Android 的UI组件Compose的用法
一:前言
Jetpack Compose 是用于构建原生Android界面的新工具包,他用更少的代码,强大的工具和直观Kotlin API,可以帮助他简化并加快Android界面开发
Compose架构的分层设计
| 由上至下 | 说明 | 运用 |
|---|---|---|
| material | 提供了Material Design一套风格体系,包含主题系统、样式化组件 | Button、AlertDialog等等 |
| foundation | 相当于面向开发者的跟基层,包含完整的UI系统和实用布局 | LazyList、Row、Column等等 |
| animation | 动画层,包含平移、渐变、缩放等等,并且提供了方便开发者的动画组件 | animate AsState、Transition、Animatable、AnimatedVisibility等等 |
| ui | ui相关的基础功能,包括自定义布局、绘制、触摸反馈等等 | ComposeView、Layout、LayoutNode等等 |
| runtime | 最底层的概念模型,包括数据结构、状态处理、数据同步等等 | mutableStateOf、remember等等 |
| compiler | 基于Kotlin的编译器插件 | 处理@Composable函数 |
二:setContent的源码分析
public fun ComponentActivity.setContent(
parent: CompositionContext? = null,
content: @Composable () -> Unit
) {
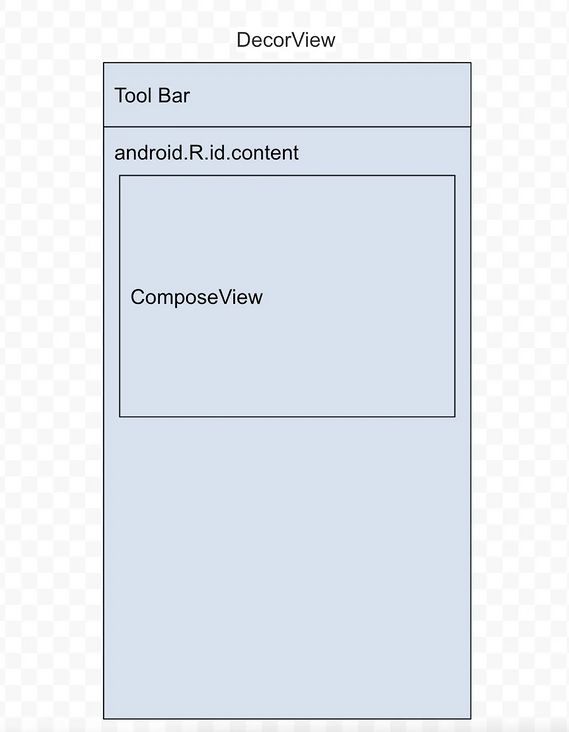
//1.通过decorView找到ContentView,再获取第一个 ComposeView
val existingComposeView = window.decorView
.findViewById(android.R.id.content)
.getChildAt(0) as? ComposeView
//2.如果ComposeView为空则走初始化流程
if (existingComposeView != null) with(existingComposeView) {
setParentCompositionContext(parent)
setContent(content)
} else ComposeView(this).apply {
// 3. 初始化ComposeView肯定为空,则进入这边
// Set content and parent **before** setContentView
// to have ComposeView create the composition on attach
setParentCompositionContext(parent)
// 4. 把入口函数对象传入ComposeView
setContent(content)
// Set the view tree owners before setting the content view so that the inflation process
// and attach listeners will see them already present
setOwners()
// 5. 把ComposeView设置进ContentView
setContentView(this, DefaultActivityContentLayoutParams)
}
}
三:Compose 的Surface的使用
@Composable
@NonRestartableComposable
fun Surface(
modifier: Modifier = Modifier,
//裁剪,根据shape属性描述的形状进行裁剪
shape: Shape = RectangleShape,
color: Color = MaterialTheme.colorScheme.surface,
//内容颜色
contentColor: Color = contentColorFor(color),
tonalElevation: Dp = 0.dp,
shadowElevation: Dp = 0.dp,
border: BorderStroke? = null,
content: @Composable () -> Unit
)Surface 从字面上来理解,是一个平面,在 Material Design 设计准则中也同样如此,我们可以将很多的组件摆放在这个平面之上,我们可以设置这个平面的边框,圆角,颜色等等。接下来,我们来用 Surface 组件做出一些不同的效果。
四:Compose 的@Preview的使用
@Repeatable
annotation class Preview(
val name: String = "",//此预览的显示名称,允许在面板中识别它
val group: String = "",//此@preview 的组名称,这允许在UI中对他们进行分组,并仅显示其中一个或多个
@IntRange(from = 1) val apiLevel: Int = -1,//呈现带注释的@Composables时使用的API级别
val widthDp: Int = -1,//将在其中渲染带注释的@Composable的最大DP宽度。使用此选项可以限制渲染视口的大小
val heightDp: Int = -1,//将在其中渲染注释的@Composable的最大高度(以DP为单位)。使用此选项可以限制渲染视口的大小。
val locale: String = "",//区域设置的当前用户首选项,对应于区域设置资源限定符。默认情况下,将使用默认文件夹。
@FloatRange(from = 0.01) val fontScale: Float = 1f,//用户首选字体的缩放因子,相对于基本密度缩放。
val showSystemUi: Boolean = false,//如果为true,将显示设备的状态栏和操作栏。@Composable将在完整活动的上下文中呈现
val showBackground: Boolean = false,//如果为true,@Composable将使用默认背景色。
val backgroundColor: Long = 0,//背景的32位ARGB颜色int,如果未设置,则为0
@UiMode val uiMode: Int = 0,//根据android.content.res.Configuration.uiMode的ui模式位掩码
@Device val device: String = Devices.DEFAULT//指示要在预览中使用的设备的设备字符串。请参阅设备中的可用设备
)栗子:
@Preview(
widthDp = 100,
heightDp = 100,
fontScale = 2f,
showBackground = true,
backgroundColor = 0xFF00FF00,
showSystemUi = true,
device = Devices.NEXUS_6
)
@Composable
fun GreetingPreview() {
MyApplicationTheme {
Greeting("Android")
}
注意:
*1.showBackground 必须为true,backgroundColor 属性才生效,并且backgroundColor 是 ARGB Long,而不是 Color 值
2.同一个函数可以使用多个@Preview注解*
3.@Preview注解 不支持具有非默认参数的可组合函数(就是preview 不能修饰带参数的函数)
4.@PreviewParameter注释 可以修饰带参数的