【Linux】生产者和消费者模型、条件变量、信号量
目录
- 生产者和消费者模型
- 条件变量
-
-
- 函数解析
- 代码举例
-
- 信号量
-
-
- 函数解析
- 代码举例
-
橙色
生产者和消费者模型
生产者和消费是操作系统中一种重要的模型,它描述的是一种等待和通知的机制。
具体可观看该文章:生产者和消费者模型
条件变量
函数解析
/*
条件变量的类型 pthread_cond_t
int pthread_cond_init(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond, const pthread_condattr_t *restrict attr);
int pthread_cond_destroy(pthread_cond_t *cond);
int pthread_cond_wait(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond, pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex);
- 等待,调用了该函数,线程会阻塞。
int pthread_cond_timedwait(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond, pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex, const struct timespec *restrict abstime);
- 等待多长时间,调用了这个函数,线程会阻塞,直到指定的时间结束。
int pthread_cond_signal(pthread_cond_t *cond);
- 唤醒一个或者多个等待的线程
int pthread_cond_broadcast(pthread_cond_t *cond);
- 唤醒所有的等待的线程
*/
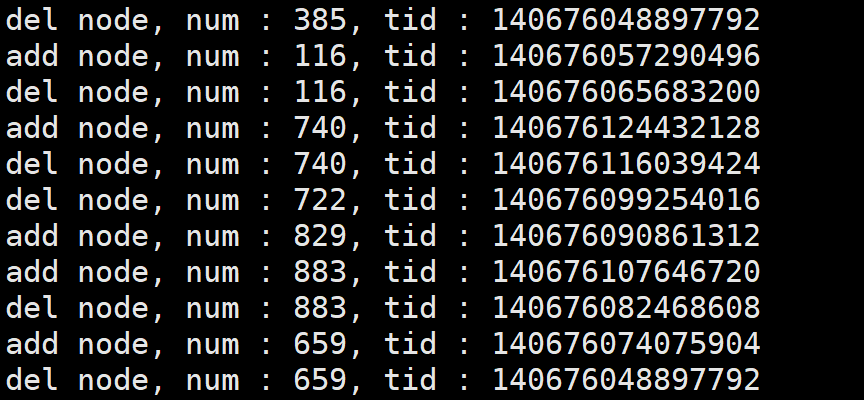
代码举例
#include 运行结果:
1、消费者和生产者这种模型下,生产者和消费者是使用同一把锁的。因为只要是多个线程操作相同的一份数据,就需要保证代码同步。
2、问:如果容器中的数据足够多,消费者不执行pthread_cond_wait(&cond,&mutex)
那么生产者中的pthread_cond_signal(&cond)信号通知给谁,或者信号哪了?
答:signal是唤醒一个或者多个睡眠的线程,如果数据足够多,线程没有休眠,即使收到了信号也不会做任何的处理。《Liunx/UNIX系统编程手册》第531页有句话,条件变量并不保存状态信息,只是传递应用程序状态信息的一种通讯机制。发送信号时若无任何线程在等待该条件变量,这个也就会不了了之。线程如在此后等待该条件变量,只有当再次收到此变量的下一信号时,方可解除阻塞状态。
3、问:当消费者执行到pthread_cond_wait对mutex进行了解锁,那么这个时候其他消费者线程会不会抢先对mutex进行加锁,从而导致生产者无法正常生产呢?
答: 其他消费者也在pthread_cond_wait等待
信号量
函数解析
/*
信号量的类型 sem_t
int sem_init(sem_t *sem, int pshared, unsigned int value);
- 初始化信号量
- 参数:
- sem : 信号量变量的地址
- pshared : 0 用在线程间 ,非0 用在进程间
- value : 信号量中的值
int sem_destroy(sem_t *sem);
- 释放资源
int sem_wait(sem_t *sem);
- 对信号量加锁,调用一次对信号量的值-1,如果值为0,就阻塞
int sem_trywait(sem_t *sem);
int sem_timedwait(sem_t *sem, const struct timespec *abs_timeout);
int sem_post(sem_t *sem);
- 对信号量解锁,调用一次对信号量的值+1
int sem_getvalue(sem_t *sem, int *sval);
sem_t psem;
sem_t csem;
init(psem, 0, 8);
init(csem, 0, 0);
producer() {
sem_wait(&psem);
sem_post(&csem)
}
customer() {
sem_wait(&csem); //当csem信号量不为0时,减一;为0时,就堵塞在这里
sem_post(&psem)
}
*/
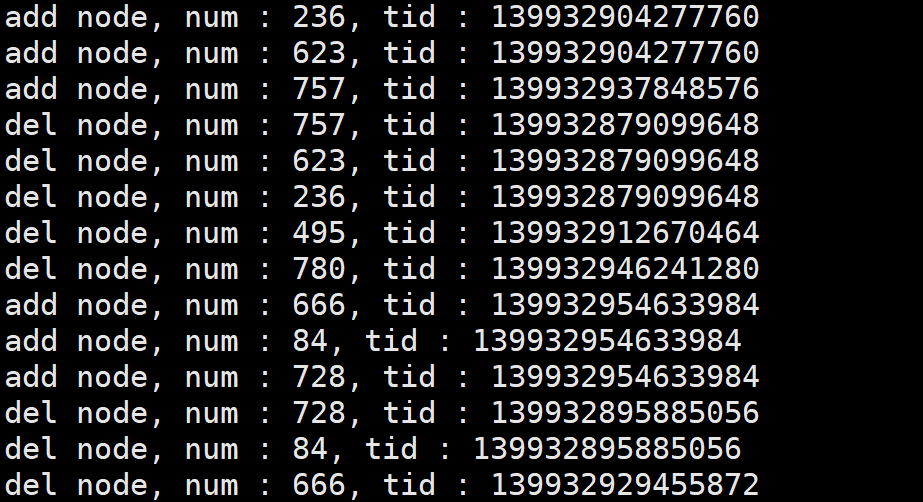
代码举例
#include 因为使用的是头插法,所以最后加入链表的最先被打印出来。