Framework学习之旅:Service的绑定过程
前言
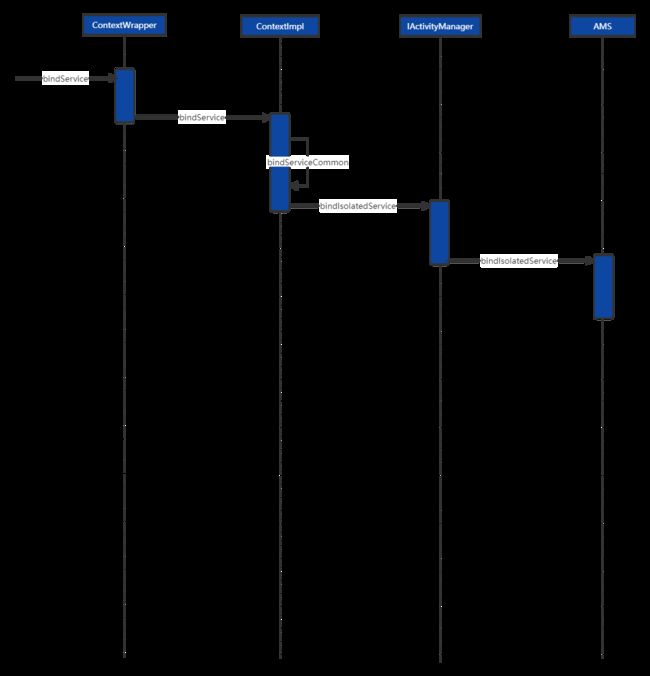
Service的绑定过程将分为两个部分来进行讲解;分别是Contextlmpl到AMS的调用过程和Service的绑定过程。
frameworks/base/core/java/android/content/ContextWrapper.java
public boolean bindService(Intent service, ServiceConnection conn,
int flags) {
return mBase.bindService(service, conn, flags);
}
通过Framework 学习之旅:Service 启动过程可知,mBase具体就是指向ContextImpl的,接着查看Contextlmpl的bindService方法:
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ContextImpl.java
public boolean bindService(Intent service, ServiceConnection conn, int flags) {
warnIfCallingFromSystemProcess();
return bindServiceCommon(service, conn, flags, null, mMainThread.getHandler(), null,
getUser());//1
}
private boolean bindServiceCommon(Intent service, ServiceConnection conn, int flags,
String instanceName, Handler handler, Executor executor, UserHandle user) {
IServiceConnection sd;
....
if (mPackageInfo != null) {
if (executor != null) {
sd = mPackageInfo.getServiceDispatcher(conn, getOuterContext(), executor, flags);
} else {
sd = mPackageInfo.getServiceDispatcher(conn, getOuterContext(), handler, flags);//2
}
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("Not supported in system context");
}
validateServiceIntent(service);
try {
// activity在系统端的 token
IBinder token = getActivityToken();
if (token == null && (flags&BIND_AUTO_CREATE) == 0 && mPackageInfo != null
&& mPackageInfo.getApplicationInfo().targetSdkVersion
< android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES.ICE_CREAM_SANDWICH) {
flags |= BIND_WAIVE_PRIORITY;
}
service.prepareToLeaveProcess(this);
// 调用 AMS
int res = ActivityManager.getService().bindIsolatedService(
mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), getActivityToken(), service,
service.resolveTypeIfNeeded(getContentResolver()),
sd, flags, instanceName, getOpPackageName(), user.getIdentifier());//3
if (res < 0) {
throw new SecurityException(
"Not allowed to bind to service " + service);
}
return res != 0;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}
在注释1处,bindService方法又调用了bindServiceCommon方法;
在注释2处,调用了LoadedApk类型的对象mPackagelnfo的getServiceDispatcher方法;它的主要作用是将ServiceConnection封装为IServiceConnection类型的对象sd,从IServiceConnection的名字我们就能得知它实现了Binder机制,这样Service的绑定就支持了跨进程。
在注释3处,调用AMS的bindIsolatedService方法。下面,先继续查看LoadedApk的getServiceDispatcher方法
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/LoadedApk.java
@UnsupportedAppUsage
public final IServiceConnection getServiceDispatcher(ServiceConnection c,
Context context, Handler handler, int flags) {
return getServiceDispatcherCommon(c, context, handler, null, flags);
}
public final IServiceConnection getServiceDispatcher(ServiceConnection c,
Context context, Executor executor, int flags) {
return getServiceDispatcherCommon(c, context, null, executor, flags);
}
private IServiceConnection getServiceDispatcherCommon(ServiceConnection c,
Context context, Handler handler, Executor executor, int flags) {
synchronized (mServices) {
LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd = null;
// 注释1
ArrayMap<ServiceConnection, LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher> map = mServices.get(context);
if (map != null) {
if (DEBUG) Slog.d(TAG, "Returning existing dispatcher " + sd + " for conn " + c);
sd = map.get(c);
}
if (sd == null) {
if (executor != null) {
sd = new ServiceDispatcher(c, context, executor, flags);
} else {
sd = new ServiceDispatcher(c, context, handler, flags);//注释2
}
if (DEBUG) Slog.d(TAG, "Creating new dispatcher " + sd + " for conn " + c);
if (map == null) {
map = new ArrayMap<>();
mServices.put(context, map);
}
map.put(c, sd);
} else {
sd.validate(context, handler, executor);
}
// 返回的是 InnerConnection 对象
return sd.getIServiceConnection();
}
}
由源码可知,注释1处mServices通过context获取对应的ServiceConnection和ServiceDispatcher。注释2处新建ServiceDispatcher对象,并且将参数传入构造方法中,最终通过ServiceDispatcher对象来获取IServiceConnection。
下面接着看LoadApk的内部静态类ServiceDispatcher:
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/LoadedApk.java
static final class ServiceDispatcher {
private final ServiceDispatcher.InnerConnection mIServiceConnection;
private final ServiceConnection mConnection;
private final Context mContext;
private final Handler mActivityThread;
private final Executor mActivityExecutor;
private final ServiceConnectionLeaked mLocation;
private final int mFlags;
.....
private static class InnerConnection extends IServiceConnection.Stub {
@UnsupportedAppUsage
final WeakReference<LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher> mDispatcher;
InnerConnection(LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd) {
mDispatcher = new WeakReference<LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher>(sd);
}
public void connected(ComponentName name, IBinder service, boolean dead)
throws RemoteException {
LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd = mDispatcher.get();
if (sd != null) {
// 回调 connected()方法
sd.connected(name, service, dead);
}
}
.....
}
@UnsupportedAppUsage
ServiceDispatcher(ServiceConnection conn,
Context context, Handler activityThread, int flags) {
mIServiceConnection = new InnerConnection(this);
mConnection = conn;
mContext = context;
mActivityThread = activityThread;
mActivityExecutor = null;
mLocation = new ServiceConnectionLeaked(null);
mLocation.fillInStackTrace();
mFlags = flags;
}
......
@UnsupportedAppUsage
IServiceConnection getIServiceConnection() {
return mIServiceConnection;
}
}
由源码可知,ServiceDispatcher构造方法中传入主线程的activityThread和context包装到ServiceDispatcher对象中,并在内部实现了IServiceConnection接口的InnerConnection,最终通过getIServiceConnection方法返回将其赋值给最开始创建的sd对象,也就是可以和远程服务进行Binder通信的本地引用。
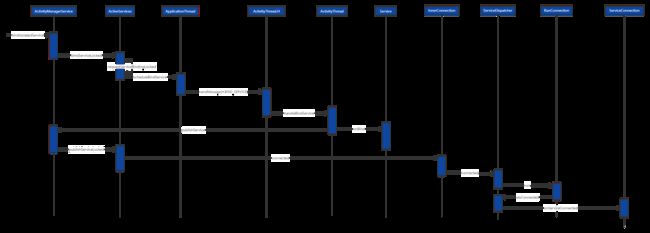
时序图:
AMS到ActivityThread启动绑定Service过程
接着分析,ActivityManagerService的bindIsolatedService方法:
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityManagerService.java
public int bindIsolatedService(IApplicationThread caller, IBinder token, Intent service,
String resolvedType, IServiceConnection connection, int flags, String instanceName,
String callingPackage, int userId) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
enforceNotIsolatedCaller("bindService");
......
synchronized(this) {
// token: Activity在系统中Token对象
// connection:客户端提供的 Binder 对象
return mServices.bindServiceLocked(caller, token, service,
resolvedType, connection, flags, instanceName, callingPackage, userId);
}
}
bindIsolatedService方法中调用了ActiveServices类的bindServiceLocked方法。
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActiveServices.java
int bindServiceLocked(IApplicationThread caller, IBinder token, Intent service,
String resolvedType, final IServiceConnection connection, int flags,
String instanceName, String callingPackage, final int userId)
throws TransactionTooLargeException {
// 获取调用者进程对象ProcessRecord
final ProcessRecord callerApp = mAm.getRecordForAppLocked(caller);
.....
ActivityServiceConnectionsHolder<ConnectionRecord> activity = null;
// 如果token不为null,则表示是activity中bindservice的
if (token != null) {
// 根据传递过来的token,获取activity对象,为空则表示在系统端没有注册,是非法的,直接结束。
activity = mAm.mAtmInternal.getServiceConnectionsHolder(token);
if (activity == null) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Binding with unknown activity: " + token);
return 0;
}
}
.....
// 通过PMS解析获取 ServiceRecord 信息
ServiceLookupResult res =
retrieveServiceLocked(service, instanceName, resolvedType, callingPackage,
Binder.getCallingPid(), Binder.getCallingUid(), userId, true,
callerFg, isBindExternal, allowInstant);
.....
// 得到ServiceRecord 对象
ServiceRecord s = res.record;
.....
// 得到AppBindRecord对象,表示该服务对应的其中一个客户端(一个服务可以被多个客户端绑定)
// 注释0
AppBindRecord b = s.retrieveAppBindingLocked(service, callerApp);
//创建ConnectionRecord对象,封装从绑定服务的发起端传递过来的conn
ConnectionRecord c = new ConnectionRecord(b, activity,
connection, flags, clientLabel, clientIntent,
callerApp.uid, callerApp.processName, callingPackage);
.....
IBinder binder = connection.asBinder();
s.addConnection(binder, c);
b.connections.add(c);
if (activity != null) {
activity.addConnection(c);
}
b.client.connections.add(c);
c.startAssociationIfNeeded();
.....
ArrayList<ConnectionRecord> clist = mServiceConnections.get(binder);
if (clist == null) {
clist = new ArrayList<>();
mServiceConnections.put(binder, clist);
}
clist.add(c);
.....
// 如果设置了BIND_AUTO_CREATE 标志
if ((flags&Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE) != 0) {
s.lastActivity = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
// 开始启动 service
if (bringUpServiceLocked(s, service.getFlags(), callerFg, false,
permissionsReviewRequired) != null) {// 1
return 0;
}
}
.....
if (s.app != null && b.intent.received) {// 2
// Service is already running, so we can immediately
// publish the connection.
try {
// 服务已经发布,通过binder调用发起端的connected()方法
c.conn.connected(s.name, b.intent.binder, false);//3
} catch (Exception e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Failure sending service " + s.shortInstanceName
+ " to connection " + c.conn.asBinder()
+ " (in " + c.binding.client.processName + ")", e);
}
// If this is the first app connected back to this binding,
// and the service had previously asked to be told when
// rebound, then do so.
if (b.intent.apps.size() == 1 && b.intent.doRebind) {//4
// 如果已经bind过,则回调onReBind
requestServiceBindingLocked(s, b.intent, callerFg, true);//5
}
} else if (!b.intent.requested) {//6
// 最终回调 onBind() 方法
requestServiceBindingLocked(s, b.intent, callerFg, false);//7
}
.....
}
在注释0处调用了ServiceRecord的retrieveAppBindingLocked方法来获得AppBindRecord , retrieveAppBindingLocked方法内部创建IntentBindRecord,并对IntentBindRecord的成员变量进行赋值。
在注释1处调用bringUpServiceLocked方法,在bringUpServiceLocked方法中又调用realStartServiceLocked方法,最终由ActivityThread来调用Service的onCreate方法启动Service,这也说明了bindService方怯内部会启动Service。
在注释2处s.app!=null表示Service已经运行,其中s是ServiceRecord类型对象,app是ProcessRecord类型对象。b.intent.received表示当前应用程序进程已经接收到绑定Service时返回的Binder,这样应用程序进程就可以通过Binder获取要绑定的Service的访问接口。
在注释3处调用conn.connected方法,其中c.conn指的是IServiceConnection,它的具体实现为 ServiceDispatcher.InnerConnection,其中ServiceDispatcher是Loaded.Apk的内部类,InnerConnection的connected方法内部会调用H的post方法向主线程发送消息,并且解决当前应用程序进程Service跨进程通信的问题。
在注释4处如果当前应用程序进程是第一个与Service进行绑定的,并且Service已经调用过onUnBind方法,则需要调用注释5处的代码。
在注释6处如果应用程序进程的Client端没有发送过绑定Service的请求,则调用注释7处的代码,注释7处和注释5处的代码区别就是最后一个参数rebind为false,表 示不是重新绑定。
首先查看bindServiceLocked方法注释0处ServiceRecord的retrieveAppBindingLocked方法:
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ServiceRecord.java
final ArrayMap<Intent.FilterComparison, IntentBindRecord> bindings
= new ArrayMap<Intent.FilterComparison, IntentBindRecord>();
public AppBindRecord retrieveAppBindingLocked(Intent intent,
ProcessRecord app) {
Intent.FilterComparison filter = new Intent.FilterComparison(intent);
IntentBindRecord i = bindings.get(filter);
if (i == null) {//1
i = new IntentBindRecord(this, filter);
bindings.put(filter, i);
}
AppBindRecord a = i.apps.get(app);//2
if (a != null) {
return a;
}
a = new AppBindRecord(this, i, app);//3
i.apps.put(app, a);
return a;
}
注释1处通过filter查找对应IntentBindRecord类型的i,如果i为null意味着当前应用程序进程没有绑定服务,那就新建了IntentBindRecord并保持;
注释2处根据ProcessRecord获得IntentBindRecord中存储的AppBindRecord,如果 AppBindRecord不为null就返回,如果为null就在注释3处创建AppBindRecord,并将 ProcessRecord作为key,AppBindRecord作为value保存在IntentBindRecord的apps (i.apps)中。
接着,bindServiceLocked方法注释1处在Service启动过程 已经分析过了,在此就不展开分析了。重点分析bindServiceLocked方法的注释5和注释7处的requestServiceBindingLocked方法:
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActiveServices.java
private final boolean requestServiceBindingLocked(ServiceRecord r, IntentBindRecord i,
boolean execInFg, boolean rebind) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
.......
if ((!i.requested || rebind) && i.apps.size() > 0) {//1
try {
bumpServiceExecutingLocked(r, execInFg, "bind");
r.app.forceProcessStateUpTo(ActivityManager.PROCESS_STATE_SERVICE);
r.app.thread.scheduleBindService(r, i.intent.getIntent(), rebind,
r.app.getReportedProcState());//2
if (!rebind) {
i.requested = true;
}
i.hasBound = true;
i.doRebind = false;
} catch (TransactionTooLargeException e) {
....
} catch (RemoteException e) {
....
}
}
return true;
}
注释1处i.requested 表示是否发送过绑定Service的请求,从bindServiceLocked 方法的注释4处得知是发送过的,因此,!i.requested为false。从bindServiceLocked方法的注释4处得知rebind值为true,那么(!i.requested||rebind)的值为true。i.apps.size()>0表示所有用当前Intent绑定Service的应用程序进程个数大于0。其中i是IntentBindRecord 类型的对象,AMS会为每个绑定Service的Intent 分配一个IntentBindRecord类型对象。具体看一下IntentBindRecord类型:
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/IntentBindRecord.java
final class IntentBindRecord {
// 被绑定的Service
final ServiceRecord service;
// 绑定Service的intent
final Intent.FilterComparison intent;
// 所有用当前Intent绑定Service 的应用程序
final ArrayMap<ProcessRecord, AppBindRecord> apps
= new ArrayMap<ProcessRecord, AppBindRecord>();//1
....
}
来查看IntentBindRecord类,不同的应用程序进程可能使用同Intent来绑定Service,因此在注释1处会用apps来存储所有用当前Intent绑定Service的应用程序进程。
下面,接着看requestServiceBindingLocked方法注释2处代码:
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java
public final void scheduleBindService(IBinder token, Intent intent,
boolean rebind, int processState) {
updateProcessState(processState, false);
BindServiceData s = new BindServiceData();
s.token = token;
s.intent = intent;
s.rebind = rebind;
if (DEBUG_SERVICE)
Slog.v(TAG, "scheduleBindService token=" + token + " intent=" + intent + " uid="
+ Binder.getCallingUid() + " pid=" + Binder.getCallingPid());
sendMessage(H.BIND_SERVICE, s);
}
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
switch (msg.what) {
case BIND_SERVICE:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "serviceBind");
handleBindService((BindServiceData)msg.obj); //1
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
}
}
在scheduleBindService方法中将Service的信息封装成BindServiceData对象, BindServiceData的成员变量rebind值为false。接着将BindServiceData传入到 sendMessage方法中。H在接收到BIND_ERVICE类型消息时,会在handleMessage 方法中会调用handleBindService方法:
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java
private void handleBindService(BindServiceData data) {
Service s = mServices.get(data.token);//1
if (DEBUG_SERVICE)
Slog.v(TAG, "handleBindService s=" + s + " rebind=" + data.rebind);
if (s != null) {
try {
data.intent.setExtrasClassLoader(s.getClassLoader());
data.intent.prepareToEnterProcess();
try {
if (!data.rebind) {//2
IBinder binder = s.onBind(data.intent);//3
ActivityManager.getService().publishService(
data.token, data.intent, binder);//4
} else {
s.onRebind(data.intent);//5
ActivityManager.getService().serviceDoneExecuting(
data.token, SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_ANON, 0, 0);
}
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
throw ex.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(s, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to bind to service " + s
+ " with " + data.intent + ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
}
}
在注释1处获取要绑定的Service。注释2处的BindServiceData的成员变量rebind的值为false,这样调用注释3处的代码来调用Service的onBind方法,到这里Service 处于绑定状态了。如果rebind的值为true就调用注释5处的Service的onRebind方法,结合前文的bindServiceLocked方法的注释4处,得出的结论就是:如果当前应用程序进程第一个与Service进行绑定,并且Service调用过onUnBind方法,则调用 Service的onRebind方法。
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityManagerService.java
public void publishService(IBinder token, Intent intent, IBinder service) {
// Refuse possible leaked file descriptors
......
synchronized(this) {
if (!(token instanceof ServiceRecord)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid service token");
}
mServices.publishServiceLocked((ServiceRecord)token, intent, service);//1
}
}
在publishService方法中调用ActiveServices类型的mService对象的publishServiceLocked方法:
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActiveServices.java
void publishServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r, Intent intent, IBinder service) {
try {
....
ArrayMap<IBinder, ArrayList<ConnectionRecord>> connections = r.getConnections();
for (int conni = connections.size() - 1; conni >= 0; conni--) {
.....
ConnectionRecord c = clist.get(i);
try {
// 回调app端的 IServiceConnection的 connected()方法
c.conn.connected(r.name, service, false);//1
} catch (Exception e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Failure sending service " + r.shortInstanceName
+ " to connection " + c.conn.asBinder()
+ " (in " + c.binding.client.processName + ")", e);
}
serviceDoneExecutingLocked(r, mDestroyingServices.contains(r), false);
}
}finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
}
}
注释1处c.conn指的是IServiceConnection,它是ServiceConnection在本地的代理,用于解决当前应用程序进程和Service跨进程通信的问题,具体实现为ServiceDispatcher.InnerConnection,其中ServiceDispatcher是LoadedApk的内部类,查看ServiceDispatcher.InnerConnection的connected方法:
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/LoadedApk.java
static final class ServiceDispatcher {
private final ServiceDispatcher.InnerConnection mIServiceConnection;
......
private static class InnerConnection extends IServiceConnection.Stub {
@UnsupportedAppUsage
final WeakReference<LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher> mDispatcher;
InnerConnection(LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd) {
mDispatcher = new WeakReference<LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher>(sd);
}
public void connected(ComponentName name, IBinder service, boolean dead)
throws RemoteException {
LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd = mDispatcher.get();
if (sd != null) {
sd.connected(name, service, dead); //1
}
}
}
.....
public void connected(ComponentName name, IBinder service, boolean dead) {
if (mActivityExecutor != null) {
mActivityExecutor.execute(new RunConnection(name, service, 0, dead));
} else if (mActivityThread != null) {
mActivityThread.post(new RunConnection(name, service, 0, dead));//2
} else {
doConnected(name, service, dead);
}
}
.....
}
在注释1处调用了ServiceDispatcher类型的sd对象的connected方法。
在注释2处调用Handler类型的对象mActivityThread的post方法,mActivityThread实际上是指向的H。因此,通过调用post方法将RunConnection对象的内容运行在主线程中。RunConnection是LoadedApk的内部类:
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/LoadedApk.java
private final class RunConnection implements Runnable {
RunConnection(ComponentName name, IBinder service, int command, boolean dead) {
mName = name;
mService = service;
mCommand = command;
mDead = dead;
}
public void run() {
if (mCommand == 0) {
doConnected(mName, mService, mDead);//1
} ....
}
...
}
public void doConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service, boolean dead) {
ServiceDispatcher.ConnectionInfo old;
ServiceDispatcher.ConnectionInfo info;
.....
// If there is a new viable service, it is now connected.
if (service != null) {
mConnection.onServiceConnected(name, service);//2
} else {
// The binding machinery worked, but the remote returned null from onBind().
mConnection.onNullBinding(name);
}
}
在注释1处RunConnection的run方法中调用了doConnected方法;在注释2处调用了ServiceConnection类型的对象mConnection的onServiceConnected方法,这样在客户端实现了ServiceConnection 接口类的onServiceConnected方法就会被执行,传入是服务端的服务名字和服务Binder对象。至此,Service的绑定过程就分析完成。