代码随想录 二叉树 Java (一)
文章目录
- (简单)144. 二叉树的前序遍历
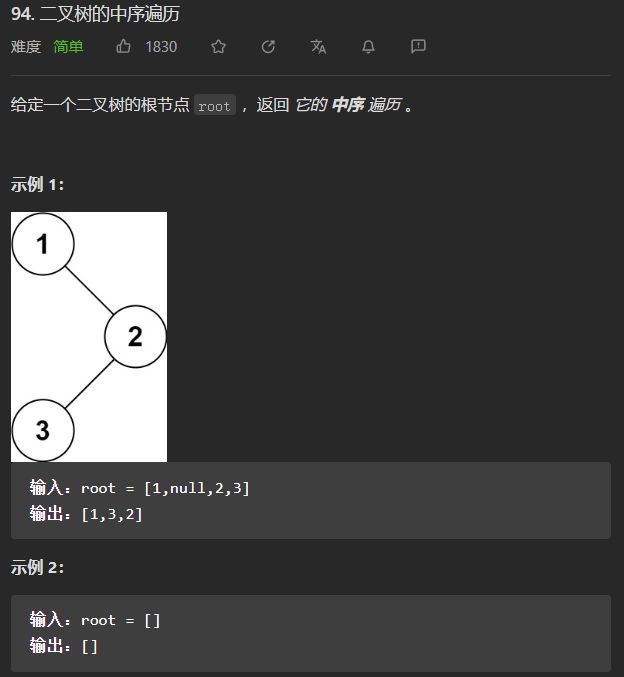
- (简单)94. 二叉树的中序遍历
- (简单)145. 二叉树的后序遍历
- 二叉树的统一遍历方法(参考代码随想录)
- (中等)102. 二叉树的层序遍历
- (中等)107. 二叉树的层序遍历II
- (中等)199. 二叉树的右视图
- (简单)637. 二叉树的层平均值
- (中等)429. N叉树的层序遍历
- (中等)在每个树行中找最大值
- (中等)116. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
- (中等)117. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针II
- (简单)104. 二叉树的最大深度
- (简单)111. 二叉树的最小深度
- (简单 经典)226. 翻转二叉树
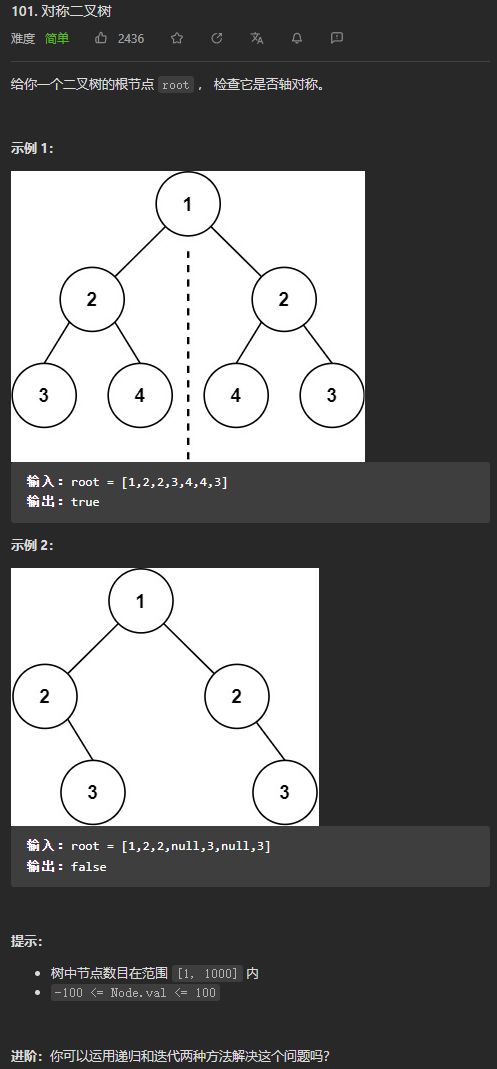
- (简单)101. 对称二叉树
- (简单)100. 相同的树
- (简单)572. 另一棵树的子树
- (简单)559. N叉树的最大深度
(简单)144. 二叉树的前序遍历
递归方式
class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
preOrder(root, list);
return list;
}
public void preOrder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> list) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
list.add(root.val);
preOrder(root.left, list);
preOrder(root.right, list);
}
}
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n),其中n是二叉树的节点数。每一个节点恰好被遍历一次。
- 空间复杂度:O(n),为递归过程中栈的开销,平均情况下为O(logn),最坏情况下树呈现链状,为O(n)。
非递归方式,使用Stack
class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) {
return list;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(root);
list.add(root.val);
TreeNode node = root.left;
while (!stack.isEmpty() || node != null) {
while (node != null) {
list.add(node.val);
stack.push(node);
node = node.left;
}
node = stack.pop().right;
}
return list;
}
}
复杂度分析:
使用BFS的思想,利用栈,实现二叉树的前序遍历
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) {
return list;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(root);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
list.add(node.val);
if (node.right != null) {
stack.push(node.right);
}
if (node.left != null) {
stack.push(node.left);
}
}
return list;
}
}
(简单)94. 二叉树的中序遍历
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) {
return list;
}
inOrder(root, list);
return list;
}
public void inOrder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> list) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
inOrder(root.left, list);
list.add(root.val);
inOrder(root.right, list);
}
}
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n),其中n为二叉树节点的个数。二叉树的遍历中每个节点会被访问一次且只会被访问一次。
- 空间复杂度:O(n)。空间复杂度取决于递归的栈深度,而栈深度在二叉树为一条链的情况下会达到O(n)的级别。
非递归方式
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) {
return list;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(root);
TreeNode node = root.left;
while (!stack.isEmpty() || node != null) {
while (node != null) {
stack.push(node);
node = node.left;
}
node = stack.pop();
list.add(node.val);
node = node.right;
}
return list;
}
}
- 时间复杂度:O(n),其中n为二叉树节点的个数。二叉树的遍历中每个节点会被访问一次且只会被访问一次。
- 空间复杂度:O(n)。空间复杂度取决于递归的栈深度,而栈深度在二叉树为一条链的情况下会达到O(n)的级别。
(简单)145. 二叉树的后序遍历
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) {
return list;
}
postOrder(root, list);
return list;
}
public void postOrder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> list) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
postOrder(root.left, list);
postOrder(root.right, list);
list.add(root.val);
}
}
复杂度分析:
后序遍历的顺序是,左,右,根
后序遍历和前序、中序遍历略微有点不同,因为每一棵子树的根节点可能需要二次入栈。从栈中弹出某一根节点时,需要判断该节点的右子树是否为空,如果为空,或者该节点的右子树已经遍历过,则将该根节点的值加入list中。如果没有遍历过该节点的右子树,则重新将根节点入栈,并开始遍历右子树。
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Stack;
class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) {
return list;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(root);
TreeNode node = root.left;
TreeNode prev = null;
while (!stack.isEmpty() || node != null) {
while (node != null) {
stack.push(node);
node = node.left;
}
node = stack.pop();
//root.right==prev,表示该节点的右子树一定遍历完成
if (node.right == null || node.right == prev) {
list.add(node.val);
prev = node;
node = null;
} else {
//还没有遍历右子树
stack.push(node);
node = node.right;
}
}
return list;
}
}
- 时间复杂度:O(n),其中n是二叉搜索树的节点数。每一个节点恰好被遍历一遍
- 空间复杂度:O(n),为递归过程中栈的开销,平均情况下为O(logn),最坏情况下呈现链状,为O(n)
前一个非递归实现的后续遍历是深度有限搜索DFS的思想
在代码随想录中还提到一种后序遍历的方式,先序遍历时根左右、后序遍历的左右根,只需要调整一下先序遍历的代码顺序,就变成了根右左的顺序,然后反转result数组,输出的结果顺序就是左右中了
这种方法是广度优先遍历BFS的思想,依照该思想,也可以实现前序遍历,已在上面的前序遍历题目中进行补充
下面代码从栈中弹出来的顺序是:根、右、左,然后将结果list反转一下即可
class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null){
return result;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(root);
while (!stack.isEmpty()){
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
result.add(node.val);
if (node.left != null){
stack.push(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null){
stack.push(node.right);
}
}
Collections.reverse(result);
return result;
}
}
二叉树的统一遍历方法(参考代码随想录)
非递归方式,也称作迭代法
在DFS的思想下,前序遍历和中序遍历的代码类似,只需要调整代码中节点值加入结果list的位置即可,和后序遍历的代码差别较大
使用BFS的思想,前序遍历和后序遍历的代码类似,只需要修改左子节点和右子节点入栈的先后顺序即可,和中序遍历的代码差别较大
但是,使用递归的方式,前序遍历、中序遍历、后序遍历都只需要微微调整一下代码就可以,代码随想录中给出了一种统一风格的代码
以中序遍历为例,使用栈,无法同时解决访问节点(遍历节点)和处理节点(将元素放进结果集)不一致的情况。
对上面这段话的简单解释:
中序遍历是左根右,先访问二叉树顶部的节点,然后一层一层向下访问,直到到达树左面的最底部,再开始处理节点(也就是把节点的数值放进result数组中),这就造成了处理顺序与访问顺序不一致的情况
为了解决这个不一致,将访问的节点放入栈中,把要处理的节点也放入栈中但是要做标记。标记的方法是把要处理的节点放入栈中之后,紧接着放入一个空指针作为标记。
使用“统一”的方式写中序遍历
再进行了一两次单步调试后,有点理解这种方式,首先,依赖栈后进先出的特性,按照右、中、左的顺序将节点压入栈中,其次是,对于已经访问过,但是还没有处理的根节点,使用null进行标记。
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Stack;
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result = new LinkedList<>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
if (root != null) {
stack.push(root);
}
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = stack.peek();
stack.pop();
if (node != null) {
if (node.right != null) {
stack.push(node.right);//右
}
stack.push(node);//中
stack.push(null);
if (node.left != null) {
stack.push(node.left);//左
}
} else {
node = stack.peek();
result.add(node.val);
stack.pop();
}
}
return result;
}
}
class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result = new LinkedList<>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
if (root != null) {
stack.push(root);
}
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = stack.peek();
stack.pop();
if (node != null) {
if (node.right != null) {
stack.push(node.right);
}
if (node.left != null) {
stack.push(node.left);
}
stack.push(node);
stack.push(null);
} else {
node = stack.peek();
result.add(node.val);
stack.pop();
}
}
return result;
}
}
使用类似的方法,实现后序遍历
class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result = new LinkedList<>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
if (root != null) {
stack.push(root);
}
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = stack.peek();
stack.pop();
if (node != null) {
stack.push(node);
stack.push(null);
if (node.right != null) {
stack.push(node.right);
}
if (node.left != null) {
stack.push(node.left);
}
} else {
node = stack.peek();
result.add(node.val);
stack.pop();
}
}
return result;
}
}
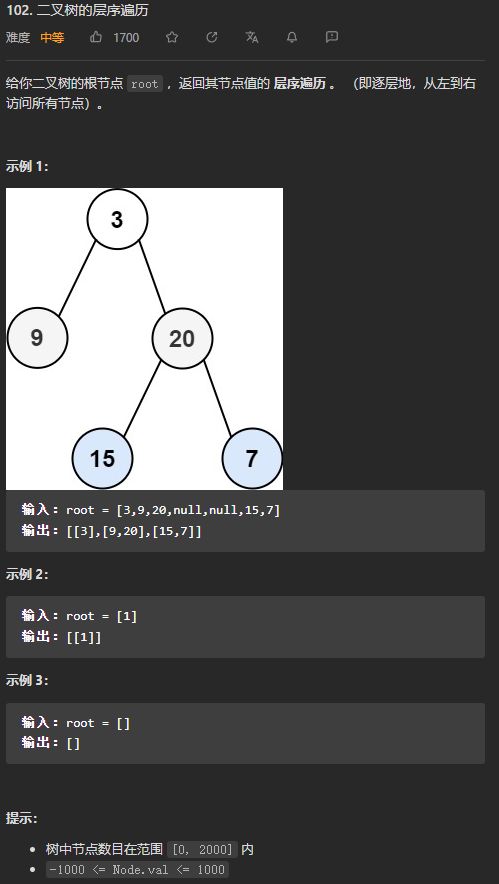
(中等)102. 二叉树的层序遍历
在处理某一层的节点之前,先记录一下队列中元素的个数,也就是这一层的节点个数,然后依次弹出这一层的节点,然后再向队列中添加该节点的左子节点和右子节点(如果有的话)
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) {
return result;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
TreeNode node;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
int size = queue.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
node = queue.poll();
list.add(node.val);
if (node.left != null) {
queue.add(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.add(node.right);
}
}
result.add(list);
}
return result;
}
}
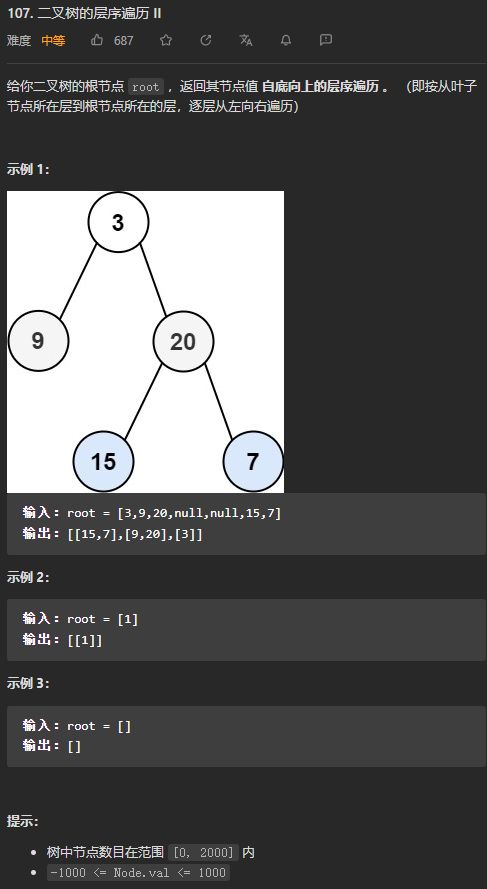
(中等)107. 二叉树的层序遍历II
因为返回的结果只要是实现了List接口就可以,所以,ArrayList、LinkedList都可以,本题中要求层序遍历是自底向上的层序遍历,依然可以按照102题中的方法去写,只不过每一次往结果List中添加结果时,需要添加在头部的位置,ArrayList底层是数组实现,所以总是从头部插入元素效率较低,所以使用LinkedList,底层使用双向链表,在头部插入元素在O(1)的时间内即可完成
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrderBottom(TreeNode root) {
LinkedList<List<Integer>> result = new LinkedList<>();
if (root == null) {
return result;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
int size = 0;
TreeNode tmp;
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
size = queue.size();
LinkedList<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
tmp = queue.poll();
list.addLast(tmp.val);
if (tmp.left != null) {
queue.add(tmp.left);
}
if (tmp.right != null) {
queue.add(tmp.right);
}
}
result.addFirst(list);
}
return result;
}
}
- 时间复杂度:O(n),其中n是二叉树节点的个数。每个节点访问一次,结果列表使用链表的结构时,在结果列表头部添加一层节点值的列表的时间复杂度是O(1),因此总时间复杂度是O(n)。
- 空间复杂度:O(n),其中n是二叉树中的节点个数。空间复杂度取决于队列开销,队列中的节点个数不会超过n。
(中等)199. 二叉树的右视图
还是使用层次遍历的思想(BFS),只不过结果列表中添加的是每一层的最右边的节点
class Solution {
public List<Integer> rightSideView(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) {
return result;
}
int size = 0;
TreeNode node;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
size = queue.size();
for (int i = 1; i <= size; i++) {
node = queue.poll();
if (i == size) {
result.add(node.val);
}
if (node.left != null) {
queue.add(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.add(node.right);
}
}
}
return result;
}
}
按照 根节点、右子树、左子树的顺序访问,就可以保证每层都是最先访问最右边的节点的。
(与先序遍历 根节点、左子树、右子树 正好相反,先序遍历每层最先访问的是最左边节点)
时间复杂度:O(N),每个节点都被访问过1次
空间复杂度:O(N),因为这不是一棵平衡二叉树,二叉树的深度至少是logN,最坏的情况下会退化成一条链表,深度为N,因此递归使用的栈空间O(N)的。
class Solution {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
public List<Integer> rightSideView(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root, 0);
return result;
}
public void dfs(TreeNode root, int depth) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
if (depth == result.size()) {
result.add(root.val);
}
depth++;
dfs(root.right, depth);
dfs(root.left, depth);
}
}
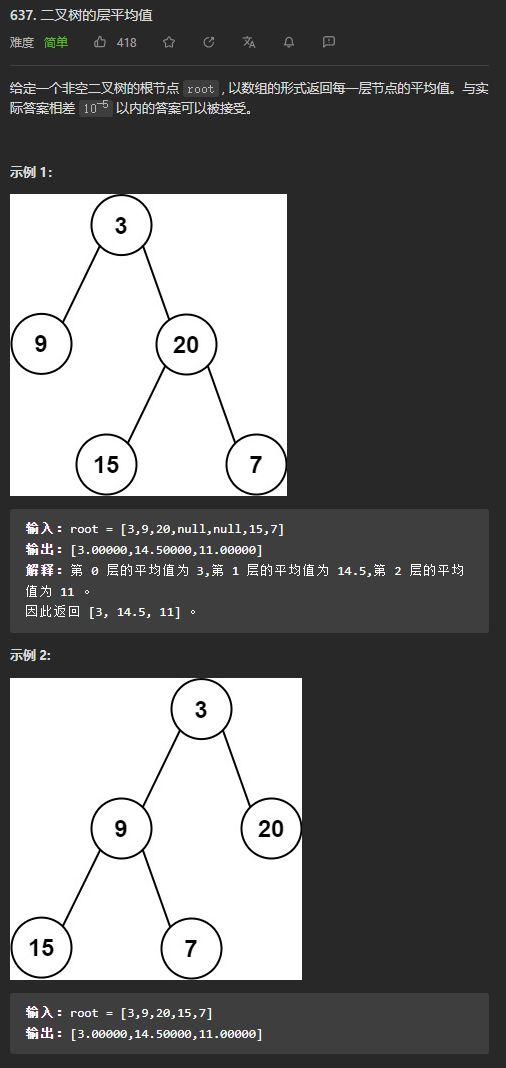
(简单)637. 二叉树的层平均值
广度优先搜索BFS
还是层次遍历的思路,在弹出每一层节点之前,记录队列当前的size,在弹出这一层每一个节点时,对它们的值进行累加求和,当这一层的节点全部弹出时,将求和的结果除以size,就是这一层的平均值,添加到结果列表中
class Solution {
public List<Double> averageOfLevels(TreeNode root) {
List<Double> res = new ArrayList<>();
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
double sum = 0.0;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
sum += node.val;
if (node.left != null) {
queue.add(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.add(node.right);
}
}
sum /= size;
res.add(sum);
}
return res;
}
}
-
时间复杂度:O(n),其中n是二叉树中的节点个数
- 广度优先搜索需要对每个节点访问一次,时间复杂度是O(n)。
- 需要对二叉树的每一层计算平均值,时间复杂度是O(h),其中h是二叉树的高度,在任何情况下都满足h<=n。
- 因此总时间复杂度是O(n)
-
空间复杂度:O(n),其中n是二叉树中的节点个数。空间复杂度取决于队列开销,队列中的节点个数不会超过n。
深度优先搜索DFS
使用深度优先搜索计算二叉树的层平均值,需要维护两个数组,counts用于存储二叉树的每一层的节点数,sums用于存储二叉树的每一层的节点值之和。搜索过程中需要记录当前节点所在层,如果访问到的节点在第i层,则将counts[i]的值加1,并将该节点的值加到sums[i]。
遍历结束之后,第i层的平均值即为sums[i]/counts[i]。
class Solution {
public List<Double> averageOfLevels(TreeNode root) {
ArrayList<Integer> counts = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<Double> sums = new ArrayList<>();
dfs(root, 0, counts, sums);
ArrayList<Double> res = new ArrayList<>();
//size表示该二叉树有多少层
dfs(root, 0, counts, sums);
int size = sums.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
res.add(sums.get(i) / counts.get(i));
}
return res;
}
private void dfs(TreeNode root, int depth, ArrayList<Integer> counts, ArrayList<Double> sums) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
if (depth < sums.size()) {
sums.set(depth, sums.get(depth) + root.val);
counts.set(depth, counts.get(depth) + 1);
} else {
sums.add(1.0 * root.val);
counts.add(1);
}
dfs(root.left, depth + 1, counts, sums);
dfs(root.right, depth + 1, counts, sums);
}
}
(中等)429. N叉树的层序遍历

这一题和二叉树的层序遍历思想一样,区别在于,二叉树的层序遍历,向结果列表中添加当前节点的值以后,需要判断该节点的左子节点和右子节点是否为空,不为空的话加入队列。对于N叉树,则需要判断当前Node对象的children属性,如果里面有不为空的子节点,需要将它们加入队列
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public int val;
public List children;
public Node() {}
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
public Node(int _val, List _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
*/
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Queue;
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(Node root) {
ArrayList<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) {
return res;
}
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
int size;
Node node;
List<Integer> list;
queue.add(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
size = queue.size();
list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
node = queue.poll();
list.add(node.val);
for (Node child : node.children) {
if (child != null) {
queue.add(child);
}
}
}
res.add(list);
}
return res;
}
}
- 时间复杂度:O(n),其中n是树中包含的节点个数。在广度优先搜索的过程中,我们需要遍历每个节点恰好一次。
- 空间复杂度:O(n),即为队列需要使用的空间。在最坏的情况下,树只有两层,且最后一层有n-1个节点,此时就需要O(n)的空间。
(中等)在每个树行中找最大值


采用层序遍历的思想,使用一个变量tmp来记录当前层的最大值,在比较完当前层的所有值以后,将其添加到结果列表中
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Queue;
class Solution {
public List<Integer> largestValues(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) {
return res;
}
int tmp;
int size;
TreeNode node;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
size = queue.size();
tmp = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
node = queue.poll();
tmp = Math.max(tmp, node.val);
if (node.left != null) {
queue.add(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.add(node.right);
}
}
res.add(tmp);
}
return res;
}
}
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n),其中n为二叉树节点个数,每一个节点仅会进出队列一次。
- 空间复杂度:O(n),存储二叉树节点的空间开销。
深度优先搜索DFS
用树的【先序遍历】来进行【深度优先搜索】处理,并用curHeight来标记遍历到的当前节点的高度。当遍历到curHeight高度的节点就判断是否更新该节点的最大值。
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
class Solution {
public List<Integer> largestValues(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) {
return res;
}
dfs(root, 0, res);
return res;
}
private void dfs(TreeNode root, int curHeight, List<Integer> res) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
if (curHeight == res.size()) {
res.add(root.val);
} else {
res.set(curHeight, Math.max(root.val, res.get(curHeight)));
}
dfs(root.left, curHeight + 1, res);
dfs(root.right, curHeight + 1, res);
}
}
- 时间复杂度:O(n),其中n为二叉树节点个数。二叉树的遍历中每个节点都会被访问一次且只会被访问一次。
- 空间复杂度:O(height),其中height表示二叉树的高度。递归函数需要栈空间,而栈空间取决于递归的深度,因此空间复杂度等价于二叉树的高度。
(中等)116. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
class Solution {
public Node connect(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
int size;
Node node;
queue.add(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
size = queue.size();
for (int i = 1; i <= size; i++) {
node = queue.poll();
if (i == size) {
node.next = null;
} else {
node.next = queue.peek();
}
if (node.left != null) {
queue.add(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.add(node.right);
}
}
}
return root;
}
}
- 时间复杂度:O(n)。每个节点会被访问一次,即从队列中弹出,并建立next指针。
- 空间复杂度:O(N)。这是一棵完美二叉树,它的最后一个层级包含N/2个节点。广度优先遍历的复杂度取决于一个层级上的最大元素数量。
官方提供的另一种方法,使用已建立的next指针
思路:
一棵树中存在两种类型的next指针
- 第一种情况是连接同一个父节点的两个子节点。它们可以通过同一个节点直接访问到,因此直接可以执行下面的操作即可完成连接。
node.left.next = node.right;
- 第二种情况在不同父亲的子节点之间建立连接,这种情况不能直接连接。
- 如果每个节点有指向父节点的指针,可以通过该指针找到next节点。第N层节点之间建立next指针后,再建立第N+1层节点的next指针。可以通过next指针访问同一层的所有节点,因此可以使用第N层的next指针,为第N+1层节点建立next指针。
node.right.next = node.next.left;

从根节点开始,由于第0层只有一个节点,所以不需要连接,直接为第一层节点建立next指针即可。该算法中需要注意一点是,当我们为第N层节点建立next指针时,处于第N-1层。当第N层节点的next指针全部建立完成后,移至第N+1层节点的next指针。
遍历某一层的节点时,这层节点的next指针已经建立。因此我们只需要知道这一层的最左节点,就可以按照链表方式遍历,不需要使用队列。
完成当前层的连接后,进入下一层重复操作,直到所有的节点全部连接。进入下一层后需要更新最左节点,然后从新的最左结点开始遍历该层所有节点。因为是完美二叉树,因此最左节点一定是当前最左节点的左孩子。如果当前最左节点的左孩子不存在,说明已经到达该树的最后一层,完成了所有节点的连接。
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public int val;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node next;
public Node() {}
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
public Node(int _val, Node _left, Node _right, Node _next) {
val = _val;
left = _left;
right = _right;
next = _next;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public Node connect(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
//从根节点开始
Node leftmost = root;
while (leftmost.left != null) {
Node head = leftmost;
while (head != null) {
//连接1
head.left.next = head.right;
//连接2
if (head.next != null) {
head.right.next = head.next.left;
}
//指针向后移动
head = head.next;
}
//去往下一层
leftmost = leftmost.left;
}
return root;
}
}
指针永远指向的是被操作行的上一层,因为上一层的next指针已经建立完毕
- 时间复杂度:O(n),每个节点只访问一次。
- 空间复杂度:O(1),不需要存储额外的节点。
(中等)117. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针II



这一题和上一题116的区别是,上一题是完美二叉树,这一题是普通二叉树,其实思路是一样的。
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public int val;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node next;
public Node() {}
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
public Node(int _val, Node _left, Node _right, Node _next) {
val = _val;
left = _left;
right = _right;
next = _next;
}
};
*/
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
class Solution {
public Node connect(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
for (int i = 1; i <= size; i++) {
Node node = queue.poll();
if (i == size) {
node.next = null;
} else {
node.next = queue.peek();
}
if (node.left != null) {
queue.add(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.add(node.right);
}
}
}
return root;
}
}

上面代码的运行效率并不是很高,这是因为我们把节点不停地入队,然后不停地出队,其实可以不需要队列,每一行都可以看成一个链表比如第一行就只有一个节点的链表,第二行是只有两个节点的链表(假如根节点的左右两个子节点都不为空)…
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public int val;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node next;
public Node() {}
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
public Node(int _val, Node _left, Node _right, Node _next) {
val = _val;
left = _left;
right = _right;
next = _next;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public Node connect(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
//cur可以把它看作是每一层的链表
Node cur = root;
while (cur != null) {
//遍历当前层的时候
//为了方便操作在下一层前面添加一个哑节点
//(注意,这里是访问当前层的节点,然后把下一层的节点串起来)
Node dummy = new Node(0);
Node pre = dummy;
//开始遍历当前层的链表
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.left != null) {
//如果当前节点的左子节点不为空
//就让pre节点的next指向它,把它串起来
pre.next = cur.left;
pre = pre.next;
}
//同理
if (cur.right != null) {
pre.next = cur.right;
pre = pre.next;
}
//继续访问这一行的下一个节点
cur = cur.next;
}
//把下一层串联成一个链表之后,让他赋值给cur
//后续继续循环,直到cur为空为止
cur = dummy.next;
}
return root;
}
}
因为上一题的二叉树是完美二叉树,也就是二叉树每一层都是满的状态。不过这一题就不是了,所以需要引入一个哑节点来,该节点的next指针指向的就是当前层的第一个二叉树节点。
(简单)104. 二叉树的最大深度
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
return Math.max(maxDepth(root.left), maxDepth(root.right)) + 1;
}
}
如果知道了左子树和右子树的最大深度l和r,那么该二叉树的最大深度即为max(l,r)+1
而左子树和右子树的最大深度又可以以同样的方式进行计算。因此可以用【深度优先搜索】的方法来计算二叉树的最大深度。具体而言,再计算当前二叉树的最大深度时,可以先递归计算出其左子树和右子树的最大深度,然后再O(1)时间内算出当前二叉树的最大深度。递归再访问到空节点时退出。
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n),其中n为二叉树节点的个数。每个节点在递归中只被遍历一次。
- 空间复杂度:O(height),其中height表示二叉树的高度。递归函数需要栈空间,而栈空间取决于递归的深度,因此空间复杂度等价于二叉树的高度。
另一种思路:广度优先搜索
层序遍历的思路,队列中存放的是当前层的所有节点。每次扩展下一层的时候,不同于广度优先搜索的每次只从队列中拿出一个节点,而是需要将队列里所有节点都拿出来进行扩展,这样能保证每次拓展完的时候队列里存放的是当前层的所有节点,即是一层一层地进行拓展,最后用一个变量ans来维护拓展地次数,该二叉树地最大深度即为ans。
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
//res记录要返回的结果
int res = 0;
//size表示当前层的节点个数
int size = 0;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
size = queue.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if (node.left != null) {
queue.add(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.add(node.right);
}
}
//该层的所有节点都已经扩展完毕,深度+1
res++;
}
return res;
}
}
(简单)111. 二叉树的最小深度
深度优先搜索
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
//该节点的左右子树都不为空
if (root.left != null && root.right != null) {
return Math.min(minDepth(root.left), minDepth(root.right)) + 1;
} else if (root.left == null && root.right != null) {
//该节点的左子树为空,右子树不为空
return minDepth(root.right) + 1;
} else if (root.left != null) {
//该节点的左子树不为空,右子树为空
return minDepth(root.left) + 1;
} else {
//该节点为叶子节点,左子树右子树均为空
return 1;
}
}
}
对于每一个非叶子节点,只需要分别计算其左右子树的最小叶子节点深度。
class Solution {
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
return 1;
}
int min_depth = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
if (root.left != null) {
min_depth = Math.min(minDepth(root.left), min_depth);
}
if (root.right != null) {
min_depth = Math.min(minDepth(root.right), min_depth);
}
return min_depth + 1;
}
}
- 时间复杂度:O(N),其中N是树的节点数。对每个节点访问一次。
- 空间复杂度:O(H),其中H是树的高度。空间复杂度主要取决于递归时栈空间的开销,最坏情况下,树呈现链状,空间复杂度为O(N)。平均情况下树的高度与节点数的对数正相关,空间复杂度为O(logN)
广度优先搜索
遍历整棵二叉树,除了可以用深度优先搜索的方法,还可以使用广度优先遍历。
当找到一个叶子节点时,直接返回这个叶子节点的深度。广度优先搜索的性质保证了最先搜索到的叶子节点的深度一定最小。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
class Solution {
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
int depth = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
depth++;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if (node.left == null && node.right == null) {
return depth;
}
if (node.left != null) {
queue.add(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.add(node.right);
}
}
}
return depth;
}
}
- 时间复杂度:O(N),其中N是树的节点数。对每个节点访问一次。
- 空间复杂度:O(N),其中N是树的节点数。空间复杂度主要取决于队列的开销,队列中的元素个数不会超过树的节点数。
(简单 经典)226. 翻转二叉树
从根节点开始,递归地对树进行遍历,并从叶子节点先开始翻转,如果当前遍历到的节点root的左右两棵子树都已经翻转,那么只需要交换两棵子树的位置,即可完成以root为根节点的整棵子树的翻转。
class Solution {
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
return root;
}
TreeNode left = invertTree(root.left);
TreeNode right = invertTree(root.right);
root.left = right;
root.right = left;
return root;
}
}
- 时间复杂度:O(N),其中N为二叉树节点的数目。需要遍历二叉树种的每一个节点,对每个节点而言,再常数时间内就可以完成交换两棵子树的操作。
- 空间复杂度:O(N),使用的空间由递归栈的深度决定,它等于当前节点在二叉树中的高度。在平均情况下,二叉树的高度与节点个数为对数关系,即O(logN)。而在最情况下,树形成链状,空间复杂度为O(N)
广度优先遍历
动画演示,参考链接
广度优先遍历需要额外的数据结构——队列,来存放临时遍历到的元素
首先需要将根节点放入到队列中,然后不断地迭代队列中的元素。
对当前元素调换其左右子树的位置,然后:
- 判断其左子树是否为空,不为空就放入队列中
- 判断其右子树是否为空,不为空就放入队列中
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
class Solution {
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if (node.left != null) {
queue.add(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.add(node.right);
}
if (node.right != null || node.left != null) {
TreeNode tmp = node.left;
node.left = node.right;
node.right = tmp;
}
}
}
return root;
}
}
(简单)101. 对称二叉树
写这一题的时候,我想的是,要判断一个二叉树是否对称,则需要判断它的左子树和右子树是否对称,如果只有左子树或者只有右子树,那么就肯定不是对称的,如果左右子树都存在,那么如果左子树的根节点的值与右子树根节点的值不一样,也不是对称的,如果值一样,则需要比较该左子树的左孩子和右子树的右孩子,以及左子树的右孩子和右子树的左孩子是否是对称的。
所以和求最大深度不同,不能只靠原有的那个方法进行递归,而是需要另外写一个方法。
class Solution {
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
return checkLeftAndRight(root.left, root.right);
}
public boolean checkLeftAndRight(TreeNode leftNode, TreeNode rightNode) {
//左子树为空,右子树不为空
if (leftNode == null && rightNode != null) {
return false;
}
//左子树不为空,右子树为空
if (leftNode != null && rightNode == null) {
return false;
}
//左子树为空,右子树为空
if (leftNode == null) {
return true;
}
//左右子树都不为空
//如果他们的值不相等
if (leftNode.val != rightNode.val) {
return false;
}
return checkLeftAndRight(leftNode.left, rightNode.right)
&& checkLeftAndRight(leftNode.right, rightNode.left);
}
}
复杂度分析:
假设树上一共有n个节点。
- 时间复杂度:O(n),因为遍历了整棵树
- 空间复杂度:O(n),空间复杂度和递归使用的栈空间有关,这里递归层数不超过n。
官方对递归方法的总结:
如果一个左子树与右子树镜像对称,那么这个树是对称的。那么问题就转化为,两棵树在什么情况下互为镜像?
同时满足下面两个条件,两棵树互为镜像:
- 它们的两个根节点具有相同的值
- 每个树的右子树与另一个树的左子树镜像对称
另一种解题思路:迭代
引入一个队列,这是把递归程序改写成迭代程序的常用方法。初始化时我们把根节点入队两次。每次提取两个节点比较它们的值(队列中每两个连续的节点应该是相等的,而且它们的子树互为镜像),然后将两个节点的左右子节点按相反的顺序插入队列中。当队列为空时,或者检测到树不对称(即从队列中取出两个不相等的连续节点)时,该算法结束。
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
class Solution {
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
queue.add(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node1 = queue.poll();
TreeNode node2 = queue.poll();
if (node1 == null && node2 == null) {
continue;
}
if (node1==null || node2==null) {
return false;
}
if (node1.val != node2.val) {
return false;
}
queue.add(node1.left);
queue.add(node2.right);
queue.add(node1.right);
queue.add(node2.left);
}
return true;
}
}
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n),n为二叉树中的节点,需要遍历整个二叉树
- 空间复杂度:O(n),这里需要用一个队列来维护节点,每个节点最多进队一次,出队一次,队列中最多不会超过n个点。
(简单)100. 相同的树
DFS思路
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if (p == null && q == null) {
return true;
}
if (p == null || q == null) {
return false;
}
if (p.val != q.val) {
return false;
}
return isSameTree(p.left, q.left) && isSameTree(p.right, q.right);
}
}
- 时间复杂度:O(min(m,n)),其中m和n分别是两个二叉树的节点数。对两个二叉树同时进行深度优先搜索,只有当两个二叉树中的对应节点都不为空时才会访问到该节点,因此被访问到的节点数不会超过较小的二叉树的节点数。
- 空间复杂度:O(min(m,n)),其中m和n是两个二叉树的节点数。空间复杂度取决于递归调用的层数,递归调用的层数不会超过较小的二叉树的最大高度,最坏情况下,二叉树的高度等于节点数。
BFS思路
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
class Solution {
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if (p == null && q == null) {
return true;
}
if (p == null || q == null) {
return false;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(p);
queue.add(q);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode n1 = queue.poll();
TreeNode n2 = queue.poll();
if (n1 == null && n2 == null) {
continue;
}
if (n1 == null || n2 == null) {
return false;
}
if (n1.val != n2.val) {
return false;
}
queue.add(n1.left);
queue.add(n2.left);
queue.add(n1.right);
queue.add(n2.right);
}
return true;
}
}
(简单)572. 另一棵树的子树
我的思路是:使用层次遍历的方式,遍历二叉树,当遇到某一根节点的val与subRoot根节点的val相同的时候,就判断这两棵二叉树是否长得一样,这块的代码和LeetCode 第100题 相同的树的代码是一样的。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
class Solution {
public boolean isSubtree(TreeNode root, TreeNode subRoot) {
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if (node.val == subRoot.val && isSame(node, subRoot)) {
return true;
}
if (node.left != null) {
queue.add(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.add(node.right);
}
}
}
return false;
}
public boolean isSame(TreeNode root, TreeNode subRoot) {
if (root == null && subRoot == null) {
return true;
}
if (root == null || subRoot == null) {
return false;
}
if (root.val != subRoot.val) {
return false;
}
return isSame(root.left, subRoot.left) && isSame(root.right, subRoot.right);
}
}
- 时间复杂度:O(s x t),s是二叉树中的节点的个数,t是子树中的节点的个数。对于每一个s上的点,都需要做一次深度优先搜索来和t匹配,匹配一次的时间代价是O(t),那么总时间就是O(s x t)
- 空间复杂度:假设s深度为ds,t的深度为dt,任意时刻栈空间的最大使用代价是O(max(ds,dt))。
官方提供的另一种思路,KMP
(简单)559. N叉树的最大深度
采用层序遍历的方式计算N叉树的最大深度,广度优先搜索
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public int val;
public List children;
public Node() {}
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
public Node(int _val, List _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
*/
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int depth = 0;
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
depth++;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
Node node = queue.poll();
for (Node n : node.children) {
if (n != null) {
queue.add(n);
}
}
}
}
return depth;
}
}
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n),其中n是N叉树的节点个数。每个节点只会被访问一次。
- 空间复杂度:此方法空间的消耗取决于队列存储的元素数量,其在最坏情况下会达到O(n)
另一种方法,深度优先搜索DFS
如果根节点有N个子节点,则这N个子节点对应N个子树。记N个子树的最大深度中的最大值为maxChildDepth,则该N叉树的最大深度为maxChildDepth+1。
每个子树的最大深度又可以以同样的方式进行计算。因此,可以使用【深度优先搜索】的方法计算N叉树的最大深度。具体而言,在计算当前N叉树的最大深度时,可以先递归计算出其每个子树的最大深度,然后在O(1)的时间内计算出当前N叉树的最大深度。递归在访问到空节点时退出。
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int maxChildDepth = 0;
for (Node n : root.children) {
maxChildDepth = Math.max(maxChildDepth, maxDepth(n));
}
return maxChildDepth + 1;
}
}
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n),其中n为N叉树节点的个数。每个节点在递归中只被遍历一次。
- 空间复杂度:O(height),其中height表示N叉树的高度。递归函数需要栈空间,而栈空间取决于递归的深度,因此空间复杂度等价于N叉树的高度。