
*
* @param newBuckets
*/
private void rehash(Node<K, V>[] newBuckets) {
//map大小重新计算
size = 0;
//将旧的桶数组的元素全部刷到新的桶数组里
for (int i = 0; i < buckets.length; i++) {
//为空,跳过
if (buckets[i] == null) {
continue;
}
Node<K, V> node = buckets[i];
while (node != null) {
//将元素放入新数组
putVal(node.key, node.value, newBuckets);
node = node.next;
}
}
}
/**
* 获取元素
*
* @param key
* @return
*/
public V get(K key) {
//获取key对应的地址
int index = getIndex(key, buckets.length);
if (buckets[index] == null) return null;
Node<K, V> node = buckets[index];
//查找链表
while (node != null) {
if ((node.key.hashCode() == key.hashCode())
&& (node.key == key || node.key.equals(key))) {
return node.value;
}
node = node.next;
}
return null;
}
/**
* 返回HashMap大小
*
* @return
*/
public int size() {
return size;
}
}
测试
测试代码如下:
@Test
void test0() {
ThirdHashMap map = new ThirdHashMap();
for (int i = 1; i <= 72; i++) {
map.put("孙悟空" + i, "看我72变" + i);
}
System.out.println(map.size());
for (int i = 1; i <=72; i++) {
System.out.println(map.get("孙悟空" + i));
}
}
}